Why do you need a grounding wire, how it works
Connecting a ground wire to a bus
The main purpose of grounding is to prevent electric shock to a person or animal. A serviceable electrical device has a complete body with reliably insulated parts that are energized. If a household appliance breaks down, live parts may touch the housing and this will lead to the fact that it will also be energized. By touching such a device, a person will inevitably receive an electric shock.
In this case, the operation of a circuit breaker is impractical, since the current flowing through the human body will not be enough to turn off the power supply. But this force, unfortunately, is enough to deprive a person of health or even life.
To eliminate the possibility of such events, you need to ground all electrical devices through conductors. Grounding household appliances at home is only possible if the house is equipped with a ground loop. Unfortunately, houses in older buildings are not equipped with such innovations. This is due to the fact that decades ago people had practically no household appliances in their homes, therefore, the load on the network was minimal.
Now another conductor is added to the two-phase wiring - a grounding wire. As a result, the wiring is already three-phase - two wires are zero and phase, and the third is protective grounding. Thus, when connecting the plug of a household appliance to a socket, the metal body of the device is automatically connected to the protective ground.
What is grounding used for and how does it work?
Any electrician, even a freshman, will tell you that grounding is a specially created connection of working electrical equipment (a point or a network node) with some grounding device.
The latter can be either specially mounted structures and devices, or soil. Both are equally effective, but are used in different cases.
The grounding device and working cables are selected depending on the purpose of the grounding. There are only a couple of main types:
- working (or functional),
- protective.
A process is called functional when it is directly necessary for the correct and proper operation of the equipment.
Protective, in turn, is grounding, which leads to safe operation of devices for humans. This type is not used directly all the time (unlike the previous one), but only in situations of breakdowns, failure or when the device is struck by lightning.
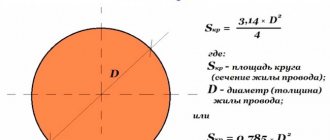
In apartments and houses, protective grounding is carried out. For domestic purposes, an inexpensive grounding conductor is usually used - a single-core cable or part of a multi-core cable. The main component of the wire is always copper, but the cross-section varies. The main question that worries home craftsmen and inexperienced electricians is what cross-section should the grounding wire be? Let's try to answer.
Criteria for selecting a grounding cable
Grounding Schemes
Before choosing a grounding conductor, you need to understand several important points.
Owners of private houses and country buildings built in 1998 and earlier are forced to carry out grounding themselves. Modern buildings are equipped with a ready-made system even during the construction process.
To choose the right grounding wire and its cross-section, you need to find out what system is installed in the house. According to the Electrical Installation Rules, 4 types can be used:
- TN-S - in the AC system, additional grounding is carried out using a neutral and a separate wire.
- TN-C is characterized by combining the zero and ground wires, the neutral is output separately. The most common method of protection, which was used in Europe several decades ago.
- TT – equipping electrical equipment with direct protective grounding.
- IT – work directly with the housings of household appliances through complete insulation of all conductive cables and the housing itself.
The grounding diagram used should always be marked. In Russia you can find two of them:
- PE – grounding;
- PEN – neutral and ground are combined in one cable.
The next important selection criterion is the type of grounding used. Depending on their purpose, they are divided into two types - portable and stationary. In domestic conditions, a stationary type is sufficient, which allows the operation of both single-core and three-core cables.
Many people who are poorly informed in these surveys have difficulty figuring out what color the ground wire is. According to the requirements of the PUE, the wire must be made in yellow-green insulation color.
After determining the type of cable and material of the system, you can proceed to the next main step - selecting a suitable cross-section.
How to do grounding correctly in an apartment
To answer this question, you need to understand what kind of protection system is installed in your home.
As a rule, in old Soviet-built houses the TN-C System , in which the neutral protective and neutral working conductors are combined into one PEN conductor, and they are combined throughout the entire system. You can recognize such a system by the two-core cable that is laid around the apartment and by the four-core cable in the common panel.
To be honest, how to properly do grounding in an apartment in an old building, then such a system only protects against short circuits and increases the likelihood of receiving an electric shock. Therefore, talking about protective grounding in this case is necessary with a certain degree of risk. There are several working options that reduce risks, but are not complete protection, and are done at your own peril and risk.
