Definition
Protection class is a set of design measures to ensure human safety when working with a device or servicing it. They depend on the presence of grounding, residual current devices, additional insulation, housing material and its design features. Another definition is that it is a system for indicating the degree of protection for a person when working with power tools and other equipment. The class is marked with signs from 0 to III, where 0 means no protection, and III means safe equipment powered by reduced voltage.
Next, we will consider the list of types of protection and each class separately. Which option to choose depends on the requirements for the electrical installation and the conditions in which it operates. At the same time, it is impossible to say specifically which one is better: from a safety point of view, the higher the better; from the point of view of the cost of equipment, the appropriateness of a particular solution depends on the specific situation.
IP (envelope protection degree)
Ingress Protection Rating is a system for classifying the degree of protection of the enclosure of electrical equipment from the penetration of solid objects and water in accordance with the international standard IEC 60529 (DIN 40050, GOST 14254-96)
The degree of protection of the enclosure of electrical equipment is marked using the international protection mark (IP) and two numbers, the first of which means protection from the ingress of solid objects, the second - from the ingress of water.
The code has the form IPXX, where the X positions are digits, or the X symbol if the degree is not defined. The numbers may be followed by one or two letters that provide supporting information. For example, a household electrical outlet may be rated IP22 - it is finger-resistant and cannot be damaged by vertical or near-vertical dripping water. The maximum protection for this classification is IP69: a dust-proof device that can withstand prolonged immersion in pressurized water.
The first characteristic digit indicates the degree of protection provided by the enclosure:
- people from accessing dangerous parts, preventing or limiting the penetration into the shell of any part of the body or object in the hands of a person;
- equipment located inside the shell from penetration of external solid objects.
If the first characteristic digit is 0, then the enclosure provides no protection against access to hazardous parts or penetration of external solid objects.
The first characteristic number, equal to 1, indicates that the enclosure provides protection against access to dangerous parts with the back of the hand, 2 with a finger, 3 with a tool, 4, 5 and 6 with a wire.
With the first characteristic digit equal to 1, 2, 3 and 4, the shell provides protection against external solid objects with a diameter greater than or equal to 50, 12.5, 2.5 and 1.0 mm, respectively.
At number 5, the shell provides partial, and at number 6, complete protection from dust.
| Level | Protection against foreign objects having a diameter | Description |
| 0 | — | No protection |
| 1 | >=50 mm | Large body surfaces, no protection from conscious contact |
| 2 | >=12.5 mm | Fingers and similar objects |
| 3 | >=2.5 mm | Tools, cables, etc. |
| 4 | >=1 mm | Most wires, bolts, etc. |
| 5 | Dustproof | Some dust may get inside, but this will not affect the operation of the device. Complete contact protection |
| 6 | Dustproof | Dust cannot enter the device. Complete contact protection |
The second characteristic figure indicates the degree of protection of the equipment from the harmful effects of water that the shell provides.
If the second characteristic digit is 0, then the shell does not provide protection from the harmful effects of water.
The second characteristic number, equal to 1, indicates that the shell provides protection against vertically falling drops of water; 2 - from vertically falling drops of water, when the shell is tilted at an angle of up to 15º; 3 - from water falling in the form of rain; 4 - from continuous splashing; 5 - from water jets; 6 - from strong water jets; 7 - from exposure to temporary (short) immersion in water; 8 - from exposure to prolonged immersion in water.
| Level | Defence from | Description |
| 0 | — | no protection |
| 1 | Vertical drops | Vertically dripping water should not interfere with the operation of the device |
| 2 | Vertical drops at an angle of up to 15° | Vertically dripping water should not disrupt the operation of the device if it is tilted from its operating position by an angle of up to 15° |
| 3 | Falling splashes | Rain protection. Water flows vertically or at an angle of up to 60° to the vertical. |
| 4 | Spray | Protection against splashes falling in any direction. |
| 5 | Jets | Protection against water jets from any direction |
| 6 | Sea waves | Protection from sea waves or strong water jets. Water that gets inside the housing should not interfere with the operation of the device. |
| 7 | Short-term immersion to a depth of 1m | During short-term immersion, water does not enter in quantities that disrupt the operation of the device. Continuous operation in immersed mode is not expected. |
| 8 | Long-term immersion to a depth of more than 1m | Completely waterproof. The device can operate in submerged mode |
| 9 | Long-term immersion under pressure | Completely waterproof under pressure. The device can operate in submerged mode at high fluid pressure. |
The additional letter indicates the degree of protection of people from access to dangerous parts and is indicated if:
- the actual degree of protection against access to hazardous parts is higher than the degree of protection indicated by the first characteristic digit;
- Only protection against the harmful effects of water is indicated, and the first characteristic digit is replaced by the symbol “X”.
