According to statistics, about 12-15% of fatal accidents are associated with violations of safety regulations when working with various types of electrical equipment. It should be noted that in everyday life such incidents have recently occurred more often than in production, where personnel must undergo appropriate training in order to obtain permission to work. As for users of household appliances, some of them do not even have basic knowledge of safety precautions. Let's remember the general rules based on excerpts from PTE and PTB.
What current is considered unsafe?
As a rule, the first sensations occur when exposed to a current of 1-1.5 mA. This value is considered a threshold. A further increase leads to involuntary contractions of the muscular system, accompanied by painful sensations.
After the level of 12 to 15 mA, the muscular system cannot be controlled. In some cases, because of this, a person caught under voltage is not able to free himself (for example, unclench his fist with a clamped wire). The current, starting from the specified point, is considered “not releasing”. Its further increase causes convulsive contractions of the heart, and a value of 100 mA leads to death.
Table of current threshold values:
| Voltage | Sensible (mA) | Non-releasing (mA) | Fatal fibrillation (mA) |
| Variable (50 Hz) | 1,0-1,5 | 12,0-15,0 | 100,0 |
| Permanent | 6,0 | 60,0 | 300,0 |
Please note that the table contains approximate data, since it depends on many factors, including the physical and psychological state of the person.
The effect of electric current on the human body
- Thermal impact. This is heating of human body tissues and burns.
- Electrolytic effect of current. This is an effect on the blood and other body fluids, causing the decomposition of their constituent elements.
- Biological (physiological) effects. Irritation and excitation of muscle and nervous tissue occurs, which leads to convulsive muscle contractions. The most dangerous contractions of the heart muscle and lungs
The result of these impacts can be divided into two types of electric shocks: electrical injuries and electrical shocks. Electrical injuries are clearly defined local tissue damage. Injuries include electrical burns, electrical marks, skin metallization, electroophthalmia, and mechanical injuries.
Material on the topic: What is the danger of resonance and what kind of phenomenon is it.
Burns. A consequence of the thermal effect of current passing through the human body, or touching very hot parts of electrical equipment, or from the action of an electric arc. The most severe burns occur when an electric arc occurs in networks of 35–220 kV and in networks of 6–10 kV with high network capacity. In these networks, burns are the main and most severe types of damage. In networks with voltages up to 1000 V, burns from an electric arc are also possible (when the circuit is disconnected with open switches in the presence of a large inductive load).
What is the difference between parallel and series connection of capacitors?
Read more
Do-it-yourself pirate metal detector - detailed instructions.
Read more
What is a tuning resistor: description of the device and its scope.
Read more
Electrical marks are clearly defined skin lesions where the electrodes come into contact. They can be round or elliptical in shape, gray or white-yellow in color with clearly defined edges. Caused by the mechanical and chemical effects of current. They can appear only some time after exposure to current. Usually the lesions are not accompanied by inflammation and pain, but cause swelling and swelling at the site of contact with the electrodes. Signs of a small area heal safely, but with a large area of lesions, tissue necrosis occurs.
Electrician safety precautions.
Electrometallization of the skin is the penetration of the smallest particles of metal into the upper layers of the skin due to its boiling and splashing under the influence of an electric arc. The damaged area of the skin becomes hard and has a rough surface. A sensation of a foreign body appears at the site of the lesion. The outcome of the injury, as with a burn, depends on the area of the affected area. Most often, metallic leather comes off without leaving a trace.
Electroophthalmia is an inflammation of the outer membranes of the eyes, resulting from strong exposure to ultraviolet rays released during the burning of an electric arc.
Mechanical damage - Bone fractures and ruptures of tendons and muscles caused by muscle contraction when current passes through them. They are the result of an electric shock.
An electric shock is the result of the biological effect of current, consisting in the excitation of nerve tissue when an electric current passes through the body. Manifested by involuntary convulsive muscle contractions.
It is important to know: What is electric current.
There are four degrees of electric shock depending on the outcome of the impact on the body, ranging from mild, without loss of consciousness (first degree) to clinical death (fourth degree). In a state of clinical death, a person has no breathing or heartbeat, the pupils of the eyes are dilated and do not react to light. The duration of clinical death is approximately 4-8 minutes. After this time, the death of brain cells occurs, leading to the irreversible cessation of biological processes in the body, the collapse of protein structures - biological death.
