Protection against static electricity at home
In order not to suffer from the effects of static electricity charges at home, it is recommended to take the following measures:
- Wipe furniture and floors daily to reduce dust formation.
- Ventilate the rooms daily to prevent the air from drying out.
- Use of special antistatic brushes when cleaning premises.
- The material from which the furniture is made must be antistatic.
- Finishing walls made of wood or linoleum with antistatic properties.
- It is not recommended to pet animals if the air is dry.
- When combing your hair, do not use plastic combs.
When filling a car with gasoline, it is recommended to use antistatic strips under the bottom.
Protective measures against static electricity
To equalize potentials and prevent sparks, all pipelines located in parallel, at a distance of less than 100 mm, are connected by jumpers every 20-25 meters. Piping and equipment systems must be grounded in at least two places. The presence of grounding is checked using a tester or megohmmeter once every 6 months and after repair work.
During loading, pumping and transportation of petroleum products, the resulting electrostatic discharges are removed by metallic connections between pumps, pipelines, tanks and other devices. In case of spillage of dielectric liquids into vessels made of glass and other insulating materials, it is necessary to use funnels made of electrically conductive materials. They are grounded and connected by copper cables to supply hoses. Each funnel should reach the bottom of the vessel. If this is not possible, then a grounded cable is passed through the funnel, reaching the bottom, along which the liquid will flow.
The loading pipe must reach the bottom when filling the container. The loading hole must have a large cross-section so that the jet cannot come into contact with the walls and surface of the liquid being poured. If these conditions cannot be met, it is necessary to reduce the loading speed as much as possible, bringing it to 0.5-0.7 m/s. The measures taken will ensure that unpleasant consequences are avoided.
How to remove static electricity
Static electricity in the apartment
Electricity from the ground
When did electricity appear?
How to get electricity from potatoes
Electricity in the house
Comparison of old and new standards
When modernizing oil and petroleum product storage facilities, as well as when using standard projects developed before 2016, you need to know how the new standards set out in the Guide differ from the previous ones.
The recommendation to protect tank farms with a capacity of more than 100 thousand cubic meters with free-standing lightning rods has remained unchanged. m (clause 78 of the Manual and clause 5.1.3 of the RD). Connections of lightning rods to down conductors, as well as down conductors to grounding conductors, must still be made by welding or clamps with a transition resistance of no more than 0.05 Ohm (clauses 84 of the Manual and 5.1.8 of the RD).
Unlike the RD, the Guidelines describe in detail the protection of tank farms with a capacity of less than 100 thousand cubic meters. m (clause 79). If the thickness of the tank roof is less than 4 mm, then you should also use free-standing lightning rods or lightning rods mounted on the tank itself. In the event that the roof thickness is more than 4 mm, and a single tank in volume is less than 200 cubic meters. m, regardless of the thickness of the roof, then lightning protection by connecting the tank body to grounding.
Clause 80 of the Guidelines describes lightning protection of breathing equipment of tanks from direct lightning, and clause 81 describes lightning protection of treatment facilities. There was none of this in RD.
Unlike the RD, the more modern Guidelines also describe protection from the secondary effects of lightning. Clause 82 requires, in fact, to connect metal elements to a single grounding circuit of the object, and also to ensure the resistance of connections in pipelines and other extended objects at a level of no more than 0.03 Ohm. Paragraph 92 describes measures to prevent electromagnetic induction between pipelines and other extended objects, which can cause strong heating and even sparking, and, as a result, a fire or explosion.
The RD and the Manual implement a different approach to the arrangement and maintenance of lightning rods and grounding for lightning protection. Clause 5.1.8 of the RD describes acceptable design options for lightning rods, and clause 5.1.9 describes the design of grounding conductors for lightning protection. The manual does not regulate in any way the design of lightning rods and grounding conductors; however, it recommends justifying their choice in the design documentation (clause 77).
An even more interesting situation arises when checking the lightning protection system. The RD requires that the entire system be inspected once a year, just before the storm season. The Guide does not regulate in any way the frequency of inspection of lightning rods, and inspection of down conductors and grounding conductors should be carried out once every 5 years. At the same time, down conductors and grounding conductors must be selectively checked for corrosion every year. For grounding conductors, a clear criterion is given when replacement needs to be made - corrosion damage to more than 25% of the cross-sectional area, but for down conductors, the Manual, unfortunately, does not give such a clear criterion.
How static electricity was discovered
About eight thousand years ago, our ancestors domesticated wild goats and sheep. They noticed that wool products had an unusual ability to accumulate charge. For the first time, the ancient Greek mathematician Thales tried to formulate the concept of static electricity. He used amber for his experiments. The stone attracts small, light particles when rubbed with a woolen cloth. Then they could not benefit from this phenomenon. Electron in Greek is amber. Much later, an elementary particle with a negative charge was named after him.
Two thousand years later, the court physician to the Queen of England, William Gilbert, describes what static electricity is. In his scientific work on physics, he emphasizes the related nature of electricity and the phenomenon of magnetism. The Briton's research became the beginning for a detailed study of the topic among colleagues in Europe. A clearer concept of static electricity was given by the experience of Otto von Guericke. A German assembled the first electrostatic mechanism. It was a ball of sulfur on an iron rod. As a result, the scientist learned that objects under the influence of electricity can not only attract, but also repel each other.