The additional letter "A" indicates that the enclosure provides protection against access to hazardous parts with the back of the hand, "B" with a finger, "C" with a tool, and "D" with a wire.
| Letter | Access protection |
| A | back of hand |
| IN | finger |
| WITH | tool |
| D | wire |
The auxiliary letter "H" denotes high-voltage electrical equipment. The auxiliary letters "M" and "S" indicate that equipment with moving parts is in a state of motion or stationary, respectively, when tested to comply with the degree of protection against harmful effects due to ingress of water.
| Letter | Meaning |
| H | High voltage equipment |
| M | During water protection tests, the device worked |
| S | The device did not work during water protection tests |
| W | Weather protection |
The degree of protection of the enclosure can be indicated by an additional letter only if it satisfies all lower levels of protection, for example: IP1XB, IP1XC, IP1XD, IP2XC, IP2XD, IP3XD.
The German standard DIN 40050-9 extends IEC 60529 to IP69K for high-temperature, high-pressure washing. Such housings not only have strong dust protection (IP6X), but are also able to withstand high water pressure during washing.
The IP69K degree of protection was originally developed for road vehicles, especially those that require regular intensive cleaning (dump trucks, concrete mixers, etc.), but is now finding application in other areas (food and chemical industries).
Protection classes
«0»
Electrical devices with protection marking “0” do not have any protective equipment against electric shock to humans. The only protective element is working insulation. In this case, all open conductive (metal) non-current-carrying parts of the device are not connected to grounding or any protective conductor. There is also no indicator of the presence of dangerous voltage on the housing.
If the working insulation is damaged, an electrical potential may appear on the housing, and only the floor covering and air will protect you. But if you touch the body while standing on a wet floor, you will probably get an electric shock.
The IEC does not recommend producing electrical appliances with protection class “0”, but the PUE allows the use of such lamps in any premises. It is worth noting that such products can be used in rooms where there are no grounded conductive elements in the vicinity and in the work area and where access to unauthorized persons is not available or is limited. In most countries they are considered unsafe. For the same reason, old heaters and electric stoves with open spirals are prohibited, because this is not only a fire hazard, but also does not meet electrical safety requirements.
«00»
In “00” everything is the same as “0”, the class differs only in that there is an indication of the presence of dangerous voltage in the housing. Provided that the operating personnel are trained and have personal protective equipment, it can be used in damp areas.
«000»
An RCD with a sensitivity of no more than 30 mA has been added, with a shutdown speed of no more than 0.08 s. Otherwise, everything is the same as protection classes against electric shock “0” and “00”.
Important: PPE is required for those who work with this equipment.
"0I"
There is working insulation, but the metal parts of the housing and other non-current carrying parts do not have insulation. In this case, unlike previous classes, they are grounded with a special wire or have mechanical contact with a grounding bus (grounding loop). The connection point of the protective conductor or contact with the circuit is indicated by the corresponding symbol.
Examples include: TP, load-lifting cranes, mobile equipment that moves on rails or in another way, but no further than the ground wire allows.
The grounding wire, according to the PUE, has a yellow-green insulation color. Grounding of electrical cabinet parts is carried out as follows:
The ground loop bars are painted in the same way:
"I"
Higher class of protection against electric shock. In such electrical appliances, an additional “ground” contact is added to the plug for connecting to the electrical network. Just like in class “000”, electrical equipment of this type has working insulation - this is the main means of protection. Conductive parts of the equipment, for example, the housing, are grounded and equipped with protection against the occurrence of voltage on non-current-carrying parts.
This class of protection against electric shock includes most household appliances: washing machines, dishwashers, food processors, etc.
