Enterprise safety
From this article you will learn how occupational health and safety at work is organized, who is responsible for the safety of workers, why an occupational safety service is created at an enterprise, how it works and who controls it.
Occupational health and safety at an enterprise is a set of measures necessary to protect workers while performing tasks assigned by the employer. According to their areas of work, they are divided into:
• ensuring the safety of electrical equipment, cable lines, power lines, lightning protection; • protection from fires, fires and smoke; • safe organization of all categories of work; • maintaining the serviceability of equipment (verification, repair, timely replacement); • maintaining buildings for various purposes, structures, structures, as well as the territory in proper condition; • neutralizing the impact of noise, dust, vibration and other harmful factors on workers; • protection of people who work in dangerous conditions: at heights, underground, in conditions of high or low temperatures, various radiations, in contact with hot or moving objects and their parts, etc.; • training of workers, students, management personnel (instructions on labor protection and safety, special courses, posters, diagrams, drawings, etc.); • monitoring of health indicators of workers (preliminary, pre-shift, annual, extraordinary medical examinations and examinations), organization of sanatorium treatment, provision of therapeutic and preventive food, milk; • public monitoring of the organization of occupational health and safety at the enterprise: the work of occupational safety officers, trade unions, and other public associations.
Taking into account the requirements of regulatory documentation that regulates the activities of specific organizations, they develop their own OSH standards. All the information employees need on the safe conduct of work is set out in the occupational health and safety instructions for specific professions or the performance of certain work (loading and unloading, fire, etc.).
This is interesting: Evacuation receiver (medical)
Safety precautions and labor protection in the organization: concept
Let us turn to the regulations that control the activities of enterprises. They indicate that the manager (according to the hierarchical system, responsibility extends with increasing degrees from the shift supervisor to the main management) is obliged to make decisions related to safety.
In companies where the number of employees exceeds 50 people, it is necessary to introduce the position of an occupational safety manager or an entire department. In practice, powers are often imposed on older personnel with additional obligations.
There is a third option - order outsourcing services, that is, invite a third-party specialist to carry out planned activities and solve unscheduled problems. The last proposed method has a number of advantages:
- A professional is savvy in knowledge of labor protection and safety standards, has active work experience and specialized education. At an affordable price you get a highly qualified employee.
- This is a freelance position, management avoids additional paperwork.
- Significant budget savings occur.
Definition of the concept
Safety precautions are a set of organizational and technical measures that are needed to create safe working conditions and that prevent industrial accidents. She determines the internal organizational routine and is responsible for ensuring that the process of conducting professional activities is as trouble-free as possible. At factories and in other organizations, to solve problems, entire services are organized under the department of the chief engineer, developing measures aimed at ensuring safe operating conditions.
Prohibition sign and safety precautions: you can’t do this
It is mandatory to systematically carry out specialized measures aimed at reducing the risk of injury and eliminating the likelihood of industrial accidents. Such activities boil down mainly to:
- improvement and modification of the designs of existing equipment to protect employees from injury;
- installation of new, modification of old designs of existing protection devices for machine tools, machines, heating installations;
- improvement of working conditions - creation of sufficient lighting, ventilation system, arrangement of dust extraction, timely elimination of production waste, maintaining optimal temperature inside the workshops;
- eliminating the risks of developing emergency situations during equipment operation, breaking grinding wheels, minimizing the risks of acid splashing, etc.;
- organized briefing of newcomers regarding the rules of behavior on the territory of the enterprise, training, testing of knowledge;
- provision of TB instructions and posters in sufficient quantities.
Accidents are still possible, largely due to workers ignoring the safety precautions for operating power plants, electrical installations, and other equipment. The relevant issues should be covered by the responsible person during the scheduled briefing. Physically outdated facilities should undergo regular inspections and updates. Responsible specialists monitor compliance with the system of rules and regulations - they are the ones who must teach the basics of proper work.
Important! Particular caution is needed in construction and areas with other high risks.
Workers who deal with welding stations, solvents in production, and other dangerous tools and materials must have an appropriate knowledge base on the practice of conducting basic operations.
