How many volts comes out of a phone charger?
Modern devices for charging phones
, smartphones and tablets, there are two main parameters that you should pay attention to.
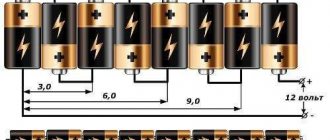
The first is the output voltage, usually 5.0-5.3V ( volts
), the second is the output current, the values of which can vary within a fairly wide range: from 0.5A (ampere) and up to 3A.
Interesting materials:
How to set up the carbon dioxide supply on a semi-automatic machine? How to set up a connected microphone to a laptop? How to set up a signature in Mozilla? How to set up a signature in Mozilla Thunderbird? How to set up a signature in Mozilla mail? How to set up a signature in Thunderbird? How to set up a signature in Thunderbird? How to set up subscriptions on YouTube? How to set the keyboard backlight on a laptop? How to adjust the backlight on a laptop?
How much power do the USB ports on my PC provide?
To test this, we don't need to install any new software and we don't need to use any special hardware to do it. You just need to enter the following into the Windows search bar: devmgmt.msc . This will bring up the Device Manager.
Once you're there, select the Universal Bus Controllers, double-click and then select the USB Root Hub, but do it by right-clicking on properties. The following window should appear:
In the same USB Root Hub properties window, select Parts and from that tab's drop-down menu, select Energy Data, which will give you information about how much power the root hub is sending to various peripherals. This goes from D0 to D3, with D0 providing the most energy and D3 the least.
Comparisons of adapters and USB cables
It's time to demonstrate the practical benefits of these devices with a bunch of numbers.
Apple iPad 2 A adapter
With one single tester, the Apple adapter delivers 1.57 amperes, while the voltage drops to 4.97 V:
Apple adapter: current 1.57 A.
In general, it releases current reluctantly, and can only reveal its full potential with devices of the same name.
Noname adapter 2.1 A
The Chinese four-porter, on the contrary, is democratic and works conscientiously with anything. And now I will demonstrate that the charging current (i.e. speed) depends no less, and sometimes even more, on the choice of USB cable.
Original high-quality Samsung cable from Galaxy Note 4, about a meter long:
Cable from Samsung Galaxy Note 4.
We connect the phone - the charge current is 1.74 amperes:
Samsung cable: current 1.74 A.
A non-original, but good-quality Hema cable two meters long - the current drops to 1.22 A:
Hema cable: 2 m, current 1.22 A.
Completely non-native, very Chinese, but damn convenient Muvit Retractable Micro USB, length when stretched is about 70 cm:
Muvit Retractable Cable.
With it, the current drops even more, to 1.11 A:
Muvit Retractable cable: current 1.11 A.
Equally Chinese, also very convenient, but a completely nameless super compact with a length of 20 cm. They cost a couple of euros per bunch on eBay, and the trick is that its ends are magnetized to each other:
Cable 20 cm.
And now a surprise - the charge current with it is exactly the same as with the original one, 1.74 A:
20 cm cable: current 1.74 A.
But the main surprise is ahead. The perfect and final Chinese noname, which arrived with some kind of cheap gadget - a Micro USB cable about half a meter long, seemingly completely ordinary. But appearances, as it turned out, are deceiving: the charge current with it drops to 220 mA, that is, almost eight times
!
Noname cable: current 0.22 A.
The phone will charge eight times longer through this wonderful product. So it goes.
Now the most exotic part. The latest in fashion, an adapter from Samsung Galaxy Note 4 (max. output current 2.1 A), decorated with the inscription Adaptive Fast Charging
, looks like a million other USB adapters, and at idle it produces the expected 5 volts.
Samsung adapter, voltage 5 V.
However, if you connect exactly the device for which it is intended, then it SUDDENLY begins to produce a voltage of 9 volts!
Samsung adapter, voltage 9 V.
The current is almost the same, so the battery should charge almost twice as fast. We can only hope that the adaptive charging circuit is not mistaken in choosing the voltage and will produce the normal five volts for other devices.
Apparently, Samsung also put a rather large capacitor in it, since, disconnected from the network, it still continues to power the tester for half a minute:
Residual charge in the adapter.
