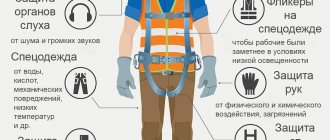
IP Definition
The abbreviation IP in this case means International Protection, in place of XX there is a two-digit digital index. This protection determines the accessibility of any electrical product to the following external damaging factors:
- solid bodies (human fingers, tool parts, wire, etc.);
- dust;
- water.
Note: It’s not for nothing that we talk about “availability” and not “protection”. The IP standard simply refers to the requirement for the manufacturer or importer to indicate on the product body what influences it is protected from, but nothing more.
Simply put, this is a classification based on the protection of shells and cases of different products. It does not apply to internal nodes.
An example of marking could be as follows: “Protection degree IP67”, “Protection class IP54”, and the like. Sometimes numbers may be followed by a capital letter of the Latin alphabet, serving as a complement.
Letter designations
Less commonly used are additional letter designations that express clarifying conditions.
An additional letter from the first group expresses the degree of human protection from the dangerous effects of the device. It is used in cases where dust protection is not specified (or marked with an X), or impact protection exceeds general protection (for example, touching parts is safe). The table shows the correspondence of the letter designation to permissible penetration into parts of the device.
LetterExplanationABCD
| Back of the hand |
| Finger |
| Tool |
| Wire |
The letter of the second group of additional symbols indicates the features of the device or test conditions.
LetterDecodingHMSW
| High voltage equipment |
| During water protection tests, the device worked |
| The device did not work during water protection tests |
| Weather protection |
What is IP protection degree
One of the most important parameters when choosing electrical equipment (electric motors, frequency converters, etc.) is its protection from environmental influences. This parameter is called the class or degree of IP protection (from the English Ingress Protection Rating). It involves protecting equipment from harmful external influences due to certain design features.
There are mainly two factors that pose a danger to electrical equipment: 1) penetration of solid objects; 2) water penetration. The choice of IP rating for a specific equipment depends on its installation conditions. For example, devices intended for installation in lockable electrical panels have minimal protection from solid objects, since the electrical cabinet housing protects them from dust and moisture. Therefore, controllers, frequency converters, contactors and similar equipment are produced with a low IP class. The opposite example is lamps designed to work on the bottom of a pool. They need maximum protection from water.
The IP degree value is applied to the housing of electrical equipment and is also indicated in the device passport. Most often, devices with high protection from dust and solid objects are also well protected from moisture.
IP for electrical devices
The abbreviation IP, accepted throughout the world, has several possible decoding options: International Protection Marking/international security code, Internal Protection/internal protection, Ingress Protection Rating/degree of protection against interference.
The marking indicates the level of protection of a technical device from dust, solid objects, and water.
The data that characterizes the class of the device is determined experimentally using specially developed verification methods.
The protection class of any electrical device is marked as follows: a combination of the letters IP and two numbers
To determine the IP level, the international standard EC60529 is used, the analogue of which is GOST 14254-96, as well as the complicated German version DIN 40050-9.
On the territory of Russia, any equipment installed indoors must comply with PEU - rules for electrical installations, technical conditions - TU, GOST R51330.20-99.
According to the accepted Russian and international classification, the maximum level of protection is marked with the IP68 code.
This designation indicates that the device is completely dust-proof, which can also remain in water for a long time, experiencing significant pressure.
A convenient table summarizes the meanings of the two letters that are used to indicate the degree of IP protection with a breakdown of all the given indicators.
The highest degree of protection provided by the DIN system is marked as IP69-K; Such marks are applied to products that can withstand high-pressure hot water washing.
You can find devices that have an undetermined degree of protection. In this case, the digital designation is replaced by the letter “X”, that is, the marking will look like “IPX0”. This designation may also be followed by one or two Latin letters.
Decoding IP protection classes
The degree of protection of the device is designated as IP-XX, where:
- IP - Ingress Protection Rating (input protection class)
- X - protection against ingress of solid objects. It has a level from 0 to 6, where 0 is completely open devices, 6 is equipment that prevents dust from getting inside.
- X - protection against moisture ingress into and onto live elements. This parameter has levels from 0 to 8, where 0 are open devices, 8 are hermetically sealed devices that can operate underwater.