Generally Accepted Safety Practices
General TB rules include:
- employees are obliged to keep the workplace in order, comply with sanitary standards, observe the work schedule, and also not cover the ventilation openings;
- during the performance of official duties, persons who do not have the appropriate authority must not be distracted or allowed to access the equipment;
- you must beware of moving parts of equipment;
- it is important to monitor lighting and ventilation;
- Only tools with certificates and passports are used;
- during work, fire safety rules are observed;
- in emergency situations, you must promptly notify the company management about the situation that has arisen, stop work, turn off the equipment, and also leave the place of employment;
- at the end of the work, the devices are turned off, the workplace is put in order and technical documents are transferred to the archive;
- While on the territory of the organization, you must give way to moving vehicles, walk in permitted places and use designated passages:
- employees are required to follow internal regulations, smoke in specially equipped areas, and not consume drugs or alcoholic beverages
Important! During the performance of work duties, the impact of various harmful factors is taken into account.
Who should be trained
According to clause 2.1.1 of the Procedure, all persons hired for work must undergo training. It is also mandatory for employees who are transferred to another job.
REFERENCE
Is safety training necessary for a person who is not on the company’s staff, but performs work or provides services under a civil contract? The answer depends on the terms of the contract. If it states that the customer pays insurance premiums “for injuries” for the contractor (performer), then training should be carried out. This opinion was expressed by the Ministry of Labor in letter No. PG/02487-6-1 dated February 21, 2020 (see “Labor safety: is it necessary to instruct workers with whom GPC agreements have been concluded?”).
Results
Conducting safety training is extremely important as a measure to prevent the creation of situations in the workplace that pose a danger to the health of workers and the safety of the employer’s property.
It is carried out in compliance with certain requirements to ensure that the employee is ready to comply with established rules of behavior that meet the requirements of safe work.
Sources: Labor Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Who conducts on-the-job training?
Depends on the type of instruction:
- the induction is carried out by an occupational safety specialist (see “How to become an occupational safety specialist”), or another employee who is assigned such responsibilities by order of the manager;
- primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted are carried out by the one who supervises the work: foreman, foreman, teacher, etc. It is necessary that this person undergo occupational safety training at an accredited training center or at an enterprise if a commission has been created there to test knowledge of occupational safety requirements (for more details, see “Procedure for occupational safety training at an enterprise in 2022: terms, rules, organization”) .
Complete training and receive a certificate of occupational safety specialist Submit an application
Who controls the work of health and safety services at enterprises
These are also supervised positions, so the work plan, as well as important decisions, must be agreed upon with the production manager. If the management has delegated authority to his deputy or another person, then the occupational safety control specialist is subordinate and reports to him.
You should also be aware of government inspections. Inspections can be scheduled or unscheduled - at the request of the prosecutor's office.
In the article, we briefly talked about safety precautions and labor protection in the workplace, about the system of organizational measures, as well as who is responsible for this - you can find additional materials on Wikipedia. To conclude the article, watch a video on this topic:
Contact Rosta LLC if you decide to buy devices for industrial use. We have manual and semi-automatic band saws in stock and on order, as well as pendulum, vertical and two-post units. The price of goods is reduced by 1.5 - 2 times compared to foreign analogues.
To clarify the information you are interested in, please contact our managers by phone. They will answer all your questions.
What does health and safety include?
Occupational health and safety at work includes a set of tasks, depending on the specifics of the duties performed:
- creating conditions for working with power lines and electrical appliances;
- provision of protective equipment and protective clothing against smoke and fire;
- guarantee of safe organization of all categories of work;
- supply of serviceable equipment , as well as its inspection, repair or partial timely protection;
- maintaining all work and utility rooms in proper condition, in accordance with sanitary and hygienic requirements;
- creating conditions for working with increased noise, vibration, dust, etc.;
- ensuring conditions at high altitudes, in underground mines, as well as when working with sudden temperature changes.
The list differs in each specific case, depending on the specifics of production. General safety regulations must be followed by all employees.
Causes of accidents at work
In organizational areas, health and safety includes:
- training of management and management personnel, main and temporary workers;
- monitoring the condition of workers (annual medical examinations, briefings, training events, issuing products according to their harmfulness, sending employees for treatment or rehabilitation to sanatoriums and health institutions);
- control over compliance with health and safety rules by higher authorities of responsible persons.
All necessary information for enterprise managers, labor safety inspectors, and working personnel is contained in the labor code and local regulations.
