You need to think carefully and responsibly about which RCD to install in a private home. The device must have the necessary operating power and, in all technical parameters, correspond to the electrical system available in the room. How to correctly select a protection element that meets the requirements?
We'll tell you how to find a device that will function correctly for a long time. The selected model will protect your home from fire situations, protect equipment from burnout, and protect users from burns and electric shocks. A list of the best offers on the market will help you make your choice.
Errors when choosing an RCD
If you need to select a protection device, you should avoid making mistakes.
The main ones are the following: incorrect choice of leakage value, no ideal insulation of wires, devices, all of them do not have an infinite insulation resistance value. As a result, leakage currents are formed. The rated current of the setting is chosen to be 3 times the total leakage value; this must be taken into account in order to ensure reliable operation of the device. To protect people, the device response values of 10 and 30 mA are selected.
It is also considered an error to accept a rated current that does not correspond to the calculated one. Failure to comply with the conditions when choosing a device can lead to fires, material losses and even death.
How to choose the right ouzo
Installing residual current devices is an effective means of protecting people from electric shock. Also, the RCD at the entrance to the apartment helps prevent fires that occur due to deterioration or damage to the insulation of electrical wiring.
Let's consider how to choose an RCD so that its operation is correct and effective.
Single-phase or three-phase
Single-phase devices are used to protect single consumers supplied by two wires - phase and neutral. To do this, they have two pairs of contacts. But they can be used not only to protect one or a group of outlets. A single-phase RCD can also be used at the entrance to an apartment or building, if an appropriate network is used for power supply.
If the power supply to a country house or cottage comes in three phases, then a three-phase device must be used at the input.
It has four contact groups, the fourth is used for switching the neutral wire. It is also used to protect three-phase consumers, for example, electric motors.
But at the same time, elements of the group distribution network of the house can be protected by single-phase protection devices.
Rated current
This parameter characterizes the ability of the contact system to withstand the load for a long time without harm to itself. The higher this value, the larger the load that can be connected. Options:
But we must not forget that the rated current of the RCD is associated with the same characteristic of the circuit breaker protecting the same line. The circuit breaker is selected for the maximum load that the cable extending from it can withstand. In the case when it is necessary to limit it, the choice of machine is determined based on the maximum permissible current for it.
In any case, the choice of RCD rating is made for a current greater than that of the circuit breaker protecting the line. This is done for the reasons that if it increases slightly, the machine will not work immediately, but after a delay. In tens or hundreds of minutes, the RCD contacts will fail.
Important
It turns out that the circuit breaker imposes a limitation not only on the outgoing cable, but also on the RCD in terms of the permissible load power.
In the data sheets of some household electrical appliances, manufacturers clearly indicate the cross-section of cables and protective devices that must be used for their safe connection. For washing machines, it is usually recommended to install a 16 A circuit breaker. This means that the RCD for the washing machine must be selected for a current of 25 A.
Differential current
This is the same current to which our protective device reacts. It, unlike a circuit breaker, does not monitor changes in rated load currents, but sums them up in all wires passing through it. Including zero. If this amount is zero, no trigger occurs.
But as soon as a leakage current appears due to deterioration of insulation or human contact with bare conductors, the balance is upset. Some of the current escapes in a way not controlled by the device. When its value exceeds a certain threshold, an instant shutdown occurs.
The leakage current, upon the occurrence of which a shutdown is guaranteed to occur and the RCD will perform its protective function, is called differential.
The table below contains information about their varieties:
The first two protect people and animals from electric shock in the event of deterioration of the insulation of wires, cables or damage inside household appliances. The remaining ones belong to the category of fire-fighting RCDs. Let's take a closer look at how to choose the right RCD for differential current in both cases.
Protection against electric shock
To protect people, the Electrical Installation Rules (RUE) require the use of an RCD in an apartment with a current not exceeding 30 mA. Why is that? If such a current flows through the body, the muscles contract convulsively. A person will not be able to release the wire on his own.
It would seem that 10 mA is the best choice of RCD for protecting outlets in an apartment. But there is a limitation: with an increase in the length of the electrical wiring and the power of the consumers connected to it, the total leakage current also increases. It is always there, because the insulation resistance of cables has a finite value and cannot be infinitely large.
