Why do you need a voltage control relay?
Household electrical appliances are designed for a voltage of 220-240 V. From time to time, emergency situations arise in the electrical network. The voltage in the outlet jumps up or down. Jumps can disrupt the operation of household appliances or completely destroy them.
Voltage drops in the network
A common case of voltage drops is a zero break. In this case, in one phase the voltage drops below the permissible level. On the other, on the contrary, there is a significant increase in voltage up to 380V.
Another situation is typical for old houses with poor electrical wiring and loose contacts. Due to the poor condition of the cables and their overload, the voltage in the sockets can drop to 170 V or lower. This is dangerous for electric motors of washing machines and refrigerators.
A voltage control relay protects electrical appliances. This small device is located in the distribution panel of the apartment. It has a compact design, is conveniently mounted on a DIN rail and performs its task completely autonomously.
Additional Information. It is necessary to distinguish voltage control relays from all kinds of stabilizers and UZMs. All of the listed devices are used to protect household appliances. The stabilizer is an active device. He is able to independently adjust the voltage in the apartment. The RN performs a simpler and more passive function. It simply turns off the consumer when the permissible threshold is exceeded and, in itself, does not affect the voltage in any way.
Understanding the 40 A voltage relay
The volt controller, as relay experts say, is used to protect large houses, as well as industrial complexes. It is necessary to study the principles of operation using an example; we chose a 40 A device as such.
This device, designed to protect the electrical network, is also necessary like a machine, but has a slightly different purpose, namely monitoring the current voltage. Random overvoltages are considered to be the main reason for the failure of expensive equipment that is sensitive to network interference. Repairing damaged equipment is expensive for the owner, because breakdowns due to voltage are not included in the list of warranty cases.
Such surges are extremely short-lived, only fractions of seconds (maximum a few seconds) until the substation’s protective mechanism is triggered. This short period of time is enough to burn out all the equipment. To imagine the problem globally, take a look at your sockets, how many devices are turned on at the moment? Most of them will “burn out” if there is a drop without a voltage relay.
Relay design features
External structure
It is better to consider the design using a live working example. We chose the 40A RN-104 relay manufactured by Novatek Electro. The housing, like most other devices, is designed for DIN rail mounting. The front panel has an indicator of three segments, by which you can determine what is currently happening with the electrical network. The device has three regulators and the same number of terminals, being one of the simplest representatives of its class of electrical devices.
The device connection algorithm looks like this:
- The phase from the machine is connected.
- A zero or a second machine is connected.
- Consumption or automatic machines are connected.
The choice in the second and third points depends on the characteristics of the target power network and whether you are building a network from scratch or improving an existing one. The connection is made according to the brief diagram shown on the side of the device.
Internal structure
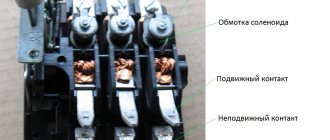
If you disassemble the device, you will see that the design is not so complicated. By looking at the device without a lid, you can understand something about its assembly. Thus, thin, neat soldering will tell us that the process took place without human intervention. We recommend selecting devices produced at enterprises where a person participates only in the test stage, and the rest is done by the production line. Then the percentage of potential defects is significantly minimized.
In fact, this relay consists of two boards: power and control. The first is a large 40 A relay, which allows the device to operate with loads up to 9 kW. Its leads are soldered to copper leads that lead the connection to screw terminals.
Relay settings
The manufacturer met the client halfway and programmed the main functions in the form of a variable menu:
- reactivation time;
- lower threshold;
- upper threshold.
In this case, all parameters are adjusted using a potentiometer, which you simply need to turn and set the number on the indicator. Full display indicators are found only on expensive models, and small digital indicators are installed on almost everything. The most ideal setting is considered to be the following:
- Automatic reclosure - 180 sec;
- lower threshold - 190;
- the upper threshold is 245.
This device has a useful hysteresis function of 5 volts: when values are close to the threshold, the device does not turn on. This helps to get rid of continuous switching off/on when the voltage in the network fluctuates on the verge of permissible. In this case, the device introduces an additional “smart” threshold and does not connect until the situation normalizes. The availability of this functionality should be checked for each model separately. We believe that it is very useful, so it is worth taking care of it.
Also, a high-quality relay has a mechanism for controlling smooth network sag. This happens when large consumers, such as an iron, microwave, or air conditioner, are turned on. At this moment, the apartment’s electrical network drops by 50-60 percent, after which it is also smoothly restored, the procedure takes from 8 to 12 seconds. A smart device can recognize such moments and not turn off the network after turning on the kettle.