Devices marked IP55
IP55 electrical and electrical appliances have satisfactory dust protection. Grains of sand and most of the fine dust remain in the housing. Devices with this marking can be used both indoors and outdoors with additional devices that limit the ingress of moisture. Even a small amount of foreign objects entering the cabinet will not damage the device or equipment.
Selecting the degree of protection for different conditions
The IP value must correspond to the characteristics of the equipment installation location. Too low a degree of protection can lead to an accident and makes the operation of the device dangerous for people. Excessive protection increases installation costs and increases the size of the electrical appliance. Here are some examples of typical conditions:
- sockets and switches in residential premises must have IP22 or IP33
- in a children's room, IP43 class is desirable
- in the bathroom and kitchen, in areas near water, sockets, switches and lamps with protection class IP44 are installed
- Electrical appliances with IP44 rating are also used in basements
- equipment installed on open balconies must have protection IP45 or higher
- devices with IP64 protection level are used outdoors
- Maximum IP68 protection is available for devices designed to operate underwater, for example, underground cable connectors and lamps that are mounted on the bottom of the pool
For industrial equipment, all low IP devices (typically IP20) are installed in control cabinets, which in turn must provide the required protection under the current operating conditions. An example of a device with IP00 is a printed circuit board operating without a housing.
Devices that operate independently, without a cabinet, are usually well protected from external influences. For example, most modern electric motors have a degree of protection IP55 or higher and can easily withstand long-term operation in conditions of heavy dust and water jets.
In general, devices with high IP are more reliable and structurally secure. However, when operating in harsh conditions for extended periods of time, it is necessary to regularly maintain the equipment to ensure long service life.
IP bathroom electrical equipment
Guided by the standards of GOST, PUE and the data in the tables, we can conclude that for the bathroom it is necessary to use lamps, sockets and switches marked IP44. This class corresponds to a socket with closing flaps. Plugs for electrical appliances in the bathroom should also have a similar class.
As for wall lights for the bathroom, their degree similarly should not be less than IP44, but it is better to use devices with IP55 protection. Since all fumes rise in the bathroom, the marking of ceiling lamps must correspond to IP65. The higher the “IP” of lamps and other electrical equipment for the bathroom, the safer and more reliable they are to use.
Despite the fact that the degree of IP protection is simply deciphered, planning the installation of electrical equipment is best left to professionals.
Source: sarstroyka.ru
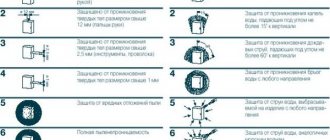
IP waterproof
[number 2] demonstrates the degree of protection against the negative effects of moisture (exposure to liquids, dampness). There are 10 degrees of protection of the case from moisture:
- “0” – no protection;
- “1” – the shell is protected from condensation moisture and raindrops falling strictly in a vertical position;
- “2” – the case is protected from drops, the angle of incidence is up to 15 degrees;
- “3” – there is protection against drops, the angle of incidence is up to 60 degrees;
- “4” – there is protection from liquid drops of any direction;
- “5” – protection from short-term exposure to a liquid flow (jet) of random direction;
- “6” – protection of the hull from prolonged exposure to a strong flow of liquid (water) of random direction, as well as from sea waves;
- “7” – there is protection against moisture penetration into the inside of the equipment body during short-term immersion in liquid (water) to a depth of 1 m. In this case, there may be penetration of a small volume of liquid into the middle, which does not have an adverse effect on the performance of the products;
- “8” – there is protection against liquid flowing into the products when immersed to a given depth for a given period of time). The body of the products in this version is completely waterproof;
- “9” – there is protection against hot water jets under pressure getting into the products.
The degree of protection of the outer casing (shell) from the influence of negative external conditions is established on the basis of performing a test of the working element. Below are tables with a detailed explanation of the degrees of protection, testing methods and sequences of their implementation.
For a convenient presentation, the classification of IP protection is shown in the figure.
Figure - Classification of IP protection
Decoding the degree of protection
If we translate the abbreviation IP from English - International Protection, then this means the level of protection against penetration or other influences (dust and moisture protection). In addition to letters, the marking is also accompanied by two numbers. The digital designation determines the level of protection of the housing (shell) of electrical equipment from the penetration of dust, fingers, moisture, and various solid objects. In addition, they indicate the level of protection against electric shock to a person when touching the housing (shell). This classification is regulated by GOST 14254-96.
First digit
The level of protection against mechanical impact is determined by the first digit:
- prevention, restriction from touching or penetration by any part of the body or object in the hands of a person;
- blocking access to dust and solid objects under the shell to protect electrical equipment.
