Brief summary. This article is intended to answer questions about the degree of protection of equipment from dust and moisture. Many people see IP markings on electrical equipment and ask questions, what does ip 65 mean? Can products with IP44 be installed outdoors? What does ip 20 mean? what is the degree of protection ip54, what does ip 54 mean? In this article we will look in detail at ip 54, what kind of standard is used in the CIS and abroad. Let's give a detailed table of abbreviations for the degree of protection IP.
- Degree of protection ip › GOST, standard
- IP waterproof
- Degrees of IP protection › Table
- IP protection class
- IP 20
- IP 30
- IP 44
- IP 54
- IP 55
- IP 65
Degree of protection ip › GOST, standard
The degree of protection IP (Ingress Protection Rating) is a systematization of the protection values of the housing (meaning the external coating) of electrical appliances and electrical equipment under the influence of various negative conditions, such as the influence of humidity, open seepage of liquid, pollution, as well as exposure to various environments.
This numeric index defines the international IP standard. Among them is the standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission IEC 60529, in the CIS GOST 14254-96, GOST 14254 and in Germany - DIN40050-9.
The current standard IEC 60529:2013 was adopted in 2013. The current GOST 14254 - 2015 in the Russian Federation was introduced on 2022.03.01. It differs from the previous GOST 14254-96 in the moisture protection index: the new current GOST 14254 - 2015 has 10 indices from 0 to 9. The ipx9 index indicates protection from high-temperature water jets supplied under high pressure (see below). Current GOSTs for IP protection level:
- IEC 60529:2013
- GOST 14254 - 2015,
- DIN40050-9,
- DIN EN 60529 (VDE 0470).
The degree of protection is provided when selecting various industrial equipment, taking into account the external environment where it will be used. So, when it is planned to change the wiring of a house, then when selecting a distribution panel, one should take into account the negative environmental conditions. There will be some impact on appliances and equipment that are located outdoors or in a building.
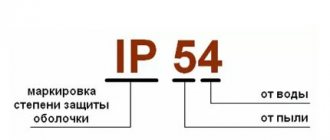
For electrical products, the protection class is given in the form IP [number 1] [number 2] .
[number 1] shows the class of protection against exposure to external environmental objects.
7 levels of protection from external objects from 0 to 6 are standardized:
- “0” - no protection from external objects;
- “1” - the casing is protected from the impact of third-party objects with a diameter of 50 mm or more, from contact with the back of the hand;
- “2” - protection from the negative effects of third-party objects with a diameter of more than 12.5 mm, from touching the case with your fingers;
- “3” - there is protection from foreign objects with a diameter above 2.5 mm, conductors, small tools (hand);
- “4” - protection from foreign objects with a diameter of 1 mm or more - these are conductors fixing nuts and bolts;
- “5” - complete protection from foreign objects of any size, incomplete protection from dirt and dust (a small amount of dust is allowed to fly inside the housing without affecting the functionality of the devices inside the electrical panel);
- “6” - complete protection from various objects, complete dust resistance.