Electronics gadgets
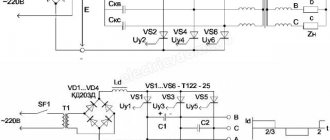
Charge controllers
OZ8555/o2micro
(Used in tablets based on RK3066 – Hyundai Hold X700, Window N101/YUANDAO N101; PIPO M1, PIPO Max-M8 pro, PIPO Smart-S2; CUBE U9GT3)
Contains a DC/DC converter for charging the battery and powering the gadget. Requires an external power supply voltage of 5.5÷5.9 V (at least 5.4 V at the input to the gadget) and is used in gadgets with a separate (non-USB) charging connector.
I didn’t find a data-sheet on the OZ8555, but it seems that its threshold for protection against insufficient supply voltage UVLO (Under Voltage Lock Out) is 5.1÷5.3 V instead of the usual 3.9÷4.5 V for 5-volt gadgets. This property would completely explain Incorrect operation from a “foreign” charger delivering less than 5.4 V.
BQ24190/TI
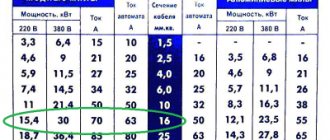
Uin-min - 3.9 V ; Iin – 1.5/3 A
BQ24190 determines the type of charging port in accordance with the BG v 1.2 , with D– and D+ shorted, it defines the port as DCP and allows itself to consume a current of more than 0.5 A .
Use USBDeview
It may happen that even though the USB root hub is specified for a certain power level, but due to some problems in the controllers, the power that is transferred to the USB ports is much lower.
To test this in software, we'll use USBDeview, a completely free and easy-to-use application that has a version for x86 processors with 64-bit support and another for 32-bit processors. Check your computer first by downloading the correct version. It will be delivered to you as a ZIP archive, which you must extract into a folder.
You can use any unzipping application to unzip the entire folder as soon as you double-click the USBDeview.exe file. This will launch the application, so it is completely portable and you can use it on any PC.
Move the bottom pane of the window to the right until you find the Power column where you can get the peripheral device's consumption, from there you can check how many milliamps each peripheral connected to the USB ports is consuming.
USB peripherals consume power in blocks of 100 mA for USB 2.0 peripherals and 150 mA for USB 3.0 peripherals. This way we can check if the peripheral devices are receiving enough power.
Why do USB ports use multiple power modes?
Please note that the USB port supports different states depending on the situation of the peripheral devices. These modes mark how much power the peripheral device requires at a given moment. For example, a peripheral that goes into sleep mode will not need as much as an active one. Also, the peripheral does not turn off in the same way as it is unplugged from the USB port.
This is why USB hubs use state machines that distribute power to different USB ports depending on the state, in general, and if we are not using a USB-C port with fast charging, the specifications are as follows:
- A USB peripheral with a battery can use up to 500mA for charging, which means it can consume 2.5W of power to charge such peripherals.
- If the peripheral device is in sleep mode, the USB port operates at 2.5 mA.
- The voltage between different ports does not add up, but the current does add up.
What voltage is supplied through the USB connector?
5 (five) volts.
Moreover, the current is limited to 500mA. Nothing can be changed. This voltage is standard and is used in computers and for other purposes. It is rigidly stabilized by circuits (internal) in the power supply. Outputs from several connectors at once can be parallelized. This is done to increase the maximum permissible current, for example, for connecting external 2.5" hard drives. The standard is five volts, and the current supplied by the bus is 500 mA.
In modern laptop models, the output current is up to 1000 mA per port and higher. Those USB ports that output 5 W are called quot;Powered USBquot;.
Very interesting information about important parameters here.
A voltage of 5 volts is output to any of the USB connectors on any computer.
Only the USB connectors themselves have differences in connection (shape) and, accordingly, the voltage is located on different pins of the connectors. Here is the pinout of some types:
The voltage supplied through the USB connector is about five volts. Using this connector you can charge your mobile phone, but you cannot use it for all kinds of testing of various equipment.
In theory, when a device connected via USB to a computer is recognized, exactly the voltage needed will be supplied to charge it. The connected device itself informs the relevant services and computer nodes of the necessary parameters for power supply, charging, data transfer, and so on.
The idea is 5 volts, but there are 3 and 4 volts or more
The voltage at the USB connector is 5 volts. Often 5 volts from the so-called duty channel. I understand that you need a pinout for the connector. Here she is:
Based on the diagram, you need pins 1 and 4. You will remove power from them. By the way, I still wouldn’t recommend heating the mug. The USB output is not that powerful. You can also burn it.
And further. Since you're asking, I suspect you've never encountered this. My advice to you, don’t go there out of sin...