Second digit
The level of protection against the harmful effects of moisture is determined by the second digit.
Additional characters
After a pair of numbers, sometimes a pair of letters may appear in the designation. The first of them indicates the degree of protection against contact with dangerous parts of equipment and electric shock when touched:
- A - from touching with a hand;
- B - from touching with fingers;
- C - from touching with various instruments;
- D - from contact with wire.
The second is auxiliary information about the level of protection. There are four of them in total. They indicate information about the tests performed and are required for electrical equipment:
- N - high-voltage devices;
- M - tested according to the level of protection against the negative influence of water (equipment in motion);
- S - tested according to the level of protection against the negative influence of water (equipment at rest);
- W - with additionally indicated means of protection.
What does the IP marking mean?
The decoding of the abbreviated letter “IP” in translation means the degree of protection against penetration. In addition to letters, the marking contains two numbers indicating the class of the shell, which serves to protect the equipment from external influences of dust, moisture and solid objects. Similarly, the class of the shell indicates the degree of protection of a person from electric shock when touching it. This classification is reflected by GOST 14254-96.
The protection class of the shell is determined by tests. They indicate how much the equipment casing will protect mechanical and current-carrying elements from the penetration of moisture and solid particles. Even during testing, the resistance of the shell to intense impacts under different conditions is revealed.
If we return to the already familiar pair of numbers, the decoding of the first indicates the degree of protection of the shell from exposure to solid objects, and the second from moisture. But marking with these numbers is not yet limited. They may be followed by one or two letters. In some cases, if the degree of protection is uncertain, the numbers are replaced by the letter “X”. Take, for example, an electrical appliance labeled “IPX0”. It indicates an uncertain degree of protection. But after the last digit there may be another letter, for example, “IPX1D”. It serves as a pointer to additional information.
Designation of the first digit
As already mentioned, the first number indicates the degree of protection of the shell from the penetration of solid objects. This also includes the possibility of penetration of a specific body part, such as a finger or hand. The first “0” indicates a complete lack of protection, which implies open access to dangerous equipment components. The degree of protection is indicated by numbers from 0 to 6.
To make the decoding clearer, let’s consider each indicator separately:
- “1” – indicates limited touch with the back of the hand or penetration of a solid object measuring 5 cm or larger;
- “2” – protection will not allow penetration of a finger or an object larger than 1.25 cm;
- “3” – will protect dangerous components from tools and other objects larger than 2.5 mm in the hand;
- “4” - indicates the impossibility of penetration of solid particles larger than 1 mm;
- “5” – indicates partial dust protection;
- “6” is the highest degree of dust resistance.
In addition, numbers from 4 to 6 indicate the impossibility of reaching dangerous equipment components with a thin wire in a person’s hand.
Designation of the second digit
The time has come to consider the second number of the marking, indicating the protection of equipment components from the negative effects of moisture. This value has a larger range from 0 to 8. As in the first case, 0 indicates a complete lack of protection. The further enumeration proceeds in ascending order, which shows a specific example:
- “1” – small drops of water falling vertically onto the equipment shell will not damage its components;
- “2” - similarly, falling drops of water will not penetrate the shell when it slopes up to 15 o;
- “3” – The housing is able to protect the working components of the equipment from rainwater, even if the drops fall at an angle of 60°;
- “4” – chaotically flying drops at any angle do not pose a danger to the equipment;
- “5” – a stream of water falling without pressure will not penetrate the shell. The surfaces of devices with this designation can be washed;
- “6” – the shell will withstand falling water under high pressure. Even sea water that gets inside will not damage the operation of the units;
- “7” – safe to dive under water for a short time;
- “8” – the shell will withstand a long stay of the equipment under water.
To better determine the degree of protection, there is a table with all the parameters indicated:
Let's take an example to see how the numbers of electrical equipment are deciphered:
- Let's take a power cabinet marked IP32. The housing will protect a person from accidental contact with electrical components and will not allow the penetration of solid objects larger than 2.5 mm. However, it is possible to penetrate inside with a 1 mm thick wire. The second number indicates the safety of water drops falling on the cabinet, even if it is installed at an angle of 15° relative to them;
- but, for example, the plastic box KMPn 2/9-2, intended for installing RCDs or automatic machines, has IP31 protection. The first digit indicates the same degree of protection as with the example of a power cabinet. The second number says that it will protect the RCDs located inside only from small, vertically falling splashes of water.