Option 1 We change the wiring in the apartment to three-wire L, N, PE, but do not connect PE anywhere. In the future, when the common house grounding is done, it will be possible to connect. We must install an RCD on groups of sockets in case of phase contact with the housing within the apartment. They do not guarantee absolute protection. But if household appliances are damaged, the RCD will de-energize the line and prevent the current from reaching dangerous levels.
Option 2 We agree with the neighbors and the management company and make a separate grounding loop near the entrance according to the same principle as in a private house. This option is the safest and most correct.
Option 3 We leave zero as is, take the PE wire from the main PEN wire. You can do it from the place where it fits the body of the floor panel. It is important that our N and PE are connected at different points. PE – on the body, N – on a bus isolated from the body, to which zero comes after the input switch or machine and the meter. However, there remains a big disadvantage in this decision. The zero may burn out at the entrance to the house. You may think that there are fewer houses than apartments and the likelihood of such a problem occurring is less, but this danger is still there. Therefore, such grounding does not work 100%.
Attention! Do not make a ground wire with a contact point on a central heating or water supply radiator. You cannot ground by connecting the neutral working and neutral protective conductors in the socket. This is dangerous, as the working zero in the shield may burn out. After this, 220V will appear on the body of your electrical appliances.
In modern apartment buildings, the TN-S system , in which the N and PE conductors are separated throughout the entire length from the substation to the consumer. This system is the safest and most preferred, but is used only in new electrical installations due to its high cost. Most houses now use TN-CS system , in which the N and PE conductors after the substation are connected into one PEN wire, and then separated at the entrance to the building.
In this case, protective grounding can be organized at the stage of electrical installation using three-wire wires, grounded sockets and protective automatic equipment. When a phase hits the device body, the circuit breaker should trip. When touching live parts, the RCD should trip.
For electrical distribution, I advise you to choose a cable with three cores in double insulation, preferably VVG NG, for socket groups with a cross-section of 3 by 2.5 for light groups 3 by 1.5. One end of the wire is inserted under the free bolt of the distribution panel bus connected to the panel body, and the other - to the “grounding” contact of the socket. At the same time as assembling the apartment panel, electricians check the connection of the grounding wire in the common house panel.
Attention! Make a separate grounding loop for the metal bathtub and sink, metal pipes of the washing machine. Correctly connect the ground cable to the metal bathtub to the specially welded tab on the bathtub body, but not to the adjustable bolted mountings of the bathtub.
The protective grounding circuit in a bathroom apartment can be schematically represented as follows.
Attention! If there is an RCD in the panel, the grounding conductor should not have contact with the N conductor anywhere, since the RCD will be triggered. Remember that the “ground” should not be broken by means of switches
How to choose the right cross-section of the grounding conductor
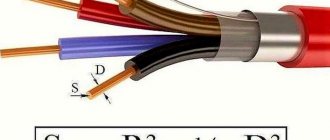
An example of a cable with a smaller cross-section of PEN cores.
To connect the protection system, not only natural grounding conductors can be used, but also artificial ones. The selection rules in each case differ from each other and have their own technical features.
Networks with a power of more than 1 kW are equipped with artificial ones; in other cases, the operation of natural ones is permissible.
The artificial segment is made of galvanized alloys, steel and copper. The cross-section is selected in accordance with the Electrical Equipment Installation Rules in special tables.
| Material | Section profile | Diameter(mm)/Cross-sectional area(mm.sq) |
| Copper |
|
|
| Cink Steel |
|
|
| Black steel |
|
|
One simple but important rule is that the conductor must have a cross-section that is equal to the cross-section of the phase wire, provided that the conductor is at least 16 mm2. In other cases, the cross section is calculated using the table given in the PUE.
| Section of phase conductors, mm.sq. | Smallest cross-section of protected conductors, mm.sq. |
| S>35 | S/2 |
| 35>S>16 | 16 |
| S<16 | S |
In an ordinary apartment, which is equipped with all the necessary equipment, it is enough to install a protection system with a single-core wire with yellow-green insulation.