What is labor protection
This is interesting: Gas fire extinguishers: types, purpose, principle of operation
Occupational Health and Safety – the importance of this area of personnel management
The security sphere of workers is enshrined at the legislative level and is controlled by municipal authorized bodies. Each company, even with a small number of employees, must have a set of measures to prevent emergencies, as well as carry out all the required measures to facilitate forecasting, timely identification of problems, as well as elimination of breakdowns and other situations in a short time.
TB awareness activities
The responsibilities of the Health and Safety Service include:
- development of internal standards;
- training and knowledge testing;
- control over execution.
There are two types of training :
- Instructions (the employer instructs the employee, after which he begins to work). Briefings can be introductory, primary at a specific workplace, repeated, unscheduled, targeted. Introductory safety training at any production or enterprise is carried out by a labor protection specialist or person in charge. It is mandatory for both newly arrived employees and trainees, regardless of their planned time of stay at the enterprise. Initial briefings are optional for employees not involved with equipment and production materials. The same ones who pass the primary ones pass the repeated ones. Unscheduled briefing is carried out in emergency cases (as prescribed, introduction of new equipment, accident). Targets are carried out according to the admission order.
- Direct training and testing of knowledge. To do this, it is necessary to have a program at the enterprise, which should include as much as possible the goals prescribed in GOSTs (for example, personal protective equipment, if necessary). A program is developed for each type of instruction.
If an employee does not pass the health and safety exam, he is not allowed to enter the workplace and is sent for re-training.
Example of an induction training log
Why do you need instruction?
In almost any workplace, an employee may encounter factors that pose a danger to his health or a threat to the safety of property provided to him by the employer.
In emergency situations, there may be a danger to the life of an employee. To reduce the negative impact of production factors and the likelihood of dangerous situations occurring, each employee is familiarized with safety rules in the workplace. As a result, he gets an idea of:
- the nature of the enterprise’s activities, the role of its workplace, equipment and materials used in it;
- factors that may pose danger or harm at this location;
- rules of behavior on the employer’s territory and a specific workplace;
- principles of safe operation on existing equipment;
- the procedure for preparing the workplace for work and the rules for its completion;
- use of personal protective equipment;
- measures to prevent fires and accidents;
- behavior in case of danger or accident;
- methods of providing first aid to victims.
For information about what factors may pose danger or harm, read the article “Dangerous and harmful production factors (list).”
It is assumed that as a result of the training, the employee acquires all the necessary knowledge about the rules of conduct in the workplace and becomes responsible for the consequences of violating these rules. Since compliance with safety regulations is one of the duties of an employee (Article 214 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and relates to labor discipline (Article 189 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), for its violation he can be punished by the employer by issuing a reprimand or reprimand, and if there is intent in the actions , creating a threat or causing serious consequences - dismissed (Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
If failure to comply with safety regulations led to material losses for the employer, then at the same time as disciplinary action, the employee can be held financially liable (Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). And in cases of serious consequences for the health or life of people, criminal liability is possible under Art. 143, 216, 217, 219 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, which, depending on the severity of these consequences, varies from a fine to imprisonment.
Timing of H&S briefings
For clarity, we have summarized them in a table:
| Type of instruction | Dates |
| Introductory | before the initial briefing |
| Primary | before starting independent work |
| Repeated | at least once every 6 months |
| Unscheduled | if necessary |
| Target |
Rules for conducting and completing workplace training
There are two types of training that always take place in the workplace.
- Primary
- Repeated
Sometimes unscheduled events are organized at the workplace. This happens if the reason is innovations directly related to the workshop, conveyor belt, etc. For example, changing technological processes or upgrading machines.
In all other cases (if the basis for the briefing is changes in the law, the requirements of the inspector, etc.), an unscheduled briefing can be carried out away from production - in the hall, assembly hall, etc.
IMPORTANT
There is a form for registering on-the-job training. It is listed in GOST 12.0.004-2015 (approved by order of Rosstandart dated 06/09/16 No. 600-st). But the application of this GOST is voluntary. Therefore, organizations and individual entrepreneurs have the right to develop their own form of journal.
Prepare labor safety documents in a special service Try for free
Provisions of the Constitution regarding the protection of citizens in the workplace
According to Art. 37 of the Constitution ensures not only freedom, but also protection of labor. Every citizen has the right to work that meets hygiene and safety requirements. Therefore, when organizing any workplace, employers must take into account the constitutional rights of employees.