How to remove static from yourself painlessly?
The spark during discharge is not as painful as it is unpleasant. How to remove static electricity from your body or, more precisely, how to discharge yourself without receiving an unpleasant electric shock? To do this, you need to take any small steel product, such as a nail file, a teaspoon or tweezers, as a result of which the positive potential of your body will spread to them. Next, you should touch the edge of the tweezers to the radiator, car or other massive metal object.
Then the spark will jump not between your fingers and the tweezers, but between the tweezers and the object you touch with them. In this case, you will not experience any negative feelings. You just have to do this over and over again at certain intervals, otherwise sooner or later the charge will accumulate in you again, and you will still receive an electric shock.
How to remove static electricity from a person and surrounding objects
Since the harmfulness of static electricity for adults and children has been proven by time, scientists have long been looking for ways to protect them from this dangerous phenomenon. Of particular importance is the issue of protecting young children from static, who are more sensitive to its manifestations. For all categories of users, several different approaches have been developed to remove the charge of static electricity that accumulates over time on the surfaces of any object.
The easiest way to get rid of static accumulated on home equipment (on a personal computer or washing machine, for example) is to ground them by connecting the case to a special ground bus.
The simplest method of removing a charge from any wearable item is to periodically spray it with a spray bottle of water, which is a good grounding.
To prevent a dangerous charge from accumulating on the car body, a special strip of conductive rubber (strap) is attached to its rear bumper. In addition, during long trips in personal vehicles, it is necessary to study the issue of the inadmissibility of accumulation of charges due to changes in body position relative to the seat. As a result of the resulting friction on the covers, sometimes a sufficient amount of them accumulates, which often leads to a noticeable and unpleasant electrical discharge. Therefore, you should periodically moisten the seats by spraying them with a special compact spray bottle.
Causes
The conditions for the emergence of potential on objects is dry air. At air humidity of 80% this natural phenomenon does not occur.
The moisture in the air prevents charges from accumulating on objects. The causes of static electricity can be:
- When one object comes into contact with another. Potential arises after their separation. Friction, winding/unwinding of artificial materials, friction of car bodies with air, etc.;
- As a result of rapid temperature changes. Thus, static electricity occurs on objects when they are placed in a heated oven;
- Radiation and ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, strong electromagnetic and electric fields;
- Guidance - the appearance of an electric field caused by a charge. The potential arises when processing sheet or roll materials. The phenomenon occurs at the moment of separation of the material and the surface. This effect can occur when one layer is moved relative to another. This process has not yet been fully studied. It can be compared to disconnecting the plates of a capacitor. In this case, mechanical energy turns into electrical energy.
The ability of objects to accumulate charges has a negative effect on technology. If you do not take any measures, it may become damaged and fail.
Danger of the phenomenon
Electronics and all mechanisms that use electronic control units are especially at risk of failure. In fire and explosion hazardous industries, sparks occur as a result of the discharge.
They may cause a fire or explosion. Protection against static electricity can completely eliminate or significantly reduce the risk of an emergency. The main danger is the occurrence of an electrical discharge.
The accumulation of charge is facilitated by dry air and reinforced concrete walls of buildings and structures. The polarity of the charge can be either positive or negative.
When operating devices that have a rotating pulley with drive belts, the charge can reach 25,000 volts. In dry weather, 10,000 volts of electrostatic electricity can accumulate on the vehicle's body.
And a person who walks on a carpet in woolen socks can accumulate up to 6,000 volts. Even in domestic conditions, the voltage of static electricity can reach significant values.
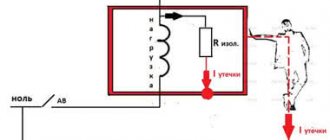
However, it is not capable of causing significant harm to a person due to insufficient power. The current flowing through a person is only a fraction of a milliamp.
In nature, this phenomenon can accumulate enormous values and manifests itself in lightning discharges. With the release of large powers that are capable of causing significant destruction.
Factors
Statics entails dangerous and harmful factors. They are especially clearly visible in enterprises where certain safety precautions must be observed when working with flammable materials. A spark can cause a fire or explosion, and when a person works with machines, it can cause injury due to muscle contraction after the discharge.
Factory fire due to spark
Negative factors also apply to devices. Equipment for precise measurements ceases to show correct data, and microcircuits in simple devices burn out after receiving a discharge. Therefore, you need to know how to remove static stress from materials and people.
Protective equipment at work
The accumulation of high static voltage is most often observed in the production of textiles, paper, foil, and PVC films. It can cause work-related injuries and even fire of materials. Therefore, to combat this phenomenon, methods such as:
- Removal of accumulated electrostatics into the environment.
- Reducing overvoltages in structures.
- Increasing the level of conductivity of solids.
- Neutralization of charges. For this purpose, special induction neutralizers or modern radioisotope agents are used.
For example, when working with semiconductor boards, high-speed charge removal is ensured. For this purpose, a floor covering with low electrical resistance is used, as well as forced shunting of the electrical board or a grounding tool.
Static electricity accumulates on workers' clothing and shoes, so they must know how to remove it. The most effective methods are:
- Grounding of industrial equipment.