Which wire to use for grounding
Grounding is the connection of non-current-carrying parts of electrical equipment to a ground electrode. This ensures the presence of ground potential on the housings of electrical appliances. This is necessary to prevent electric shock from touching housings and other structural parts of damaged equipment. Connection to the grounding bus is made using a wire or cable. In this article we will tell you what the grounding wire should be like so that you can choose the right brand, cross-section and other parameters.
Briefly about the terms
To make the article understandable even for those who are far from electrical engineering, we have provided an explanation of the terms that will be used in it.
The ground electrode is the basis of the grounding system. Usually it consists of metal pins driven into the ground at an equal distance from each other, forming a figure like a triangle.
A grounding bus or GZSh is a metal strip laid along the perimeter of the room or near the protected devices, which connects all the grounding conductors of electrical devices to the ground electrode.
The grounding wire or conductor is the conductor that provides the connection of the ground electrode to the main switch.
Metal bonding is a concept that characterizes the contact between metal parts of electrical equipment housings, including the doors of electrical panels or cabinets with their housings.
Ground wire size
To ensure reliable protection against electric shock and the operation of protective switching devices, the grounding wire is selected depending on the phase cross-section. This is necessary so that in the event of an accident it can withstand high currents and not burn out. If this happens, the protection will not work, and dangerous potential will appear on the body of the electrical device.
The cross-section of the ground wire should be:
- If a phase is used with a cross section of up to 16 sq. mm - the grounding conductor must be of a similar size.
- If the cross-sectional area of the phase is from 16 to 35 sq. mm, then at the “ground” it should be 16 square meters. mm.
- When the phase cross-section is more than 35 sq. mm - the minimum cross-section of the ground wire must be at least half the cross-section of the phase wire.
Wire marking
Grounding wires have another characteristic feature - markings.
Ground color
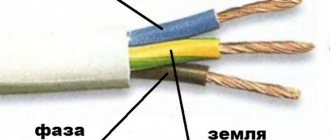
Grounding, according to the rules of the PUE, must be painted yellow-green. However, it is rare to see light green or all yellow wires. The cable can also be equipped with a blue braid at the fixation points, which indicates grounding along with zero.
In the distribution panel it is connected to the busbar, housing and panel door made of metal. In the box, the connection tends to the ground wires. The grounding conductor must not be connected to the residual current device.
Symbols on electrical diagrams: for direct current, standard grounding, to the electrical equipment housing, clean and protective.
Neutral color
An example of the appearance of a neutral wire.
The neutral conductor is strictly blue in color. In the distribution panel it must be connected to the neutral bus, which is designated by the letter N. All remaining blue conductors are connected to it. Through an electric meter or directly without installing a machine, the bus is connected to the input. In the distribution box, all wires, with the exception of blue, should not be used for switching. Neutral conductors in sockets are connected to the contact designated N - located on its back side.
Phase color
Compared to ground and neutral, phase has a wider range of colors. Any colors except blue, yellow and green can be used to designate a wire. The most common are black, red and brown.
In the distribution box, the phase that leaves the consumer is connected to the contact of the automatic switch located at the very bottom, or the residual current equipment. The switches carry out phase switching.
Independent wire designation
From time to time there are conductors with unusual colors. Such solutions do not comply with the standards set out in the PUE. To make the task easier, it is recommended to label the wires yourself with the necessary colors. Colored electrical tape and heat-shrinkable tubing are used for this.
Another task of the master is to write down the meanings of the colors separately on a piece of paper.
Wire color and connection features
What color should the ground wire insulation be? Grounding conductors and buses are always yellow-green striped. This allows you to accurately (if the installation is correct) determine the purpose of the wires when repairing the wiring. The phase conductor may be brown or another color, and the neutral conductor is almost always blue. In DC circuits, positive is often marked red and negative is black. This issue is discussed in more detail in the article: color marking of wires.
If you received a cable with color markings that do not comply with GOST standards, you can mark ground, phase and zero using electrical tape or heat-shrinkable tubing. In addition to color markings, there are also alphabetic or numeric markings:
- L – Line or phase.
- N – Neutral or neutral, zero.
- PEN or PE – protective conductor or ground.
For connections in the input distribution panel (and other places), ground and neutral buses are often used. This is a strip with a set of holes and screw terminals where the wires are connected. To connect the ground wire to a stranded conductor, you must tin it or crimp it with a pin lug like NShVI and the like. This rule also applies to connecting any flexible conductors to machine terminals and other screw connections.