If a specialist is confident that the head of an enterprise is violating his rights by not providing optimal working conditions, then it is advisable to report these violations to employees of the labor inspectorate or prosecutor’s office, and you can also file a claim to receive material and moral compensation.
What types of safety training are there?
Introductory training on occupational safety
Needed by everyone who got a job or came on a business trip. Also, apprentices and students in practice, as well as people from third-party organizations involved in the company’s production activities, are required to undergo induction training.
Initial briefing on labor protection and safety in the workplace
It is intended for all newly hired workers, including seasonal workers and those who have signed an employment contract for less than two months.
Primary training is also given to:
- part-time workers;
- homeworkers using materials, tools or machinery;
- employees transferred from other structural units;
- persons who are entrusted with a new job;
- those who came on a business trip from other organizations;
- trainees;
- everyone who in one way or another participates in the production activities of the company.
ATTENTION
The employer has the right to approve a list of professions and positions exempt from initial instruction. The list can include workers not involved in the operation, maintenance, testing, adjustment and repair of equipment. It is permissible to include in it those who do not use electrified and other tools, do not store or use raw materials.
Compose HR documents using ready-made templates for free
Repeated safety briefing
Necessary for everyone who attended the initial training. Repeated events are held regularly.
Unscheduled briefing on labor protection
Needed in case:
- changes or introduction of new laws and other regulatory legal acts on labor protection, instructions on occupational safety;
- changes in technological processes, replacement or modernization of equipment, devices, tools and other factors affecting labor safety;
- violation by employees of occupational safety requirements if there is a real threat of serious consequences: accident, breakdown, etc.;
- requirements of officials of state supervision and control bodies;
- a break in work for more than two months (for work with harmful and (or) dangerous conditions - more than 30 calendar days);
- the employer making an appropriate decision.
Targeted training on labor protection
It is suitable for performing one-time work and holding public events. Other reasons for targeted training are liquidation of the consequences of accidents and natural disasters; work that requires a work permit, permit or other special document.
Features of conducting labor safety briefings
Do remote workers and homeworkers need to be instructed? Yes need. After all, the working conditions of a homeworker must comply with labor safety requirements (Article 311 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). And remote employees must be trained in safe methods of working with equipment and tools that are recommended or provided by the employer (Article 312.7 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Also see “Remote work in 2021, read the new law on remote work.”
All types of training, including initial training, are required for office staff. The fact is that exemption can only be given to those who do not deal with the equipment. Whereas office workers use computers. Therefore, they must undergo initial training.
Employer Responsibilities
The employer must fulfill his responsibilities directly in terms of occupational safety, which include:
- provide employees with Codes, legal acts, laws;
- select and approve the staff of the labor protection service;
- create and approve a system for the functioning and management of the labor protection service;
- together with the responsible persons, he must develop safety instructions for each staff unit and develop programs;
- safety instructions are created for each full-time position available at the enterprise;
- create a workplace and a thematic office for the labor protection service, ensure the availability of visual aids and safety materials if necessary.
In addition, the employer is obliged to provide employees not only with training material, visual aids, illustrations, etc., but also to organize workplaces according to requirements, provide them with special clothing, and organize a rest room if necessary. The employer is obliged to personally monitor the health status of employees and take measures for treatment, prevention and recovery.
OT office
Responsibilities of the OT service
The main document regulating the responsibilities of the labor protection service is Resolution No. 14 of the Ministry of Labor dated 02/08/2000. It develops recommendations for the creation of this production unit and the specifics of its activities. I repeat that department employees develop training programs and instructions on labor protection, conduct the necessary briefings and organize regular advanced training for management and members of the occupational safety commission in specialized organizations. In addition, they are obliged to investigate accidents that occurred at the enterprise, in accordance with the “Regulations on Investigation...” No. 73, approved. Resolution of the Ministry of Labor dated October 24, 2002. And report them in a timely manner not only to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, but also to the State Tax Inspectorate, the prosecutor's office, local executive authorities, etc. in the case of a group NS, severe NS or fatal outcome.
Another area of work for OT specialists is the organization of medical examinations of employees, in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of April 12, 2011 No. 302n, and psychiatric examinations in accordance with Government Decree No. 695 of September 23, 2002.
