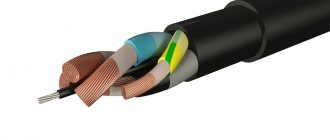
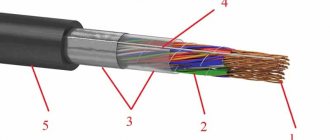
AVBBShv cable design
Let's look at the structure layer by layer.
- In the central part there is a conductor that conducts current. It is aluminum, soft, with a round cross-section (for cables rated at 6 kV, cores woven from three wires are typical).
- The cores are enclosed in insulating sheaths; For these purposes, non-flammable, reflective and fairly durable PVC plastic is used.
- Shielding layers (metal or plastic, with a winding made of paper electrical conductor) - only for products designed for a network voltage of 6 kV.
- Armor. Consists of galvanized steel strips twisted in a spiral.
- Filler-layer (it can be PET film, plastic compound or other material with similar properties.
- Protection in the form of a casing (PVC plastic, non-flammable, UV resistant).
What to choose AVBBSHV or VBBSHV
In both cases, we are talking about armored power cables with one or several cores (up to five pieces) of the same cross-section. As stated above, starting with a three-core product, an additional conductor of reduced cross-section can be added. The cross-sectional shape can be round or sector (quarter circle).
The difference between AVBbShv and VBBShV is due to the fact that in the first case the cores are made of aluminum, as evidenced by the initial letter of the abbreviation, in the second - from copper, as indicated by the absence of the letter “A” at the beginning. Otherwise, VBBShV stands for copper cable with heat-resistant insulation, two armored tapes and a polyvinyl chloride sheath.
Operation of AVBbShv under severe deformation is unacceptable, therefore it is important to observe the bending radius in difficult and limited areas. The operating conditions for this cable were described above. It remains to add to them the possibility of use in fire-hazardous rooms, in partially flooded objects and at an altitude of no more than 4000 m above sea level.
To provide additional protection for electrical equipment, the conductor must be grounded. This eliminates the harmful effects of short circuit currents and other external factors, and also protects a person from electric shock.
To carry out grounding, one of two methods is used - double-sided or one-sided. In the first case, the shielded film of the cable is connected to the ground loop. The main disadvantage of the method is the potential reduction in service life.
In the case of the one-way method, only one end of the shield is connected to the grounding equipment. This requires a special device, as well as strict adherence to safety precautions.
VBBShV can be laid and used both on land and in water. It supports various climatic conditions. The wire can be placed in the air, along bridges, in dry and wet rooms, in fire hazardous areas, explosive areas or underground.
In the latter case, it is necessary to ensure protection from mechanical damage. In an aggressive environment, the wire is hidden in polyvinyl chloride pipes.
Technical characteristics of the cable AVBbShv
Unom - 0.66, 1, 3 and 6 kV. Rated frequency - 50 Hz. Operating mode, t - from -50 °C to +50 °C. Relative air humidity (at t0 +35 °C) – up to 98%; Service life: 30 years. Warranty: 5 years (from the date of start of operation). Carrying out installation work without preheating at temperatures from -15 °C and above.
Tmax permissible heating of cores for devices: - during operation: up to +70 °C; — in emergency condition: up to +80 °C. — with a short circuit: up to +160 °C.
Rmin of bending during installation: - for single-core devices ? 10 external?; — for multi-core devices ?7.5 external?;
Construction length - with a cross-section of 1.5-16 mm2 - 450 m. - with a cross-section of 25-70 mm2 - 300 m. - with a cross-section from 95 mm2 - 240 mm2 - 200 m.
More clearly in the table:
Installation work
The AVBbShv power cable can be installed both indoors and on walls, as well as in the thickness of the soil, in difficult areas (sewers, mines, subways, trenches, etc.), subject to the permissible bending radius and at a certain ambient temperature. Severe deformation of the product is contraindicated.
Application area
This power cable is used for transmitting electric current in stationary installations operating at a rated voltage of 1000 V and a current frequency of 50 Hz. The wire is often used in installations connected to a constant voltage source, the value of which can reach 2400 V.
AVBbShv can be used in different conditions. Objects with installations can be placed on land, lakes and rivers. The altitude above sea level should not exceed 4000 m. It is possible to lay the cable in special trenches of varying corrosive activity, provided that you reduce the tensile load to a minimum.
The wire can be used both in dry and in rooms with high levels of humidity, including production workshops, collectors, mines, cable mezzanines, canals and even flooded structures.
Finally, air laying is possible, which allows you to protect the power line if there is a risk of damage during operation. The cable can be used in rooms with increased fire hazard, as well as in explosive areas.