This natural leakage current can be calculated. For each meter of phase wire of the electrical wiring, there is approximately a leakage current equal to 0.01 mA. And for every load ampere, another 0.4 mA is added.
Advice
Now it’s clear how to calculate leakage: find out the calculated parameters of the load and measure the length of the electrical wiring to it. And then multiply by the corresponding numbers and add.
The result obtained should not exceed half the differential current of the RCD.
But, in our Khrushchev buildings, when choosing this option, you should take into account the wear of the wire insulation. Here the calculation proposed above does not work. Therefore, selection is only possible experimentally, because even a 30 mA device can disconnect electrical wiring that is not damaged.
There is an easier way out. It is advisable to use devices with a differential current of 10 mA to protect single electrical receivers with a rated current of no more than 16 A.
For example, they can protect one or two single sockets for connecting a small load.
But it is no longer suitable for a washing machine: manufacturers are aware of this feature and do not produce 10 mA devices with a rated current exceeding 16 A.
You can install an RCD for lighting, where the currents are negligible, but the PUE does not require protection of the lighting wiring with such devices.
Fire protection
To ensure protection against electrical wiring fires, PUE recommends the use of an input RCD with a difcurrent current not exceeding 300 mA. It is placed in a panel at the entrance to a house, bathhouse or apartment, and is connected after the general circuit breaker.
Here again, precise calculations will be required to determine the differential current of the selected devices. But we can limit ourselves to the fact that the RCD for the entire apartment, not entangled through electrical wiring, is enough to set the device to 100 mA.
Larger values will be required only for multi-storey cottages, but in this case it is better to additionally install 100 mA devices in each floor panel.
This is how the protection works selectively: why turn off the entire house at once if the damage occurred in one area and can be successfully localized.
What absolutely needs to be protected
First of all, devices located or operating in hazardous conditions are protected from leakage. These are sockets in wet rooms and outdoors. It is necessary to install an RCD on the boiler or on other types of water heaters, washing machines. It is mandatory to use an RCD for bathroom sockets.
Which residual current device to choose
Considering that the majority of electricity consumers require alternating current, it is worth choosing the AC type. For several objects, a group device must be used for protection.
To determine how to choose an RCD, the following must be considered:
- parameters for calculating leakage current for selecting RCDs;
- rated current values.
Residual current device for home
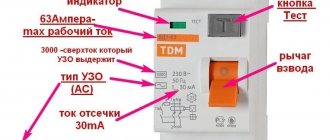
Protection in a private home is specific. The order of installation of devices: at the input - a disconnect device - 100 mA or more, set to type S, rated value 63 A.
Separate load groups are protected by individual devices of type A (AC) at 30 mA, rated load ratings are 16/25/32 A. To understand how to calculate an RCD for a home, the parameters of the devices that need to be installed are specified - several single, group.
The second parameter is the shutdown current
The shutdown current is selected from the series in Table 3. Electrical receivers and wiring, due to imperfect insulation or internal structure, contain their own, natural
leak. Before installing a protective shutdown, it is advisable to have it measured by a competent energy supply organization. The leakage current can be calculated based on the natural leakage of 0.4 mA per 1 A of consumption for the load and 10 μA (0.01 mA) per 1 meter of wiring. According to the rules (PUE), the nominal value should not be less than three times the natural value.
| Shutdown current value, mA | Consumer (according to PUE) |
| 6 | PUE is not regulated, but is used for low-power consumers or for wet rooms (kitchens, bathrooms, boiler rooms) |
| 10 | Single device consuming no more than 16A |
| 30 | Sockets, portable consumers, metal buildings |
| 100 | Groups or stationary consumers - electric stoves, heaters |
| 300 — 500 | Fire protection. |
TABLE 3. Nominal range of RCDs and recommended electricity consumer.
Let's continue with example 1. Let's take the current consumption equal to the value of the machine (in practice, the value is indicated in the device passport) - 2A, the wiring will be 20 m long. Based on these data:
Iest=2x0.4 + 20*0.01 = 0.8 + 0.2 = 1 mA. We select differential protection with a minimum value of 6 mA.
Selecting a device based on network parameters
It is necessary to select a device according to the parameters of the electrical network, taking into account the main characteristics of the device.
These operating parameters include:
- rated leakage current;
- load current.
