Rules for handling electrical appliances
Safety rules when contacting electrical appliances must be observed everywhere. At home, on the street, at work, in production, there are different conditions for using electrical equipment. Consequently, the requirements for working with them will be somewhat different.
General actions
Home electrical appliances
Household appliances in the apartment are located in every room, with a particularly large number of them concentrated in the kitchen. The highest danger is when using equipment in combination with water, as the likelihood of electric shock increases.
To avoid serious consequences, you should follow safety precautions with household electrical appliances:
- Grounded outlets must be used to operate the equipment.
- Do not handle wires or operating equipment with wet hands.
- Do not pull the plug from the outlet by the cord.
- It is prohibited to use faulty devices.
- Do not disassemble or repair equipment that is plugged into an outlet.
- It is prohibited to simultaneously turn on a number of electrical appliances that exceeds the permissible number for a given consumer.
- It is dangerous to touch metal surfaces while holding a running electrical device.
Electrical safety at home
Note! Do not leave high-risk equipment unattended: irons, steam generators, air conditioners, heaters, electric stoves. Do not leave irons, hair straighteners, hair dryers on!
- Electric stoves should be installed at a distance of 50 cm from the curtains.
- In the kitchen, appliances must be placed at least 50 cm from the water tap.
- When turning on the equipment, there should be no knots or kinks on the cord to avoid insulation damage.
- Under no circumstances should you touch exposed wires or lighting fittings during installation.
- The cable should be connected first to the electrical appliance and then to the power source.
- You cannot dry things on electric heaters.
- Wires must be kept away from gas pipes, heating radiators, heaters, electric stoves, and other heating devices.
- Before connecting a new electrical appliance, you must carefully study the instructions.
Important! Do not screw in light bulbs with wet hands or while standing on a wet floor!
Only if the requirements are met will it be safe to work with equipment.
Outdoor electrical appliances
On the street, a person is surrounded by a huge network of wires and electrical installations. Rain, dew on the grass, puddles are an additional risk of electric shock. Accordingly, safety requirements increase when working with electrical appliances:
- It is prohibited to walk on wet ground, especially without shoes, while holding the device on.
- Do not tie clotheslines to drainpipes located near power lines.
- You cannot install, adjust, or repair antennas near wires.
- It is dangerous to touch any objects located on non-de-energized lines.
Danger of power lines
- It is prohibited to open transformer booths and other similar premises.
- Do not handle broken cables.
Note! For electrical safety on the street, one general rule can be drawn: it is prohibited to perform any actions near power lines or broken cables, especially during rain.
Handling electrical appliances in the office and at work
When hired, each employee undergoes safety training. All documentation on electrical safety is collected in the “Rules for labor protection during the operation of electrical installations”. After reading the instructions, the employee signs in the journal. This makes him responsible for improper handling of equipment and electrical appliances. In case of non-compliance with the regulations, the violator may be subject to administrative and even criminal liability.
In production, only specialists with appropriate education are allowed to work with electric current. And it is allowed to assign workers who have undergone training and certification to perform duties at electrical installations and receive a certificate. The procedure is also carried out by bosses and foremen who do not have direct contact with electricity, but are responsible for their subordinates.
Safety precautions at work and in the office require compliance with the following requirements:
- Work is permitted in special clothing.
- The equipment must be operated in good condition and strictly for its intended purpose.
- Placing power tools is permitted in premises of the appropriate protection class.
- When working in a damp environment, it is necessary to use a tool of a suitable protection class.
- Outsiders should not be allowed while working in laboratories, workshops, or other hazardous areas.
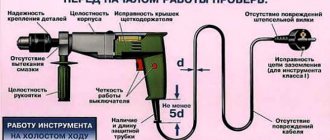
- Before starting the equipment, you should check the integrity of the wires and the serviceability of the sockets.
Equipment check
- Repair and replacement of spare parts is allowed only after de-energizing the devices.
- Do not twist or nail wires or cover them with any kind of floor covering.