How dangerous is electric shock?
Current in the human body
The most dangerous is the passage of current through the respiratory organs and heart along the longitudinal axis (from head to feet). Proportion of total current passing through the heart:
- hand-to-hand path – 3.3% of the total current;
- path left hand - legs - 3.7% of the total current;
- path right hand - legs - 6.7% of the total current;
- leg-leg path – 0.4% of the total current.
It will be interesting➡ What is electromagnetic induction?
At voltages up to 250-300 V, alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz is approximately 45 times safer than direct current; at higher voltages, direct current is more dangerous. A current is considered safe if its prolonged passage through the human body does not cause harm and does not cause any sensations. Its value does not exceed 50 μA. A current between 0.5 mA and 1.5 mA is called the threshold sensible current. It causes a slight tingling sensation, a sensation of heating the skin. At a current of 2-5 mA, pain in the hand and trembling of the hand appear.
Possibility of death from electric shock.
Increasing the current to 10-15 mA causes unbearable pain and complete cessation of muscle control. If a person simply touches live areas, he can free himself from the action of the current by withdrawing his hand. If the wire is clamped in the hand, then at this current value the person cannot voluntarily release his fingers from the live parts and remains under voltage.
For this reason, a current greater than 10-15 mA is called non-releasing. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that if a current of the same magnitude passes through the muscles that control the flexion and extension of the fingers.
Table - Average values of threshold currents.
The flexor muscles, being more powerful, create a slightly greater force, so the fingers are clenched into a fist. When an industrial frequency current of up to 10-15 mA passes through the arm, the influence of biological impulses at the will of a person can still create a greater force in the extensor muscles than in the flexor muscles, and the victim can be freed from the action of the electric current. With a higher current, the effect of biological impulses on muscle control is completely lost and their contraction is determined only by the action of an external current.
A threshold non-releasing current can conditionally be considered safe for humans in the sense that it does not cause immediate damage. But with prolonged passage, the magnitude of the current increases due to a decrease in body resistance, which can result in circulatory and respiratory problems and death.
At a current of about 50 mA, a convulsive contraction of the chest muscles begins, constriction of blood vessels and an increase in blood pressure, which leads to loss of consciousness and death. When a current of more than 100 mA passes along the path arm - arm or arm - legs for 2 - 3 seconds, it leads to death (lethal current).
Since after 1-2 seconds cardiac fibrillation may occur (chaotic, scattered contractions of individual fibers of the heart muscle). As a result, the heart stops working and blood circulation is impaired. Fibrillation continues even after the current stops, resulting in death.
Damaging factors
The effect of electric current on a person can be of the following nature:
- thermal, causes burns, leads to heating of blood and blood vessels;
- electrolytic, leads to blood decomposition;
- biological, due to irritation the activity of the respiratory organs and (or) circulatory system may cease.
As for injuries caused by electric current, they are of two types:
- electrical injuries, manifested in the form of burns, marks, metallization, electroophthalmia, damage caused by contraction of the muscular system;
- electric shocks of I – IV degrees may be accompanied by shock and reflex effects on various organs.
Measures for safe work performance
Safety regulations when working on electrical installations provide for a number of organizational measures that are aimed at their strict compliance:
- work within the framework of ordinary operation of electrical units is documented in orders, orders or lists;
- preparation of the work area and access to it is issued with the appropriate permit;
- To carry out work manipulations, permission is required in accordance with the assigned electrical safety group;
- provision of insurance and control during the period of work;
- official registration of the beginning and end of a break in work, as well as their complete completion or transfer of the team to another site.
