The constant development of technology causes the development of its power sources, including batteries. If previously models with liquid electrolyte were most widespread, now gel electrolyte is increasingly being used as the basis for chemical reactions. Despite their high cost and difficulty in maintenance, such energy storage devices have a number of key advantages.
Comparison
What is the difference between a gel battery and a regular acid battery?
It contains the electrolyte not in liquid form, but in a silicon-bound gel substance. Accordingly, all the advantages of such an energy storage device grow from this factor. This:
- Long service life. The gel is not as chemically active as the alkaline-acid liquid in conventional batteries. There are cases of restoration of drive performance characteristics 12-14 years after the end of its service life. Yes, the gel dries out, but the rate of its deterioration is much lower than that of a conventional electrolyte.
- Virtually no maintenance procedures required. Therefore, gel energy storage devices in 99% of cases come in a hermetically sealed case, without the possibility of gaining access to the chemical fillers of the battery cans.
- Very weak sensitivity to shaking, swaying, and even complete turning over. What makes the device ideal for use in small equipment - scooters, hydraulic and regular motorcycles, mopeds. Such gel batteries are popular in the aircraft industry and among shipowners. Smaller sizes compared to classic batteries, with equal capacity, make them ideal for various devices, such as uninterruptible power supply devices.
- Low self-discharge. No more than 20% of energy leaves the drive when there is no load.
- A greater number of charge-discharge cycles compared to classical types allows longer and more intensive use of the energy storage device.
- Less sensitivity to temperature changes.
- No liquid acid solutions. Therefore, even if the seal of the case is broken, the battery will continue to work. This also provides greater safety for humans, since the gel does not flow.
- We can allow the battery to be discharged very low without impairing its reverse charging capabilities.
But as they say, the advantages of the drive also come with some disadvantages in its use, this is most noticeable in particular when charging gel batteries:
- Overheating when recharging. Batteries of this type are very sensitive to overheating. If the gel boils or peels off from the electrodes, then not only can the housing rupture as a result of the release of gases from the boiling gel, but the chemical cycle of energy conservation will also be disrupted. Accordingly, the device will no longer save energy.
- Memory effect. If the charge is carried out incorrectly, the efficiency of the energy element becomes much lower.
Design features
If we talk about what a standard gel car battery consists of, then we can highlight several elements. Namely:
- positive electrodes;
- negative plates;
- electrolyte in the form of a gel;
- overpressure relief valves;
- terminals;
- plastic sealed case;
- separator plates.
The operating principle is the same as other lead-acid batteries. That is, the battery, when charged, supplies the accumulated current to start the engine and power consumers when the generator is inactive. When a charge is released, the voltage gradually drops, and the density of the electrolyte decreases.
Therefore, it cannot be said that a gel battery is in fact significantly different from the acid version of the battery, where there is not a gel inside, but a liquid medium. In addition to sulfuric acid and distilled water, a thickener is also added to gel batteries.
Because of this, many are interested in how to distinguish a gel battery from a liquid lead-acid battery. Everything is simple here. Focus on the markings. On the gel ones you can see the inscription GEL. Plus, all GEL batteries are maintenance-free, their housing is completely sealed.
Safe charging with a conventional charger
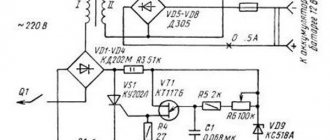
Conventional chargers are not very suitable for charging gel drives, however, they can be used. How to properly charge and charge a gel battery with a regular charger? The basic safety principle for the subsequent operation of the battery is control and correct calculation of current components.
First you need to calculate how much current in amperes is required to charge the battery. To do this, information is taken on the maximum capacity in ampere hours for a specific model (often written directly on the case), and from there 10% is calculated for fast charging, or 5% for a safer current used. For example, the battery has a capacity of 150 Ah (ampere hours), which means the maximum charge current should be set to 15A, and ideally (but the charge recovery time for a gel battery will double) to 7.5A.
As for the volts supplied from the charger terminals, they must be set to the position intended for the standard battery voltage, 6V, 12V or 24V.