- You cannot plug multiple electrical appliances into an outlet.
Correct equipment of the workplace and compliance with safety regulations are necessary factors for preserving the life and health of personnel.
Electrical Safety Tips
Thus, you should never forget about precautions; you should use high-quality and serviceable equipment and tools. It is advisable to involve only qualified specialists in repairs or to take on the work competently and in good condition. Also important:
- turn off the plugs on the dashboard before starting repairs;
- post a warning sign;
- check the presence of electricity using a special tester;
- Do not use faulty sockets, sockets, switches and electrical appliances.
It will be interesting➡ What is electrolysis and where is it used in practice?
In bathrooms and other rooms with high humidity, only lamps specifically designed for this purpose can be used. Lamps can only be washed after unplugging the lamp from the socket. And if there are children in the room, you need to be extremely careful and explain to them how to handle electrical equipment.
It is important to remember that the safety of residents and their families depends solely on themselves, be careful, do not rush and do not skimp on light bulbs and wires. And then, if everything is done correctly, electricity will only bring benefits.
What to do if electrical appliances catch fire
Safety precautions when working with an iron
In everyday life, at work, or in nature, you may encounter an electrical appliance fire. The most important thing in any critical situation is to remain calm, because panic is a provocateur of mistakes.
Important! Do not put out a fire with water when an electrical appliance is plugged in!
In the event of a fire, it is necessary to de-energize the living space and unplug the wire from the power source. Only after this, cover with a thick, airtight fabric (blanket, bedspread, plaid). The lack of oxygen at the source of the fire will stop the process. The fire will not spread to other objects.
Extinguishing a fire device
If it is not possible to turn off the power to a device that has caught fire, the flame can be extinguished by covering it with dry soil from a flower pot, soda, and sand. This method will also block the air supply and stop the fire.
In case of electrical wiring fire, the technology is similar. You must first turn off the power to the room and then extinguish the fire. In offices and workplaces, safety precautions require the presence of a fire extinguisher.
It’s also nice to have such a device in the house. A carbon dioxide fire extinguisher is suitable for extinguishing a live appliance. But its use is harmful to human health.
Important! A carbon dioxide fire extinguisher may only be sprayed in ventilated areas.
For apartments and private houses, it is better to use a powder fire extinguishing agent. It can be used for fires under voltage up to 1000 V. In case of a power outage, foam or water fire extinguishers can be used.
Working under voltage
You should always work in the absence of voltage, no matter 220 V or 32 V. Any statements that real electricians work under voltage should not be taken seriously - professionals will never put themselves at risk unless absolutely necessary. Only in extreme cases, if there is no other way out, can you work under voltage, but remember that in such cases you should always wear protective equipment against electric current: certified dielectric gloves and boots, namely certified ones, and not “..and my grandfather had I had it in the attic somewhere, I bought it in my youth...”
Don't skimp on your safety and life! And another important factor: you should always have an observer, assistant or partner with you, who can help if something happens. If you are not confident in your abilities or doubt that this work is not so simple, do not take it, because... electricity is like a mine: make the wrong move and at best you can get away with fright. Therefore, if you’re not sure, don’t bother. I’m sure – check everything again and go ahead!
Danger of household electrical appliances.
How to help the victim
Safety precautions when working with an angle grinder
The problem is that, having grabbed the source of danger with his hands, a person is not able to let go of the wire due to muscle spasm. Therefore, it is necessary to stop the impact of electricity on the victim:
- It is necessary to unplug the wire from the socket using non-conducting objects (wood, rubber, fabric) or cut it with pliers.
- If it is impossible to turn off the power to the device, you need to drag the victim away from it to a remote distance.
Methods for releasing a live element
Note! Do not touch the skin of a person under the influence of electric current with your bare hands!
After the measures have been completed, it is necessary to assess the person’s condition and begin providing first aid, taking into account the degree of electrical damage:
- While conscious, place it on a hard surface, treat the skin around the affected areas with iodine or potassium permanganate, and apply a dry bandage to the wounds.
