Grounding is one of the main factors providing protection against electric shock. In accordance with Chapter 1.7 of the PUE, all grounding systems for electrical installations can be divided into two groups: - systems with a solidly grounded neutral, these include the TN grounding system (NC, TN-CS, TN-S) and the TT grounding system; — systems with an isolated neutral, these include the IT grounding system;
The first letter of the abbreviation indicates the nature of the grounding of the power source, and the second - the nature of the grounding of the open conductive parts of the power receiver:
- T (from the French terre - earth) - grounded;
- N (from the French neutre - neutral) - connection to the neutral of the power source (grounding);
- I (from the French isolé - isolated) - isolated from grounding.
The article also contains the following abbreviations:
- N - functional (working) zero - neutral conductor used to connect an electrical receiver.
- PE - protective zero - a protective conductor designed for grounding electrical equipment housings.
- PEN is a conductor that combines the functions of zero protective and zero working conductors.
Now we will analyze in detail the listed types of grounding systems.
Designations in grounding systems
The system designations use Latin letters:
- T (ground);
- N (neutral or functional zero);
- I (isolated);
- C (connection of protective and functional “zero”);
- S (separate application of protective and functional “zero” throughout the entire network).
In system designations, the first letter determines the type of grounding of the power source, the second letter indicates the type of grounding of the open components of the electrical receiver.
Properly designed and implemented grounding is one of the basic conditions for ensuring electrical safety of facilities where household or industrial electrical equipment is operated. When performing grounding, you must be guided by the requirements of the PUE (Electrical Installation Rules).
TN: grounding system with solidly grounded neutral
In this system, protection is carried out by connecting a solidly grounded neutral to non-insulated components of the electrical installation. In the TN grounding system, the conductor is PE, that is, the “zero” conductor. That is, when arranging it, housing screens and parts of electrical consumers that conduct current must be connected to a common “zero” - a conductor that is connected to the neutral.
The functional “zero” in this case is designated by the letter “N”, and the combination of the “zero” functional and protective conductor is “PEN”. This grounding system has three subtypes TN-CS, TN-C and TN-S. The differences between them lie in the different ways of connecting the “PE” and “N” conductors.
This system does not use the method of neutral grounding using an arc suppression reactor, which in other types of systems is used as a compensating device.
System designation, decoding
To designate each system, a letter index consisting of several letters is used.
The first letter in the index indicates the nature of the grounding of the main power source of the devices (transformer substation), and the second letter indicates the grounding of open sections of electrical installations.
For designation, certain letters of the Latin alphabet are used, each of which has its own decoding:
- T – grounded (from “Terre” – earth);
- N – neutralized, connected to the neutral of the source (from “Neuter” - neutral);
- I – isolated (from “Isole” – isolation).
These three letters are used to designate grounding systems that are included in the international standard.
Three grounding systems according to IEC are designated:
- TN (which in turn is divided into subsystems TN-C, TN-S, TN-CS);
- TT;
- IT.
Additionally, the classification introduced the letter designation of neutral conductors involved in grounding systems:
- N – worker;
- PE – protective;
- PEN – combined (combined), including both working and protective neutral conductors.
All of these systems have their own design features, which determine their scope of use.
For residential use, TN grounding subsystems are more suitable.
The TT system is applicable for mobile buildings (construction and other trailers, kiosks with metal surfaces), but IT is used mainly for organizing the grounding of laboratories.
The grounding system used for electrification of premises must be indicated in the design documentation, since in order to carry out maintenance and repair work it is necessary for the electrician to know exactly which system is used.
The existing standard for the grounding system is international, so we also use it.
Moreover, all the regulations in force in our country concerning grounding systems are fully spelled out in the rules for the construction of electrical installations (PUE). Moreover, the PUE operates both on the territory of the Russian Federation and Ukraine.
These rules are general provisions for the correct implementation of electrification, operation of electrical appliances and protection.
Next, we will consider the features of each of the systems, as well as their positive qualities and disadvantages.
TN-C: system with working and protective “zero” in one conductor
The standard TN-C grounding system is a 4-wire current supply circuit with “zero” and three phase wires. This system involves combining zero working and protective conductors into one throughout its entire length. In other words, in TN-C the PEN conductor is common; it is used both for connecting current receivers and for “grounding” their cases (open conductive components).