Moreover, the shutdown setting is selected to be 3 times greater than the total network leakage. To coordinate the circuit breaker with the protection device, the following condition must be met: if the AV is set to 32 amperes, then the RCD must be set to a higher value. In this way, the device will also be protected. An input circuit breaker is installed before the supplied protection device.
Purpose
The most important thing to understand is that a circuit breaker protects the electrical network from overcurrents, and an RCD provides human protection. If, as a result of an insulation breakdown, potential appears on the body of an electrical appliance, touching it is likely to result in an electric shock. To prevent this from happening, immediately when a current leak occurs, the protective shutdown device will react and turn off the damaged section of the circuit.
It is important to know! RCDs do not protect against overloads and short circuits, so circuit breakers must be connected in series with them in the circuit.
Protection in apartments and houses
When choosing a protection device, you need to understand why you need an RCD in an apartment or house. A correctly selected device will protect a person from electric shock and protect the apartment from fire.
The devices are installed in electrical panels, observing the following connection sequence: at the entrance to the house they install a general circuit breaker, an electricity meter, an input device, individual circuit breakers and protection devices. In a private house, a fire protection or fire protection RCD is installed at 100 or 300 mA, depending on the size of the general leaks.
How many devices to install in a private home depends on the number of consumer groups.
Where is RCD used?
In order to answer where it is necessary to use an RCD, let us turn to the PUE (7th edition), namely paragraphs 7.1.71-7.1.85. Let’s make a “squeeze” from these requirements:
- An RCD is necessary to disconnect damaged sections of the circuit and to prevent electric shock to a person or fire of the wiring;
- RCDs are used on group lines that supply plug sockets and sockets for portable electrical receivers;
- In residential buildings, it is recommended to install RCDs on apartment panels; their installation on floor panels is allowed. For a private house - in the distribution panel or ASU;
- It is recommended to use an RCD with an overcurrent shutdown function (differential circuit breaker) for lines supplying plug sockets. If there are many such lines, in order to save money, you can use a group of circuit breakers after the RCD. (clause 7.1.79);
- For lines supplying plug sockets, it is necessary to use an RCD with a differential. operation current no more than 30 mA. (clause 7.1.79). For fire protection, a 300 mA RCD is used. Such an RCD is installed after the meter, before distribution to outgoing lines;
- The time setting (maximum permissible parameter value) for the input RCD should be 3 times greater than the RCD setting on the outgoing lines. This will ensure selectivity of protection. That is, if there is a fault on the outgoing line, the incoming RCD will not have time to trip, and only the damaged section will be disconnected. (clause 7.1.73);
- The RCD should not trip when the voltage in the network disappears.
Where to put it?
We install them in distribution panels of apartments and panels of private houses on the lines that supply sockets. For three-phase receivers (for example, three-phase machines) we use a four-pole (3-phase) RCD, for single-phase receivers we use a two-pole (single-phase) RCD. It is impossible to use a 3-phase RCD for 3 outgoing lines. An asymmetrical load will cause false tripping of the RCD (for example, after a 3-phase RCD, the phases went to different buildings).
Number of RCDs in the apartment
The number of protection devices is selected according to the number of points that need to be protected. In addition, it is necessary to provide a device for the group, installed at the entrance to the apartment behind the meter.
To reduce the number of products, it is possible to divide consumers into groups. For example: lighting group; a group of electrical household stationary appliances (refrigerator, hob); groups of especially dangerous rooms (bathroom, kitchen). Moreover, it is possible to use one RCD for a group of circuit breakers that protect certain consumers from overloads. An introductory RCD must be installed after the meter.
Technical features of RCD selection
The technical side of the selection is as follows:
- It is necessary to select a device with the ability to open all phases and the neutral wire. This will protect against possible complications.
- Do not allow electrical contact between the working “zero” connected through the device and the protective “zero”.
- It is advisable to select a protection device taking into account a 30% margin for the rated load current.
- Some devices do not allow the use of aluminum wires.
Before starting work on installing devices, it is necessary to conduct a thorough inspection of the existing wiring and replace areas that do not meet the technical requirements for leaks.