Illumination standards
| Types of premises | Standard lighting (lux) | |
| Russian (SNiP 23-05-95) | International (ICE) | |
| Shared offices using computers | 200–300 | 500 |
| Large offices with free design | 400 | 750 |
| Drawing offices | 500 | 1000 |
| Conference rooms | 200 | 300 |
| Stairs, escalators | 50–100 | 150 |
| Corridors, corridors | 50-75 | 100 |
| Archives | 75 | 200 |
| Shops, supermarkets, car dealerships, car dealerships | — | 500 |
| Handouts | 50 | 100 |
Lighting standards for various rooms
| Name of buildings and premises | Working surface illumination, lux | Cylindrical lighting, lux | |
| With combined lighting | Under general lighting | ||
| Administrative buildings, design and research organizations | |||
| – Offices and other work spaces | 400 * / 200** | 300 | – |
| – Design, drafting and drawing studios | 600 * / 400** | 500 | – |
| – reading rooms | 400/200** | 300 | 100 |
| – Computer rooms, exhibition halls | 750/300** | 400 | – |
| – Conference rooms, meeting rooms | – | 200 | 75 |
| – Laboratories | 750 * / 300** | 300 | – |
| Financial institutions, credit and insurance institutions | |||
| – Operating rooms, cash desks | 400 * / 200** | 300 | – |
| – Collector's office | – | 300 | – |
| Schools, secondary and higher educational institutions | |||
| – Auditoriums, auditoriums, auditoriums, laboratories | – | 500 (vertically in the center of the board) | |
| – | 300 (horizontally on tables and desks) | ||
| – Classrooms and teachers’ offices | – | 200 | |
| - GYM's | – | 200 | |
| - Rest | – | 150 | |
| Preschools | |||
| – Reception rooms, locker rooms, games rooms, dining rooms | – | 200 | |
| – Bedrooms | – | 75 | |
| Sanatoriums, holiday homes | |||
| – Rooms and bedrooms | – | 150 | |
| Spectacular buildings | |||
| – Auditorium for events of republican significance | – | 500*** | 150 |
| – Theatres, concert halls | – | 300*** | 100 |
| – Club auditorium, theater foyer | – | 200*** | 75 |
| – Exhibition halls | – | 200*** | 75 |
| – Foyer of a cinema, club | – | 150 | 50 |
| The shops | |||
| Trading halls: | |||
| - grocery stores | – | 400 | 100 |
| – stores of clothing, linen, shoes, fabrics, fur products, hats, perfumes, jewelry | – | 700 | 100 |
| – dishes, furniture, sporting goods | 500 | 75 | |
| Assembly booths | – | 300 (vertical 1.5 m from the floor) | |
| Hotels | |||
| – Service office | – | 200 | |
| – Living rooms | – | 150 | |
| – Rooms | – | 100 | |
| Buildings and utility rooms | |||
| - Toilet: | |||
| bathrooms, toilets, smoking rooms | – | 75 | |
| showers, changing rooms | – | 50 | |
| – Entrance hall and changing rooms for outerwear: | |||
| in schools, universities, theaters, clubs, hotels and the main entrances of large industrial and public buildings; | – | 150 | |
| in other industrial, auxiliary and public buildings | – | 75 | |
| – Stairs: | |||
| front entrances of public and industrial buildings; | – | 100 | – |
| staircases of residential buildings; | – | 10 | – |
| the rest of the stairs | – | 50 | – |
| – Corridors and passages: | |||
| main | – | 75 | – |
| floor by floor in residential buildings | – | winds | – |
| other corridors | – | 50 | – |
| Notes: | |||
| * horizontal lighting at a height of 0.8 m from the floor with the combined effect of general and local lighting; | |||
| ** the same thing, but only from general lighting; | |||
| *** when using incandescent lamps the level is normalized |
Illumination created by natural and artificial light sources
| Bright stars | 0.00005 lux |
| Sun during the day | 32000-100000 lux |
| Moonlight | 1lc |
| Screen backlight (TV studio) | 1000 lux |
IP waterproof
[number 2] demonstrates the degree of protection against the negative effects of moisture (exposure to liquids, dampness). There are 10 degrees of protection of the case from moisture:
- “0”—no protection;
- “1” - the shell is protected from condensation moisture and raindrops falling strictly in a vertical position;
- “2” - the case is protected from drops, the angle of incidence is up to 15 degrees;
- “3” - there is protection against drops, the angle of incidence is up to 60 degrees;
- “4” - there is protection from liquid drops of any direction;
- “5” - protection from short-term exposure to a fluid flow (jet) of random direction;
- “6” - protection of the hull from prolonged exposure to a strong flow of liquid (water) of random direction, as well as from waves at sea;
- “7” - there is protection against moisture penetration into the inside of the equipment body during short-term immersion in liquid (water) to a depth of 1 m. In this case, there may be penetration of a small volume of liquid into the middle, which does not have an adverse effect on the performance of the products;
- “8” - there is protection against liquid flowing into the products when immersed to a given depth for a given period of time). The body of the products in this version is completely waterproof;
- “9” - there is protection against hot water jets under pressure getting into the products.
