Among the various possibilities for making your home safe, grounding in a private home occupies a special place: the electrical network diagram of any modern home will not be approved if it does not provide for a connection to a grounding loop.
Grounding diagram for a private house Source tirez.ru
There are several options and schemes for grounding a private house, plus clear requirements of the PUE (electrical installation rules) - all this must be known and understood in order for the electricity in the house to be safe.
Reasons why electric shock occurs
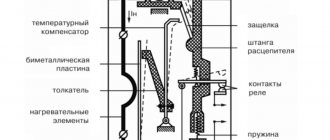
In most cases, the cause of electrical injury is a phase short circuit to the metal body of the device. This occurs due to the deterioration of the insulation on the wires due to aging or overheating. A person who touches the body becomes energized and receives an electric shock.
Appliances that work with water are especially dangerous: boilers, washing machines, dishwashers, etc. Moisture conducts electricity well.
If it comes into contact with a current-carrying element, for example, the spiral of a heating element when its tube is depressurized, then not only the housing, but also the communications along with the water flowing through them come under voltage.
general description
Among the terrestrial planets in the solar system, which includes Mercury, Venus and Mars, Earth is the largest. The planet is the third in distance from the Sun, it is the fifth in diameter, mass and density. The age of our planet is compared to the age of the entire solar system and is approximately 4.5 billion years. There is a hypothesis that the Earth was formed from gas and dust that remained from the formation of the sun. The oldest rocks that have been studied were formed approximately 100 - 200 million years ago. And conditions favorable for the emergence of life on the planet arose only 3.5 billion years ago. We, as a modern type of person, were formed only 40,000 years ago.
The earth is spherical in shape, flattened at the poles. The length of the Earth's equator is 40,076 km, the equatorial radius is 6,378 km, the polar radius is 6,357 km and the average radius is 6,371 km.
The Earth, and we along with it, revolves around the Sun in a circular orbit, the radius of which is 150 million km. The period during which the Earth rotates in an elliptical orbit occurs at a speed of 29.8 km/s and lasts 365 days. The approximate distance to the Sun is 149,543,000 kilometers.
The earth also rotates around its imaginary axis (from west to east). A full revolution is completed in approximately 23 hours 56 minutes. The rotation axis is tilted 66.5 degrees relative to the orbital plane, and as a result of this movement, the cycle of day and night occurs. And since the earth simultaneously rotates around the Sun, sometimes approaching and sometimes moving away from it, the seasons change.
General concept of grounding
Grounding (Pe from protection earth) is understood as the intentional connection of electrical installations or parts thereof to a conductor buried in the ground. For the system to perform its functions, it must have low resistance.
Purpose
The soil is capable of absorbing electrical charge like a capacitor with infinite capacity. This property is used to solve a number of problems.
Grounding ensures electrical contact between the electrical installation and the ground.
Areas of use
According to the method of use, grounding is divided into 2 types:
- Working. Acting as a neutral, it ensures the functioning of powerful electrical installations - transformers, generators, arresters, arc extinguishers, etc. This type also includes Pe-circuits of lightning rods and surge protection devices.
- Protective. Protects users from electric shock.
The second type comes into effect in emergency situations, when a phase is shorted to non-current-carrying metal parts of the electrical installation. Further we will talk only about this type of grounding.
Why do you need grounding in a private house: principle of operation
Grounding in a private home is considered an important part of the power supply system. It is installed for the following purposes:
- Protection of home inhabitants from electric shock (when touching a device with damaged electrical wiring insulation);
- Correct operation of modern electrical devices;
- Safe operation of gas equipment;
- Effective operation of lightning protection.
The principle of operation of the system is based on the elementary laws of physics, which say that electric current always moves in the direction of least resistance.
If the insulation of the device is damaged, the current flows out (short circuit) to the housing. This situation is fraught with malfunctions and breakdowns, not to mention the danger for a person to receive a sensitive discharge by accidentally touching the surface with his hand.
Principle of operation
A person touching a live body and the grounding system can be schematically represented as 2 parallel branches connected to a point with a high potential. From Ohm’s and Kirchhoff’s laws, the following relationship of currents and resistances flowing in them follows:
I1/I2=R2/R1.
In simple terms, electrical charge flows along the path of least resistance. The lower the circuit resistivity Pe, the weaker the current in the human body.
The maximum permissible resistance values for protective grounding are established by the PUE:
| Consumer | Resistance, Ohm |
| Home electrical network with a total power of simultaneously operating devices up to 100 kVA | 10 |
| The same over 100 kVA | 4 |
| Telecommunication systems | 2 |
| Server equipment | 1 |
Main types of grounding
The structure that provides contact with the ground can have different purposes. Depending on this, grounding is divided into 2 types.
