In a comprehensive system of ensuring safety when carrying out work at any facility (enterprise or organization), labor protection takes an honorable leading place. Without the consent of a TB specialist, no work operation is carried out on them in which there are elements of a threat to human health or a danger of injury.
PTEEP
According to safety requirements, any employee of the enterprise, before starting such work, must obtain a special permit, which is an official confirmation of his readiness for it. So, in order to obtain the 3rd group in electrical safety (which gives the right to carry out work with electrical equipment), you will need to pass a special commission that evaluates the level of training of the applicant.
Therefore, when preparing for the exam, you will need to familiarize yourself with a large list of questions on electrical safety contained in the exam cards, as well as study the current regulatory documentation and a number of additional manuals (a photo of one of them is given below).
Immediately before certification, it is also advisable for the future owner of the third group of admission to review the characteristic errors that arise in the answers to questions asked during certification. Moreover, their total number, according to various sources, may exceed one hundred, which will require the applicant for the third group to make certain efforts.
Features of preparation for certification
In order for the preparation for the exam to be successful, just studying all the regulatory documentation (including PUE, PTEEP and others) will not be enough. The fact is that during the certification, very specific questions are asked regarding various work situations, the answers to which are usually not given in ordinary sources.
They consider only general requirements and standards relating to the operation of electrical installations with voltages above 1000 Volts. Therefore, you will have to give answers on electrical safety according to the same principle (that is, taking into account specific situations and conditions, as well as broken down by topic).
And this is only possible if the examinee was able to get somewhere and carefully analyze tickets with answers on electrical safety, group 3, developed under the patronage of Rostechnadzor. As a rule, such tickets “travel from hand to hand” and are quite accessible to anyone who would like to get acquainted with correctly formulated answers.
In addition, there are specially developed systems such as Olympus OKS (they are considered and called alternative) for persons taking all known groups from the second to the fifth. To use them, you will need to try a little and surf the Internet.
Additional Information. The Olympus OC system is designed both for individual acquisition of knowledge and for classes in groups of thirty people or more.
Good support for all those who need a preliminary study of the questions themselves and the answers to them is provided by a website specially created for this purpose called tests24. Anyone applying for the third group can access this very useful resource if they type tests24.ru in the address bar and go to the desired address.
Another assistant in preparing for the certification is a resource called “testsmart”. It is here that all the most important questions are grouped strictly by topic, which will greatly facilitate the preparation for passing the certification.
General concepts
To obtain the 3rd group in electrical safety, you will need to familiarize yourself with a fairly large number of questions. An interesting fact is that some of them were previously encountered during certification for group 2 in electrical safety, so remembering them will be quite easy.
Rules for the construction of electrical installations (PUE) with amendments and additions
General concepts about conductors in electrical equipment include the following questions that can be found in exam papers:
- What electrical equipment is operational?
Electrical equipment that is powered wholly or partly by electricity. Such energized installations have switching devices that supply electricity to the equipment.
- What is the correct designation for the neutral conductor on circuits and equipment?
This wire differs from the others in a special color - blue, and is also designated by the letter N.
- What is the correct symbol used to identify a grounding wire that protects personnel from electrical hazards?
Typically, in all types of electrical equipment, the grounding type of wires is colored green and yellow, which run along the entire length of the conductor and have the same width. The grounding wire differs not only in color, but also has a special letter designation - PE, which is used in many countries around the world. This rule is valid for tires with a width from 15 to 100 mm.
Neutral and ground wires used in various types of electrical equipment
- How to correctly distinguish the combined type of wires, which includes both a protective type of conductor and a working one?
Such a wire should have a blue color, extending over its entire length, and at the ends it should be painted with stripes of two colors - yellow and green. In addition to color, this conductor has a written designation PEN, which is used both in drawings and in the electrical equipment itself.
- How are the tires used to transmit three-phase current designated by the color of the element and the designation by letters?