The importance of purchasing a quality RCD
An irresponsible approach to choosing a residual current device, that is, purchasing a device that does not suit the characteristics of a house or apartment, can cause certain problems:
- false alarms, since small electrical leaks are a natural situation for wiring that was installed a relatively long time ago;
- untimely receipt of information about a dangerous incident if an overly powerful RCD is selected, which can lead to electric shock;
- the inability of the RCD to function with existing wiring made of aluminum conductors, because almost all devices operate only on copper wires.
In order not to make a mistake when choosing an RCD, it does not hurt to carefully familiarize yourself with the device’s parameters before purchasing.
Table: main parameters of RCD
RCD parameter Letter designation Description Additional information Rated voltage Un Voltage level, which is selected by the manufacturer of the device and is necessary for its operation. Usually the rated voltage is 220 V, sometimes 380 V
Uniform voltage in the electrical network and the rated voltage of the residual current switch, as the RCD is also called, is an important condition for the trouble-free operation of the device. Rated current In The highest current value at which the RCD operates over a long period. The rated current value can be as follows: 10, 13, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 63, 80, 100 or 125 A. In relation to the differential circuit breaker, this value also acts as the rated current of the circuit breaker in the RCD configuration
For differential circuit breakers, the rated current value is selected from the range: 6, 8, 10, 13, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 63, 80, 100, 125 A. Rated differential breaking current Idn Leakage current. This characteristic of a residual current device is considered the main one, since it indicates what amount of differential current will cause the device to react. RCDs are produced with the following parameters of the rated residual current: 6, 10, 30, 100, 300 and 500 mA. Rated conditional short circuit current Inc An indicator by which one can judge the reliability, strength and quality of an RCD. The rated conditional short-circuit current shows how well the electrical connections of the mechanism are made. The value of the rated short circuit current is standardized and can be equal to 3000, 4500, 6000 or 10000 A. Rated differential short circuit current IDc Another indicator of the quality and reliability of the device. Similar to rated conditional short-circuit current. The only difference is that the overcurrent passes through one conductor of the residual current device, and testing of the operation of the device is carried out after turning on the test current in turn across different poles of the RCD. Non-breaking overcurrent limit value - This is a characteristic that reflects the ability of the residual current circuit breaker to ignore symmetrical short circuit currents and situations where the network is overloaded. This indicator has nothing to do with the current value at which the residual current device is required to block the power supply. The minimum non-switching current must correspond to the rated load current increased by 6 times. Rated making and breaking (switching) capacity Im A parameter that depends on the degree of technical preparation of the RCD, that is, on the power of the spring drive, the raw materials used and the quality of the power contacts. The switching capacity can be equal to 500 A or a value 10 times higher than the rated current level. For high-quality devices it is 1000 or 1500 A. Rated making and breaking capacity for differential current IDm A characteristic that is also determined by the technical design of the residual current switch. This parameter is comparable to the previous one (Im), but differs from it in that the flow of differential current is taken into account. It is often assessed during a short circuit to the housing of the electrical receiver in the TN-CS system.
Selection of RCD by power
The shutdown device works in conjunction with the AV. There are rules on how to select an RCD and an automatic circuit breaker based on power for reliable joint operation.
To select an RCD based on power, it is necessary to calculate the RCD based on power and consumer lines. Then the current is determined by power, which serves to select the device with the nearest larger standard value.
An example of choosing an RCD without calculation
Sometimes the choice of device has to be made without calculation, and in this case questions arise about how to choose the right device. For this purpose, the rated and differential currents are determined. First, the RCD is selected by current. A separate network component is protected by a device up to 16 A; if it is necessary to protect all electrical equipment in an apartment, then you need to choose from 32 A. The values are specified by calculation.
Leak trigger settings are selected from 10, 30 mA. For example, if there is a 20A machine at the entrance, then you will need a type A device with a rating of 25A.
Design and basic principle of operation of an RCD
The body of the protective device contains a magnetic circuit made of a radial core, input current (I1) and output current (I2). In the equilibrium state of the network, these currents are equal, and the electrical system operates in a safe mode. When a leakage current appears on the body of electrical equipment (Id), the balance of the currents is disturbed and a current flows through the measured winding circuit of the core, having a value proportional to the current Id.
Operating principle
The relay is triggered because it is powered from this measurement winding, the electrical circuit opens, and no current flows to the equipment body. As a result, the device implements user protection against current Id. The current difference is considered differential, and a protective device combined with an RCD is considered a differential circuit breaker.
Additional RCD function