Natural
Such systems use existing metal structures dug into the ground as a Pe-circuit.
Examples:
- parts of buildings and structures, reinforcement of their foundations;
- pipelines, except those transporting flammable and explosive substances;
- well casings;
- lead cable sheaths;
- rail tracks of non-electrified railways.
Natural grounding is preferable because allows you to reduce the cost of installing the system.
Artificial
In such a system, a Pe circuit is used, specially made to discharge the charge into the ground. This option is used in situations where there is no natural grounding or it has a high resistance to current flow.
Connecting grounding to electrical appliances
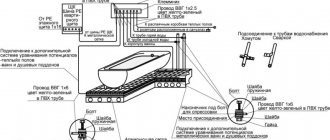
To ground household appliances (provided that there is an external grounding loop), you will need a cable with three wires marked in different colors (neutral - blue (N), phase - brown (or white, black, the color of the phase as a whole is not standardized) (L) and grounding (PE) – yellow-green). These wires are pulled from the electrical panel to three-pin sockets or directly to electrical appliances. In this case, the grounding wire is attached to the corresponding busbar in the panel.
In a private house, depending on the grounding system, the electrical network, as a rule, has its own external ground loop - a device consisting of a group of electrodes connected to each other and mounted around the building along its contour. If there is no such circuit, then it is necessary to invite specialists to install it.
Note!
Self-installation of an external ground loop requires knowledge of the principles of its design and manufacturing rules. In addition, there may be hidden objects underground (sewerage, electrical cables, gas pipelines), which can be accidentally damaged when installing the ground loop. Therefore, if you do not have the information, it is better to entrust this work to professionals!
As mentioned above, all modern electrical appliances of protection class I, in which a breakdown of current to the outer part of the housing is possible (for example, water heaters, electric stoves, ovens and washing machines) have Euro plugs with a grounding contact, which must be connected to a three-pin socket. If the wire needs to be connected directly to the device from the electrical panel, for example, to a voltage stabilizer or UPS, then for this purpose a special block with a grounding terminal is provided on their body.
Manufacturers of household appliances assume that users will connect their products, which have three-pin Euro plugs, to a three-wire network. However, today in our country, in many houses and summer cottages there are systems with two-wire networks. What to do in such cases?
In such cases, to create a reliable protective system, for example, in a country house, it is better to install your own grounding loop and lay a separate PE grounding wire in the premises and then connect it to sockets and the load.
If there is no grounding terminal in an apartment building, independent installation of the circuit is not allowed, since, as a rule, there will be a large number of communications in the ground next to the building.
Some users believe that they can do without grounding and simply install an RCD. However, although the protective device will help combat leakage currents, it will not be able to provide complete protection of electrical appliances throughout the house.
Note!
Installation of an RCD is necessary in any case, even if the house has a grounding system. All powerful electrical equipment must be connected via an RCD.
Types of ground loops
There are 2 layouts of rods in multi-electrode grounding electrodes. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
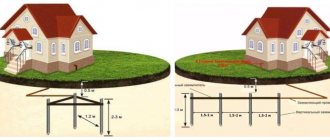
Triangle
In this embodiment, vertical electrodes are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. The minimum distance between them is 1.2 m, the optimal distance is equal to the length of the rods.
If you install the electrodes closer than 1.2 m, they will influence each other, increasing the resistance to spreading.
Advantages of a triangular scheme:
- Easy installation. Work on installing and connecting the rods is carried out in a spacious pit.
- Reliability. If one of the jumpers is destroyed, all 3 electrodes remain connected to the circuit.
- Compactness. Triangular ground electrodes, all other things being equal, occupy the smallest area.
Linear outline
In this embodiment, the electrodes are placed in a straight line. Such a contour lacks the advantages of a triangular one, but it can be increased.
Linear grounding switches are used to equip facilities where network expansion with an increase in power consumption is expected in the near future.
General characteristics of the Earth
The planet's surface consists of 80% water and only 21% land, which consists of 6 continents (Eurasia, Africa, Australia, North and South America, Antarctica), and a large number of islands.
The continents are separated by oceans and differ in geological structure. Modern outlines were obtained as a result of the movement of lithospheric plates. There are two types of continental structure: folded belt and platform.
The platform is the most stable section of the earth's crust; earthquakes do not occur here. Examples of platform regions are Siberian, African, Hindustan, North American, South American, Australian and Eastern European.
Fold belts include: the Pacific, Ural-Mongolian, Mediterranean, North Atlantic and Arctic belts.
The largest continent is Eurasia, which includes Europe and Asia, the smallest is Australia.
The highest point is Mount Everest, 8852 meters above sea level.