Estimated weight for cable AVBbShv
| Number of cores and nominal cross-section, mm2 | Weight of 1 km cable, kg | |
| 0.66 kV | 1 kV | |
| — 407 464 551 702 — 456 529 639 833 1002 1224 1491 1810 2133 2503 2934 3659 — 511 — | ||
| 2 ? 4 2 ? 6 2 ? 10 2 ? 16 2 ? 25 3 ? 4 3 ? 6 3 ? 10 3 ? 16 3 ? 25 3 ? 35 3 ? 50 3 ? 70 3 ? 95 3 ? 120 3 ? 150 3 ? 185 3 ? 240 4 ? 4 4 ? 6 4 ? 10 | 327 365 457 536 685 360 407 511 621 812 979 1199 — — — — — — 404 461 589 | |
How to decipher the AVBbShv markings
There are hundreds of brands of cables. In order not to get confused, each of them is assigned its own letter marking. It is applied to the outer insulation of the cable and is located along its entire length. Additionally, markings can be found on the bay in which it is supplied. It contains basic information about the material of the product, its purpose and operating conditions.
In the name of the cable AVBBSHV, the decoding of the letters carries the following information:
- A - indicates that the conductors are made of aluminum;
- B – polyvinyl chloride based insulation is used;
- B – the cable is equipped with armor made of galvanized steel tape;
- b – the protective layer between the conductors and the armor is excluded;
- Shv – outer sheath based on PVC hose.
Next comes the typical designation for all cables for the number of current-carrying cores and their cross-section. For example, 3x25 + 1x16 means that 3 main (phase) wires have a cross-section of 25 square meters. mm each. And one grounding or zero - 16 square meters. mm.
Additionally, information about climatic operating conditions may be indicated. The abbreviation “HL” means cold-resistant, and “T” means tropical.
Note! If in the future it is planned to increase the power of the consumer, which is powered through the cable, then it is better to take its cross-section with a reserve, i.e. buy a conductor with a larger diameter.
Advantages and disadvantages of AVBbShv
The main advantages of the cable include:
- Strength, resistance to mechanical stress;
- Versatility in laying methods;
- Wide range of cross-sections;
- Long-term service life.
The disadvantage can be considered the large weight, in the presence of an armored layer, which creates some inconvenience when laying, especially by air, and the high price compared to other brands without armor.
Approximate prices for 1m of cable in Russia:
| AVBbShv 5x2.5 | from 38.37 rub. |
| 5x4 | from 50.59 rub. |
| 5x6 | from 56.51 rub. |
| 5x10 | from 79.88 rub. |
| 5x16 | from 106.10 rub. |
| 5x25 | from 151.27 rub. |
| 5x35 | from 195.47 rub. |
| 5x50 | from 248.65 rub. |
| 5x70 | from 372.53 rub. |
| 5x95 | from 483.13 rub. |
| 5x120 | from 573.88 rub. |
| 5x150 | from 700.09 rub. |
| 5x185 | from 830.01 rub. |
| 5x240 | from 1058.46 rub. |
Service life AVBBShv
According to the technical characteristics, the cable in question is suitable for use for 30 years. The warranty period is 5 years. In fact, cables can last much longer. However, to extend the service life, it is necessary to create mitigating operating conditions:
- The cable must be insulated from water as much as possible. Despite the fact that the external insulation of AVBbShv is airtight, moisture from the air or soil will still necessarily penetrate through micropores.
- The maximum permissible short-circuit temperature for AVBbShv is 140 °C, and the non-ignition temperature is 350 °C. However, such abnormal operating modes should be avoided, as they can lead to overheating of the cable and partial melting of its insulation.
- Overvoltage is also undesirable. According to the requirements, the cable must withstand testing with a 2.5 kV megohmmeter for one minute. However, prolonged operation in such modes will lead to a decrease in insulation resistance and its inevitable breakdown.
How to avoid becoming a victim of counterfeiting
Unscrupulous manufacturing plants are interested in making cable production as cheap as possible and selling it at the price of a quality product. Therefore, there is always a risk of purchasing a fake.
Most often, manufacturers cheat with the diameter of current-carrying conductors. The cable may be marked to indicate that the cross-section of the current-carrying conductors is 32 square meters. mm. In fact, this parameter will be underestimated by 10-15%, which will serve as a violation of GOST 31996-2012 and will lead to a deterioration in the characteristics of the product. This is worth paying attention to first.
Determining the cross-section of a triangular monolithic conductor AVBbShV in a warehouse or store will be very problematic. However, if the cable consists of many individual round wires, then you can use a caliper and measure the diameter of one of them. Then, using the formula S=pD2/4, determine its area. The resulting value should be multiplied by the number of wires in the core and thereby find out its real cross-section.