“Grounding” the housing is necessary in case of damage to the insulation or a break in the phase wire, in which case it may short out to the housing. With this scheme, this will trigger the automation, which will turn off the voltage.
TN-C has some disadvantages. The most critical disadvantage of this grounding system is the lack of protection circuits in case of burnout or mechanical damage (break) of the “zero”. In such a situation, voltage is created on the housings of equipment and devices, which poses a threat to life. Another drawback is that it does not use a PE grounding conductor - that is, the sockets that are connected to it are not grounded, which leads to the need to ground any connected electrical equipment.
Important! Those who live in a house that uses a TN-C grounding system need to know that when forced to connect household appliances to zero in bathrooms, additional potential equalization lines cannot be used.
At the moment, TN-C is morally outdated. It is still used in private homes and buildings built in the early and mid-20th century. It can also be used where the risk is low - for example, in street lighting.
IT system
The IT system is intended for use in institutions where highly sensitive instruments can be used (laboratories, medical facilities).
The peculiarity of IT comes down to the fact that the neutral of the transformer substation is insulated in relation to the ground, or special instruments and devices with high resistance are used for grounding.
But open areas of electrical installations are grounded in the classical way - through a grounding loop.
The use of an IT system ensures minimal exposure to electromagnetic fields on sensitive equipment.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: How to ground a washing machine.
TN-S: effective, but expensive
TN-S, in comparison with the TN-C grounding system, is a more modern, efficient and safe system in which the solidly grounded neutral of the transformer (or generator) is used to connect conductors with a “zero” on the side of the current source. When using it, the risk of high voltage occurring on the housings of electrical equipment is eliminated - even if the power line is damaged.
Meanwhile, there are two reasons why TN-S is not widely used in Russia. The first is that the Russian energy industry is mainly focused on 4-wire, 3-phase power supply circuits. The second reason is the high cost of using the TN-S grounding system.
During installation, when connecting three phases, you will need to use 5 wires to connect the equipment to the power source. For a single-phase connection, 3 wires are required. Due to the prevalence of 4-wire circuits for three phases in Russia, the use of TN-S will be inappropriate, since in this case it will be necessary to extend a separate line consisting of 5 wires from the transformer substation.
The new edition of the PUE, as well as GOST R50571, contains instructions for installing the TN-S system at facilities that require a high degree of electrical safety. Also, these regulatory documents prescribe its arrangement during construction and major repairs of buildings.
TN-CS: connection of a combined “PEN” with a solidly grounded neutral
TN-CS is a common grounding system that provides a higher level of electrical safety than TN-C while being less expensive than TN-S. The principle of this type of connection is to supply power using a combined “PEN”, which is connected to a solidly grounded neutral. Upon entering the building, it is divided into a protective zero (“PE”) and a conductor, which on the consumer side performs the function of “N”, that is, the working zero.
In accordance with the requirements of the PUE (clause 1.7.135), at the point where the working and protective zero are separated, busbars or clamps must be used for the connected conductors. The combined “PEN” must be connected to the bus or terminal of the protective zero “PE”.
According to clause 1.7.135 of the PUE, at the point where the PEN conductor is divided into the neutral protective (PE) and neutral working (N) conductors, it is necessary to provide separate clamps or busbars for the conductors, connected to each other. The PEN conductor of the supply line must be connected to the terminal or bus of the neutral protective conductor. In this case, the cross-section of the jumper located between the tires should not be less than the cross-section of the combined PEN.
Pros: the TN-CS grounding system is more reliable than TN-C: it eliminates the risk of a zero break, and the cost of its installation will be only slightly higher than for this outdated system.
Disadvantages: burnout or breakage of the PEN wire along the line from the facility to the substation leads to the formation of life-threatening voltage on the surface of electrical appliances. Because of this, when installing a TN-CS system, it is necessary to ensure reliable protection against damage to the combined PEN line.