And you can’t ignore the Kola superdeep well, which is the result of human activity and is included in the Guinness Book of Records. It is located in the Pechenga district of the Murmansk region, near the city of Zapolyarny. The depth of this well is 12262 meters.
The planet has four main climatic zones - equatorial, tropical, temperate and polar. There are also four transitional ones - subequatorial, subtropical, subarctic and subantarctic.
At the equator the highest temperatures reach + 70, and the coldest is in Antarctica, where the thermometer drops to -85. The average t on the planet is approximately 12 degrees.
View of planet Earth
Hydrosphere
Water was not discovered on any of the planets. Our planet is the only one with a hydrosphere, and its most important part is the World Ocean. The world ocean is conventionally divided into the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic oceans. The lowest point, 11,022 meters below sea level, is located in the Mariana Trench, Pacific Ocean. The world's oceans are the most active participant in the water cycle in nature.
What is the atmosphere for?
Our planet is protected from many unpleasant things by the atmosphere, a kind of shield. Thanks to it, meteorites that burn in the upper layer do not reach the planet; it is precisely it that does not allow dangerous ultraviolet radiation to pass through.
Many have seen the mesmerizing photographs of the Earth taken by astronauts. shrouded in clouds and emitting blue light - the most beautiful planet. This glow is possible thanks to oxygen, which is contained in the air and makes up 21% of the total volume. 80% is nitrogen content, approximately 1% is argon, and the remaining gases: carbon dioxide, neon, methane, helium and others complement the composition of the air.
The lowest layer is the troposphere; the presence of this layer makes the stay of all life on Earth comfortable, because it contains up to 80% of atmospheric air. The troposphere extends up to 8 km in the north and up to 18 km in the south from the surface of the planet. This is the main “forge” of weather and climate on Earth - cyclones, anticyclones, clouds and winds are all formed in this layer.
Then comes the stratosphere - the ozone layer located here blocks solar radiation. Ozone occurs when oxygen reacts photochemically with ultraviolet radiation. Located at an altitude of 11 to 50 km. Airplanes fly in the lower layers of the stratosphere.
The mesosphere extends its boundaries up to 90 km. Meteors begin to burn up in this layer. Scientists have nicknamed it the “ignorosphere” because it is the least studied layer in the atmosphere.
The thermosphere originates at an altitude of 90 km and extends up to 800 km. Unmanned satellites fly here.
Exosphere - begins above 500-1000 km and gradually passes into the vacuum of space.
In addition to the atmosphere, we are also protected by the Earth’s magnetosphere - the outer and longest shell. This sphere does not allow solar and cosmic radiation, which is harmful to all living things, to penetrate to the earth. Scientists are still studying the origin of the magnetic field.
By the way, thanks to the magnetosphere, people admire the northern lights. Charged particles of the solar wind are successfully reflected, but some lucky ones manage to penetrate the magnetic field. When they collide with molecules of oxygen (red, yellow, green) and nitrogen (shades of purple and blue), they form a beautiful glow.
The best places for observation are the north of Russia, Norway, Finland, Sweden, Iceland, Canada, as well as Alaska and Greenland. The best period is from October to February. The main thing is that there are no city lights nearby, and the sky is free of clouds. We will get acquainted with the structure of the Earth in more detail in the following articles.
Grounding schemes
Several Pe-schemes are used in distribution networks. They are designated by an alphabetic code, the first letter of which corresponds to the method of grounding the current source, i.e. transformer or generator, the second - consumer. Next, a dash indicates the method of connecting them.
Letter meanings:
- T – earth (terra);
- N – neutral;
- C – combined;
- S – separate.
TN-C system
In this option, only the transformer at the substation (T) is grounded. On the consumer side there is a neutral (N), and the protective conductor is combined with it (C). There is nothing to connect the grounding contact to; only grounding is possible.
The only advantage of the TN-C system is its low cost, which is explained by the use of 2- and 4-core cables.
Disadvantage: low level of security.
To protect consumers, an RCD (residual current switch) is used.
The TN-C scheme is valid only in old housing stock from the times of the USSR; connecting new objects in this way is now prohibited.
Performing calculations
At the design stage of the ground electrode, it is necessary to select its parameters so that the resistance of the device is within acceptable limits. To do this, a series of calculations are performed.
Soil resistance
The resistance to charge spreading for a single rod is calculated by the formula:
Ro = (Peq/2π*L) *{ln(2L/d) + 0.5 ln((4T + L)/(4T – L)}
If the electrode is placed in heterogeneous soil (2-layer), the resistance is calculated using the formula:
Peq = (Ψ*P1*P2*L)/( P1(L – H + tg) + P2(H – tg)), where
- Ψ – coefficient taking into account seasonality;
- P1 and P2 – specific resistivity of the first and second layers of soil, Ohm/m;
- H – thickness of the top layer, m;
- T – depth of immersion of rods;
- Tg – depth of the vertical pin (distance from the top of the ground electrode to the surface of the earth).