All three phases have different colors. One phase is indicated in yellow. Also has a designation in the form of the letter “A”. The second phase is green in color and the letter used to designate it is “B”. The latter is red and has the letter “C”.
- What are the differences between buses that carry direct current and those that carry alternating current? How are they designated?
The buses through which direct current passes are divided into three conductors. The first is a positive bus with a “+” sign. The second tire is a minus and is indicated by a “-” sign. The last bus is zero, designated by the letter “M”. In addition to the designations in the form of signs, these conductors are painted in different colors: “+” - red, “-” - blue and “M” - blue.
- What electrical networks with a voltage of 10 kV can have neutral grounding modes?
There are several main types of neutral grounding. The first is isolated (ungrounded). The second is solidly grounded, connecting directly to the ground loop. The third is grounding through a resistor. The fourth is grounding through an arc suppression reactor.
Examples of general questions
Tickets with answers on electrical safety
Among the variety of test tasks, which can include one hundred questions, the main attention is paid to the general provisions of the current regulatory documentation. In order to obtain the 3rd group of electrical safety clearance, first of all, you will need to carefully check all the proposed questions with the provisions of the PUE (taking into account the latest changes and additions).
The section called “general” includes the following typical examples (questions and answers are given in turn below):
- Which of the electrical devices operating at the enterprise can be classified as operating electrical equipment (including systems designed for voltages above 1000 Volts);
- How are neutral conductors correctly indicated on diagrams and on the housings of station units (they are in the middle in the photo below);
Neutral conductor
- How is the grounding wire required to protect service personnel from electric shock marked?
- How is the so-called “combined” conductor, which includes a protective and working busbar, correctly designated?
- How, according to TB requirements, are tires intended for supplying three-phase voltage to the consumer distinguished (by color and letter marking);
- How are the busbars used in DC power lines different and designated?
The answer to the first general question looks like this: the category of operating electrical installations includes equipment that is currently fully or partially energized. It must be equipped with switching devices through which it is supplied with a power supply of 220 or 380 Volts.
The correct answer to the second of these questions will be this: the neutral conductor differs from other connecting conductors in the blue color of the protective insulation, and in diagrams (and sometimes in reality) it is designated by the English letter N.
Also, the person taking the exam should know that protective busbars, in order to distinguish them from other conductors, are laid in insulation with alternating green and yellow stripes of the same width applied along the entire length. To designate them, allowing the color difference to be duplicated, a double PE icon is used (in the photo it is the bottom one).
Protective conductor PE
Note! The designation PEN usually refers to a combined protective conductor that simultaneously performs a working and protective function.
When answering the fifth of the questions included in the tests, you should note the following points:
- Power buses laid to provide the user with a three-phase voltage of 380 Volts are marked in different colors at the station;
- The first, usually called tire “A”, is painted yellow, and the second “B” is painted green;
- The last third tire is marked in red and designated with the letter “C”.
Buses that pass direct current through them must also have different colors (see photo below).
Designation of DC buses
The first (1), having the schematic designation “+”, is usually marked in red. The second of these conductors is negative and is marked with a “-” icon (its standard color is blue).
And finally, an applicant taking the exam for the 3rd admission group should know that the third of the wires, related to the zero buses, is designated by the letter “M” and is placed in blue protective insulation.
EB 302.2. III group for electrical safety up to 1000 V
EB 302.2. Tests for group 3. All materials presented in this electrical safety section are compiled according to the Olimpox , which is used during certification for the electrical safety clearance group in Rostechnadzor . Educational materials and information are not an official source and are used for self-study for the electrical safety clearance group.
Topic 1. General information about electrical installations 40 questions
Basic information about electrical installations and electrical equipment. Terms and Definitions.
General requirements of safety rules for the operation of consumer electrical installations.