The document defines the circle of workers who are responsible for the safety of work processes at electrical installations:
- those signing permit orders, issuing orders or certifying a list of work on the current use of electrical units (the required electrical safety clearance group is 4-5) - they are required to first assess the need to perform the work and the possibility of its safe implementation; the composition of the teams, the selection of the supervisor and work contractor and preliminary briefing must meet safety requirements;
- permitting the preparation of work areas (access group - 4-5 or administrative and technical employees authorized by order of the enterprise management) - are responsible for the timely and safe disconnection of electrical equipment from the network and its grounding, coordinating working hours and the location of operational teams, accounting for teams and their members, tracking information about the timing of current manipulations and the time of supplying voltage to electrical installations;
- designated responsible work managers (access groups - 4-5, are appointed when using various mechanisms and lifts, de-energizing electrical equipment, on cable communication lines near transport highways, on newly launched overhead lines or their phase repairs, when working with induced voltage and in a number of other cases) - are required to monitor the implementation of the stages of preparation of the workplace, the sufficiency and correctness of instructions to team members, the general safety of working moments, and take additional electrical safety measures;
- those allowed to work (member of electrical technical personnel with access group 3-4) - bears responsibility for the sufficiency of safety measures, their compliance with the permit or order, the requirements of upcoming manipulations on electrical equipment, the correctness and scope of the instructions provided;
- direct performers (electrical approval group - 3-4) - are responsible for the correctly prepared work area, the presence, sufficiency and serviceability of individual and general electrical protective equipment, tools and devices, visual information in the form of safety icons or warning posters, fencing of dangerous places, for following safety rules for all team members and control over the safety of their actions during the work process;
- observers in teams (electrical admission group - 3) - monitor the compliance of the work area with safety measures; clarity and sufficiency of preliminary briefing; safety of locks on drives, fences and grounding devices; protection of workers from electrical injuries;
- All employees - members of the team carrying out routine work on electrical installations are required to comply with safety regulations, instructions and instructions regarding the safety of their labor.
The admitter may also be a member of the work team. In general, for each employee of a brigade team with the 3rd electrical safety group, you can hire one worker with the 2nd group, but in total no more than three such workers are allowed.
Passage of current
The damaging factor is greatly influenced by the path along which the current passes through the human body. The most common options are from hand to hand (1 in Fig. 2), from leg to leg (7) and through arms and legs (2-6, 8, 9).
Paths of electric current flow through the human body
The greatest threat to life occurs in cases where the organs responsible for the body's vital functions (for example, the heart or brain) are in the path of current flow through the human body. This occurs when passing through arms and legs (2-6, 8, 9), from arm to arm (1), and also through the head to arms (10, 13, 14) or legs (11, 12, 15). Accordingly, the less dangerous path is from foot to foot (7). The latter option is typical for damage caused by step voltage.
Employer Responsibilities
First of all, responsibility for compliance with electrical safety rules at the enterprise lies with its managers, therefore they are required to know the specified standards. Their activities include:
- Maintaining electrical installations in working order and in good condition so that they meet safety requirements and are not a source of emergency;
- Monitoring equipment maintenance, as well as timely changes to technical documentation and electrical installation passports;
- Conducting electrical safety briefings among workers and maintenance personnel, selecting employees with the required qualifications, as well as certifying them for compliance with the required clearance category;
- Notifying control authorities about the occurrence of an emergency, promptly making decisions to localize and eliminate the accident. At the same time, the authorized person conducts an investigation of the incident, draws conclusions and provides them to the management of the enterprise;
- Development of job descriptions, evacuation plans and algorithms for employee actions during industrial accidents;
- Installation and provision of protective devices for equipment, machines and electrical installations. The manager’s responsibilities also include providing personal protective equipment to workers involved in the repair and installation of electrical installations;
- Carrying out and monitoring the testing of repaired or newly installed equipment, putting it into operation;
- Compliance with the instructions of state control bodies and departmental institutions.
All of the listed responsibilities of the management team of the enterprise are basic and are included in the collection of rules on electrical safety and labor protection.
Requirements for personnel servicing electrical installations
A complete set of requirements can be found in the rules on labor protection during the operation of electrical installations; here is a selection of the main ones.
According to existing standards (Order No. 302n of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated April 12, 2011), employees must undergo a medical examination:
- preliminary, carried out before hiring;
- regular (periodic), carried out once a year;
- extraordinary, can be appointed in special cases (at the request of the employee, when an occupational disease is detected, etc.).
This requirement is due to the fact that for professions related to the maintenance of electrical installations (for example, electricians or electricians), there are a number of health restrictions.
Employees must be familiar with regulatory documents and mandatory requirements. The briefing is carried out at the place of work, and there must be a corresponding entry in the log about its completion.
Example of a page from a safety training log
In addition, maintenance personnel must understand the design of electrical equipment and the principle of its operation.