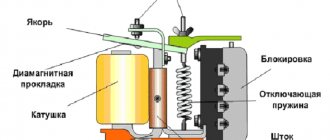
Design and principle of operation of a voltage relay
As can be seen in the figure above, the voltage relay consists of two main blocks: a measuring and an actuating block (relay).
When voltage is applied to the relay, the measuring unit determines its value and if the measured value of the mains voltage is within the range of values set in the relay settings, the measuring unit sends a signal to the executive unit (relay) which, in turn, closes the power contact, thereby including the load.
The measuring unit continuously monitors the mains voltage; if the voltage drops or increases above the value set in the settings, the measuring unit immediately sends a signal to the actuator (relay), which, in turn, turns off the load. After the voltage value is restored, the measuring unit, after a time delay set in the settings (usually can be set in the range from 5 seconds to 15 minutes), sends a signal to the actuator, which turns on the load again.
Voltage relay RN 113, connection methods and 4 modes of operation
RN-113 is designed to disconnect consumers in the event of unacceptable voltage fluctuations in the 220V supply network.
After restoring the parameters of the power supply network, the relay independently restores power to electrical appliances. On the front panel there is a seven-segment LCD indicator showing:
- mains voltage;
- the value of the parameter being set;
- network parameters when disconnected (indicator blinking);
- time before switching on.
Parameters are set using the knobs on the front panel.
The rated current of the device is 32A. If it is necessary to connect a load of higher power, it is connected through the starter.
Operating modes
The device operates in four modes:
- Conventional voltage relay. At the same time, full consumer protection is provided.
- Maximum protection. Shutdown occurs only when the supply network overvoltage exceeds the specified limits.
- Minimal protection. Triggers when the potential drops below the permissible level.
- Time relay with turn-on delay.
Before connecting the PH 113, you can watch a video on this topic on the Internet.
The picture shows a diagram of connecting the voltage relay RN 113 for the house cx to a 220V network.
Connection RN-113
Types of launch vehicles
Various types of devices need protection from voltage surges. Some of them operate on household voltage 220 V and consume minimal power. Examples of such devices include smartphone chargers or LED light bulbs. Others also operate on 220 V, but already consume thousands of watts of power, for example, electric kettles and irons. Still other devices require three-phase power supply of 380 V. A conventional single-pole LV is not suitable for them. Among such consumers are industrial machines and powerful asynchronous motors. Therefore, all relays for voltage control are usually divided by type of housing and type of load.
By case type
This classification indicates which devices and in what quantities can be connected to the relay. According to the type of execution, the launch vehicle is divided into 3 types:
- rosette;
- in the form of an extension;
- with installation on DIN rail.
The first type is the easiest to use. This surge protection relay plugs directly into an outlet. On one side of the case there is a corresponding connector in the form of a plug. On the other part of the device there is a standard socket for connecting the load. This type of LV can be quickly removed and connected to another location.
It will be interesting➡ How to connect an LED strip? Simple ways to connect LED strip
The second type is made in the form of an extension cord. On its surface there are several sockets for loading. Unlike type 1, this relay is equipped with a cable and plug. The device is convenient for stationary connection of office equipment.
The third type is the most professional. The pH is installed in the shield. It has an extended list of functions, high throughput, and at the same time protects all electrical appliances in the apartment.
By number of phases
Electrical consumers operating on alternating current are divided into 2 groups. The voltage control relay has a similar division. Namely:
- single-phase LV;
- three-phase.
Single-phase modification is suitable for home use. These relays are installed in apartments, garages and cottages. They pass through one phase and zero. That's why they are called single-phase.
The operating voltage for such LVs is 220V. Their contacts are designed for a current of 30-40 A, which corresponds to the maximum values for residential wiring. The device has a minimal list of settings and, if you read the instructions, is suitable for use by an ordinary person without specialized education.
Three-phase voltage monitoring relay ZUBR 3F
The second type of relay is more complicated. It controls voltage on 3 phases simultaneously. This modification is suitable for units consuming 380 V from a network. The relay has an expanded list of adjustments and requires minimal experience in setting up automation systems.
Classification and types
To protect the electrical network of a private house, apartment in old and new residential buildings, different devices are needed. Voltage relays are divided into two categories:
- by connection type;
- by number of phases.
By connection type
There are two main categories of voltage relays depending on how they are connected:
- stationary;
- portable.
Stationary control devices are divided into two types. Devices for installation in electrical panels and built-in sockets. Let's take a closer look at each type.