Now, as for chargers that do not have a current regulator. It is imperative to lower it, otherwise there will be unforeseen consequences. Amperes can be reduced by connecting a load in parallel to the electric charger - an incandescent lamp. You can use a buffer lead-acid battery for this. With a lamp, the voltage will also drop, but as for the buffer battery, it’s interesting. Scheme:
In theory, a regular battery will lower the amperes, since it is a stronger consumer and is located at the beginning of the parallel circuit. The volt parameters for both batteries should be the same. The remainder of the amperes will go into the gel electrolyte, which will help produce a “softer” charging. Only after assembling the circuit and turning it on should you check whether the gel storage has started to heat up. This can happen if the regular one is faulty.
Specialized chargers for gel batteries
There are also specialized chargers that, having low ampere output currents, allow you to charge such drives either in a fully automatic mode or semi-manually. Such chargers are made taking into account the charging characteristics of gel batteries. The most complex of them allow you to restore batteries of different voltages. When purchasing simpler ones, you need to pay attention to the correspondence of the output current (if there is no switch).
Reference! It is not recommended to charge gel batteries more than a couple of times a year.
Marking of gel batteries
The label that is placed on the top or side of the battery will tell you a lot. The main characteristics (capacity, starting current), as well as the production date, will necessarily be present here. True, the latter is most often present in encrypted form, and manufacturers are capable of coming up with the most exotic encryption methods. For example, batteries under the Optima brand use four digits, the first of which indicates the year (for example, 8 is 2018), and the remaining three indicate the day of the year (of which there are 365). So you will have to determine the month and date with a calculator in hand.
But at least everything is clear here, but a code consisting of two letters and two numbers is applied to the Delta battery. There are no problems with the latter - they indicate the day of the month, the month can also be determined by the letter (A - January, B - February, and so on), but the year cannot be determined simply by the letter - you need to look for a correspondence table.
A not entirely clear coding is also used in Varta batteries: the fourth digit indicates the year, and 5–6 indicates the month, with values from 17 to 20 indicating January–April, and May starts from 53 and then goes up.
Other manufacturers have a similar situation, and all because of the lack of labeling standards (they exist, but they are different for Europe, Asia, and the USA).
Requirements
Basic requirements for specialized memory devices:
- Regulation of the charging voltage of the gel battery.
- Adaptation of the current used for various external conditions (air temperature in the room where the charge level is restored).
- Adaptation of the number of amperes, depending on the temperature of the battery itself at various stages.
- Automated voltage change, depending on the stage. It is desirable to have a charger that allows saturation of the battery in three stages: 1 - increased voltage;
- 2 - constant voltage support, with a decrease in the number of amperes;
- 3 - minimum recharging with a minimum of volts and amperes.
Main selection criteria
For long-term battery operation, you need to select a charger with a certain set of characteristics, so as not only not to damage the battery, but also to help extend its service life. The following criteria are decisive:
- Charge current range. To determine the normal level of this parameter, you need to be guided by approximate calculations: 0.05-0.2C, which means a small part of the battery capacity (C), the unit of measurement of which is Ah. If a multi-type car charger for powering gel batteries operates at currents no higher than the minimum limit of the stated interval (0.05 C), then the battery charging process will take a very long time. In the opposite situation, when the battery is connected to a power source with an increased charge current, there is a high risk of its failure. The optimal values of this parameter for GEL type batteries are in the range of 0.15-0.2C.
- The ability to adjust the charge current, which allows you to set the permissible limit of this parameter when powering a battery of a certain capacity. It is not recommended to connect a charger operating at a charging current exceeding the above limits, which will gradually lead to a reduction in battery life.
- The battery voltage must match the charging type. For example, there is a different type of charger for powering 12V or 24V gel batteries, and if you need a device for powering a battery with a voltage of 6V or, for example, 48V, in this case it is possible to make it to order.
- Temperature compensation. This function allows you to control the battery heating level. The best option is temperature compensation, the temperature sensor of which is remote to obtain more accurate measurements.
- The number of stages of the charging process, which implies a combination of cyclic and buffer modes, the first of which allows you to charge the battery first with constant current, then with constant voltage, and the second maintains an already charged battery at a high level.
- Acceptable ambient temperature values. It is usually recommended to use the device in the range from +5 o C to +40 o C.
If there is one more nuance: the charger for sealed lead-gel batteries should have a lower charge voltage than in the case of liquid-acid batteries. Otherwise, again, we can talk about the imminent failure of such a battery.