- If he faints, free him from constricting clothing, try to bring him back to consciousness with ammonia and treat the burns.
- In a state of clinical death, resuscitate using chest compressions and artificial ventilation. If the muscles of the mouth are in spasm, then breathing should be done “mouth to nose.” The procedure should be performed before the ambulance arrives.
The consequences of an electrical injury can vary from mild dizziness to cardiac arrest. Timely first aid can save the victim’s life.
The effect of electric current on the human body
- Thermal impact. This is heating of human body tissues and burns.
- Electrolytic effect of current. This is an effect on the blood and other body fluids, causing the decomposition of their constituent elements.
- Biological (physiological) effects. Irritation and excitation of muscle and nervous tissue occurs, which leads to convulsive muscle contractions. The most dangerous contractions of the heart muscle and lungs
The result of these impacts can be divided into two types of electric shocks: electrical injuries and electrical shocks. Electrical injuries are clearly defined local tissue damage. Injuries include electrical burns, electrical marks, skin metallization, electroophthalmia, and mechanical injuries.
Material on the topic: What is the danger of resonance and what kind of phenomenon is it.
Burns. A consequence of the thermal effect of current passing through the human body, or touching very hot parts of electrical equipment, or from the action of an electric arc. The most severe burns occur when an electric arc occurs in networks of 35–220 kV and in networks of 6–10 kV with high network capacity. In these networks, burns are the main and most severe types of damage. In networks with voltages up to 1000 V, burns from an electric arc are also possible (when the circuit is disconnected with open switches in the presence of a large inductive load).
What is the difference between parallel and series connection of capacitors?
Read more
Do-it-yourself pirate metal detector - detailed instructions.
Read more
What is a tuning resistor: description of the device and its scope.
Read more
Electrical marks are clearly defined skin lesions where the electrodes come into contact. They can be round or elliptical in shape, gray or white-yellow in color with clearly defined edges. Caused by the mechanical and chemical effects of current. They can appear only some time after exposure to current. Usually the lesions are not accompanied by inflammation and pain, but cause swelling and swelling at the site of contact with the electrodes. Signs of a small area heal safely, but with a large area of lesions, tissue necrosis occurs.
Electrician safety precautions.
Electrometallization of the skin is the penetration of the smallest particles of metal into the upper layers of the skin due to its boiling and splashing under the influence of an electric arc. The damaged area of the skin becomes hard and has a rough surface. A sensation of a foreign body appears at the site of the lesion. The outcome of the injury, as with a burn, depends on the area of the affected area. Most often, metallic leather comes off without leaving a trace.
Electroophthalmia is an inflammation of the outer membranes of the eyes, resulting from strong exposure to ultraviolet rays released during the burning of an electric arc.
Mechanical damage - Bone fractures and ruptures of tendons and muscles caused by muscle contraction when current passes through them. They are the result of an electric shock.
An electric shock is the result of the biological effect of current, consisting in the excitation of nerve tissue when an electric current passes through the body. Manifested by involuntary convulsive muscle contractions.
It is important to know: What is electric current.
There are four degrees of electric shock depending on the outcome of the impact on the body, ranging from mild, without loss of consciousness (first degree) to clinical death (fourth degree). In a state of clinical death, a person has no breathing or heartbeat, the pupils of the eyes are dilated and do not react to light. The duration of clinical death is approximately 4-8 minutes. After this time, the death of brain cells occurs, leading to the irreversible cessation of biological processes in the body, the collapse of protein structures - biological death.
How dangerous is electric shock?
Current in the human body
The most dangerous is the passage of current through the respiratory organs and heart along the longitudinal axis (from head to feet). Proportion of total current passing through the heart:
- hand-to-hand path – 3.3% of the total current;
- path left hand - legs - 3.7% of the total current;
- path right hand - legs - 6.7% of the total current;
- leg-leg path – 0.4% of the total current.