Upon hiring (and subsequently once a year), the employee’s knowledge is tested. After its successful completion, a certificate of assignment to one or another electrical safety group is issued, or a record of compliance is made (during periodic inspection).
Sample ID
If a specialist does not have a certificate, or has not undergone a medical examination or instruction, then he cannot be allowed to work with electricity or maintain existing electrical equipment. This prohibition also includes persons under 18 years of age or under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Personnel are prohibited from performing actions that contradict the norms and requirements prescribed in the PTE and PTB. Upon receipt of such an order, the employee must refuse to comply with it and inform management or the relevant service of the enterprise about this.
The electrician's golden rule
Touch the exposed conductors with the back of your hand so that the muscles of the hand, experiencing the shock of electricity, clench the hand into a fist, thereby pushing the limb away from the contact. Otherwise, the palm will tightly grasp the conductor and it will be impossible to unclench it, and the person will be under the continuous influence of the current. To clearly prove to a partner or another person that there is no voltage in the electrical installation (which you yourself must have de-energized and verified with a tester that there is no voltage), you should touch the bare back of your hand.
Electrical Safety Tips
Safe current and voltage for humans:
- Constant voltage up to 42 V
- Variable voltage up to 36 V
- Current up to 50 mA
Now you understand why even 50 V voltage is dangerous. Therefore, you should resort to basic safety measures and always follow the following points that can save your life:
- Turn off the voltage at the work site;
- Post a warning sign “Do not turn on! People are working!” (for a machine gun, packet bag, switch or shield - the main thing is to be visible);
- Check the tools and protective equipment for serviceability and mechanical damage (dielectric gloves, boots, boots, etc.);
- Check the probe (voltage indicator) first on the working equipment to make sure it is in good condition, and then check that there is no voltage at the work site;
- Make sure by touching the back of your hand that there is complete absence of tension;
- Protect the work area by wearing electrical protective equipment;
- Get to work.
What is needed to work with current.
Safety requirements when working with power tools
Persons with electrical safety group 2 (or higher) can work with electric tools in production. TB training should be conducted with them quarterly. An entry about this must be made in the journal and certified by the signatures of the instructor and employee.
During work, the use of individual and dielectric protective equipment is prescribed.
Individual protection means
The latter must be subject to regular inspection, the passage of which is certified by the appropriate stamp.
Stamp confirming that electrical footwear has been tested (marked with a red circle)
At the site of repair or other types of work, appropriate technical measures must be carried out, these include the installation of protective grounding, warning signs, fences, etc.
The class of the power tool must correspond to the conditions of work, in accordance with the following standards:
- 1st class – intended for safe premises;
- 2nd class - used for outdoor use or in high-risk areas. The instrument is marked accordingly;
- Class 3 - used in places with unfavorable working conditions (for example, in boilers and tanks) or in rooms classified as particularly dangerous. This tool is designed for low-voltage power supplies up to 42 V (parameters are indicated on the body).
Power tools must not be used in the following cases:
- for work in explosive areas (a spark from the electric motor commutator can cause an explosion);
- in places where there is a chemically active environment that can destroy insulation or metal.
When working outdoors during rain or snow, it is allowed to use only electric tools that have the appropriate protection class (indicated as a marking).
Marking corresponding to the protection class
Basic Safety Precautions
Expert commentary
Lagutin Vitaly Sergeevich
Engineer with a degree in Computer Software and Automated Systems, MEPhI, 2005–2010.
Ask a Question
Since the wiring in the apartment is usually hidden, you cannot randomly drill holes and hammer nails. If you are not sure that there are no wires running in the area, use a special double insulated electric drill.