Separately, mention should be made of the preparation of the necessary documents for conducting regular and unscheduled SOUT, in accordance with Federal Law dated December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ.
Why should you follow safety precautions in the workplace?
Occupational safety and health at school: instructions and safety precautions
The main reason for the urgent need for strict adherence to safety regulations is to minimize the risk of injury during the production process. But there are other reasons, let’s name them:
- protecting the health and life of the employee, preventing disability;
- probable damage to third parties;
- failure to provide guarantees and benefits (for example, deprivation of 13 salaries for violation of discipline);
- deterioration in the quality of services and products;
- dismissal at the discretion of the employer.
Important! At least 2 thousand people die every year in production facilities in the Russian Federation, and 4 thousand become disabled. The reason is non-compliance with safety regulations.
Occupational safety in catering
compliance with safety regulations at the enterprise is directly related to equipment that has reciprocating moving or rotating movements of working parts; such mechanisms must have fences with warning signs, an alarm system and door locks. Before starting the equipment, you must make sure that the working chamber is empty, the working body or moving parts are free, and there are no foreign objects. it is necessary to inspect the place in front of the mechanism, there should be no foreign objects there, put the overalls in order, paying attention to the hanging parts. Check the serviceability of the electrical wiring, starting equipment, reliable connection of the replaceable parts of the machine; before starting, you must turn on the machine at idle speed and make sure that all mechanisms are functioning clearly and correctly. Only workers who have been familiarized with safety precautions at scientific centers are allowed to access the mechanisms. The organization of safety precautions at an enterprise is a very important element in the functioning of the entire mechanism. People, feeling safe, perform the necessary actions much faster and better. It is not without reason that control over the organization of safety precautions at an enterprise is carried out by the Federal Labor Inspectorate.
| Attention Bearing Buyers Dear customers, send your questions and requests for the purchase of bearings and components by email or call now: Delivery of bearings throughout the Russian Federation and abroad. Bearing catalog on the website |
Attention Bearing Buyers
Dear customers, send your questions and requests for the purchase of bearings and components by email or call now: +7 [email protected] Delivery of bearings in the Russian Federation and abroad. Bearing catalog on the website
themechanic.ru
Industrial labor protection
Occupational health and safety at ATP
Occupational health and safety at an enterprise is a set of measures necessary to ensure minimal risk conditions for workers’ activities. System directions:
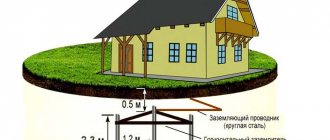
- cable lines, electrical equipment, power lines, lightning protection;
- prevention of fires and smoke;
- safe performance of work of various categories;
- maintaining equipment in good condition;
- maintenance of the territory and buildings;
Poster about safe work, health and life
- neutralization of the negative influence of vibrations, noise, dust;
- protecting people working in hazardous conditions;
- personnel training (regular briefings in the organization);
- tracking employee health indicators;
- public monitoring of general TB at the enterprise.
Note! Labor protection and safety standards at the enterprise regulate the activities of organizations taking into account internal OSH standards. The information required by employees regarding the safe performance of work is prescribed in safety instructions, as a rule, for each profession separately.
Who is responsible for worker safety?
The leader is responsible.
In any situation, the employee is responsible for his own safety. For example, he should not begin work unless he makes sure that all mechanisms and equipment are in good condition.
If even a minor defect is discovered, he is obliged to inform the manager. Responsibility for compliance with safety measures lies with the immediate supervisor, and this must be documented, namely:
- A local regulatory document is issued on the responsibility for occupational safety assigned to the manager. This may be an order, an order or an enterprise standard;
- the manager must be additionally familiarized with the responsibilities assigned to him;
- further, the manager is obliged to pay attention to the state of the workplace, if necessary, take measures to eliminate deficiencies, and respond to comments from the labor protection service and workers about the presence of potential dangers.
Example from practice. If an accident occurs, an investigation is carried out, that is, all existing documents on the issuance of protective clothing, training are reviewed, and the workplace is inspected.
Based on the results of the investigation, an act is drawn up, which specifically states the percentage of guilt of the employee and the employer.
Usually, even if the employee is completely to blame for the injury, then still only 25% of the blame is assigned to him, and the rest is given to the manager.