In general, everything is clear with the numbers; it remains to find out what the decoding of the additional letters means.
Additional and auxiliary designations
There may be an additional letter immediately following the digital designation. There are four of them in total. Each letter characterizes the degree of human protection from penetration of live parts of electrical equipment or dangerous mechanical components. If you take a closer look, the additional letter plays the same role as the first number, only it is intended for a detailed explanation.
There is a table where you can see the decoding of additional letters:
The additional letter may be followed by an auxiliary letter. There are only three of them. Previously, another fourth was used - W, but now according to GOST it is not used. For electrical equipment, these letters are required to indicate background information and test parameters performed. The decoding of the letters can be found in the table:
In the absence of additional or auxiliary designations, the letters in the marking are not replaced by anything, but are simply absent.
Transcript example
The common designation is IP54. It follows from the table that the housing is dust-proof and completely resistant to splashes from any angle and does not allow you to touch live parts with your hands or tools.
Most Common Levels of Protection
- IP20 - marking implies protection of the electrical equipment housing from foreign bodies 12.5 mm and above (see table). There is no protection from moisture, the shield is installed in a dry room, and there is no mechanical impact. Conclusion - a shield, installed in the hallway or living room of a residential building (apartment);
- IP30 - not protected from moisture, but has higher protection from mechanical impacts of objects from 2.5 mm;
- IP44 - means that electrical equipment is protected from mechanical impacts from objects of 1 mm and from splashes from any angle. Installed in a room with humidity in proximity to tools and machines.
- IP54 - marking means it differs from 44 in partial dust protection and complete protection from foreign objects. Installed outdoors and indoors without open water jets and dust formation.
- IP55 - the housing of such equipment is protected from mechanical interference and partially from dust. Withstands water jets. Recommended for installation outdoors without a canopy. Installed anywhere in the garden.
- IP65 - the housing is dust-proof and can be installed both outdoors and indoors.
IPX7 - degree of protection of the device from moisture
IPX7 is among the eight degrees, the second most protected from moisture. A device with this designation can only remain under water for a short time at a depth of about a meter without losing its functionality. Nowadays, many devices have this IP degree, including some telephone models.
IP20 value
The inscription IP20 appears on electrical equipment that can only be used in dry rooms. The first protection digit 2 indicates that the device body is capable of protecting internal components from objects whose size does not exceed 12 mm. This is a fairly low level of insulation that requires special conditions. For example, in residential apartments, rooms without dust and humid air.
The second digit IP20 - 0 indicates that the device is completely moisture resistant. The slightest ingress of moisture can lead to irreversible consequences. For example, sockets and other similar objects should not be installed in a bathroom or restroom. Where there is a possibility of water ingress or moisture evaporation.
Illumination standards
| Types of premises | Illumination according to standards (lux) | |
| Russian (SNiP 23-05-95) | International (IKO) | |
| General offices using computers | 200-300 | 500 |
| Large, open-plan offices | 400 | 750 |
| Drawing offices | 500 | 1000 |
| Conference rooms | 200 | 300 |
| Stairs, escalators | 50-100 | 150 |
| Corridors, halls | 50-75 | 100 |
| Archives | 75 | 200 |
| Shops, supermarkets, car dealerships, showrooms | — | 500 |
| Storerooms | 50 | 100 |
Lighting standards for various rooms
| Name of buildings and premises | Illumination of working surfaces, lux | Cylindrical illumination, lux | |
| With combined lighting | With one general lighting | ||
| Administrative buildings, design and research organizations | |||
| – Offices and other work rooms | 400*/200** | 300 | – |
| – Design, engineering and drawing bureaus | 600*/400** | 500 | – |
| – Reading rooms | 400/200** | 300 | 100 |
| – PC rooms, display rooms | 750/300** | 400 | – |
| – Conference rooms, meeting rooms | – | 200 | 75 |
| – Laboratories | 750*/300** | 300 | – |
| Financial institutions, lending and insurance organizations | |||
| – Operating rooms, cash registers | 400*/200** | 300 | – |