Recommendations for electrical safety:
- before starting repair work associated with the danger of getting an electric shock, you should turn off the group circuit breaker on the panel in the apartment or on the staircase;
- it is necessary to place a warning sign on the electrical panel on the staircase, otherwise a neighbor may accidentally turn on the electricity at the most inopportune moment;
- before starting work, using an indicator screwdriver, you need to make sure that there is actually no electricity in the network;
- fuses (plugs), which are not currently used in construction, are still installed in some houses, so you should remember that they are replaced only when they burn out. Handicraft repairs in the form of installing wires (“bugs”) can lead to a fire;
- The main condition for the safe use of electricity in everyday life is the good condition of insulation, electrical equipment, safety panels, switches, sockets, lamp sockets, lamps, and cords. The insulation should be checked regularly and updated if necessary. In order not to damage it, it is not recommended to hang wires on nails, iron and wooden objects, twist them, place them behind gas and drain pipes, radiators, use them as a hanger, pull the plug from the socket by the cord, cover them with paint and whitewash, lay them on working lamps. Do not use lamps with a damaged plug, cord or switch;
- when leaving the apartment, do not forget to turn off the lights and electrical appliances, since this not only saves electricity, but also significantly reduces the risk of a fire;
- Portable lights should not be used in the bathroom. When buying a lamp for it, you need to carefully read the instructions, since there are lamps for damp rooms, the design of which uses special elements to make them safe;
- It is necessary to approach the issue of electrical safety most carefully in rooms where children are usually located;
- The power of the light bulb in the lamp must correspond to the permissible limit for it. As a result of a violation of the thermal regime, a short circuit and, as a result, a fire may occur;
- It is not recommended to wash switched-on lighting fixtures and electric lamps - this is dangerous;
- Lighting devices should not be hung on live wires - only on special devices.
Current in the human body.
Activities prior to working with power tools
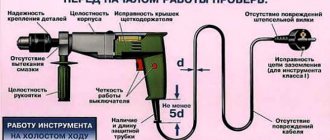
In accordance with mandatory safety requirements, before operating a power tool it is necessary to check:
- reliable fastening of all parts and their completeness;
- integrity of electrical components: power cable, plug, insulation of main parts of the case (checking is carried out by external inspection);
- the performance of the gearbox (the spindle rotates several times when the power is off);
- hull integrity;
- operation in idle mode;
- presence of grounding (this requirement applies only to class 1).
If high-altitude work is to be done, the reliability of the scaffolding (including decking and scaffolding) and the presence of enclosing structures are checked. According to safety rules, in this case it is strictly forbidden to use ladders.
Prevention of electrical injuries
A set of organizational and technical means and measures designed for work safety is the basis for the prevention of electrical injuries.
The theoretical part includes regulated actions during equipment operation and repair work, including measures aimed at preventing electrical injuries. Many years of international experience in the operation of electrical installations and safety accumulated by different countries are briefly summarized in this material.
Personnel decide everything, therefore it is necessary to attract qualified personnel for work in electrical installations. Annual electrical safety exams for groups make it possible to reduce the risks of emergency situations and incidents. The issuance of work orders to teams when working on electrical installations up to 1000 V is carried out by an authorized person with an electrical safety permit of at least group 4; when working on electrical installations above 1000 V - group 5. All regulations for organizational measures are prescribed in the safety regulations and individual parts of the document describing the protective equipment used in electrical installations.
Technical measures require implementation in a strict sequence, since they are associated with complete or partial stress relief:
- measures to prevent spontaneous switching on of equipment or voltage supply as a result of erroneous actions or human factor
- placement of special prohibiting, warning, or ordering posters or barriers in required work areas
- grounding the necessary equipment of electrical installations in accordance with safety rules, only after disconnecting the voltage of the current-carrying parts of the installations.
Technical and organizational measures working together can significantly reduce electrical injuries thanks to safety precautions. In addition to preventing accidents by turning off the voltage supply, with the help of protective equipment (grounding and grounding), the protection of personnel working with live installations is ensured.
However, even these measures are not enough to completely eliminate the occurrence of accidents when working with electrical installations. Accidents, at home and at work, are not isolated.
Average statistical figures regarding serious safety violations directly influenced by the human factor and indiscipline of workers in Russia fluctuate around 80%. It is worthy of attention that these violations are created by experienced workers.
Summary:
- A significant reduction in injuries when working with electrical installations can be achieved only with full compliance with the “Rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations” and compliance with safety precautions by workers with the necessary permission.
- Only by having statistical data on an incident involving electrical injury to a person can one identify the cause of electrical injury and take measures to prevent such injuries in the future.
TB at work
If you need to change the attachment or use another tool, you must turn off the power.
During work, it is necessary to monitor the location of the power cable so as not to damage it. To do this, according to the general rules, the wire must be hung at a height of at least 2.5 meters. If the cable is located above a passage or driveway, its suspension height increases to 3.5 and 6 meters, respectively.
Power must be supplied to the power tool only after it has been installed in its intended operating position.