Responsible persons
Occupational health and safety in hot and cold workshops
The safety of workers, in addition to themselves, must be taken care of by the security service and the employer.
What an employer must
A superficial acquaintance with occupational safety and health may lead to the idea that the occupational health and safety engineer is responsible for the safety of employees. This is not true - the main responsible person will be the immediate supervisor. The corresponding responsibilities are assigned to management at different levels - departments, divisions, enterprises.
OT service
The OT service is organized specifically to solve problems such as:
- conducting investigations, analyzing the causes of accidents;
- creation and implementation of programs and activities aimed at improving working conditions;
- organizational, methodological support;
- participation in knowledge testing;
Security service guarding the rules
- assistance in preparing papers on occupational health and safety issues;
- compiling lists for the provision of food, protective clothing, payment of benefits, and undergoing regular medical examinations;
- preparation and submission of reports;
- storage of documentation;
- organization of training;
- regular inspections of the health status within departments;
- conducting introductory briefings.
Service specialists have the right to inspect premises, equipment and machinery at any necessary time, look at documents, and monitor the process of work performed by workers.
Important! To successfully solve current problems, OT specialists cooperate with various enterprise services, commissions, and trade unions.
Who monitors the services?
Occupational safety specialists report to the head or deputy head of the company in which they work. Representatives of third-party organizations are required for professional monitoring of the quality of performance of duties. These include departmental, state, non-departmental, and public bodies. Inspections are carried out as planned, and the OT service is properly notified of the activities provided.
Instructions
Basic requirements for TB:
- when starting to perform each type of work that has not been done before, additional instruction is needed;
- extreme attentiveness is required, it is not recommended to be distracted by extraneous conversations or affairs;
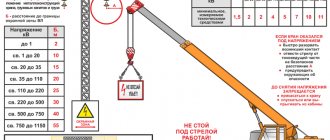
- On the territory of the plant you cannot walk around the workshops, ignore the signals of crane operators and vehicle drivers. It is imperative to bypass unloading and loading areas, and bypass places not intended for passage. You cannot touch terminals, electrical wires, equipment, fittings, lighting devices, especially with tools or scissors;
- In case of injury or any ailment, the injured person needs to stop the work process and seek medical help.
Workers perform various operations at the site
Before starting to perform direct work duties, employees must get their uniform in order, put on personal protective equipment, if necessary, and special shoes. You should also inspect the workplace, restore order, and remove unnecessary items. There should be enough light, but not blinding to the eye, it should be directed towards the work area.
It is necessary to inspect the floor - there should be no potholes, slippery areas or other defects. Hoists and hoists can only be used in good working order. When moving or lifting heavy loads, the signal must be given by one worker. The slinging is made reliable; high-strength cleats are used for mooring.
Sharpening tools on grinding wheels can only be done by first wearing safety glasses. There is a protective screen; it should not be moved to the side. Be sure to check that the tool rest is installed correctly and bring it as close to the grinding wheel as possible. You need to stand half a turn towards the wheel while sharpening. You cannot remove chips by hand.
Safety rules for students in technology lessons
Before giving children dangerous tools (scissors, needles, glue guns, etc.), you need to explain the rules for working with them. In this material, I share my safety rules for technology (home economics) lessons for girls.
Safety precautions when working with scissors
1. Scissors must be well adjusted and sharpened.
2. Store scissors in a specific place (box or stand).
3. When using scissors, you should not be distracted and wave your arms, or bring the scissors to your face.
4. When passing the scissors, hold them by the closed blades.
5. Place scissors on the right with closed blades directed away from you.
6. When cutting, the narrow blade of the scissors should be down.
7. Don't leave scissors open.
8. Use scissors as intended.
Safety precautions when working with needles and pins
1. Store needles and pins in a certain place (needle bed, special box, etc.), do not leave them at your workplace.
2. Do not use rusty or bent needles and pins when working.
3. Sew only with a thimble.
4. Do not put needles or pins in your mouth or stick them into clothing.
5. Do not leave needles and pins on the work surface of the table
6. Pass the needle only in a needle bed and with thread.
7. Before and after work, check the number of needles.
8. Store the pincushion with needles only in the same place.
9. Attach the patterns to the fabric with the sharp ends of the pins facing away from you.
10. Don't be distracted while working with the needle.
11. Upon completion of work, remove all needles and pins into special boxes and pads.
Safety precautions when working on a sewing machine
1. Put on overalls, tuck your hair under a scarf, and fasten the sleeve cuffs. The ends of ties and scarves should not hang down.