A voltage relay installed in a distribution board has a number of advantages. The device is mounted at the network input to protect all electrical equipment of a house or apartment. If it is used, there is no need to use additional relays to protect individual consumers, which significantly saves the budget.
Socket voltage relays represent an excellent alternative when it is not physically possible to install the device in the panel. Sockets are used for spot protection of appliances such as refrigerators, boilers, washing machines, etc.
Tip : To save money, choose double sockets!
Portable relays are available in two types: plug-socket and extension cord. They are used when installing a protective device at the network input is impossible. Despite the bulky parameters, portable devices are in demand. This is due, first of all, to their portability and ease of use (no installation required).
The socket outlet is designed to protect only one consumer. The device connects to a standard outlet and monitors voltage drops in the node without monitoring the general condition of the network. Suitable for protecting expensive and powerful electrical appliances.
An extension cord with a built-in monitoring relay is used to protect a group of devices from power surges. A convenient and simple solution has only one main limitation - the maximum load power.
By number of phases
Depending on the type of electrical network, there are two types of relays:
- single-phase;
- three-phase.
A single-phase relay is designed to control electrical networks with an operating voltage of 220 V. When properly configured, the device is suitable for protecting almost all household electrical appliances.
Three-phase protective devices are used mainly in country houses and new housing stock, where a three-phase power supply connection is provided. Moreover, the RKN controls the voltage of each phase.
Voltage relay selection
The choice of a voltage relay begins with the choice of its design (type).
The following types of voltage relays exist:
— By type of electrical network: single-phase and three-phase
— By installation method: stationary and portable.
As shown in the picture above, permanent installation voltage relays are divided into two subgroups:
— voltage relays intended for installation in electrical panels are, as a rule, used to protect all electrical appliances connected to the network; this is also their main advantage; when installing a general voltage relay in the input electrical panel, the entire electrical network is protected, accordingly, the need to install several voltage relays disappears, thereby significantly reducing the cost of organizing the protection of the electrical network from voltage surges.
- socket relays - voltage relays built into the socket, used if for some reason it is not possible to install a voltage relay in the electrical panel, and can also be used in conjunction with the above relays, if there is a need to set individual settings for specific equipment. For example, because It is recommended to turn on refrigerators after a power outage no earlier than 5 minutes; to protect them, an additional voltage relay is often installed, so after a drop and restoration of the normal voltage value, the general relay turns on the load, for example, after 1 minute, and the socket relay installed for connection The refrigerator will turn it on only after 5.
Finally, portable voltage relays can be of two types: plug-socket and extension cord. The design of these relays is similar to stationary socket outlets, and although they are more bulky, these types of relays have become quite widespread due to three important advantages: no need for their installation; portability, i.e. the ability to take them with you on the road to protect against surges in any place, for example in the country; and, as in the case of stationary socket relays, the ability to set individual settings for specific equipment.
— By type of protection: simple, with protection only against voltage surges and with combined protection.
An example of a relay with combined protection is a current-voltage relay, which controls not only the voltage, but also the current of the electrical network, thereby protecting it from both voltage surges and overloads, i.e. additionally performs the function of a power limiter.
IMPORTANT! A voltage-ampere relay does not provide network protection against short-circuit currents and therefore cannot replace a circuit breaker!
Example of a current-voltage relay:
Having selected the desired type of relay from those listed above, you can begin to determine its required characteristics.
The main characteristic of a voltage relay is its rated current; the value of the rated current is indicated on the relay body and in its passport.
Rated current is the current that the relay is capable of passing through itself for a long time while maintaining its functionality. This implies the main condition for choosing a voltage relay: the rated current of the voltage relay must be greater than or equal to the current of the protected electrical network.
Inom. RN⩾I network
Standard relay rated current values are: 10; 16; 25; 32; 40; 50; 63 and 75 Amps (the values shown are the most common)
The calculation of the power supply current can be determined using our online calculator, or you can calculate it yourself as follows:
1) We determine the power of the network by summing the powers of all electrical appliances connected to the network protected by the calculated voltage relay:
Pnetwork=(P1+ P2…+ Pn)*Ks, kW
where: P1, P2, Pn are the powers of individual electrical receivers; Ks - demand coefficient (takes into account the non-simultaneous connection of electrical appliances to the network) Ks is taken from 0.65 to 0.8, if only 1 electrical receiver is connected to the network or a group of electrical receivers that are connected to the network at the same time Kc = 1.
Note: Network power is determined in kilowatts (1 kiloWatt=1000Watt)
It will be interesting➡ Electromagnetic radiation is an invisible killer.