How to make a ground loop
In apartment buildings, the transition to the TN-CS grounding system is usually carried out by specialized enterprises. They make the appropriate switches in the ASU of the house or entrance and install an additional grounding loop. Practice shows that there are cases when residents who are illiterate in electrical engineering, but not overly active, try to modernize the power supply circuit for their individual apartment on their own. For this purpose, they try to use water supply or heating risers as a grounding loop, which is strictly prohibited, because This method inevitably leads to electrical injuries and has a detrimental effect on the service life of pipelines and heating devices.
For the conditions of a private home, it is not difficult to make additional grounding; the most popular and reliable is a closed circuit in the form of a triangle:
The electrode immersed in the ground is angle steel, the jumper is a steel strip, the grounding conductor is a steel rod. We talked in more detail about how to make grounding in the house in a separate article!
TT grounding system: a new product in the Russian energy sector
This system implies “solid” grounding of the neutral of the power line. In this case, the grounding of open parts of the electrical installation capable of conducting current is carried out using a device that is “autonomous” from the solidly grounded neutral. With a 3-phase connection, the voltage is transmitted through 4 wires, in which the fourth represents “N”, that is, functional zero. A grounding conductor (most often modular-pin) is mounted on the consumer side. Then the protective zero conductors are connected to the grounding switch, which are connected to the housing components.
In the Russian Federation, the TT grounding system was approved relatively recently. It has become widespread in overhead power lines, which are used to supply electricity to rural areas, country houses, cottage villages and other suburban settlements. Another area of use of this system is power supply lines for temporary mobile trade facilities in urban environments.
TT has become a successful replacement for the TN-CS system, which in the specified area of application does not guarantee the reliability of the protection of the combined “PEN”.
When using this type of grounding, it is necessary to provide protection against lightning strikes. You also need to use special automation that provides protective shutdown. One more point - the PUE contains instructions on the use of the TT grounding system - supplying current to electrical installations with its use is practiced only when electrical safety cannot be ensured in the TN system.
Types of artificial grounding systems
Electrical installations with regard to electrical safety measures are divided into:
- electrical installations with voltages above 1 kV in networks with a solidly grounded or effectively grounded neutral;
- electrical installations with voltages above 1 kV in networks with an isolated or grounded neutral through an arc suppression reactor or resistor;
- electrical installations with voltage up to 1 kV in networks with a solidly grounded neutral;
- electrical installations with voltage up to 1 kV in networks with an insulated neutral.
Depending on the technical features of the electrical installation and supply networks, its operation may require different grounding systems. As a rule, before designing an electrical installation, the sales organization issues a list of technical conditions that stipulate the grounding system used.
The classification of types of grounding systems is given as the main characteristics of the supply electrical network. GOST R 50571.2-94 “Electrical installations of buildings. Part 3. Basic characteristics" regulates the following grounding systems: TN-C , TN-S , TN-CS , TT , IT .
For electrical installations with voltage up to 1 kV, the following designations are accepted:
- TN system - a system in which the neutral of the power source is solidly grounded, and the open conductive parts of the electrical installation are connected to the solidly grounded neutral of the source through neutral protective conductors;
- TN-C system - TN
, in which the neutral protective and neutral working conductors are combined in one conductor along its entire length; - TN-S system - TN
, in which the neutral protective and neutral working conductors are separated along its entire length; - TN-CS system - TN
, in which the functions of the neutral protective and neutral working conductors are combined in one conductor in some part of it, starting from the power source; - IT system - a system in which the neutral of the power source is isolated from the ground or grounded through devices or devices having high resistance, and the exposed conductive parts of the electrical installation are grounded;
- TT system - a system in which the neutral of the power source is solidly grounded, and the exposed conductive parts of the electrical installation are grounded using a grounding device that is electrically independent of the solidly grounded neutral of the source.
The first letter is the state of the neutral of the power source relative to ground
- T - grounded neutral (lat. terra
); - I - isolated neutral (English insulation
).
The second letter is the state of exposed conductive parts relative to ground
- T - open conductive parts are grounded, regardless of the relation to the ground of the neutral of the power source or any point of the supply network;
- N - open conductive parts are connected to the solidly grounded neutral of the power source.