- Human contact with a pipeline or battery equipped with grounding.
- Application of coatings and sprays with antistatic properties.
It is especially important to follow safety regulations when interacting with substances and materials that are flammable. After all, any spark can cause a fire. To prevent this from happening, you should prevent the generation of static electricity in the work area. This can be done with:
- Air ionization.
- Competent selection of interacting materials.
- Coronation.
- Elevations of the working surface.
Additional methods
Moist air has sufficient conductivity for the resulting charges to flow through it. Thus, in the appropriate environment they practically do not arise. Based on this, air humidification is the most common and easiest way to combat static electricity. There are also other security methods. We are talking about air ionization. It is also a common method of dealing with electrical charges. The fact is that ions help neutralize them. They are produced by a special device. A household ionizer has many advantages. First of all, it helps to improve the aeroionic composition of the indoor air environment. This eliminates electrical charges that occur on clothing, synthetic flooring and carpets. As for production, they use powerful ionizers. There are various designs. However, electric ionizers are the most common.
Pros and cons of static manifestation
Dangerous manifestations of electrostatics primarily include the constant friction of poor-quality clothing on the human body and the accumulation of electrical charges on the skin. In the technical field, this effect is especially acute when working as specialist installers in soldering microcircuits. In this case, it threatens the failure of expensive chips or even entire devices assembled on their basis.
When assembling valuable and rare microchips, safety requirements provide for special measures to protect against these unpleasant manifestations.
In technologies associated with the soldering of some microcircuits, electrostatic protection involves wearing a grounded bracelet on the hand, in the presence of which the danger is eliminated by the flow of charges to the ground. Such preventive measures mainly concern outdated K-MOS structures, which are increasingly being replaced by modern microchips that have built-in protection against static electricity.
Danger to humans
Manifestations of static electricity as such that are dangerous to humans include:
- thunderstorm discharges accompanied by lightning - they are caused by prolonged friction of air flows; in terms of possible consequences, including fire danger, they far exceed all other manifestations;
- the impact of charges on the biological surface (skin) and the appearance of severe irritation on it;
- dangerous and unpleasant discharges of electricity through the human body when touching metal parts of ungrounded equipment.
The latter phenomenon has nothing to do with critical electric shocks caused by emergency situations when dangerous voltage enters the body of a household appliance.
All these questions relate only to the external side of the manifestations of static electricity, which can be eliminated with the help of technical means of protection. A closer study of this process reveals that the impact of statics on somatics and the human body can lead to more serious consequences:
- systematic sleep disorders;
- changes in the tone of the cardiovascular system;
- severe fatigue;
- the occurrence of problems with the nervous system;
- slight deviations in the functioning of muscle tissue.
Although these disorders are not very noticeable at first, over time changes accumulate in the body that can lead to serious abnormalities. The consequence of poor sleep is mental problems, which in turn leads to other diseases. The harm from this effect in this case is beyond doubt.
Doctors recommend paying close attention not only to the material of clothing you constantly wear, but also to the choice of household bedding, on which a dangerous charge accumulates.
The benefits of static electricity
Many scientists and inventors at one time tried to find ways to control static charge for the benefit of humans. They developed bulky and very expensive units, the returns from which, as a rule, remained very low. The only breakthrough in this area is the discovery by scientists of the so-called “corona discharge”.
The unique capabilities of this phenomenon are used not only in production, but also in ordinary everyday conditions. Due to the development of modern techniques for controlling electrostatic phenomena, they are widely used in the following technological processes:
- painting frame bases, as well as surfaces of metal structures and other prefabricated products;
- purification of gases from impurities in the mining industry;
- use in many areas related to materials processing (modern nanotechnology).
Coronary discharge is also widely used in medicine, where it is used to limit the impact of electrostatic discharges on diseased human organs. In addition, based on this effect, many devices have been developed that can ionize the air not only in industrial premises and factory floors, but also in a typical city apartment. One of these useful inventions is an electrostatic filter designed to remove aerosol and mechanical particles from the surrounding air. Thanks to its use, it is possible to get rid of soot, soot and smoke, as well as small dust particles that accumulate in excess in any modern home.
RESPONSIBILITY
RESEARCH RESEARCH What's wrong? RESULTS RESULTS. RESULTS, CONTENTS RESULTS RESULTS. RESULTS е RESEARCH ASSURANCE »ÐµÑ. RESULTS. RESULTS, RESULTS. RESULTS полÑзÑ. RESULTS. RESULTS ½ÑаÑнÑÑ ÑаÑÑиÑÑ Ñ Ð¾ÑÑиÑаÑелÑнÑм заÑÑÐ ´Ð¾Ð¼.