2) We determine the network current by multiplying the calculated network power by a conversion factor (Kp) equal to: 1.52 for a 380 Volt network or 4.55 for a 220 Volt network:
Ineti=Pneti*Kp, Ampere
Based on the calculated value of the mains current, we select the nearest higher standard value of the rated current of the voltage relay.
Note: It should be remembered that the voltage relay does not protect the electrical network from overcurrents (overload and short circuit currents), therefore the voltage relay itself must be protected from them by a circuit breaker installed in series with it, therefore the rated current of the voltage relay can be taken based on the rated current of the machine based on the condition that the rated current of the relay must be greater than or equal to the rated current of the machine installed before it:
Inom. RN⩾ I nom. AB
Bottom line
The internal design of the EZ9C1240 voltage relay from the Easy 9 line is designed for long and trouble-free operation. In particular, all relays have flexible connectors inside them, which have a number of advantages over other types of electrical connections. The fact is that the relay is a maintenance-free device, and all internal connections are made using spot welding, the quality and reliability of which directly affects the service life of the product.
It is the flexible connection that allows you to get the most reliable contact, which is also not subject to mechanical stress because such a connection is made with a margin of length. In addition, flexible connections are more resistant to vibrations that inevitably occur during the operation of electrical equipment.
For this reason, this type of connection is used almost everywhere in electrical equipment, for example, in modular circuit breakers and differential devices of any manufacturer, in molded circuit breakers up to 630 A and even in medium voltage equipment 6-10 kV (for example, Evolis circuit breaker from Schneider Electric). A voltage relay is installed at the entrance to the electrical panel, immediately after the input circuit breaker.
Voltage relay connection diagram
Let me show you once again what the connection of a voltage relay in an electrical panel looks like:
Voltage relay installed in the electrical panel. Voltage 220V.
The photo shows a Digitop voltage relay, as a review I can say that I connected these several times, there were no problems.
The voltage relay must be protected by an input circuit breaker. The machine can be placed before or after the counter, but it must be there in any case. The rating of the machine is one step less than the rated current of the voltage relay. In the above case, this rule does not apply:
Automatic machines, counter, voltage relay
In justification, I can say that in voltage relays they usually put a relay one step larger. I discovered the Ukrainian Barrier and Digitop, for example, with a nominal value of 32 A, the voltage relay circuit contains a 40 A relay, which is very commendable.
How to install
So, we have looked at the purpose and advantages of this type of protective automation. Now let's talk about how to properly connect a voltage control relay to a single-phase network and install it on a DIN rail with your own hands! To make the instructions more convenient and understandable for you, we will provide them step by step with photo examples of correct installation:
- Turn off the power at the input panel.
- Install the new type of relay on a DIN rail so that the housing is placed as close as possible to the input circuit breaker after the meter.
- Determine where the phase is on the machine and where the zero is using an indicator screwdriver.
- Cut the phase wire coming from the machine to the apartment (or house) in the middle yourself so that both parts of the wire can be connected to the voltage control relay.
- Connect the cut end of the wire that comes from the machine to the terminal labeled “IN”.
- Fasten the remaining cut conductor to the “OUT” terminal. Thus, current should flow from the input on the floor to the apartment wiring not directly, but through a protective relay.
- Using a small piece of electrical wire of a suitable cross-section, connect the remaining “N” terminal to the neutral bus in the distribution panel. Ultimately, the connection diagram in a single-phase 220 Volt network should look like this:
- Check the quality of all connection points and if the wires are securely fastened in the connectors, turn on the power at the input circuit breaker.
Electrical installation features
The second option for connecting the device to your home network
That's all the technology for connecting a voltage relay to a circuit breaker with your own hands
As you can see, there is nothing complicated and even an electric kettle can connect the device! We draw your attention to the fact that there are other types of new type protective relays, which can be represented by a product that looks like a tee with a digital display. This design option allows you to protect one separate electrical appliance in the apartment from overvoltage.
Installing and connecting this type of protection is not difficult, so we won’t dwell on these instructions!
One phase or three?
The next point you should pay attention to is what current the device is designed for:
- Single phase. The most commonly used type of connection in residential premises (apartments, houses, cottages). If your wiring is designed for 220 V, then you should install a single-phase voltage relay.
- Three-phase. Such relays are used to protect powerful consumers (machines, refrigeration equipment, welding machines, etc.) that require 380 V for their power supply. They control voltage in three phases. If one of them is de-energized, all three are switched off.
If you do not have high-power consumers that require a three-phase connection, it would be better to install a single-phase relay. And if there is, then it will be more reliable to make the connection using a contactor.