If there is a need to change location, the electrical machine must be de-energized by disconnecting from the power supply. When carrying, you must hold the tool by the handle or handles designed for this purpose.
At the end of the work process or a break in it, electric tools must be physically disconnected from the power supply.
Electrical Safety Tips
Thus, you should never forget about precautions; you should use high-quality and serviceable equipment and tools. It is advisable to involve only qualified specialists in repairs or to take on the work competently and in good condition. Also important:
- turn off the plugs on the dashboard before starting repairs;
- post a warning sign;
- check the presence of electricity using a special tester;
- Do not use faulty sockets, sockets, switches and electrical appliances.
It will be interesting➡ What is electrical resistance
In bathrooms and other rooms with high humidity, only lamps specifically designed for this purpose can be used. Lamps can only be washed after unplugging the lamp from the socket. And if there are children in the room, you need to be extremely careful and explain to them how to handle electrical equipment.
It is important to remember that the safety of residents and their families depends solely on themselves, be careful, do not rush and do not skimp on light bulbs and wires. And then, if everything is done correctly, electricity will only bring benefits.
TB during operation of household electrical appliances
In this case, it is necessary to adhere to the rules and regulations that indicate safety precautions when working with electrical equipment. Following them will minimize the risk of electric shock. We recommend focusing on the following points:
- Do not use faulty household electrical appliances;
- if there are signs of abnormal operation (sparks, smoke, change in noise level, etc.), shutdown should be performed immediately;
- stationary electric heating devices (boilers) must be grounded and connected only through an RCD.
The last point requires a little explanation. The heating elements installed in such devices may lose their tightness over time; the result of this is clearly shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8. The probe shows the presence of phase in the water coming from the boiler
The presence of the phase in water can pose a serious danger to life. Many fatal accidents have been recorded due to this reason. That is why when installing a boiler, special protection based on RCD circuit breakers is required. But for its reliable operation, it is necessary to ensure that the body of the electric heating device is grounded. Actually, this requirement is specified in the instructions for the electrical device, which states that operation without grounding is prohibited.
Video
Electric shock
XXI CENTURY Candy Fudge Scented water
266 ₽ More details
Video baby monitor Motorola MBP36S (white)
12900 ₽ More details
Women's dresses short
What are the most common traumatic situations?
Electrical hazard may occur:
- when using electrical appliances with damaged insulation, electric stoves with an open spiral; homemade electric furnaces, electric water heaters, when filling electric heating devices connected to the network with water;
- if the order of connecting the device to the electrical network is violated, according to which the cord is first connected to the device and then to the network;
- when using bare wire ends instead of a plug;
- in some cases, two systems for turning on appliances appear in the kitchen: with grounding and without grounding the housings, which leads to an increased likelihood of electric shock;
- from the use of electric lighters powered from a 220 V network for igniting gas burners. The wires for these lighters are made with plastic insulation; you often have to pass the power wire through a burning burner, as a result it melts and the insulation is broken. If one of the subsequent ignitions occurs, severe electrical injury may occur.
Safety precautions in military installations
Particular attention is paid to safety precautions during the operation of military stationary and mobile electrical installations. Thus, it is strictly forbidden to remove fences from rotating elements of installations, terminals of generators, electric motors and electric converters
Personnel involved in the operational maintenance of military electrical units must wear helmets or headgear, as well as special clothing, parts of which cannot be pulled into rotating parts of the machines.
Thus, it is strictly forbidden to remove fences from rotating elements of installations, terminals of generators, electric motors and electric converters. Personnel involved in the operational maintenance of military electrical units must wear helmets or headgear, as well as special clothing, parts of which cannot be pulled into the rotating parts of the machines.
Operating personnel of military electrical units must work in normal lighting; electrical safety is ensured by the use of dielectric matting, as well as a number of other protective measures:
- have an electrical approval group of at least 3;
- make sure that the edges of work clothes and cleaning rags are not pulled into the units;
- do not touch conductive parts of different charges, phases or grounding at the same time;
- if it is necessary to grind contact ring collectors and other rotating parts of electrical units, it is necessary to reduce the engine speed as much as possible, such work is carried out strictly in glasses that protect the eyes; it is prohibited to perform such manipulations alone;
- if an accident occurs, smoke or fire appears, electrical machines or communication equipment must be immediately de-energized;
- in the event of a malfunction of the drive device, motor or excessive vibration, which may compromise the integrity of the electrical installation, or overheating of bearings, military electrical units must also be immediately stopped and inspected;
- It is not allowed to cover operating units with tarpaulins or other sheets, but frame structures, as well as shields and casings, can be used, provided that this does not interfere with the natural cooling of the electrical installation;
- during repair maintenance of generators, electric motors and energy converters, signs “do not turn on - people are working” are placed on keys and switches;
It is necessary to post a sign about the work being carried out
The supply cable must be de-energized by disconnecting it from the distribution panel or removing the fuses.