Dimensions and distances for ground electrodes
The minimum length of the rod is 2.5 m. If this condition is met, the base of the electrode with a 100% guarantee will be below the freezing mark of the soil, where acceptable resistance to charge spreading is maintained all year round.
The method for calculating the number of rods depends on what the ground electrode consists of.
If only from vertical electrodes, use the formula:
No = Ro *Ψ/Rн, where
Rн – resistance to spreading recommended by standards.
If the structure has horizontal elements, the number of rods is equal to:
N = Ro/( Rв*ηв), where
ηв – grounding conductor utilization coefficient, taking into account the mutual influence of the electrodes on each other.
In a linear design it is higher, so the calculation result is rounded up.
Structure of the Earth
Based on various studies, scientists have divided the Earth into three parts - core, mantle and crust.
The core is the heaviest part of our planet, its radius is about 3500 km, and its temperature is 4000 degrees and above. It is supposedly divided into an outer liquid part, consisting of sulfur and iron, and a solid inner part, containing an alloy of iron and nickel.
The mantle is not yet available for full research, so all data was obtained using geophysical and geochemical methods. It is in a solid state, from 30 to 3000 km from the surface and consists of ultrabasic rocks, refractory elements.
On top of the mantle lies the earth's crust, consisting mostly of rocks and minerals. It is on it that the oceanic and continental crust is located. Its thickness ranges from 5 to 10 km under water and up to 80 km on land.
Scientists have hypothesized that the oceanic crust was initially formed, and as a result of various processes that occurred inside the planet, folds were formed - sections of mountains. Over time, the thickness of the crust increased, forming the continental crust.
Norms and requirements
According to the PUE, the following can be used as electrodes:
- strip with a cross section of 48 sq. mm;
- rod - from 10 sq. mm;
- corner with a thickness of 4 mm;
- a pipe with a diameter of 2.5 cm and a wall thickness of 3.5 mm.
These dimensions are adopted in order to ensure the durability of the rods within 5-10 years.
Pin driving depth
According to the PUE (Chapter 1.7.), the minimum immersion depth of the rod is 0.7 m. The strip connecting the vertical grounding conductors is placed on the edge.
Grounding and lightning protection
The PUE prescribes connecting the protective grounding circuits of electrical installations and lightning protection of the second and third categories, i.e. all objects except explosive ones. Communication is carried out by at least 2 conductors (PUE, clause 1.7.55).
If the circuits remain disconnected, a breakdown between the lightning rod and the home electrical network may occur during a lightning strike. This will lead to failure of the electronics, fire or destruction of some elements, incl. plastic water pipes.
Compliance with safety regulations
Before carrying out any work on the grounding device, you must do one of two things:
- cut off power to the house;
- disconnect the ground wire from the main bus.
Grounded parts of electrical installations may become live at any time, incl. and during manipulations with the contour. If it is not turned off, the user will receive an electric shock.
Before performing work on the electrical panel, the house must also be de-energized. After turning off the machine, make sure there is no voltage using the phase indicator (indicator screwdriver).
Difference between grounding and neutralizing
The term “zeroing” means connecting the non-current-carrying part of the installation to the working zero. If it is energized, a short circuit will occur and the electromagnetic release will trip in the machine. The network section will instantly be de-energized.
The disadvantage of this method of protection is that if the zero above the connection point of the protective conductor is damaged (broken), all neutralized elements will be energized. The further this point is from the consumer, i.e. the closer it is to the substation, the lower the probability of an accident and, accordingly, the safer the system.
Formally, TN-CS and TN-S are zeroing.
But in the second case, the point of connection of the protective conductor to the neutral is located at the substation, which practically eliminates a zero break above it. Full grounding of consumers is implemented only in TT and IT systems (with isolated neutral).
What is an RCD?
If you are not satisfied with these methods of ensuring electrical safety, and it is not possible to install grounding, then there is another powerful tool that can reliably protect you from the traumatic effects of electric current. This is a residual current device, better known by the abbreviation RCD. It compares the phase current with the zero current. If the current in the phase wire is at least slightly greater than the current in the neutral wire, then there is a leak and part of the current returns to the substation through the ground. In this case, the RCD will instantly disconnect the line and if the cause of the leak is a person who has come under voltage and through whom the current flows into the ground, then nothing bad will happen to him. The RCD will have time to turn off the current before it has time to harm a person. Although electrical accidents in the home are very rare, you should not skimp on such devices. After all, human life is too precious to neglect such a danger.