A contactor (starter) is a device used for frequent remote switching on/off of electrical circuits. Its use is required for heavy loads (more than 7–8 kW). To choose the right contactor, you need to calculate the load under which it will be operated.
Which type is preferable?
If the user is concerned about the safety of an expensive model of a refrigerator, for example, and all other devices are already protected by a stabilizer, it is more convenient to purchase a sample of the “socket-plug” type.
In this case, installing a general automatic device will be unnecessary, as it will lead to unjustified costs. This option is more suitable for residents of city apartments who do not want to spend money on installing an RKN in the distribution panel (for this you will have to invite an electrician).
Regardless of the operating conditions of the control relay, it should be understood that installing several devices in an outlet will cost more than one in a panel.
When there is no stabilizer in the house, and its owner wants to reliably protect kitchen and room equipment, it is wiser to choose a device mounted on a DIN rail. By installing several relays - one for each protected line - the possibility of breakdown of expensive equipment is completely eliminated. They are optimally suited for a private home, where they can also control a three-phase network.
Connecting multiple voltage monitoring relays
Technical conditions allow connection to a private house or apartment of three phases. If three-phase units are used to protect electrical equipment, then in the event of an emergency, all equipment on one branch will be de-energized, which is not very convenient. This problem is solved by three relays connected separately to each phase.
From the bottom terminal of the machine we make a connection to the input of the first block. From the other terminal - to the input of the next block. For ease of maintenance and repair, this should be done with multi-colored wires, while remembering that blue is always “zero”. We connect the neutral wire to the neutral bus.
You can install separate input circuit breakers so that, if necessary, de-energize the desired relay if you suddenly have to turn it off. As you can see, the installation is no different from the examples discussed above, only instead of one block there are three at once, each for its own phase.
We connect the relay outputs to automatic machines, which each go directly to their own load: lighting, sockets, boiler. Accordingly, each relay can be set to a different delay time.
Features of the ILV installation
The general procedure for installing a relay in an electrical cabinet is determined by the requirements of current standards (PUE, in particular). Each specific ILV model can be installed in accordance with the functions it performs. The following options for installing a relay in the electrical wiring line are possible:
- placement immediately after the electric meter (this method is considered classic);
- connection together with an RCD and a linear machine, which expands the functionality of the device;
- installation before the electric meter, allowing you to protect the metering device itself from overvoltages.
The latter option is possible only after obtaining permission from Energosbyt representatives.
Depending on the method of connection to the load, various types of RLVs are installed either according to a direct connection to the load, or through the power contacts of a magnetic starter. The second option significantly expands the device’s load current capabilities.
Nuances of choosing a device
When choosing a voltage relay, you need to pay attention to the following parameters:
- Element performance.
- Possibility of regulation (setting the required delay time, as well as response limits).
- Rated current value.
If the device has a digital indicator, it will be easier to configure, but in general the presence of such a component does not play a significant role. Before you go shopping or order a device online, it would be a good idea to visit specialized forums and read reviews.
Pay attention to whether manufacturing company employees communicate with users. Openness indicates that the company is confident in its products.
Voltage measurement before choosing
In general, voltage relays are a budget option, and today they should be installed in every apartment. It’s just that the upper and lower thresholds for infrequent triggering need to be set correctly. And for this you need to at least have a multimeter and experimentally measure the input voltage during peak load hours.
It is advisable to take three measurements - in the morning, in the evening and at night. And after that, based on the results, set the relay response thresholds.
Any normal person would be afraid to set such response thresholds on the relay without any other protection, and continue to use electricity with such unsatisfactory indicators.
Advantages of relays compared to stabilizers
Using a voltage relay for an apartment or for a house, if the stability of the line allows it, is in many ways preferable to installing stabilizers. Let us list the main advantages of the RKN:
- Compactness. This device takes up much less space than any stabilizer.
- Easy to install. The network voltage control element can be installed inside the electrical panel on a DIN rail, and you don’t even have to bother with connecting cables for a long time. And to install the stabilizer, you will have to cut into the line (when installing the device indoors) or place the device inside a specially made protective box, next to the shield.
- Fast response. This is the main advantage of the voltage control relay. With a sudden jump in the potential difference, the element is triggered in just a few milliseconds. In this matter, only triac stabilizers, the price of which is an order of magnitude higher, can compete with RKN.
- Silence. The relays operate quietly, while the operating stabilizer can be heard even at a fairly long distance.
- Economical. In comparison with stabilizing devices, potential difference control elements consume a negligible amount of electricity.
- Low price. As already mentioned, voltage control relays are many times cheaper than stabilizers.