The degree of protection of the outer casing (shell) from the influence of negative external conditions is established on the basis of performing a test of the working element. Below are tables with a detailed explanation of the degrees of protection, testing methods and sequences of their implementation.
For a convenient presentation, the classification of IP protection is shown in the figure.
Figure - Classification of IP protection
Protection against water ingress (second digit in the IPXX index):
- 0 - the device is not protected from water penetration;
- 1 - protection against vertically falling drops;
- 2 - protection from vertically falling drops when the device is tilted at an angle of up to 15° from the working position;
- 3 - protection against splashes falling vertically or at an angle of up to 60°;
- 4 - protection against splashes falling from any angle;
- 5 - protection against water jets from any direction;
- 6 - protection from strong water jets from any direction;
- 7 - protection against immersion to a depth of 1 meter for up to 30 minutes;
- 8 - protection against immersion to a depth of more than 1 meter for up to 30 minutes with the ability to operate the device under water;
- 9 - protection against high-temperature water jets under pressure.
If we take specific examples, current flagship gadgets from different companies have different degrees of protection. For example, Apple has all devices of the iPhone 12 family certified to the maximum IP68 level, and Samsung has the Samsung Galaxy S21 line with the same IP68 level, but the latest foldable Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 3 and Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 3 have IPX8 protection - that is They are protected from moisture, but do not have protection from dust.
You can often find a double type designation, for example, IP65/IP68, which indicates the protection of the device from water both when immersed in depth and when exposed to jets. You must understand that protection levels above 6 do not guarantee protection at levels 5 and 6 - working underwater does not mean that the electronics will withstand the jet test without breakdowns.
Even if your smartphone is certified to the maximum level of IP68, you should always be careful and cautious. Tests are carried out in laboratory conditions, which in the vast majority of cases differ from real life - if in clean and warm water the electronics behave perfectly during tests, then cold or hot water, even with a little dirt, can be disastrous.
Do not forget that over time, during operation, the degree of dust and moisture protection may decrease, and this parameter is definitely negatively affected by falling devices, their damage and repairs - even the intervention of qualified specialists reduces the likelihood of electronics “surviving” without consequences in the rain, and even if inside the gadget if someone from among non-specialists got in, then this practically guarantees the loss of protection and the transformation of the degree, conditionally, IP68 and IPXX.
The conclusion is simple - if you want to extend the life of your electronics, try not to drop them, do not trust repairs to unqualified workers, and just in case, avoid exposing devices to extreme conditions of increased dust and moisture. Certification is certification, but careful operation is more reliable.
By the way, we recently tested the Samsung Galaxy XCover 5, which is protected (not only from water/dust, but also from shocks) - look at the video in our article to see what it is capable of. We also have a review of the new JBL Xtreme 3 speaker, which is IP67 protected.
Degrees of IP protection › Table
It is convenient when the degrees of protection of electrical equipment ip are summarized in tables. Below are three tables for IP decryption protection. They comply with GOST 14254 - 2015.
Table of degrees of IP protection from access to dangerous parts , indicated by the first digit of the index
IP protection table (first digit)
Table of the degree of protection of electrical equipment IP from water (second digit)
In addition to the first two digits, the protection degree marking may contain two letters. The one that comes first after two numbers is called additional, and there may also be a letter with auxiliary information. The additional letter indicates the level of human protection from access to dangerous parts.
When a person touches electrical equipment, the following types of protection are distinguished:
- “A” - with the back of the hand;
- “B” - fingers;
- “C” - hand tool;
- "D" - single conductors.
The first number after IP and the additional letter in the marking have different meanings. The number indicates the protection of the housing from the negative influence of a person or any objects, and the additional letter indicates the protection of a person from the negative influence of elements of the electrical equipment itself.