| – Collection | – | 300 | – |
| Schools, secondary and higher educational institutions | |||
| – Classrooms, auditoriums, study rooms, laboratories | – | 500 (vertical in the middle of the board) | |
| – | 300 (horizontal on tables and desks) | ||
| – Offices and rooms of teachers | – | 200 | |
| – Gyms | – | 200 | |
| – Recreation | – | 150 | |
| Children's preschool institutions | |||
| – Reception rooms, dressing rooms, group rooms, playing rooms, dining rooms | – | 200 | |
| – Bedrooms | – | 75 | |
| Sanatoriums, holiday homes | |||
| – Chambers and sleeping rooms | – | 150 | |
| Spectacular buildings | |||
| – Auditoriums for events of republican significance | – | 500*** | 150 |
| – Theater auditoriums, concert halls | – | 300*** | 100 |
| – Auditoriums of clubs, theater foyers | – | 200*** | 75 |
| – Exhibition halls | – | 200*** | 75 |
| – Lobbies of cinemas, clubs | – | 150 | 50 |
| The shops | |||
| Trading halls: | |||
| – grocery stores | – | 400 | 100 |
| – clothing, linen, footwear, fabric, fur, hats, perfume, jewelry stores | – | 700 | 100 |
| – tableware, furniture, sporting goods | 500 | 75 | |
| Fitting booths | – | 300 (vertical at 1.5 m from the floor) | |
| Hotels | |||
| – Service Bureau | – | 200 | |
| – Living rooms | – | 150 | |
| – Rooms | – | 100 | |
| Auxiliary buildings and premises | |||
| – Sanitary facilities: | |||
| washrooms, latrines, smoking rooms | – | 75 | |
| showers, dressing rooms | – | 50 | |
| – Lobbies and dressing rooms for outerwear: | |||
| in schools, universities, theaters, clubs, hotels and main entrances to large industrial and public buildings; | – | 150 | |
| in other industrial, auxiliary and public buildings | – | 75 | |
| – Stairs: | |||
| main staircases of public and industrial buildings; | – | 100 | – |
| staircases of residential buildings; | – | 10 | – |
| the rest of the stairs | – | 50 | – |
| – Corridors and passages: | |||
| main | – | 75 | – |
| floor-to-floor in residential buildings | – | 20 | – |
| other corridors | – | 50 | – |
| Notes: | |||
| * horizontal illumination at a level of 0.8 m from the floor with the combined action of general and local lighting; | |||
| ** the same, but only from general lighting; | |||
| *** when using incandescent lamps, the level is standardized | |||
Illumination created by natural and artificial light sources
| Light-stars | 0.00005lux |
| Sunlight during the day | 32000-100000lux |
| Moonlight | 1lux |
| Screen light (TV studios) | 1000lux |
IP protection class
Often, when they mean “degree of protection,” they say “IP protection class.” From a technical point of view, these are the same thing, that is, synonymous terms. In the regulatory literature, the wording “IP protection classes” is usually not used, but you can often come across questions: “IP54 protection class” or “IP65 protection class”, or “IP21 protection class, what is it?” In these cases, an appropriate degree of protection is meant. In this case, no other or separate standards are provided beyond those indicated above.
Let us next consider the commonly used degrees of protection of electrical products and equipment. Let's give examples of IP decoding and determine where and in what cases the bodies of these markings are used. To be specific, let’s take the case of electrical switchboard housings.
IP 20
IP 20 – there is protection from large, large objects with a diameter above 12.5 mm (indicated by “2”), there is no protection from water, since the corresponding position is “0”. Such IP 20 equipment is suitable for installation in dry buildings, where the appearance of water (splashes) on the housing is not expected, and there is no exposure to objects with a diameter of up to 12.5 mm. In the case of a switchboard housing with IP 20, it should be installed in rooms, apartment corridors, but should not be used, for example, in a bathroom.
IP 30
IP 30 - the presented marking indicates that the product is also not protected from moisture. The difference from the previous one is greater protection from mechanical influences. The IP 30 electrical panel is protected from objects with a diameter of 2.5 mm or more.
IP 44
IP 44 – degree of protection indicates that the shell or outer casing of the product is protected from foreign objects with a diameter of 1 mm or more. These include various wires, pins, nuts, hand tools, screwdrivers, etc. In addition, there is protection from humidity and random splashes of water. Equipment with such a housing can be used in structures with high humidity, damp, and also outdoors, but water should not be allowed to enter by stream. The product with an IP 44 housing does not have dust protection. If the dust content of the room or premises is high, you should not use a shield with IP44.