It will be interesting➡ Switch connection diagram
Considering the above advantages of RKN, it becomes clear why, if possible, you should choose them. And yet, having become familiar with the advantages of these elements, there is no need to get carried away and install them everywhere instead of stabilizers.
If you use a relay as a voltage cut-off for a refrigerator, and the potential difference in the network regularly jumps, then constant switching on and off of the power will result in the expensive unit breaking down in a few months.
How to choose a voltage relay for an apartment or house
Many who do not know what a voltage relay is, very often confuse it with a stabilizer. However, there is not much in common between these two devices. The confusion arises due to the fact that, as in the case of a voltage stabilizer, the relay allows you to automatically control the current parameters, but not regulate it (increase or decrease it, as a voltage stabilizer can do).
The main functions of the voltage relay are control:
- You can program the voltage relay to have an upper and lower operating range. For example, the relay will turn off if the voltage in the electrical network drops to 160 Volts or, conversely, rises to 240 Volts;
- You can independently adjust the voltage indicator readings if it is not displayed correctly on the relay display;
- Set the voltage relay delay (the time after which the relay will begin voltage control before turning on again).
As mentioned above, the main parameter of a voltage relay is the response speed. The lower the shutdown speed, the faster the voltage relay will operate. For modern protection devices, this parameter fluctuates around 0.02-0.05 seconds.
What you need to know about the power of voltage control relays
Also, when choosing a protective relay, you need to take into account the power of the connected devices and the phase pattern. There are three-phase and single-phase voltage relays. It is single-phase relays that are most often chosen for installation in houses and apartments. In this case, the voltage relay can be installed on a special DIN rail, when the whole house will be connected through it, or to a regular outlet, if it is necessary to protect only individual electrical appliances.
An equally important parameter when choosing a protective relay is power. If you incorrectly select the power of the voltage relay for the entire house, then if the permissible load is exceeded, the relay will turn off. In turn, a relay with much higher power than needed will not be turned off, but its cost will be an order of magnitude higher.
Therefore, when choosing a voltage relay based on power, you should take into account the rating of the installed circuit breakers in the house and the consumed load. If there are 25A circuit breakers, then you will need a 32-40A voltage relay to protect the entire house. Sometimes you need to choose a voltage relay that is more powerful, for example, 50-63A, here everything largely depends on what load will be connected to it.
Main criteria when choosing a protective relay
So, to choose the right voltage relay, you need to consider:
- Phasing;
- Power;
- Response speed;
- Adjustable voltage range (if the network voltage is lower than it can be set in the relay, the protection device will be turned off all the time, and it will not be possible to use it normally);
- Possibility of self-adjustment of the voltage indicator (if it is distorted on the display);
- The presence of thermal protection against internal overheating of the voltage relay.
So, having figured out the choice of a protective device, it should be added that installing it on the entire house or apartment is both a plus and a minus. The advantages include the fact that in this case absolutely all electricity consumers in the house will be protected. As for the disadvantages, if there is a strong voltage drop, the entire house will be de-energized, which is completely inconvenient.
Purpose of the voltage control relay (VCR)
All consumer equipment operates from the rated voltage inherent in the networks, equal to 220 V. In fact, voltage fluctuations are constantly present and the client receives constant surges at the output of the electrical networks. Deviations of 10% are considered normal. But it is not uncommon for measuring instruments to record drops in readings of up to 70 V, surges of up to 370 V. Equally low and high voltages are dangerous for electrical consumers. Operating such a system without protective devices is extremely undesirable. General view of the voltage control relay
The protective shutdown assigned to the voltage relay will de-energize the electrical device during a voltage drop, and the automatic shutdown (turn on) function will save the life of the product or its individual electronic devices (fuse, motherboards, relays, etc.). Do not confuse RKN with devices for monitoring the break of zero, neutral, short circuit, etc.
The protective voltage relay is used:
- to protect single-phase and three-phase networks;
- for protection against sticking, breakage, phase imbalance, excessive load currents;
- to protect equipment from malfunctions;
- in devices using highly loaded motors;
- in public organizations with large sets of devices with high load current and load power of the electrical network.
Advantages and disadvantages of stabilizers
The advantages of a stabilizer include the ability to equalize voltage. The most advanced devices of this type (inverter class) maintain the specified parameter with a deviation of no more than 1%. But even the cheapest stabilizer models will not allow deviations of more than 5%. Of course, this mode is most favorable for electrical appliances and can extend their service life.
Stabilizers have high efficiency. Another plus is the minimal impact on the quality of the analog signal. It is easy to connect stabilizers to the network, so there is no need to invite a specialist to install this protective device.