RESULTS ¹ÑºÐ¾Ð¹ коÑÐ¾Ð»ÐµÐ²Ñ Ð£Ð¸Ð»ÑÑм ÐилбеÑÑ Ð¾Ð¿Ð ¸ÑÑваеÑ, ÑÑо Ñакое ÑÑаÑиÑеÑкое ÑлекÑÑиÑеÑÑво. Ð ÑвоÑм наÑном ÑÑÑде по Ñизике он п¿¾Ð´ÑеÑк RESULTS ²Ð»ÐµÐ½Ð¸ Ñ Ð¼Ð°Ð³Ð½ÐµÑизма. RESULTS ´Ñобного изÑÑÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ ÑÐµÐ¼Ñ RESEARCH. RESULTS ¸ÑеÑÑве даД опÑS ÐÑÑо Ñон ÐеÑике. RESULTS °Ð½Ð¸Ð·Ð¼. ROYAL RESEARCH. RESULTS RESULTS CONTENT ваÑÑÑÑ, но и оÑÑалкиваÑÑÑÑ Ð´ÑÑг Ð¾Ñ Ð´ÑÑга.
Danger of static electricity
Under the influence of static electricity, there is a disruption in the operation of mechanisms and technical devices. If work is carried out in explosive industries, sparking is observed.
Based on the conducted research, it has been established that such phenomena can lead to fire and even cause an explosion. Only competent protection will help eliminate the manifestation of these negative phenomena. The main danger arising from charges is the occurrence of electric discharge.
The accumulation is facilitated by the creation of dry air, as well as reinforced concrete structures of buildings. Moreover, the polarity is noted, both negative and positive.
If dryness is created in the external environment, then a charge accumulation of 10 thousand volts is possible. When a person walks on a carpet in synthetic socks, he accumulates a total of up to 6 thousand V. But causing harm in this case will be insignificant, since the power indicator here is not so high.
A natural phenomenon is an electrical discharge in the form of lightning. In this case, large amounts of power are released and, as a result, significant damage occurs.
Protection rules
Protection against the effects of accumulated charges, depending on the type of production, is established in accordance with the regulations.
If the industry is chemical:
- Devices for removing the charge are specially installed at pipeline tanks intended for unloading.
- To protect personnel when performing technological operations, induction and submersible neutralizers, special nozzles for flow diversion and relaxation tanks are used.
- It is imperative to ensure that liquids do not splash around.
How discharges are removed from vehicles and personnel:
- The mechanisms are made from materials that conduct electric current.
- It is planned to make the base of the flooring from conductive materials in rooms where tanks move.
- Personnel must be provided with special shoes.
- It is not allowed to work in containers where explosive mixtures are stored and to wear clothes made of synthetic fabrics.
Methods of protection against static in production
Providing protection from static electricity charges in production is carried out, we are developing a set of measures.
List of events:
- The properties of materials are enhanced, which ensures dissipation of charges.
- Reducing the speed when processing metal products, which significantly reduces the level of formation of a dangerous factor.
- Grounding must be carried out in accordance with the regulations.
- The resistance of machines and mechanisms to discharges increases.
- No electrical current should enter the work area.
The main method is to discharge the charge into the ground. This optimally helps to reduce the level of harmful factors, and the implementation is carried out along the contour.
Ways to combat electrostatics at home
To know for sure about the presence of a charge, you can use a special device - a static electricity meter. This device will help to obtain information about it on electrical appliances, various objects or on human clothing.
To protect yourself from the consequences of this phenomenon in everyday life, you need to know how to remove static electricity and in what cases it accumulates:
- The easiest way is to take measures to prevent unpleasant situations. For example, when combing your hair, it is preferable to use a wooden comb.
- Static static is also removed from hair using special products. A small amount of this product should first be applied to the palm of your hand and then distributed evenly throughout the hair. In this situation, special napkins are also used. They wipe the hair, after which the effect of static electricity stops.
- You should give preference to clothes made from natural materials - cashmere, cotton, linen and others. Unlike synthetic ones, natural materials absorb moisture well, so there is no accumulation of electrical charge on them. When wearing clothes made from natural fabrics, a person does not have to do anything to remove static electricity.
- It is worth paying attention to the rules for operating electrical devices. Usually their cases are grounded, and this is a reliable way to get rid of electrostatics.
- Dust on TV and computer screens can also accumulate electrostatics. To fix this, you should wipe the screens with a special cloth or use an antistatic spray more often.
- We get rid of static on clothes by adding conditioner to the washing water. Things treated in this way will be pleasant on the body and at the same time safe.
- When wearing clothes made of synthetic fabric, it is recommended to use a special antistatic compound to remove the problem.
- Electricity is removed from the car using a special strip touching the ground. The accumulated charge flows down it. If it is not possible to use antistatic tape, you can ground yourself using a metal object.
Static electricity can be removed by simply humidifying the air. This increases air conductivity and prevents the accumulation of charges. Sometimes antistatic liquids are used for this purpose.
It must be remembered that dry air in an apartment contributes to a more active formation of charges not only on various objects, but also on dust particles. If you regularly clean your house, this significantly reduces the rate of electrification. Thorough ventilation also helps.
Electrical appliances are potential sources of static electricity. To reduce the risk of charge accumulation, they should not be placed all in one place in the room. You can avoid problems by using grounding.
Static electricity in everyday life does not pose a great danger. Simple methods are used to combat it. This phenomenon manifests itself much more dangerously in production. Here it can even cause fire of flammable materials.
Ensuring the safety of your home and apartment
Free electric charge is accumulated by: rubber shoes, synthetic clothing, linoleum and plastic, carpets, reinforced concrete walls. To protect residential premises, you first need to ensure that the air humidity is at least 60%.