IP 44 electrical panel enclosures are suitable for buildings with high humidity, as well as for installation outside residential premises, but under the roof. This will prevent open exposure to the water jet.
IP 54
IP 54 – the presented degree of protection differs from IP 44 in that there is more complete and reliable protection from foreign objects. A housing with this degree of protection should be selected for areas where dust may occur. Electrical equipment in an IP 54 enclosure will receive only a small amount of dust and will not have a negative impact on the functions of the product.
IP 55
IP 55 – the product body is fully protected from the mechanical negative influence of various objects and partly from the penetration of dust. IP 55 is used in damp rooms, outdoors, where short-term exposure to the shell (housing) of equipment may occur in the form of a jet of water. Typically, electrical panel housings intended for outdoor installation have an IP rating of 55. This panel can be installed almost anywhere on the house’s site. It does not require a canopy.
IP 65
IP 65 – has complete protection against dust, it is completely dust-proof. The IP 65 electrical panel can be installed or used in any environmental conditions, both indoors and outdoors.
IP68 marking
Digital electronics manufacturers proudly display the IP68 mark on their products. Not all devices can bear this abbreviation, since a moisture resistance index of 8 is the maximum. And this means that this product can continue to work even if it is completely immersed in water. Additionally, the technical specifications must indicate the number of meters that the device can withstand.
The dust protection index is also maximum in the IP68 marking. Unlike the previous degree (7) means complete obstruction of dust. Similar markings can be found on many devices: waterproof watches, mobile phones, video cameras, etc. Let's continue to decipher the markings IP65, IP66, IP55, IP67, IP44, IP40 and others.
How to read labels
Deciphering the index requires certain knowledge. Here, the first digit shows the level of access to dangerous parts inside the product for factors that can damage it mechanically. These are any solid objects, from hands to thin wire, as well as dust.
The second number indicates the moisture protection that this product has.
The numbers are in ascending order. The higher the number, the higher the level of protection. If the marking is IP00, it means there is no protection at all (for example, it is a bare wire). If a product is marked as IPxx, then the degree of protection is not defined. Then it should be considered zero.
The format index, for example, IP4x means that according to the “mechanics” the protection class is defined and corresponds to four, and the moisture protection class is undefined (considered zero).
The letter after the numbers means an addition, increased security according to some parameter, and the product must correspond to its main class. Also, a letter can replace the missing first digit (a rare situation). A number of letters refer to high-voltage equipment: it determines the reliability of products operating under high voltage when in contact with water.
Electrical safety in the bathroom: IP class
A high degree of security is especially important for devices that have to operate in difficult conditions. Such rooms in the house include the bathroom, the air of which contains a high percentage of water vapor.
The high humidity inherent in bathrooms requires particularly careful selection of electrical appliances. In such conditions, it is necessary to use devices with a high degree of moisture protection. Before equipping this room, a plan for the placement of electrical appliances should be developed in advance, taking into account their distance from sources of moisture.
The highest, almost 100 percent, degree of humidity is observed directly next to the shower or bath. In this area, it is required to use low-voltage luminaires with the highest protection levels IP67 or IP68.
The area above the font or shower stall is also considered quite dangerous: splashes and steam enter here in large quantities. Devices marked IP45 are suitable for installation. If the lamp is planned to be mounted in the center of the room at some distance from sources of moisture, it is enough to choose an option with class IP24 or higher.
For the driest part of the bathroom, a product marked IP22 is recommended. Some degree of protection must be provided due to the background moisture content of the room and the possibility of steam release.
Combinations of letters and numbers indicating the protection class are applied to all types of electrical appliances. As a rule, it can be found on the body
When selecting a waterproof outlet, it is better to give preference to one with a moisture protection class in the range of 4-6. If it is intended to be placed at a distance from a shower or font, marking 4 is sufficient. If located closer to possible splashes, the level of protection should be higher - 5 or 6.
To equip a bathhouse or sauna with lamps and/or other electrical appliances, you need to choose electrical accessories of class IP54 and higher.
Designation table
The easiest way to present information is in a tabular format. Let's start with the first number.