But there are also disadvantages. Stabilizers are quite large in size, and the most powerful models make noticeable noise and heat up during operation. The cost of these devices is also quite significant.
The individual use of stabilizers allows you to compensate for shortcomings. Devices for connecting loads up to 1.5 kW remain relatively compact and affordable, which cannot be said about models designed for loads of 3 kW or more.
Tips for choosing RKN
To correctly and rationally choose a device to protect devices and equipment, you must follow the following tips:
- It is advisable to purchase equipment at specialized retail outlets, where they will provide advice on the selection, installation, operation of the product and provide a guarantee for the goods sold;
- The more complex and functional the device, the higher its cost. The price of the RKN depends on the following factors:
- type of device - socket type will be the least expensive, rack type - the most expensive;
- manufacturer;
- design, material of relay parts;
- additional product functions;
- correct selection of the device according to the power of the protected household appliances. For normal operation of the system, it is advisable to use a relay with a power 25% higher than the rated one based on the sum of all consumers included in the electrical circuit. That is, with a rated power of the transformer used of 10 A, it is necessary to install a protective relay with a threshold of at least 13 A. It is worth noting that all three-phase devices are designed for 16 A;
- the presence of a digital indicator (display) for visual monitoring of network operating parameters;
- the body material should preferably be made of materials that do not support combustion;
- the presence of a function for adjusting the protective shutdown time to prevent frequent operation of the device;
- availability of a passport with the technical characteristics of the device, electrical diagram;
- the presence of a function to protect the device from overheating, measuring network power to disconnect the load.
Description of popular models
The connection diagrams and settings of most models offered by domestic manufacturers have much in common; they may differ only in details.
Devices under the Zubr brand
Protective devices of this series are activated in the power supply circuit in two ways:
- simplified internal connection;
- together with RCD and circuit breaker.
In the first case, the load is connected directly to the output of the device, and in the second, the control circuit is closed through an RCD and an AV. This inclusion of the Bison allows you to protect the line not only from voltage surges, but also from current leaks.
The devices have various designs, differing in rated currents (25-63 Amperes). The upper response threshold is from 220 to 280 in steps of 1 Volt, and its lower value is from 120 to 210 Volts. The time to reconnect to the line varies from 3 to 600 seconds. The adjustment step is 3 seconds.
RN series
Model RN-113 is switched on after the electric meter and allows manual setting of the values of the lower and upper response thresholds, indicated on the display built into the front panel. The device is capable of automatically connecting the power supply when its parameters are restored after strong power surges.
For normal operation of devices in this series, a power reserve of at least 20% is required.
In addition to the limit values, the indicator displays the network parameters when the consumer is disconnected, as well as the time remaining before switching on. Rated current is 32 Amps; if desired, it can be increased by installing a magnetic starter.
UZM series
The UZM-51M device, installed immediately after the electric meter, is designed for a rated current of up to 63 Amperes and occupies 2 modules on a DIN rail at once. Its standard width is 35 mm. The maximum setpoint for the upper voltage limit is 290 Volts. The lower threshold for overvoltage is 100 Volts.
The restart time, manually set by the user, can take two fixed values - 10 seconds and 6 minutes. Devices of the UZM series can be installed in networks with any grounding system: TN-C, TN-S or TN-CS.
Devices from
V-protector series VLVs are used only for protection against voltage surges. They are designed for rated currents from 16 to 63 Amps. The upper threshold is set in the range from 210 to 270, and the lower – from 120 to 200 Volts. The time for automatic restoration of the on state is from 5 to 600 seconds. The three-phase V-protector 38 device is designed for a maximum current of no more than 10 Amperes.
Reasons for operation of the voltage relay
Installing this protection allows you to avoid failure of household and industrial equipment, as well as prevent possible fire of devices.
Electrical wiring fault
One of the cases when the protection is triggered is when the neutral wire burns out in the input panel to the building. Moreover, instead of 220V, the outlet can have any voltage - from a few volts, which leads to failure of electric motors of refrigerators and air conditioners, to 380V, at which any equipment burns out - from light bulbs and chargers for mobile phones to TVs and computers.
Why does the voltage fluctuate?
The first step is to understand why voltage fluctuations may occur and assess the risk of this occurring in your home.
The requirements of the standard (GOST 29322-92) specify the parameters of electrical power in one phase (230 V) and between two phases (400 V). However, in many villages and urban settlements there are quite frequent fluctuations in the voltage value. And for cities, the situation when the readings of a voltmeter in a socket deviate from standard values is not something impossible.