- Use grounding and grounding of electrical wiring in residential premises.
- Get rid of dust and prevent it from accumulating on carpets.
- Follow electrical safety rules.
- Treat synthetic clothing with antistatic agent.
Protection against free electrical charges will help preserve health, avoid explosions and fires, and improve the operation of technological devices and electronic devices. These measures are very important both for the protection of each home and for the safety and improvement of conditions for workers at work.
What is static electricity?
All substances are made up of atoms. An atom has a nucleus around which there are equal numbers of electrons and protons. They are able to move from one atom to another. When moving, negative and positive ions are formed. Their imbalance leads to static. The static charge of protons and electrons in an atom is the same, but has different polarity.
Static appears in everyday life. Static discharge can occur at low currents but high voltages. In this case there is no danger to people, but the discharge is dangerous for electrical appliances. During the discharge, microprocessors, transistors and other circuit elements are damaged.
Multilayer varistors
Rice. 3. MLV design
MLV (Multilayer Varistors) components consist of alternating layers of metal electrodes and ceramic or zinc oxide (Figure 3).
Zinc oxide ceramics serve as an insulator under normal conditions. However, when the voltage increases (as in the case of ESD), the zinc oxide leads move from high to low resistance values and thereby shunt the protected line to ground (Figure 1b).
MLV is the most robust of the ESD suppression technologies and can be used to protect line voltages ranging from 3.5 to 120 VDC or 2.5 to 107 VAC. They can also be used to provide protection against EFT (Electrical Fast Transients). In addition, their own capacitance (65...4500 pF) can provide filtering from high-frequency interference.
The new MLV family of MHS Series products are available in capacitance values of 3, 12 and 22 pF and can be used in high data rate circuits (up to approximately 125 Mbit).
RESPONSIBILITY RESULTS
RESULTS ROOM ек пÑоÑÑо не зР°Ð¼ÐµÑаеÑ; ROOM ºÐ½ÑÑÑ Ð¿Ñи иÑп¾Ð»Ñ·Ð¾Ð²Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ð¸ Ð¾Ð´ÐµÐ¶Ð´Ñ Ð¸Ð· ÑеÑÑÑи или ÑинÑеÑики. ROOM е и не оÑÑавлÑÑÑ ÑÑавм. RESULTS. OPTION, OPTION, OPTION ¾ ASSURANCE RESEARCH SOS. RESULTS LOSS OF RESEARCH. RESEARCH, ASSURANCE, RESEARCH, RESEARCH ¾±Ð»Ð°Ð´Ð°ÑÑ Ð·Ð½Ð°ÑиÑелÑнÑм поÑенÑиР°Ð»Ð¾Ð¼.
RESPONSIBILITY ¸ÑеÑкое поле Ñ Ð²ÑÑокими показаÑелÑми на пÑженноÑÑи Ð ÑÑой обÑÑановке наѾдиÑÑÑ Ð½Ðµ ÑолÑко некР¾Ð¼ÑоÑÑно, но и опаÑно Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð·Ð´Ð¾ÑовÑÑ. RESULTS with the help of ¾¶¶ ° ñ ° ñ ñ ð¿ð ° ñ ð½ ñññññ ðñәµñ bodies ð½ ° ¿¿¶µ police. RESULTS I'm sorry. RESULTS ÑÑ Ð¶Ð¸Ð´ÐºÐ¾ÑÑми, гоÑÑÑими газами и ÑмеÑми. RESULTS ¸.
Protection in enterprises
Static electricity and protection against it are issues that are seriously considered when creating safety regulations in enterprises.
Compliance with them should protect personnel from electric shock and prevent disruptions to the technological process. Measures taken in production consist of reducing the intensity of field generation and removing charge. To reduce the intensity use:
- Purification of flammable gases and liquids from contamination by solid and liquid impurities.
- Refusal, if possible, from crushing and spraying substances in the technological cycle.
- Compliance with the design speed of movement of materials in highways and devices.
To discharge the charge, grounding of all metal and electrically conductive parts of the equipment, metal casings and pipelines is required. Moving devices and rotating elements that do not have constant contact with the ground should be grounded. An increase in the conductivity of dielectric materials also promotes charge removal. This is achieved by using surfactants that increase the conductivity of dielectrics. Maintaining air humidity at least 60−70% is a successful method of combating static electricity.
Neutralizers are used if technological measures are not enough. These devices are used to neutralize surface electrical charges with ions of different signs. Induction and high-voltage neutralizers are used to ionize air with a high-voltage electric field.
Individual methods of protection are special shoes and clothing.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Gl0HhRgL3aw
Protection of pipelines and industrial equipment from static voltage
The discharge can cause the most severe consequences if it affects pipelines at industrial facilities. The consequences of such exposure will be especially severe at a chemical or oil refinery enterprise. This also applies to gas pipelines used in everyday life. To avoid them, measures are taken that are aimed at protecting industrial pipelines from static electricity.
Protection rules
The list of such measures in the Russian Federation is regulated by rules that were approved on January 31, 1971, and are in force to this day.
Pipeline protection is regulated by special rules
Protection methods
The regulatory document provides for the following measures aimed at preventing the occurrence of static electricity charges:
- Grounding. According to the rules, all structures in which a charge of static electricity can form must be grounded.