Full charge time
How long does it take to charge a gel battery? It is very easy to calculate - the battery capacity ampere*hours is divided by the set current of the charger. The result obtained is the time in hours that the battery requires to be completely saturated with energy. This time cannot be exceeded! Overheating will begin. It is even recommended to keep charging a little less time. Let the battery not be charged to 100%, but at least it will remain intact.
Advice! When charging, if the battery becomes hot, it must be immediately disconnected from the charger and allowed to cool. If this is not done, the boiling gel will destroy the battery beyond repair. In addition, when recharging, it is worth reducing the current.
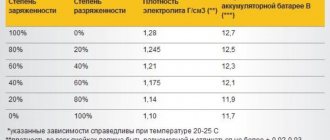
How to check a gel battery for the level of already accumulated charge, so as not to miss the moment of shutdown? To do this, use a regular multimeter. The battery is periodically disconnected from the charger and the voltage at the storage terminals is measured. If the voltage there rises above 12.6V for 12 volts, 6.6V for 6V, or 24.6V for 24V, then the charge is fully charged. There is no point in charging further, especially since this can lead to heating of the element of the battery collector cans.
Preparing the battery for charging
Before charging the battery for the first time, you need to familiarize yourself with its parameters, first of all:
- S tandby - voltage during storage and waiting for use, readiness. If the battery voltage is lower, the charging voltage should be reduced by approximately half, if the charger allows this. Charging should be done periodically: half an hour of charging, half an hour of break. After two or three cycles, switch to normal mode.
- Cycle use - maximum voltage during charging. The standard value is 14.1 - 14.4 Volts. Most conventional chargers have a nominal voltage of 14.5 to 15.5 volts. That is why they are not suitable for gel batteries (without modification).
- " Max initial current " - maximum charge current. If this parameter is not specified, it is selected at about 10% of the capacity. For example, if the battery capacity is 50 amp-hours, select a current of 5 Amps.
Nowadays, serviceable gel batteries have appeared on sale; in this case, before charging, you should loosen the plugs so that possible degassing occurs.
Maintenance of gel batteries
Over time, the gel dries out, losing its electrolytic properties. This happens, of course, at a lower speed than in lead-acid batteries. But this is a common reason for a decrease in battery efficiency.
How to restore and revive the gel battery in such cases? The density can be increased to a certain limit by adding distilled water to the battery jars. To do this, carefully remove the caps on each of the battery tanks, then the rubber plugs, then pour the distillate into each with a small 2 ml syringe. With the plugs open, the battery is left for three to four hours to allow the reaction to occur and the liquid to be absorbed into the gel. Check the voltage level at the battery terminals. If everything is in order, the caps are put back in place and the battery is charged.
Actually, increasing the density, as well as periodically recharging up to 100% twice a year, is actually all the available maintenance for gel batteries.
How to extend the operating life of the device?
Despite the fact that the 12 Volt gel battery is maintenance-free, its service life can be extended. A swollen battery cannot be resuscitated; it must be disposed of. In this case, the gel is separated from the plates, and energy production becomes impossible. Internal damage is difficult to detect. These include wear of the fiberglass, electrodes or electrolyte.
When the filler dries, restoration is possible. To do this, remove the plastic cover and remove the rubber valves. Using a syringe, pour 2 ml of purified water into each jar. The liquid should slightly cover the plates. After moistening the gel, excess water is pumped out with a syringe. The caps and lid are returned to their place.
How to check a gel battery
Some types of testing of gel drives:
- First you need to lightly shake the battery while listening. If an extraneous sound is heard inside, then with a 90% probability the battery plates have come loose. This type of storage device can only be recycled. It will not be possible to restore it at home.
- If the battery is swollen or even one bank on it is “swollen,” it is also beyond repair.
- If everything seems to be intact, but the voltage on the contacts is zero, and the gel battery does not take a charge, then this is a classic discharge of the device to zero. A charger will help here; it can be used to “push” the battery so that it begins to gain energy. Why do they first try to charge it with an increased current (for 12V -15V, for 6-8V, for 24 - 26V). As soon as the battery begins to charge, the voltage is lowered to standard charging parameters. In this case, the drive's operating parameters will most likely deteriorate.