Voltage fluctuations can occur for several reasons:
- When phase imbalance occurs (uneven distribution of load between phases), a voltage drop occurs on the most loaded branch, and an increase occurs on less loaded branches. It is the frontal misalignment that is the main cause of short-term fluctuations.
- Zero burnout. Since the neutral wire is relatively thin, its breakage or burnout is more likely than phase burnout. In this case, 380 V appears in the sockets.
- The short circuit of the neutral and phase wires also creates 380 V in the sockets.
Problems with the quality of electricity supply are typical for older housing stock. However, judging by reviews from thematic forums, even apartments in new buildings are not completely free from this scourge.
Since all devices are designed for a standard voltage value, any fluctuation can lead to serious consequences. Thus, when the voltage decreases, air conditioners and refrigerators often fail (due to low voltage, the compressor motor cannot start and the windings burn out). High voltage is harmful to almost all household appliances and electronics.
Operating principle and functionality
Multifunctional relay DigiTOP VA-32A
The operating principle of the device, known to most amateurs under the name 220V voltage limiter, can be understood after familiarizing yourself with its device. The composition includes the following units:
- electronic control module, adjustable for lower and upper limits;
- control signal generator;
- an electromagnetic relay that turns off the device when the set point is exceeded.
When the network voltage reaches one of the maximum levels, the electronics generates a control signal that supplies power to the control relay. It is triggered and de-energizes the line, protecting household appliances connected to the sockets.
Relay operating principle
The functionality of such products in comparison with the same stabilizer is significantly expanded:
- You can set two response thresholds (upper and lower).
- The devices have LED indicators built into the front panel and provide monitoring of the presence of voltage at the input and output.
- There is a liquid crystal display on which the values of the main mains power parameters are recorded.
Questions and answers on Chinese voltage relay
— Is it necessary to connect the neutral wire through the device?
The neutral conductor in the device is a feed-through bus and if there is no need, the neutral wire does not have to pass through the device. It is enough to connect the neutral with any wire to one of the neutral contacts (top/bottom) to power the device.
- Cycle in modes 5,6,7 - what is it?
Timing relay, the load will turn on and off cyclically after a set time. Three timers: second, minute and hour. Configurable to turn off in “oP” and turn on in “CL” in the range from 1 to 999 (if it is in seconds - up to 16 minutes, in minutes up to - 16 hours, in hours up to - 41 days).
— Why does the relay connect the load after overload protection if the overload is not eliminated?
This is necessary to measure the load current: if it is normal, it leaves it on, if there is an overload, it turns it off again.
— IC protection from bad load (pure resistive load limit)?
It’s not entirely clear, but apparently this function limits cos φ from above, because it increases when heaters are turned on, etc.
-2.9. “In overcurrent protection mode, you can also select malignant load protection (pure resistive load limit), which is used for electrical safety of apartments and student dormitories.”
-12. “Load limit identification limit (pure resistive load), for apartments with rental restrictions, electric kettle, electric rice cooker and other powerful resistive equipment.”
That is, this is a restriction so that powerful electric heating devices are not used.
Pure resistive load
In this case, active, reactive and apparent power for a purely resistive load:
- Active: P=I2R=240 W.
- Reactive: Q=I2X =0 var.
- Full: S=I2Z=240 VA.
— How to reset the accumulated energy kW/h?
Have not found. It’s possible that it won’t reset!
LV modes:
- automatic is on
- automation is enabled, but activation is disabled (enable manually)
- automation is disabled, the “switch” is turned off
- automation is disabled, the “switch” is turned on
- 5/6/7 — automation disabled, timer enabled (cyclic switching of load on/off state)
Why is high voltage dangerous?
We figured out why increased voltage occurs in the electrical network, but what is its danger? This phenomenon on the network is dangerous primarily for household appliances. Although modern devices install switching power supplies with stabilized output circuits, their input stages experience increased loads and may fail prematurely.
Heating devices are also affected - boilers, electric stoves, heating elements of washing machines, etc. Due to the high voltage, increased current flows through their spirals. Accordingly, more power is released and service life is reduced. This is especially dangerous for air heating elements, for example, convector filaments and spirals.
Such a problem with the electrical network is also unfavorable for equipment with engines, such products include refrigerator compressors, air conditioners, fans and pumps. Their windings will heat up and may eventually fail. The same applies to network transformers.
Do not forget that since the high voltage increases the current consumption, the wiring is also loaded. At best, the consequences will lead to damage to contact connections (especially if there are twists), and at worst, to burning of wires, melting of insulation and fire.