- A decrease in surface resistivity in a material where a charge can form. This indicator depends on the total area of the object. The smaller it is, the less resistance.
- Use of neutralizers. Static electricity can be neutralized using devices that are designed specifically for this purpose. Most often they generate an induction field or emit radioisotopes. This prevents a large number of electrons from accumulating the same charge and causing static voltage.
You might be interested in this All about signal duty cycle
Methods for getting rid of static on clothes
Most often, static electricity accumulates on synthetic clothing, which causes unpleasant sensations - small current charges, electrified hair, etc.
The following tools will help you cope with the problem:
- antistatic agents, special detergents, antistatic cloths for drying clothes. Modern advances in the chemical industry make it possible to quickly and permanently get rid of the problem, but they must be used regularly if synthetics predominate in your wardrobe;
- baking soda. During washing, add a quarter cup of detergent to the washing machine drum (more can be done, depending on the number of items). Baking soda creates a protective layer that prevents the accumulation of electrons and the appearance of static;
- vinegar. After finishing the main wash cycle, pause the washing machine and add 50 ml of apple cider vinegar. Run the washing machine in rinse and spin mode;
- safety pin. Pin a metal pin to the inside of the garment. A metal that is a good conductor of current will remove the charge of electrons, preventing the formation of static on products. Changes folded in pockets and metal hangers on which things are stored work in a similar way;
- natural fabric. When washing synthetic items, add a couple of cotton or linen items along with them. Natural material will take away the bulk of the static charge.
When washing, place a small ball of foil in the washing machine drum. This will neutralize electrons and prevent static electricity. However, never put foil in the laundry dryer.
How to get rid of static electricity on your body and hair
Representatives of the fair sex often face the problem of electrified hair, which is caused by its friction against different surfaces (comb, hat, accessories) or temperature changes. This phenomenon spoils the hairstyle, creates a “dandelion” effect and dishevelment, which negatively affects the appearance and causes irritation.
Simple tips will help:
- Use leave-in products (sprays, oils, lotions) that prevent electron buildup. Spray a small amount of product along the entire length of still damp curls or distribute with your palms, avoiding the area at the roots;
- wash your hair once every 2-3 days. With daily washing, an insufficient amount of sebum is synthesized, which leads to increased dryness of the hair and creates favorable conditions for the accumulation of electrons;
- use high-quality combs made of wood or silicone with natural bristles. To reduce the area of friction, choose accessories with sparse teeth;
- use modern hair gadgets with ionization function (hair dryers) and tourmaline coating (curling irons, curling irons);
- Choose your headgear wisely. Avoid wearing items made from synthetic materials; replace them with wool or cotton.
As an emergency, use an antistatic agent or thermal water - just spray your hair with the chosen product and it will look normal
To remove static from your body, wear shoes with leather soles, regularly moisturize your skin with cream or lotion, and choose high-quality clothing made from natural materials.
Static electricity is a common problem that every person faces at home or in contact with other people. Getting rid of this unpleasant phenomenon is quite simple with the help of antistatic agents, air humidification and keeping the apartment clean, as well as choosing clothes and interior items made from natural materials.
Who invented electricity
The invention of electricity in the 19th century became possible thanks to the discoveries of a whole galaxy of great scientists. In 1752, Ben Franklin conducted his kite, key and storm experiment. It just proved that lightning and tiny electrical sparks are the same thing.
Ben Franklin Experiment
Italian physicist Alessandro Volta discovered that certain chemical reactions could produce electricity, and in 1800 he created the voltaic cell, an early electrical battery that produced a constant current of electricity. He also accomplished the first transfer of current over a distance by linking positively and negatively charged terminals and creating a voltage between them. Therefore, many historians believe that 1800 is the year of the invention of electricity.
In 1831, electricity became possible to use in technology, when Michael Faraday created an electrodynamo, which practically solved the problem of generating a constant electric current. A fairly simple invention using a magnet moving inside a coil of copper wire to create a small current flowing through the wire. It helped the American Thomas Edison and the British scientist Joseph Swan, each separately, to invent the incandescent lamp around the same time in 1878. Light bulbs themselves were invented by other researchers, but the incandescent light bulb was the first practical device that provided light for hours on end.
In the 1800s and early 1900s, Serbian-American engineer, inventor, and electrical master Nikola Tesla was one of the pioneers of commercial electricity. He worked with Edison, made many revolutionary developments in the field of electromagnetism, and is well known for his work with alternating current motors and polyphase power distribution systems.
Note! Russian scientist and engineer A. N. Lodygin invented and patented in 1874 a lighting lamp, where the function of an incandescent filament was performed by a carbon rod placed in the vacuum environment of a vessel made of glass
These were the first light bulbs in Russia. Only 16 years later in the 1890s. he used a thread made of a refractory metal - tungsten.
It is impossible to say definitely in what year the light appeared. Despite the fact that many historians believe that the light bulb was invented by the American Edison, the first lamp with a platinum filament in a vacuum glass vessel was invented in 1840 by the English inventor De la Rue.
Additional Information. The Russians were grateful to the Russian scientist P. N. Yablochkov for the appearance of the electric arc lamp, and although its service life did not exceed 4 hours, the lighting device was widely used on the territory of the Winter Palace for almost 5 years.