2. Make sure there is a dielectric mat on the floor near the machine.
3. Do not lean close to moving parts of the machine.
4. Check if there are any foreign objects on the machine platform.
5. Make sure that the sliding plate is closed.
6. Make sure that your hands are in the correct position so as not to prick your fingers with the needle.
7. Before stitching, make sure there are no pins or needles on the seam line of the product.
8. Stitch thickened areas at low speed.
9. When cleaning, lubricating the machine, installing the needle, bobbin case, or threading the machine needle, do not keep your foot on the machine pedal.
10. Do not come close to those working on machines, do not distract them from their work. Do not transmit any items through them.
11.If you feel electric current when touching any parts of the equipment, stop working immediately and notify your teacher.
12. When using an electric sewing machine, do not leave the machine plugged in unattended.
13. If you smell burning rubber or smoke, unplug the machine and notify your teacher.
14. After finishing work, disconnect the machine from the power supply.
Safety precautions when working with an electric iron
1. Do not leave the iron plugged in unattended.
2. Turn the iron on and off with dry hands.
3. Place the iron on an insulated stand.
4. Monitor the normal operation of the iron and report any malfunctions to the teacher.
5. Make sure that the sole of the iron does not touch the cord.
6. Unplug the iron only by the plug.
Safety precautions when working with crochet and knitting needles
1. Hooks and knitting needles should be well polished and stored in a certain place.
2. Knitting needles and hooks should be stored in appropriate cases, covers, boxes and drawers.
3. Do not use knitting needles or hooks that have rust, they can ruin the yarn or fabric.
4. It is necessary that the body position is correct when knitting. You need to sit leaning back in your chair. The light should come from the left.
5. You should not make sudden movements with your hand with a hook while working - you can injure the person sitting next to you.
6. After work, put the hook and knitting needles in a case or in a certain place.
Safety precautions when working with a glue gun
1. When heating the gun, be sure to place a ceramic, glass stand or saucer under the nozzle so that the glue does not drip onto the table.
2. It’s good if the table has a smooth surface, but if not, it will be difficult to scrape off the glue, even a drop;
3. The pistol has a stand, which is usually removed during operation, and when the pistol is placed, it is pulled out.
4. Make sure that when the gun is placed on the table, the stand is extended. Otherwise, the gun will stick its nozzle into the stand or into the wooden table and may burn or damage both;
5. Do not grab the nozzle or heated glue with your hands. The temperature of the nozzle and glue at its exit from the nozzle is 200 degrees. A burn will occur even if you simply touch the nozzle or glue.
6. Do not forget to turn off the gun from the network after work and even during work, so that the gun does not overheat.
Safety precautions when
preparing food
1. When performing culinary work, wear overalls and tuck your hair under a scarf.
2. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
3. During work, observe the rules of sanitary hygiene.
4. Place tools on the table so as to prevent them from falling. 5. Do not block the passages between tables with foreign objects.
6. Follow the teacher’s instructions carefully and clearly.
7. When cutting, keep your fingers at a distance from the knife blade.
8. Pass the knife to each other only with the handle away from you.
9. Open cans with a special key.
10. Be careful when working with hand graters. Reliably hold processed products. Do not process small parts.
11. Be careful when peeling vegetables. Peel potatoes with a grooved knife, fish with a scraper.
12. Cut food products on a cutting board.
13. Cut bread, gastronomic products, vegetables and other products with well-sharpened knives on cutting boards, observing correct cutting techniques. Cut raw and cooked vegetables, meat, fish, bread on cutting boards in accordance with their labeling.
14. Before turning on electrical appliances, check the serviceability of the cord.
15. Turn electrical appliances on and off while holding the plug with dry hands.
16. Do not fill the pan with liquid 4-5 cm to the top.
17. When the liquid boils, reduce the heat.
18. Take the lid of the hot dish with a towel or oven mitt and open it, lifting it away from you.
19. Carefully pour food into boiling liquid. 20. When frying, carefully place food on the heated fat and make sure that no drops of water get in, use special spatulas.