To connect the wire to the grounding bus, you must use round terminals NKI, NVI or other types of cable lugs with terminals in the form of a ring.
This may be required when laying grounding from the circuit to the panel. They are usually of two types:
- Crimping. In order to secure them to the cable, they are crimped with a special tool. You should not do this with pliers, because you will not achieve reliable crimping. The best compression is provided by press pliers (another name is crimper) with hexagonal (hexagonal) clamps.
- With shear screws - to tighten them, simply tighten the screw until its head breaks off.
That's all we wanted to tell you in this article. Now you know what section and brand the grounding wire should be. Finally, we recommend watching a useful video on the topic:
Main brands of grounding cable
Options for color marking of the ground wire
When choosing a cable brand, you need to study its type: mobile or stationary use. Stationary is designed to protect equipment, distribution panels and structures. The best option is multi-core stranded cables (VVG, PVG) and single-wire modifications (NYM). If the ground cable is colorless, the ground is directed towards the core.
- NYM cable – the sheath is painted in accordance with all rules and regulations, and the inside is equipped with copper conductors. It also has an intermediate additional sheath, which increases the service life of the cable even with prolonged use. Does not cause any difficulties during installation.
- VVg - equipped with conductors made of copper of the first and second class of twist. It has an unusual color that is worth paying attention to. Earth is yellow-green, and zero is blue. The outer sheath and insulation are made of polyvinyl chloride, thanks to which the cable will not burn even in the event of a fire.
- PV-6 – copper wire, the sheath is made of transparent PVC. It is possible to contemplate the work of a conductor. Operating temperature range -40 – +50 degrees Celsius, very flexible material.
- ESUY has one standard application - system short circuit protection. Capable of withstanding enormous loads, they are often used in junction boxes and on railways.
- PV-3 can be produced in 11 colors and consists of a large number of copper threads, which are placed in a polyvinyl chloride shell. The peculiarity of the outer shell is fragility if improperly stored or used.
The issue of choosing a grounding cable is extremely important, since an incorrectly selected core will be unable to perform all the technical tasks assigned to it. If you have difficulties making your own choice, it is better to consult a specialist.
A little theory
It is quite difficult for an ordinary person who does not particularly go into the basics of electrical engineering to understand all these nuances. Especially when they begin to operate with such concepts as grounding, grounding, solidly grounded or effectively grounded neutral. Therefore, first, let’s try to explain in accessible language the essence of all these designations, and determine the main purpose for which they were invented.
- There are five main schemes for connecting the neutral of electrical equipment. The neutral is the common point of the windings of electrical equipment connected in a star. A star connection is when the three beginnings of the windings are connected to the corresponding phase wires, and the ends of these windings are connected to each other - neutral.
- At the point where the ends of these windings connect, under ideal conditions the potential will be zero. The earth has the same potential. Therefore, the neutral wire is grounded using a bus or conductor. It is usually connected to a special busbar of a stationary grounding conductor.
- Such a system is called a TN or solidly grounded neutral system. In our country, it is widely used in electrical installations up to 1000V and is divided into three subtypes.
- But before we begin to analyze these subspecies, let's define what a neutral and protective wire is. As the instructions say, a neutral or neutral wire is a conductor connected to the neutral. In diagrams, this wire is usually designated “N”.
- In addition, there is also a so-called protective grounding conductor. It is designated "RE". Using KS 066 1 ground wire socket clamp or other similar type of connection, it is connected to the ground and to the equipment housing, thereby ensuring zero potential on the housing. But as we remember, in networks with a solidly grounded neutral, it is also connected to the ground.
It is precisely based on this condition that there are three types of connections in TN networks:
Important: Referring to the TN-C grounding system, some would-be electricians are trying to implement it at home, using the neutral conductor as both neutral and protective. But according to clause 1.7.132 of the PUE for single-phase networks, this is prohibited. This is due to the fact that if the neutral wire breaks, there is a high probability of voltage appearing on the housing of the protected equipment. Therefore, if there is no separate grounding loop, then it is better to do without it altogether than to connect the equipment housing to the neutral conductor.