Subsequent (after N) letters - combination in one conductor or separation of the functions of the zero working and zero protective conductors
- S - zero working ( N
) and zero protective (
PE
) conductors are
separated
; - C - the functions of the neutral protective and neutral working conductors are combined in one conductor (PEN conductor) ( combined
); - N - zero working (neutral) conductor; (English neutral
) - PE - protective conductor (grounding conductor, neutral protective conductor, protective conductor of the potential equalization system) (English: Protective Earth
) - PEN - combined zero protective and zero working conductors (English: Protective Earth and Neutral
).
Systems with solidly grounded neutral (TN systems).
Systems with a solidly grounded neutral are usually called TN
-systems, since this abbreviation comes from the French.
Terre-Neutral
, meaning "ground-neutral".
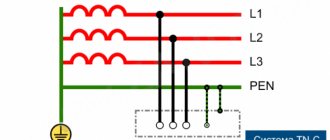
Rice. 1. Schematic diagram of the TN-C system, in which the neutral protective and neutral working conductors are combined in one conductor along its entire length
The scheme is most often found in old houses, where:
- 1 – grounding conductor of the neutral (midpoint) of the power source;
- 2 – open conductive parts;
- N – zero working (neutral) conductor;
- PEN – combined neutral protective and neutral working conductors.
Rice. 2. Schematic diagram of the TN-S system, in which the neutral protective and neutral working conductors are separated along its entire length, where:
- 1 – grounding conductor of the neutral (midpoint) of the power source;
- 2 – open conductive parts;
- N – zero working (neutral) conductor;
- PE – protective conductor
Rice. 3. Schematic diagram of the TN-CS system - a TN system in which the functions of the neutral protective and neutral working conductors are combined in one conductor in some part of it, starting from the power source where:
- 1 – grounding conductor of the neutral (midpoint) of the power source;
- 2 – open conductive parts;
- N – zero working (neutral) conductor;
- PE – protective conductor (grounding conductor, neutral protective conductor, protective conductor of the potential equalization system
- PEN – combined neutral protective and neutral working conductors
TN-C system
System TN-C (French Terre-Neutre-Combiné
) was proposed by the German concern AEG in 1913.
The working zero and PE
conductor (English:
Protection Earth
) in this system are combined into one wire.
The biggest drawback was the possibility of linear voltage appearing on the housings of electrical installations in the event of an emergency zero
. Despite this, this system is still found in buildings in the countries of the former USSR. Of modern electrical installations, such a system is found only in street lighting for reasons of economy and reduced risk.
TN-S system
System TN-S (French Terre-Neutre-Séparé
) was developed to replace the conventionally dangerous
TN-C
in the 1930s. The working and protective zeros were separated directly at the substation, and the ground electrode was a rather complex structure of metal fittings. Thus, when the working zero was broken in the middle of the line, the electrical installation housings did not receive line voltage. Later, such a grounding system made it possible to develop differential circuit breakers and current leakage circuit breakers capable of sensing small currents. Their work is based on Kirchhoff's laws, according to which the current flowing through the working zero must be numerically equal to the geometric sum of the currents in the phases.
- You can also observe the TN-CS
, where the separation of zeros occurs in the middle of the line, however, if the neutral wire breaks before the separation point, the housings will be under line voltage, which will pose a threat to life if touched.
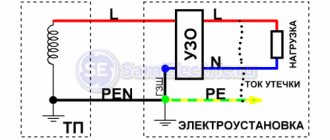
TN-CS system
In the TN-CS , the transformer substation has a direct connection of the current-carrying parts to the ground and a tightly grounded neutral. To ensure communication between the transformer substation and the entrance to the building, a combined neutral conductor (N) and protective conductor (PE), designated PEN, are used. When entering the building, it (PEN) is divided into a separate neutral (N) and protective conductor (PE).
- Advantages: a simpler lightning protection device (it is impossible for a voltage peak to occur between PE
and
N
), the ability to protect against phase short circuits on the device body using ordinary “automatic devices”. - Disadvantages: extremely poor protection against “zero burnout”, that is, destruction of PEN
on the way from the transformer substation to the separation point.
In this case, phase voltage appears on the PE
on the consumer side, which cannot be turned off by any automation (
PE
cannot be turned off). If inside a building the protection from this is provided by the EPS (everything metal is energized, and there is no risk of electric shock when touching 2 different objects), then in the open air there is no protection from this at all.