Electric arc lamp by P.N. Yablochkov
Examples of ESD protection
The main component of many electronic boards is the microcontroller. As a rule, he has a set of peripheral blocks, which are the connecting link with the outside world. For example, data transmission buses such as USB, RS-232, Ethernet and their connectors for connecting external devices have become widely known. In addition, there are connectors for connecting audio, memory cards, as well as various buttons for performing certain functions of user programs. All of these peripheral devices must have adequate ESD protection.
Let's look at a few specific examples. Figure 21 shows ESD protection for USB 2.0.
Rice. 21. ESD protection for USB 2.0 bus
The USB cable connection diagram must include a device that reliably protects the microcontroller from static electricity and at the same time has low capacitance to ensure compatibility with the USB protocol eye diagram. The USBLC6 is ideal for these applications, providing a USB 2.0 compliant eye diagram and ±15 kV discharge rating per IEC61000-4-2. Recommendations for the layout and PCB design for the USBLC6 can be found in the reference design for the STM32L4 microcontroller.
Figure 22 shows the connection diagram for RS-232.
Rice. 22. ESD protection for RS-232 bus
In this example, as in the USB example, two functions need to be provided: protection against static electricity and satisfactory data transmission characteristics. For the RS-232 bus, a protective device ESDA14V2BP6 is used, which performs both functions. Recommendations for the layout and PCB design for the ESDA14V2BP6 can also be found in the reference design for the STM32L4 microcontroller.
Figure 23 shows the button connection diagram.
Rice. 23. ESD protection for buttons
The buttons are connected to the I/O ports of the microcontroller, so protecting the buttons from static electricity is actually protecting the microcontroller ports. Although the buttons are made of non-conductive material, they are sensitive to static electricity. ESDA5V3L performs the functions of protecting microcontroller ports from static electricity. In addition, this diode assembly combines two diodes in one package, thus allowing the overall size of the printed circuit board to be reduced, which is also important. Recommendations for routing and circuit design for buttons are given in the reference design for the STM32L4 microcontroller.
Rice. 24. ESD protection for STM32MP1-DK2 board
Figure 24 shows the STM 32 MP 1- DK 2 and specifically highlights all the components responsible for protection against static electricity. As can be seen from the figure, all peripheral devices of the microprocessor, including I/O ports and the SD card connector, are reliably protected from static electricity. All these protection measures result in a device that complies with the IEC61000-4-2 standard at the system level.
To easily and effectively select the components needed for ESD protection, STMicroelectronics has developed a special PROTECTION FINDER application, available for both Android and IOS (Figure 25). This application has a user-friendly graphical interface and allows you to select the right security device for a specific application in just four menu selection steps.
Rice. 25. ST PROTECTION FINDER application details
Protection against static electricity is a necessary element of any modern device. To unify protection requirements, a number of standards have been developed that describe tests for various application conditions. Compliance with these standards requires the use of specific devices and PCB design practices. All STMicroelectronics products are designed to meet the most stringent ESD requirements. In addition, a number of additional tools, such as available design examples and dedicated software applications, make it easy for users to create their own devices in accordance with all required standards. COMPEL specialists are always happy to help you make the right choice for a specific application.
•••
What physical phenomena are used to neutralize static charges in everyday life and industry?
As we can see from the examples above, to eliminate static, the principle of deliberately connecting opposite potentials is used. This issue can be resolved in only two ways:
- connecting problem areas to a prepared conductive circuit;
- or humidification of dry air up to 50%.
In the first case, it is necessary to create in advance a system that ensures potential equalization and constantly use it.
The second method is often implemented by spraying special compounds with conductive properties into the air. The industry produces them in cans, which are commonly called antistatic spray.
It covers the treated surface with a thin layer and evens out static charges on it.
Antistatic spray works well with clothing, car interior trim and other household materials.
In production, special devices are used that produce anions and cations, which are directed to the surface being treated. They, interacting with oppositely charged ions on it, eliminate static charges.
This is how they work with:
- labels;
- big bag type packaging (soft container made of polypropylene fabric);
- shrink films;
- feed units for sheet or roll materials;
- textiles;
- packaging products;
- material cutting equipment;
- screen printing.
Serial neutralizers can be produced in the form of:
- antistatic fan blowing rolled or sheet products;
- an antistatic gun used by the operator to clean irregularly shaped objects or hard-to-reach places;
- point modules for working in confined spaces.
On an industrial scale, static electricity neutralization devices are used to remove the effects of electrification of products and equipment.
They are produced by manufacturers of complex pneumatic equipment. The operating principle is based on the creation of an ionized air flow, which is formed by a corona discharge smoldering at the tip of the electrode needle.
It acts as a precision electrostatic filter with a smart function. For this purpose, the sign of the generated ions is determined automatically by the device’s sensors, which allows high-quality discharges of accumulated static.
A pneumatic type neutralizer works more efficiently than conventional models that do not use a jet of compressed air.
Directed streams of ionized and blown air effectively treat surfaces, and the tip of the needle with a corona discharge always remains clean.