Responsibility and supervision of compliance with norms and rules of work in electrical installations
•Rules for technical operation of consumer electrical installations (PTEEP)
•Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated July 24, 2013 N 328n “On approval of the Rules for labor protection during the operation of electrical installations”
•Rules for electrical installations (PUE)
Topic 2. Requirements for personnel and their training 21 questions
Personnel tasks. Characteristics of administrative and technical, operational, maintenance, operational and repair electrical personnel. Characteristics of electrical engineering personnel.
Personnel training. Electrical safety groups and conditions for their assignment
•Rules for technical operation of consumer electrical installations (PTEEP)
•Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated July 24, 2013 N 328n “On approval of the Rules for labor protection during the operation of electrical installations”
Topic 3. Procedure and conditions for safe work in electrical installations 42 questions
Organizational measures to ensure work safety. Responsible for work safety. Brigade composition. Technical measures to ensure the safety of work with stress relief. Safety measures when performing certain works
•Rules for technical operation of consumer electrical installations (PTEEP)
•Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated July 24, 2013 N 328n “On approval of the Rules for labor protection during the operation of electrical installations”
Topic 4. Grounding and protective measures for electrical safety. Lightning protection 25 questions
Methods for performing grounding. Insulation of electrical installations. Basic measures to ensure electrical safety. Lightning protection.
•Rules for technical operation of consumer electrical installations (PTEEP)
•Rules for electrical installations (extraction) (PUE)
•Instructions for the installation of lightning protection of buildings, structures and industrial communications (SO 153-34.21.122-2003)
Topic 5. Rules for the use and testing of protective equipment used in electrical installations 21 questions
Requirements for protective equipment used in electrical installations.
Rules for using protective equipment
•Instructions for the use and testing of protective equipment used in electrical installations (SO 153-34.03.603-2003)
Topic 6. Rules for releasing victims from electric current and providing them with first aid 13 questions
General rules for first aid. The effect of electric current on the human body. The procedure for freeing the victim from live parts that are energized. Rules for providing first aid to victims of electric shock
•Instructions for first aid in case of accidents at work (approved by RAO UES of Russia)
Electrical receivers
Electrical Safety Group 4
In addition to a good knowledge of the rules for marking and designating elements of electrical mains, a person being tested for electrical safety must also have an understanding of electricity receivers.
Explanation. Such receivers mean a variety of devices designed to convert electricity from one type to another (see photo below).
Electrical receivers
In addition to understanding the principles of operation of these units, the third tolerance group, assigned based on the results of the test subject’s certification, presupposes knowledge of which category the electrical equipment operating at a given facility belongs to.
So, one of the questions characteristic of this section is: what types of electricity receivers are classified in the 2nd group in terms of reliability?
When answering this question, you should know that electrical installations belonging to this group are considered to be units and structures, the emergency shutdown of which can lead to significant losses at a given enterprise.
During the knowledge test, the test taker must explain to the examiner that in general all types of electrical installations equated to socially significant objects must have this category.
A complete and objective testing of the applicant may include the following question: which of the electricity receivers are usually assigned category 3 in terms of their reliability?
This group should include installations operating with voltages up to and above 1000 Volts, a forced interruption in the energy supply of which can lead to irreparable material losses. Thus, any production facilities, the interruption of current supply to which may pose a threat to the safety and health of people, should be equated to the third group.
Of the variety of exam tasks (remember that their number can exceed one hundred), a special place is occupied by questions related to regulatory and technical documentation regulating the procedure for carrying out work in electrical installations.
Answers to such tasks must list all regulations and documents used in daily work that are directly related to electricity. The list of basic standards must include PUE, PTEEP, MPBEE, as well as SNiPs and GOSTs relating to tools and individual parts used during work operations.
In conclusion, we note that modern technical training systems (simply one hundred) can include a wide variety of topics and questions used in the preparation of test tasks for certification for the safety group when working with electrical equipment. Accurate knowledge of all the answers, the number of which can sometimes exceed one hundred, will allow the examinee to receive a certificate in a timely manner, as well as significantly increase the guarantee of safety at work.