Grounding pin on plug:
"I+"
Similar to the previous class, but an RCD is required. When the grounding is disconnected, the class is equal to “000”. The photo shows an RCD on a wire and for mounting on a DIN rail:
"II"
The main difference between electrical equipment with the second class of protection against electric shock is the presence of double reinforced insulation of conductors. However, the chassis remains ungrounded and there are no additional grounding pins on the plug. It is possible to use such equipment in wet areas up to 85% humidity, provided that the protection class is below IP65.
It is designated as follows:
The equipment comes with an insulated shell (casing) and metal. For the latter, it is possible to connect a grounding conductor, but this is regulated by standards and specific electrical appliances. Depending on the design, there may be a protective resistance on the contacts and power terminals, circuits monitoring the health of the protective circuits.
Examples: street lamps on poles, electrical equipment of trolleybuses.
Among household appliances, we can cite as an example fixed (TV) and movable electrical equipment with a low probability of damage (hair dryer, drill, vacuum cleaner, other power tools).
"II+"
It differs from the second class in the presence of an RCD. In turn, there is no grounding of the case, as well as a grounding contact on the plug. The graphic designation differs from “II” by the presence of a “+” sign inside.
Personal protective equipment against electric shock
The main factor that is taken into account when choosing PPE is the supply voltage and the class of protection of the tool against electric shock. When working with equipment corresponding to classification II and higher, no additional means are required.
More hazardous work may require:
| Voltage up to 1000V | Voltage over 1000V |
| Dielectric gloves | Dielectric gloves |
| Galoshes | Bots |
| Dielectric carpets |
Dielectric gloves
When touching live parts of devices, protect against electric shock. These gloves are made from thick sheet rubber. They usually have a universal size and are marked with the letters:
- EV - for work above 1000V, additional PPE.
- En - for work below 1000V, basic PPE.
Dielectric mats
Special rubber mat that does not allow current to pass through. They are made of thick sheet rubber, onto which a corrugated pattern 3-5 mm high is additionally applied. Such measures reduce the contact area. The voltage from which the mats can be used to protect is indicated on the product. Usually they are laid on the floor of switchboards, in front of electrical cabinets and in similar places where there is a high risk of injury during work.
Dielectric shoes
Special rubber shoes are used to protect against step voltage when carrying out any type of work in electrical installations. Boots are marked EV, galoshes - En, designed to work with the voltage corresponding to the marking.
Bots are able to protect even under direct exposure to high voltage up to 2 kV. The thickness of their sole is more than 6 mm, the height with folded flaps designed to prevent water from entering is from 16 cm. They are also equipped with an internal lining made of non-conductive material.
Dielectric shoes are worn over regular work boots, are not intended for constant wear, and have additional restrictions on working conditions depending on temperature, humidity, etc.
Electrical safety classes of power tools
Carrying out work using devices that use current is always associated with certain risks, both for the health of the person himself and for the surrounding area.
For this reason, a special classification has been created that will help a campaign employee or a home handyman accurately determine the choice of tool for their tasks, as well as protect themselves and loved ones.
Next, we will consider the basic principles of dividing devices into groups according to protection class.
Marking of power tools
At the moment, two types of markings are widely used for tools that work with electrical voltage.
The degree of danger of the device is depicted in the form of a simple schematic image:
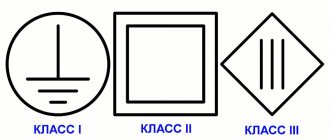
- A round icon, inside of which three horizontal lines are connected to one vertical in the form of an inverted letter T, means that this is a class 1 device;
- A small square enclosed in a large one indicates the relation of the instrument to the second class;
- The third is marked with a diamond with three vertical lines in the center.
Another marking method is also used, which indicates protection against penetration of the external environment into the device. The designation is implemented in a digital-alphabetic format, where the abbreviation IP appears first, and after the hyphen there are two numbers expressing the protection indicator.
The first value is responsible for the ingress of dense particles, where
- – the device does not pass objects larger than 5 cm in diameter;
- – protected from “falling through” of human fingers, that is, 12.5 mm (examples: electrical outlet, shield);
- – objects larger than 2.5 mm, such as tools or cables, will not pass through;
- – sealed against particles larger than 1 mm;
- – full protection;
- – recommended for rooms with a lot of dust, completely insulated.