Industrial Safety Measures
To protect enterprise workers from the adverse effects of static electricity, the following safety precautions are observed:
- Ensure constant contact between the worker and the grounding loop. The body of a person working in production must be in constant contact with a grounded circuit. This ensures that the discharge passes quickly through the tissue without causing any harm.
- In this regard, it is good to humidify the air, then sudden lightning of static electricity does not occur as often as when the content of evaporated liquid in the atmosphere is low. As its quantity increases, the risk of their occurrence decreases significantly.
- Ionization is carried out. If you saturate the air with positively and negatively charged particles, the possibility of “skew” in one direction, causing the appearance of a charge, is reduced.
Static voltage is a spontaneously generated electrical charge. Its appearance is especially dangerous in production (in pipelines, ventilation systems), as it can cause fire and detonation. The concept of static electricity and a list of methods of protection against it are given in special rules. Such means as grounding, reducing surface resistivity, and increasing humidity are used.
increase in electrical conductivity of dielectric materials
Another common way to protect against static electricity is to increase the electrical conductivity of dielectric materials , due to which they are able to remove free electrons.
This is achieved by applying conductive coatings or materials to dielectric objects, for example, a surface film of conductive material, thin foil, etc.
In particular, in everyday life, you can use special products, so-called antistatic agents, I think many women understand what we are talking about.
This antistatic spray usually consists of a conductive polymer dissolved in a mixture of deionized water and alcohol. After treating the surface, the solution evaporates, and the polymer remains in the form of a thin conductive film, which prevents charge from accumulating on the surface of the object.
A similar effect is also achieved by increasing air humidity to 60-70%, at which a thin film of moisture appears on the surface of the dielectrics, due to which sufficient surface electrical conductivity of the materials is ensured.
Influence
The most striking manifestation of static electricity can be found in industrial production. Due to his fault, unexpected ignitions of flammable materials occur due to sparks generated when the operator comes into contact with grounded equipment. Electrostatic energy can carry a discharge of 1.4 joules, which is enough to ignite flammable substances.
Interesting! To prevent such situations, GOST was developed, according to which the accumulated energy from a static charge cannot exceed 40% of the required energy for ignition of substances or materials.
The effect of static electricity affects the hair
Humans are carriers of particles that accumulate on clothing. In this case, the main condition for the accumulation of charge is the presence of shoes with soles that do not allow electricity to leave the body.
A person feels static on himself in the form of prolonged tension or as a momentary discharge. In the first case, there is a slight tension over a long period of time, and in the second there is a short-term release, felt as a tingling sensation. Rarely does the discharge power exceed 7 joules, so electricity does not pose a direct danger, but there is an indirect effect. It manifests itself in the form of muscle contraction, which can cause work-related injuries.
Attention! After muscle contraction, body parts can involuntarily become caught in working and moving mechanisms. Constant discharges begin to affect a person
It becomes more difficult for him to work, irritability and fatigue increase. The rhythm of sleep and the functioning of the nervous system as a whole worsens
Constant discharges begin to affect a person. It becomes more difficult for him to work, irritability and fatigue increase. The rhythm of sleep and the functioning of the nervous system as a whole worsens.
Methods for relieving static tension
The ESD Guidelines also provide a number of measures to help minimize and eliminate the harmful effects of a discharge. Here are the main ones:
- purification of gases and liquids passing through pipelines from foreign impurities (for example, solid particles);
- prevention of spraying and splashing of substances;
- strict compliance with pipeline speed requirements.
You may be interested in this The danger of step tension
To prevent foreign impurities from entering the pipeline, filters are used. The photo shows a gas
Who are the founders of the science of electricity?
Here is a list of some famous scientists who contributed to the development of electricity.
French physicist Andre Marie Ampère
The founders of the science of electricity are:
- French physicist André Marie Ampère, 1775-1836, who worked on electromagnetism. The SI unit of current, the ampere, is named after him.
- French physicist Charles Augustine of Coulomb, 1736-1806, who pioneered studies of friction and viscosity, charge distribution on surfaces, and the laws of electric and magnetic force. The SI unit of charge, the coulomb, and Coulomb's law are named after him.
- Italian physicist Alessandro Volta, 1745-1827, who invented the direct current source, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1921, and the SI unit of voltage, the volt, is named in his honor.
- Georg Simon Ohm, 1789-1854, German physicist, discoverer who influenced the development of the theory of electricity, in particular Ohm's law. The SI unit of resistance, the ohm, is named after him.
- Gustav Robert Kirchhoff, 1824-1887, German physicist who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, is known for his two laws of circuit theory.
- Heinrich Hertz, 1857-1894, German physicist demonstrating the existence of electromagnetic waves. The SI unit of frequency, the Hertz, is named in his honor.
- James Clerk Maxwell, 1831-1879, a Scottish mathematician and physicist, formulated a system of equations about the fundamental laws of electricity and magnetism, called Maxwell's equations.
- Michael Faraday, 1791-1867, English chemist and physicist, founder of the law of induction. One of the finest experimentalists in the history of science, he is generally considered the father of electrical engineering. The SI unit of capacitance, Faraday's constant, is named after him.
- Thomas Edison, 1847-1931, American inventor with over 1,000 patents, is best known for developing the incandescent light bulb.
Thomas Edison