Cable networks for military electrical installations (in a mobile version) are made only from service wires; the presence of mechanical damage to the insulating layer is not allowed; if they are detected, the commanders of the units to which the electrical units are assigned must prevent them from being put into operation and repair the damage.
Safety regulations for the operation of consumer electrical installations comply with the basic requirements of current laws, state standards and industry norms; they also take into account the experience of operating electrical units with voltages up to 1 thousand volts and more than 1 thousand in various conditions and the suggestions of repair and adjustment specialists. This is the main official document aimed at protecting workers and protecting the industrial environment.
Instructions for labor protection when performing electrical installation work in existing electrical installations
Local regulations of a manufacturing enterprise are valid on the territory of the organization itself and apply either to all employees or to a certain group of officials to whom they are addressed. One of the most important acts in the company is the instruction on labor protection for electricians or other specialties who are directly involved in this type of work.
State acts to ensure the safety of employees during activities related to electricity pay special attention, regardless of the typical profession, be it an auto electrician, a high-altitude worker, an electrician, an electrician of electrical equipment, a network electrician, a premises repair electrician.
Basic safety when handling electrical installations during the work process
As a rule, all these professions are directly related to the negative impact of electric current and in order to minimize the possibility of negative consequences, it is imperative to create a special internal document and comply with special regulations, which are safety precautions when performing electrical installation work. Such a document contains a list of requirements for behavior, as well as sections on the safety of labor activities in the field of legal relations.
Important! In addition, during inspection actions by government agencies, it is mandatory to check the presence of such instructions and the procedure for implementing its instructions. If violations are detected against officials, administrative violation protocols are drawn up
A stand describing the necessary measures to ensure the safety of the labor process
General safety requirements
The general provisions of the document contain standard requirements and take into account the specifics of the organization in this area. According to these rules, the working day procedure, the use of certain protective equipment, the status of the employee himself, the receipt of equipment during the work process, new legislation on labor protection, as well as the procedure for setting up and servicing entrusted equipment are determined.
Safety requirements before starting work
Before starting any work involving exposure to electric current, the employee must be briefed on safety precautions at work. Instruction is especially important when carrying out adjustment and commissioning types of work that are associated with new or repaired equipment. After carrying out such activities, the worker puts a special mark in the logbook.
Basic requirements for a worker when working with electricity
Safety requirements during operation
During work activities, the employee is obliged to comply with instructions and labor safety rules, be sure to use all protective equipment and avoid emergency situations. He must also be guided by the orders of management for carrying out routine maintenance.
Safety requirements in emergency situations
In the event of an emergency, the worker is obliged to report this fact to the work supervisor, use primary protective equipment to minimize the consequences of the accident, provide assistance to the injured, or, in a certain situation, leave the work site through special emergency exits.
Typical protective equipment when working with live installations
Safety requirements upon completion of work
At the end of their work, the working personnel must notify management of its completion and hand over the used protective equipment, as well as insulation equipment, for signature, and note it in the work log.
Dielectric tools
Usually a person far from electricity cannot name any special tools other than a set of dielectric screwdrivers. In fact, there are quite a lot of them, because the work requires specific devices. Let's take a closer look.
How does a dielectric tool differ from a regular one? It has a moisture-proof insulation layer and good electrical resistance. The device must be resistant to acids, oils, and gasoline. The strength of the tool is no less important; it must withstand falls, including from great heights.
As for the set of dielectric screwdrivers, their handles should be long (from 10 centimeters) and well insulated. Long rods must be insulated up to the working length, and short ones must have stops that prevent the tool from slipping out of your hands. Typically handles are made of plastic, hard rubber or rubber.