For example, the first number “3” indicates the protection of the housing from hand-held tools, that is, the equipment will not be damaged when exposed to hand-held tools. The additional letter “C” certifies that personnel will be protected from the influence of unfavorable factors, namely electric shock, if the shell is exposed to hand tools.
The second letter of the protection category marking after the numbers displays auxiliary information.
- "H" - high voltage equipment,
- “M” - the test was carried out while moving,
- “S” - the test was carried out in a stationary (motionless) state.
"M" and "S" are usually used for equipment with moving parts.
Samples of protection degree markings with additional and/or auxiliary letters - IP 20C, IP 67S, IP 55DS.
Additionally, instead of numbers, there are “X” symbols. This symbol means that protection from foreign objects or water is not standardized for these components of the electrical product. Marking examples – IP X5, IP 1X, IP XX.
In addition, the product may be marked with not one, but several degrees of protection. Multiple degrees of protection are noted if it is necessary to indicate protection simultaneously from several negative influences, and the latter correspond to different degrees when classifying protections. For example, the product is protected from the effects of low water flow and short-term immersion in liquid. Under such conditions, the following marking can be given - IP 65 / IP 67.
How to read labels
Deciphering the index requires certain knowledge. Here the first digit shows the level of access to hazardous parts inside the product for factors that can mechanically damage it. These are solid objects, from hands to thin threads, as well as dust.
The second number indicates the degree of moisture protection that this product has.
The numbers are arranged in ascending order. The higher the number, the higher the security level. If the marking indicates type IP00, then there is no protection (for example, it is a bare wire). If a product is marked IPxx, the degree of protection is not defined. So it should be considered zero.
A format index, for example IP4x, means that the mechanical protection class is defined and corresponds to four, but the humidity protection class is not defined (considered zero).
A letter after the numbers means an increase, increased safety in some respects, and the product must correspond to its main class. Also, a letter can replace the first missing digit (which is rare). A number of letters refer to high-voltage equipment - it determines the reliability of products operating under high voltage when in contact with water.
IP protection class
Often, when they mean “degree of protection,” they say “IP protection class.” From a technical point of view, these are the same thing, that is, synonymous terms. In the regulatory literature, the wording “IP protection classes” is usually not used, but you can often come across questions: “IP54 protection class” or “IP65 protection class”, or “IP21 protection class, what is it?” In these cases, an appropriate degree of protection is meant. In this case, no other or separate standards are provided beyond those indicated above.
Let us next consider the commonly used degrees of protection of electrical products and equipment. Let's give examples of IP decoding and determine where and in what cases the bodies of these markings are used. To be specific, let’s take the case of electrical switchboard housings.
Let's look at examples
IP55 protection degree means that the housing or shell of the product can be anything, an electrical cabinet, a starting device, an automatic device, an RCD, a circuit breaker, etc. In this case, slight penetration of dust inside is allowed (the housing is not sealed), which should not cause interruptions in the operation of the device. It also has reliable rain protection. This is a class of product, but it will no longer be able to withstand splashes of water, for example, from a bucket.
Protection class IP44 is a “safe” version of products designed for indoor use, but in conditions of high humidity. Sockets, switches and other elements located, for example, in the bathroom, must correspond to this class. In fact, they can resemble sockets with lockable lids and automatic shutters on the contacts. They should not be protected from dust, but a short circuit from accidental moisture is excluded. They are also safe to touch with wet fingers.
Note: Even the highest safety classes do not mean that the product cannot be disassembled. This is a civilian safety standard and cannot and should not apply to products specifically designed for military or similar applications.
What can a low protection class offer? Let's get acquainted with the degree of protection class IP20. A product of this class protects its contents only from the penetration of fairly large objects with a diameter of about a finger. From a structural point of view, this could be, for example, a back drawer. It may have small technical holes for tools: tester contact probes, screwdrivers, and so on. It can only be placed inside or inside another electrical cabinet with a high degree of protection, since even from above such a product is not protected from moisture.