In accordance with the PUE, this is the main and recommended system, but at the same time, the PUE requires compliance with a number of measures to prevent the destruction of PEN
— mechanical protection
PEN
, as well as repeated grounding
of the PEN
overhead line along poles over a certain distance (no more than 200 meters for areas with the number of thunderstorm hours per year up to 40, 100 meters for areas with the number of thunderstorm hours per year more than 40).
In cases where it is impossible to comply with these measures, the PUE recommends TT
.
TT
also recommended for all outdoor installations (sheds, verandas, etc.)
In city buildings with PEN
usually a thick metal frame that runs vertically through the entire building.
TN-CS
is used in urban buildings .
In rural areas in Russia, in practice, there are a huge number of overhead lines without mechanical protection PEN
and repeated groundings.
TT
system is more popular in rural areas .
, TN-CS was usually used
with a division point based on the electrical panel (
PEN
) next to the meter, while
PE
was carried out only for the electric stove.
In modern Russian buildings, a “five-wire system” is also used with a division point in the basement; independent Ns
and
P.E.
_
TT system
Rice. 4. Schematic diagram of the TT system (option 1), where
- 1 – grounding conductor of the neutral (midpoint) of the power source;
- 2 – open conductive parts;
- 3 – grounding switch of open conductive parts;
- N – zero working (neutral) conductor;
- PE – protective conductor.
Rice. 5. Schematic diagram of the TT system (option 2), where
- 1 – grounding conductor of the neutral (midpoint) of the power source;
- 2 – open conductive parts;
- 3 – grounding switch of open conductive parts;
- PE – protective conductor
In the TT , the transformer substation has a direct connection of live parts to the ground. All open conductive parts of the building's electrical installation have a direct connection to the ground through a ground electrode, electrically independent of the neutral ground electrode of the transformer substation.
- Advantages: high resistance to N
on the way from the transformer substation to the consumer.
This destruction has no effect on PE
. - Disadvantages: requirements for more complex lightning protection (the possibility of a peak appearing between N
and
PE
), as well as the inability for a conventional circuit breaker to trace a phase short circuit to the device body (and further to
PE
). This is due to a fairly noticeable (30-40 Ohm) resistance of the local grounding.
Due to the above, the PUE recommends TT
only as an "additional" system (provided the supply line does not satisfy the
TN-CS
for re-earthing and mechanical protection
PEN
), and in outdoor installations where there is a risk of simultaneous contact with the installation and physical earth (or physically grounded metal elements).
However, due to the poor quality of most air lines in rural Russia, the TT
extremely popular there.
TT
requires the mandatory use of an RCD.
Typically, an introductory RCD is installed with a setting of 300-100 mA, which monitors short circuits between the phase and PE
, followed by personal RCDs for specific circuits at 30-10 mA to protect people from electric shock.
Lightning protection devices such as ABB OVR
, differ in design for
TN-C-
S and
TT
, the latter having a gas arrester between
N
and
PE
and varistors between
N
and the phases.
Systems with isolated neutral. IT system.
Rice. 6. Schematic diagram of an IT system - a system in which the neutral of the power source is isolated from earth or grounded through instruments or devices having high resistance, and exposed conductive parts are grounded where:
- 1 – grounding resistance of the neutral of the power source (if available);
- 2 – ground electrode;
- 3 – open conductive parts;
- 4 – grounding device;
- PE – protective conductor (grounding conductor, neutral protective conductor, protective conductor of the potential equalization system).
IT system
It is used, as a rule, in electrical installations of buildings and structures for special purposes, which are subject to increased reliability and safety requirements, for example, in hospitals for emergency power supply and lighting.
You can get detailed consultations and cost of services by contacting us:
- tel/fax:
IT: grounding system with isolated neutral "I"
The two main features of this system are the presence of a protective ground line (“T”) and an independent neutral “I”. When using IT, a minimum of wires are used to transfer current from the source to the consumer. In this case, it is necessary to ensure reliable connection to the grounding electrode of all components of electrical equipment housings capable of conducting current. Another nuance of the IT grounding system is the absence of a functional zero “N” on the current source-electric consumer line.