Table 1 - fool proof and dust protection
| Protection class | Objects of protection | Explanation |
| 0 | – | There is no protection. |
| 1 | From objects with a diameter of 50 mm and above. | Back of the hand; accidental touch. |
| 2 | From objects with a diameter of 12.5 mm and above. | Fingers, large bolts. |
| 3 | From objects with a diameter of 2.5 mm and above. | Tools - screwdrivers, pliers, thick cables. |
| 4 | From objects with a diameter of 1 mm and above. | Fasteners, wires and cables. |
| 5 | Dust. | Minor dust penetration is acceptable but does not affect the operation of the device. |
| 6 | Dust. | Absolute dust protection. |
Designs with safety levels 5 and 6 completely protect their contents from contact with the surface of the human body, even accidental.
Table 2 - protection from water
| Class | Water hazard level |
| 0 | There is no moisture protection. |
| 1 | Drops of water falling strictly vertically. |
| 2 | Water dripping vertically or with a deviation relative to the vertical of up to 15 degrees. |
| 3 | Falling large drops with a deflection angle of up to 60 degrees. The product is protected from light rain. |
| 4 | Large drops, splashes flying in any direction. |
| 5 | Water jets of any direction. The product will withstand heavy rain. |
| 6 | Sea or river waves (short-term splashing with water). |
| 7 | Short-term immersion to a depth of 1 m. Permanent operation in water is not guaranteed. |
| 8 | Dive to a depth of 1 m or slightly more for up to 30 minutes. Protected nodes perform their functions under water. |
| 9 | Long-term exposure to high-pressure hot water jets, the device can withstand high-temperature pressure washing. |
Table of decoding code values
1-digit protection against solid foreign bodies 2-digit protection against moisture
| no protection | no protection | ||
| 1 | From solid objects larger than 50 mm; parts of the body, arms, legs, etc. or other objects measuring at least 50 mm. | 1 | From vertically falling drops |
| 2 | From solid objects larger than 12 mm; fingers | 2 | From falling drops at an angle to the vertical no more than 15° |
| 3 | From solid objects larger than 2.5 mm; blacksmith tools, wire | 3 | From jet drops falling at an angle of 60° to the vertical |
| 4 | From objects larger than 1 mm; wire and other objects of at least 1 mm. | 4 | From drops and splashes from any angle. |
| 5 | Partial protection against dust and complete protection against all types of penetration. | 5 | From jets falling at any angle. |
| 6 | Complete protection against dust and accidental penetration. | 6 | From pressure injectors. |
| 7 | Protection against water damage without causing damage | ||
| 8 | Protection in water for an unlimited time. |
Let's look at examples
IP55 protection degree means that the housing or shell of the product - it can be anything, a power cabinet, starter, machine, RCD, switch, etc. - provides complete protection against accidental contact of internal components under current with a finger, screwdriver or thin probe . In this case, slight penetration of dust inside is allowed (the housing is not sealed), which should not cause interruptions in the operation of the device. It also has reliable protection against rain. This is a “street” class of product, but it will no longer withstand being doused with water, for example, from a bucket.
The degree of protection class IP44 is a “safe” design of products designed to work indoors, but in conditions of high humidity. This class must correspond to sockets, switches and other elements located, for example, in the bathroom. In fact, they can look like sockets with lockable covers and automatic “shutters” on the contacts. They should not be protected from dust, but a short circuit from accidental ingress of moisture is excluded. Touching them with wet fingers is also safe.
Note: none, even the highest safety classes, imply that the product cannot be disassembled. This is a civilian safety standard; it cannot and should not apply to specially designed products for military and similar needs.
What can a low protection class offer? Let's get acquainted with the degree of protection class IP20. A product of this class protects its contents only from penetration of fairly large objects, about a finger in diameter. From a constructive point of view, this could be, for example, an installation box. It may have small technical holes for tools - tester contact probes, screwdrivers, and so on. It can only be placed indoors or inside another electrical cabinet with a high degree of protection, since even from above such a product is not protected from moisture.
The most common protection classes and their scope
Despite the fact that theoretically there can be any combination of degrees of protection, certain classes are most common. A description of the possible area of their use will be given in this paragraph.
- IP 20 . The devices are intended for use in heated rooms with normal humidity levels. They provide a sufficient level of protection from electricity, but do not protect from moisture.
- IP 21/22 . The devices can also be used indoors, but without heating, as well as outdoors under canopies.
- IP 43/44 . The equipment can be used in damp areas.
- IP 54/55 . Can be installed outdoors in the open air, withstands rain, snow, and icing.
- IP 67/68 . The equipment can be immersed in water. This class of protection for luminaires is needed to organize pool lighting.