IP 20
IP 20 – there is protection from large, large objects with a diameter above 12.5 mm (indicated by “2”), there is no protection from water, since the corresponding position is “0”.
Such IP 20 equipment is suitable for installation in dry buildings, where the appearance of water (splashes) on the housing is not expected, and there is no exposure to objects with a diameter of up to 12.5 mm. In the case of a switchboard housing with IP 20, it should be installed in rooms, apartment corridors, but should not be used, for example, in a bathroom. Table - Explanation of the degree of protection IP20 (dust and moisture protection)
| Protection from external solid objects (dust protection IP20) | Water protection (IP20 waterproof) |
| 2 | 0 |
| Protected from external solid objects with a diameter greater than or equal to 12.5 mm | No protection |
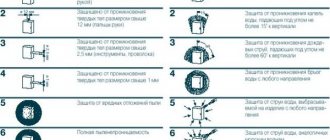
Protection against ingress of solid objects (first digit in the IPXX index):
- 0 — the device is not protected from penetration of foreign objects;
- 1 - protection from objects with a diameter of ≥50 mm, no protection from deliberate contact;
- 2 - protection against objects with a diameter of ≥12.5 mm (finger protection);
- 3 - protection from objects with a diameter of ≥2.5 mm (tools, cables);
- 4 - protection from objects with a diameter of ≥1 mm (wires, bolts);
- 5 — dust protection (dust can get inside, but does not affect the operation of the device);
- 6 — dustproof (no dust getting inside the device).
IP 44
IP 44 – degree of protection indicates that the shell or outer casing of the product is protected from foreign objects with a diameter of 1 mm or more. These include various wires, pins, nuts, hand tools, screwdrivers, etc. In addition, there is protection from humidity and random splashes of water. Equipment with such a housing can be used in structures with high humidity, damp, and also outdoors, but water should not be allowed to enter by stream. The product with an IP 44 housing does not have dust protection. If the dust content of the room or premises is high, you should not use a shield with IP44.
IP 44 electrical panel enclosures are suitable for buildings with high humidity, as well as for installation outside residential premises, but under the roof. This will prevent open exposure to the water jet.
Transcript example
The common designation is IP54. It follows from the table that the housing is dust-proof and completely resistant to splashes from any angle and does not allow you to touch live parts with your hands or tools.
Most Common Levels of Protection
- IP20 - marking implies protection of the electrical equipment housing from foreign bodies 12.5 mm and above (see table). There is no protection from moisture, the shield is installed in a dry room, and there is no mechanical impact. Conclusion - a shield, installed in the hallway or living room of a residential building (apartment);
- IP30 - not protected from moisture, but has higher protection from mechanical impacts of objects from 2.5 mm;
- IP44 - means that electrical equipment is protected from mechanical impacts from objects of 1 mm and from splashes from any angle. Installed in a room with humidity in proximity to tools and machines.
- IP54 - marking means it differs from 44 in partial dust protection and complete protection from foreign objects. Installed outdoors and indoors without open water jets and dust formation.
- IP55 - the housing of such equipment is protected from mechanical interference and partially from dust. Withstands water jets. Recommended for installation outdoors without a canopy. Installed anywhere in the garden.
- IP65 - the housing is dust-proof and can be installed both outdoors and indoors.
IPX7 - degree of protection of the device from moisture
IPX7 is among the eight degrees, the second most protected from moisture. A device with this designation can only remain under water for a short time at a depth of about a meter without losing its functionality. Nowadays, many devices have this IP degree, including some telephone models.
IP 55
IP 55 – the product body is fully protected from the mechanical negative influence of various objects and partly from the penetration of dust. IP 55 is used in damp rooms, outdoors, where short-term exposure to the shell (housing) of equipment may occur in the form of a jet of water. Typically, electrical panel housings intended for outdoor installation have an IP rating of 55. This panel can be installed almost anywhere on the house’s site. It does not require a canopy.