21. Handle hot dishes with oven mitts
22. After finishing work, turn off electrical appliances, wash and put away working tools in the place designated for them, and clean the workplace. 23. Do not leave the workshop without the teacher’s permission.
Briefing: types, how it is carried out
The first type of instruction is introductory. It is carried out for all new employees, regardless of length of service or level of education. Travelers, temporary workers, students, students undergoing internships should know the instructions. A complex of knowledge necessary for work is mastered.
Important! Certain categories of persons may be exempt from instruction. Their lists are compiled by management.
The next type of instructions is the primary one in the workplace. It is carried out for all new employees, including those who work under the terms of a short-term employment contract and are hired seasonally. Primary instructions are needed for business travelers and employees transferred from one unit to another within the organization. They introduce technologies, equipment, features of preparation for performing work duties, requirements for clothing, footwear, and personal protective equipment. The instruction also covers issues of first aid and responsibility for ignoring TB. It is carried out by the head of a specific type of work in computer science classrooms, directly at workplaces, and in other equipped premises.
After initial instructions, the employee undergoes an internship for 2-14 shifts, during which time his activities must be supervised by a responsible specialist. When the internship is completed, a review is carried out. All entries are entered into a journal.
Why is it important to follow instructions?
The third type of instruction is repeated. It is taken by workers with any experience, education, or skill level. The minimum frequency is every six months. Responsible person, teacher - work manager. Lesson programs developed specifically for these purposes are used.
Unscheduled OT briefing is the fourth type. It is needed when introducing revised or completely new rules, standards, or after changes in technological processes. If employees violate labor safety requirements, unscheduled instructions are also mandatory. The implementation of measures may be required by officials of control and state supervision bodies.
The last type of briefing is targeted. They are introduced when performing one-time work not related to the direct duties of specialists, to eliminate the consequences of disasters, natural disasters, and accidents. Other reasons are excursions, organization of public events at the plant, in the company. You must act in accordance with the regulations.
Responsibility for violation of safety rules
Responsibility for violation of safety rules can be assigned to the manager, the safety service, or employees. Appointed officials are primarily responsible. Employees are directly responsible for violation of safety rules, as for violation of labor discipline (with the exception of criminal liability).
Responsibility may be:
- administrative and criminal , depending on the severity of the consequences and the intentionality of failure to comply with the instructions;
- disciplinary;
- material.
The resulting administrative liability provides for fines in various monetary amounts.
Disciplinary liability includes demotion , reprimand, reprimand, removal from a position for a certain period or temporary or complete removal from duties in whole or in part.
Financial liability is expressed in compensation for damage caused by careless handling of entrusted property, resulting in its damage or in the event of theft of property. Issues that arise can be resolved on the spot between the employee and management or through the court. Recovery can be carried out in whole or in part by deducting small amounts from wages.
Criminal liability arises in situations where, through the fault of an employee, another person is injured, as a result of which he becomes disabled or dies.
Responsibility for violation of labor protection rules - Article 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
Magazines
In accordance with current legislation, logs for registering briefings at workplaces are filled out in accordance with the established form. They record all types of work performed. The employer monitors the availability and correctness of the document. If there is no log, employees of regulatory authorities may accuse management of non-compliance with labor safety rules.
Important! The journal is certified by the responsible person. The type of document production is typographic.
The filling form is used uniformly for all divisions of the company. The forms are kept by an engineer or other responsible employee. The specialist who conducts the instructions can take the log from the occupational safety engineer. The pages of the document are numbered, laced, and stamps are required.
What is the OT service responsible for?
Basically, the task of an authorized specialist is to develop a plan, instructions, and also monitor the completion of the training. The proof is usually a document with the signatures of each participant listening to the lecture.
In addition, the person responsible for the state of occupational health and safety technology advises management, makes recommendations, and also participates in internal investigations and helps establish the cause of negligence and accidents.
Instructions from safety service specialists
If a violation is detected, the professional draws up a paper that describes a detailed list of requirements. Simply put, it indicates what needs to be fixed and within what time frame. The document is signed by the manager and given to an authorized person, for example, a senior engineer. Filling out such a form is done with reference to regulations, specific clauses, that is, in accordance with the law.
The second task is to monitor compliance with the instructions.