The last number indicates the possibility of moisture getting into the device:
- – the device will not allow vertically falling drops to pass through;
- – protection against oblique falling drops (about 15 degrees);
- – up to 45 degrees;
- – protected from all sides;
- – does not allow liquid to pass under pressure. It can be used outdoors during rain;
- – invulnerable when submerged under water for a short period of time. This protection class is suitable for use on ships.
Thus, the presence of the IP-XX marking indicates the degree of protection of the device from the ingress of solid and liquid particles inside.
GOST power tool classes
The state standard for the safety of electrical appliances looks like this:
- Class 0 – characterized by the absence of grounding, implies the use of additional protective equipment;
- 01 – assumes the presence of a grounding device;
- 1 – safety level for household and computer equipment, has working insulation, a core in the wire, a ground-contact plug, and a grounding device. As long as wiring and surrounding maintenance standards are observed, it is safe to use;
- A class 2 device does not have grounding parts, the parts are well insulated;
- Class 3 devices operate at low voltage no higher than 42 V and do not require grounding.
How to decipher the insulation class?
During the operation of electrical appliances, some parts invariably heat up, which leads to possible dangerous consequences, especially if a low-quality tool is chosen. The insulation class characterizes the resistance to thermal loads of the insulating material itself.
In this case, the designation takes the form of Latin letters and is deciphered as follows:
- Y – has the worst indicator. The winding is made of cotton, silk or cellulose fibers. Maximum heating is about 90 degrees;
- A – the same insulating materials, but they are already treated with a special compound, the temperature range is slightly wider, up to 105 degrees;
- E – winding made of resin or film, the limit is 120 degrees;
- B – mica is used, up to 130 degrees;
- F – synthetic materials and asbestos, resistant up to 155 degrees;
- H – usually fiberglass, withstands up to 180;
- C – the highest class, temperature limit at 180 degrees. ceramics, glass, quartz, inorganic materials.
Portable power tool classes
- Zero class indicates the absence of grounding, but working insulation is available;
- The first class tool is already equipped with grounding, as well as a power cord and plug. The marking can also be in the form of a circle with the inscription “earth”, PE, or an image of white and green lines;
- The second has reinforced insulation, but does not have grounding, and is marked with a double square;
- The third means low voltage operation and is marked with a diamond with triple lines.
CLIMATE DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
Trivial - climatic design determines the operating conditions of electrical equipment for the corresponding climatic regions (zones). Indicated by an alphanumeric code.
The letter part indicates the climate zone, and the digital part indicates the location (conditions) of placement (see table).
| Letter part | Climate (version) | Digital part | Accommodation |
| U | Moderate | 1 | on open air |
| HL | Cold | 2 | in conditions excluding direct sunlight |
| UHL | Moderate and cold | 3 | closed room without air conditioning (heating, ventilation) |
| T | Tropical | 4 | closed room with air conditioning (heating, ventilation) |
| M | Marine temperate | 5 | rooms with high humidity, without air conditioning |
| ABOUT | General climatic, except sea | ||
| OM | General climatic marine | ||
| IN | All-climate |
Tags: , machine, sconce, view, harm, choice, house, , grounding, sign, insulation, test, how, computer, circuit, , magnet, marking, monitor, installation, voltage, neutral, nominal, heating, transfer, connection , potential, rule, touch, wire, project, start, , work, row, light, lamp, network, system, connection, means, ten, type, current, transformer, , installation, shield, electricity, effect
How to decipher the insulation class
Markings on instruments are indicated in Latin letters. They mean the following:
- Y is the lowest indicator, which indicates that the device has a cotton winding. Maximum heating should be no more than 90 °C;
- A - denotes a tool in which the same materials, but processed, are used to wind parts;
- E - the material used is film or resin with maximum heating up to 120 ° C;
- B - mica winding;
- F - synthetic material.
Maximum class with a heating limit of up to 180 °C.
Thus, during operation of the electric tool, it heats up. If this process is not controlled, unpleasant consequences can occur. Classification helps to correctly plan the work, preserving both the health of the worker and the integrity of the tool.
Source: ohranatryda.ru