The handles of wire cutters, pliers and other tools are also protected. So that the tools can be used not only by electricians, but also by representatives of other professions, dielectric covers are made on the handles, which are easily removed. An electrician can work without problems, because the covers do not slip and have stops. And if someone else needs the tool, he will simply remove the covers and use it. It is especially convenient that if damaged, it is enough to simply change the covers.
Protective equipment includes insulated tools, special dielectric gloves and voltage indicators. They are most in demand for panel work up to 1000 V with the voltage turned on.
We should also talk about dielectric gloves. Safety precautions at the workplace of an electrician of any category require the presence of dielectric gloves. Typically, they are made of latex. A mandatory mark is a stamp indicating the test date; it is important that the deadline is met. Before work, gloves are checked for integrity; the easiest way to do this is to inflate them with air. The gloves have a socket that needs to be tightened; if the pressure drops, the gloves are unsuitable. Put gloves on over the sleeves.
Voltage indicators are also necessary for electricians in their work. They are divided into double-pole and single-pole. With their help, it is not the magnitude of the voltage that is determined, but its presence. The devices have lights that light up when there is voltage. The single-pole version resembles a screwdriver with an indicator and an upper finger contact. The current is connected to the ground through the finger. The safe ignition voltage should not exceed 90 V, and the current should not exceed 0.6 mA.
Bipolar indicators are a pair of probes connected to each other by a wire. One of the probes is equipped with a light bulb, which lights up from time to time. To check the voltage, you need to attach one of the probes to the object being tested, and the other to the ground. To eliminate errors, check the indicators on an object that is energized before work.
There is also a special tester that shows the voltage and current values. The device is not only pointer, but also digital.
We remind you that before work you must check the integrity of each tool and its serviceability. If you do not do this, you can endanger not only your life, but also the lives of other people.
Dielectric tool
To avoid a threat to life, it is important to use the right tools, which include a dielectric tool set. What it is? This is the name for instruments with dielectric handles. If they are marked 1000 Volts, then using the equipment you can service electrical networks.
Attention! When a cable or wire is found to be damaged, it must be replaced. Under no circumstances should you repair the damaged area, as this is fraught with subsequent breakdowns.
All activities related to the maintenance of grounding elements, fuses, distribution boards are carried out only by people who have an electrician’s license. Moreover, even electricians are not allowed to work without the appropriate permits and documents.
Actions in the absence of fuses
In some cases, when working with electricity, additional technical measures are required. This situation may arise if the device does not have standard or additional fuses that would protect it from power surges. In this case, it is imperative to de-energize the installation and check the presence of voltage before carrying out work.
The absence of fuses means the danger of a short circuit during voltage surges, since it is the fuse that takes on excess voltage during a technical failure. In its absence, a short circuit results in equipment failure, which can lead to both a fire inside the device and injury to operating personnel.
Important! Recording and checking the technical condition of a device with missing fuses must be carried out under the strict supervision of a responsible electrical safety specialist, since such installations represent a source of increased danger
Direct implementation of technical and routine work on installations with voltages over 1000 V
Emergency procedures
If the electrician’s safety precautions were violated and a person was electrocuted, then the entire team must provide first aid. What are we talking about?
- The victim must be freed from exposure to electricity.
- The victim must be checked for consciousness, pulse, and breathing. This will help doctors assess the person’s condition.
- Contact an ambulance as quickly as possible.
- If there is no pulse or breathing, then resuscitation measures must be started as soon as possible to restore signs of vitality.
Safety rules at home
Following the recommendations developed on the basis of many years of practice and GOST standards will help to avoid the possibility of injury during repairs and using wiring at home:
- carefully study the new device before connecting it to the network or performing maintenance and the attached instructions;
- application for reliable fixation of metal clips;
- Avoid connecting multiple devices with high power consumption for simultaneous use;
- It is prohibited to touch wet parts of the body to devices plugged in, or to touch any elements while taking a shower or being in the bathroom;
- If sparking is noticed, immediately disconnect the device from the power supply;
- It is strictly forbidden to pull the plug from the socket by the cord;
- Before starting work, remove all metal products and jewelry from yourself.
By following all the rules and following the tips outlined above, you can significantly reduce the potential threats even from such dangerous activities. Your safety depends entirely on your ability to listen to the right advice and never be in unnecessary haste.