It will be interesting➡ What is a Faraday cage
At voltages up to 250-300 V, alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz is approximately 45 times safer than direct current; at higher voltages, direct current is more dangerous. A current is considered safe if its prolonged passage through the human body does not cause harm and does not cause any sensations. Its value does not exceed 50 μA. A current between 0.5 mA and 1.5 mA is called the threshold sensible current. It causes a slight tingling sensation, a sensation of heating the skin. At a current of 2-5 mA, pain in the hand and trembling of the hand appear.
Possibility of death from electric shock.
Increasing the current to 10-15 mA causes unbearable pain and complete cessation of muscle control. If a person simply touches live areas, he can free himself from the action of the current by withdrawing his hand. If the wire is clamped in the hand, then at this current value the person cannot voluntarily release his fingers from the live parts and remains under voltage.
For this reason, a current greater than 10-15 mA is called non-releasing. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that if a current of the same magnitude passes through the muscles that control the flexion and extension of the fingers.
Table - Average values of threshold currents.
The flexor muscles, being more powerful, create a slightly greater force, so the fingers are clenched into a fist. When an industrial frequency current of up to 10-15 mA passes through the arm, the influence of biological impulses at the will of a person can still create a greater force in the extensor muscles than in the flexor muscles, and the victim can be freed from the action of the electric current. With a higher current, the effect of biological impulses on muscle control is completely lost and their contraction is determined only by the action of an external current.
A threshold non-releasing current can conditionally be considered safe for humans in the sense that it does not cause immediate damage. But with prolonged passage, the magnitude of the current increases due to a decrease in body resistance, which can result in circulatory and respiratory problems and death.
At a current of about 50 mA, a convulsive contraction of the chest muscles begins, constriction of blood vessels and an increase in blood pressure, which leads to loss of consciousness and death. When a current of more than 100 mA passes along the path arm - arm or arm - legs for 2 - 3 seconds, it leads to death (lethal current).
Since after 1-2 seconds cardiac fibrillation may occur (chaotic, scattered contractions of individual fibers of the heart muscle). As a result, the heart stops working and blood circulation is impaired. Fibrillation continues even after the current stops, resulting in death.
Workplace requirements
The minimum workplace area for one person is 6 m2. Light should come from artificial and natural sources. The lamps do not reflect from the screen, and excess sunlight must be contained with fabric curtains. It is undesirable to illuminate the room exclusively with the help of overhead ceiling light.
It is unacceptable to place computer wires near the heating system; their insulation must be intact. The system unit should not be placed in a table niche or other enclosed space where normal ventilation is impaired
To eliminate all kinds of risks, you need to responsibly treat all stages of using a computer. The user can and should control the entire cycle of interaction with technology. The process of compliance with all these simple rules must be continuous and comprehensive.
What current is considered unsafe
Safety precautions when working with a sewing machine Electric current differs in the degree of effect on a person. It is classified as follows: tangible; not letting go; fibrillation. The voltage of the first type of current is 0.6 mA. When struck by this type of current, the victim feels irritation. The second type of current can cause convulsive movements of the muscles of the limbs in contact with exposed wires. The third type of current can cause serious problems in the functioning of the heart. Death from cardiac arrest is possible.
In different situations and under different conditions of the body, the consequences of electric shock can also be different. A current of 15 mA is considered dangerous to humans. In this case, a person cannot free himself from its influence on his own. A current of 50 mA causes serious damage to human health. A current of 100mA for 1-2 seconds can become dangerous and cause cardiac arrest. A current whose frequency is 50-500 Hz is considered dangerous.
Main factors influencing safety Safety precautions when working with electrical appliances The following factors affect the safety of a person using electrical equipment or performing work with electrical equipment: technical condition of electrical installations and devices; method of using devices (organization of work on devices); qualifications of the employee (user); operating conditions of electrical devices in the environment.
Consequences of electric shock.
FAQ
What should you not do when helping a person struck by an electric shock?
When providing first aid to an electrical victim who is still in contact with the conductor, never touch the exposed surface of his body. You will be subjected to exactly the same electric shock and there will be two people in need of help.