Permissible distances to live parts that are energized
2. List of works performed in the order of routine operation.2.4.1. Small-scale types of work performed during a work shift and permitted for production in the order of routine operation must be contained in a list of works previously developed and signed by the technical manager or the person responsible for electrical equipment, approved by the head of the organization.
In this case, the following requirements must be met:
work in the order of current operation (list of works) applies only to electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V; the work is performed by operational or operational-repair personnel on the equipment or area assigned to these personnel. Preparation of the workplace is carried out by the same employees who subsequently perform the necessary work. 2.4.2. Work in the order of routine operation, included in the list, is permanently permitted, for which no additional instructions, orders, or targeted instructions are required. 2.4.3. When drawing up a list of works in the order of current operation, one should take into account the safety conditions and the possibility of individual performance of specific works, the qualifications of personnel, the degree of importance of the electrical installation as a whole or its individual elements in the technological process. 2.4.4. The list must contain instructions defining the types of work permitted to be performed by the team. 2.4.5. The list must indicate the procedure for registering work performed in the order of current operation (notification of higher operational personnel about the place and nature of the work, its beginning and end, recording the work as an entry in the operational journal, etc.).
2.4.6. Work performed as part of routine operation in electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V may include:
work in electrical installations with one-way power supply; disconnecting and connecting cables, electric motor wires, and other equipment; repair of magnetic starters, switches, contactors, start buttons, and other similar starting and switching equipment, provided that it is installed outside panels and assemblies;
repair of individual electrical receivers (electric motors, electric heaters, etc.); repair of separately located magnetic stations and control units, maintenance of the brush apparatus of electrical machines; removal and installation of electricity meters, other instruments and measuring instruments; replacing fuses, repairing lighting wiring and fittings, replacing lamps and cleaning lamps located at a height of no more than 2.5 m;
other work performed on the territory of the organization, in office and residential premises, warehouses, workshops, etc. The given list of works is not exhaustive and can be supplemented by the decision of the head of the organization. The list must indicate what work can be performed individually.
Non-industrial consumers group 3 up to and above 1000V general questions from 07/09/2021
Apply to EPT from 02/01/2021 (as amended from 07/09/2021)
The update was officially carried out in January 2022. It should be noted that the RTN website contains questions approved on 07/09/2021. These questions were posted on the EPT without official notification:
- Who does the Labor Safety Rules apply to when operating electrical installations?
- How are the results of testing the knowledge on labor protection of Consumers formalized?
- Under what conditions can workers who do not service electrical installations be allowed into switchgears up to 1000 V?
- Who gives permission for voltage relief in accidents to free the victim from the effects of electric current?
- In what cases is the procedure for storing and issuing keys violated?
- What does the concept of “Permission Work Order” include?
- How many copies of the permit must be issued?
- Is it possible to issue a work permit electronically?
- For what period is it allowed to issue a work permit from the date of commencement of work on existing electrical installations?
- For how long can a permit for work on electrical installations be extended?
- Who has the right to extend the permit?
- Who has the right to extend work permits?
- How can permission to extend a work permit be transferred?
- After what period can work permits be destroyed, the work on which has been completely completed and there have been no accidents, incidents or incidents?
- In electrical installations, how are records of work performed according to work permits and orders kept?
- What requirements are established by the Labor Safety Rules during the operation of electrical installations for maintaining a log of work according to work permits and orders?
- Is it permissible for one or more team members to stay separately from the work producer in the event that team members are dispersed among different work places?
- Who is allowed to work alone in electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V, located in rooms other than especially dangerous ones?
- In which electrical installations can work be performed as part of routine operation?
- Which of the listed works can be classified as work performed as part of routine operation in electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V?
- Which of the listed activities must be taken into account when drawing up a list of works performed in the course of routine operation?
- What prohibiting posters are posted on the drives of switching devices to prevent voltage from being applied to the workplace during repairs or routine inspection of equipment?
- Who has the right to service batteries and chargers?
- How should potential protection be ensured when working on wires from a telescopic tower?
- How are power tools and hand-held electrical machines classified according to the method of protection against electric shock?
- What class of power tool can be used without the use of electrical protective equipment when working in metal containers with limited ability to move and exit?
- What are the conditions for using Class II power tools in hazardous locations?
- What is prohibited for an employee when performing work using portable power tools?
- What are the requirements for posted personnel?
- What must seconded personnel undergo upon arrival at the place of their assignment to perform work in existing electrical installations?
- Who provides initial training to seconded personnel when carrying out work in electrical installations up to 1000 V?
- Who prepares the workplace for construction and installation work?
- Who determines the list of professions and jobs that require production personnel to be assigned to electrical safety group I?
- How is group I assigned to personnel who have mastered electrical safety requirements?
- Which electrical installation is considered operational?
- What is the definition of the term "Operation"?
- What is the definition of the term “Transformer substation”?
- Who is covered by the Rules for the Technical Operation of Consumer Electrical Installations?
- Who should ensure the reliability and safety of electrical installations?
- What should an employee do if he notices a malfunction in the electrical installation or protective equipment?
- Who approves the List of positions and professions of electrical personnel who need to have an appropriate electrical safety group?
- Who has the right to test the knowledge of non-electrical personnel with the assignment of clearance group I?
- Within what period of time from the date of the last knowledge test can employees who received an unsatisfactory assessment be re-tested?
- What knowledge testing is carried out on personnel upon appointment or transfer to another job if new duties require additional knowledge of rules and regulations?
- When is an extraordinary personnel knowledge test carried out?
- Which electrical safety group should the chairman of the commission for testing the knowledge of personnel of an organization with electrical installations up to 1000 V have?
- How are the results of testing personnel knowledge on electrical safety documented?
- How are grounding conductors connected to the ground electrode and grounding structures?
- What color should exposed grounding conductors be painted?
- What is the frequency of visual inspection of the visible part of the grounding device?
- Is it possible to use the ground as a phase or neutral wire in electrical installations up to 1000 V?
- What kind of water should be used to top up batteries?
- How should emergency lighting luminaires differ from task lighting luminaires?
- What personnel are allowed to work with portable electrical receivers?
- How are premises classified in relation to the risk of electric shock to people?
- Which premises are classified as premises with an increased risk of electric shock to people?
- What, according to the Electrical Installation Rules, is called an electrical energy receiver (electrical receiver)?
- What, according to the Electrical Installation Rules, is called an electrical energy consumer?
- What is the definition of the term "Protection against direct contact"?
- What is the definition of the term "Grounding"?
- What is the definition of the term "Artificial Grounding"?
- What is the definition of the term "Natural Earther"?
- What is the definition of the term "Grounding"?
- What is the definition of the term "Protective Grounding"?
- What can be used as natural grounding agents?
- How should the connection of grounding and neutral protective conductors and potential equalization conductors be made to open conductive parts?
- What types, according to the Electrical Installation Rules, are emergency lighting divided into?
- What, according to the Electrical Installation Rules, is safety lighting intended for?
- Are paint coatings insulating against electric shock?
- Indicate the sequence of actions to assess the situation and ensure safe conditions for providing first aid: 1. Determination of threatening factors for the life and health of the victim; 2.Identification of threatening factors for one’s own life and health; 3. Elimination of threatening factors for life and health; 4. Termination of the effect of damaging factors on the victim; 5. Estimation of the number of victims; 6. Removing the victim from the vehicle or other hard-to-reach places; 7.Moving the victim.
- Provide a correct list of comprehensive first aid measures. (Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated May 4, 2012 No. 477n).
- Provide a comprehensive list of first aid measures. (Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated May 4, 2012 No. 477n).
- Indicate the sequence of actions to restore airway patency and determine signs of life in the victim. (Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated May 4, 2012 No. 477n).
- List of conditions for which first aid is not provided in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated May 4, 2012 No. 477n?
- List the measures to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation until signs of life appear. (Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated May 4, 2012 No. 477n).
- What actions are taken to maintain airway patency? (Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated May 4, 2012 No. 477n).
- List the measures for a general examination of the victim and temporary stopping of external bleeding. (Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated May 4, 2012 No. 477n).
- What actions of the person providing assistance do not relate to measures for a detailed examination of the victim in order to identify signs of injuries, poisoning and other conditions that threaten his life and health, and to provide first aid in the event of detection of these conditions: (Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated May 4, 2012 No. 477n )?
- At what stage are emergency medical services and other special services called, whose employees are required to provide first aid in accordance with federal law or with a special rule in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated May 4, 2012 No. 477n?
- Who approves the procedure for working with personnel in the organization?
- Which personnel are not trained for the new position (workplace)?
- How are the results of the knowledge test recorded?
- Is it permissible to attach the lanyard of the safety harness of supporting and tensioning multi-chain insulating pendants to the insulator garland?
- What index must be indicated when filling out the column “name of work” in the field “Certificate of the right to carry out special work” in the certificate of an employee authorized to work under voltage on live parts in electrical installations of 6-20 kV?
- Who can register the keys to electrical installations that do not have local operating personnel?
- What is not prohibited when conducting inspections of switchgear above 1000 V?
- What should electrical installations be equipped with?
- How many schemes exist to ensure the safety of personnel when performing live work on live parts in accordance with the Labor Safety Rules during the operation of electrical installations?
Electrical receivers
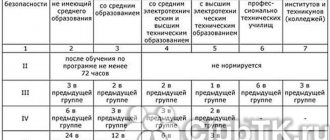
Comparison of electrical safety groups
In addition to knowledge about the correct marking and designation of electrical wires, buses and cables, those taking the exam for group 3 on electrical safety must have extensive knowledge about electrical energy receivers - various devices whose purpose is to convert electricity into another type of energy. In addition to understanding their participation in the technological process, the worker must know which category of electrical receivers this or that equipment belongs to.
Electrical receivers are equipment in which electrical energy is converted into another type of energy.
Tickets for certification of the 3rd group on electrical safety may include the following questions regarding electrical receivers:
- Which electrical receivers belong to the 2nd reliability group?
The second group of electrical receivers includes equipment and structures, the emergency cessation of which will lead to significant losses at the enterprise due to undersupply of the required quantity of products. Also, all types of installations, the de-energization of which will lead to disruption of the normal activities of socially significant objects and the population, are equated to category 2.
- Which electrical receivers are equivalent to the 3rd reliability category?
This group includes all equipment and installations, the interruption of the supply of electricity to which would lead to large material losses, both for enterprises and civilians. Any facilities, the de-energization of which will affect the level of human safety or create a dangerous situation for the security of the country, are also equated to this group in terms of reliability.
- What number of uninterruptible power supplies is considered minimum for electrical installations belonging to the second reliability category?
The required minimum number of power supplies required for this category is 2 units, operating independently, but with the ability to replace each other.
Consumer power supply circuit with reliability category 2
- According to the rules of the PUE, what precautions should be applied to electrical equipment protected by lockable and enclosing structures?
The main purpose of such structures is to prevent exposure to equipment by persons who do not have a clearance group. Therefore, all covers and housings must be locked with a key or using special tools.
- What can be the highest voltage from which welding machines and other current sources for devices of this type are powered?
The maximum permissible voltage for welding equipment is 660 V. The most common in production are lines with 380 V.
- How many groups are power tools divided into in terms of protection against electric shock?
There are 4 main classes into which all electric tools are divided - third, second, first and zero.
Questions about electrical receivers, their classification and safety in operation can be found in tickets for certification of the 3rd group on electrical safety.