Cable cross-section
Important! It is better not to purchase electrical goods from an unverified supplier. A conscientious seller always carries with him all the necessary product certificates. This is especially true for cables, which generally cannot be returned after purchase.
Features of laying, cutting and connecting cables
The trench for the cable must be at least 0.7 m deep and at least 0.5 m wide.
The very structure of the cable with an armored sheath presupposes its laying in conditions where powerful mechanical impacts on it are possible, which it successfully withstands. Therefore, it is not recommended to lay an expensive cable with armor where it can be done with another less expensive one. AVBbShv is often laid underground, from power transmission towers or transformer substations to the switchgear of objects to which power is supplied.
Taking into account the weight and rigidity of the cable, laying is carried out from a drum, which is installed above the trench on special trestles. The cable is sequentially unwound and placed on the bottom of the trench, sprinkled and compacted with a 7-10 cm layer of sand.
Afterwards, everything is covered with sand to a depth of 5-7 cm, laid with a layer of brick, and warning tape is placed on top. The brick and tape provide a protective layer in case of excavation work to prevent damage to the cable.
At the ends of the cable at the connection points, the cable is cut, the layer of insulation and armored tape is removed. To prevent moisture from entering by sucking condensate under the insulating layer or by direct flow of water, in networks up to 10 kV, the ends are sealed in different ways:
- Steel funnel;
- Rubber glove;
- PVC funnel with epoxy resins;
- Polyvinyl chloride tapes and heat-shrinkable tubes;
Removal of the insulating and armored layer is carried out at a certain distance from the ends, depending on the device used to seal the ends of the cable.
- G – bare ends of cores;
- F – insulating layer of the current-carrying core;
- P – layer of belt insulation;
- O – intermediate insulation shell;
- 4 – armored cable tapes;
- A – cutting distance from the ends of the cable to the armored tape
Dimensions for cutting with epoxy funnels KVEp and KVEZ
| Types of epoxy resin funnels | Cutting dimensions, cm | ||||
| A | ABOUT | P | G | B | |
| KVEp-1, KVEp-2 | 17 | 3,5 | 2 | 4,0 | — |
| KVEp-3, KVEp-4 | 21 | 5,0 | 2 | 4,5 | — |
| KVEp-5, KVEp-6 | 24 | 5,0 | 2 | 5,0 | — |
| KVEp-7 | 24,5 | 5,0 | 2 | 3,5 | — |
| KVEZ-1 | W+5.5 | 3,5 | 2 | — | 9,0 |
| KVEZ-2, KVEZ-3 | W+5.5 | 3,5 | 2 | 2,5 | 9,5 |
| KVEZ-4, KVEZ-5 | W+5.5 | 3,5 | 2 | 2,5 | 12 |
The sizes of the funnels are selected according to the size of the cable; for rubber gloves and PVC tapes, the cutting of insulation has different dimensions
An example of installing a cable with a rubber glove at the end in a switchgear or control panel
Dimensions for cutting cables for KVV PVC tape:
| Sealing type | Cable cross-section in mm2, voltage, kV | Cutting length in cm | ||||
| 1 | 6 | 10 | A | ABOUT | P | |
| KVV-1 | Up to 24 | — | — | W+6.5 | 3,0 | 1,5 |
| KVV-2 | 36…50 | 10…24 | — | W+7.0 | 5,0 | 2,0 |
| KVV-3 | 70…94 | 35…51 | 16…24 | F+10.5 | 8,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-4 | 120… 151 | 70…94 | 35… 71 | F+10.5 | 8,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-5 | 184 | 120…151 | 95…121 | F+12.5 | 10,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-6 | 241 | 184 | 151 | F+12.5 | 10,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-7 | — | 241 | 184 | F+12.5 | 10,0 | 2,5 |
| KVV-8 | — | — | 241 | F+12.5 | 10,0 | 2,5 |
Aluminum lugs along the cross-section of the conductor are attached to the ends of the current-carrying conductors using a crimping method, then they are screwed to the busbars on switchgears. A wire with a tip must be soldered to the armored tape, which is attached to the ground loop on both sides of the cable.
terms of Use
The technical characteristics of the AVBbShv cable are designed for its above-ground and underground operation. Thanks to the presence of armor, the wire is able to withstand pressure from the ground. But this is only true if the latter has low corrosive activity. Also during the installation process, it is worth considering that the cable is susceptible to tensile forces.
The wire is no less actively used in tunnels, mines and other premises. The cable can be used in open areas. The laying line must be stationary with a vertical, inclined or horizontal arrangement. The humidity level should not exceed 90%, and operating temperature indicators are indicated in the technical specifications of the cable.
Comprehensive supply of cable and wire products and fittings
The AVBbShv power cable (this marking is already outdated - the product is currently marked AVBShv) is an armored product equipped with aluminum conductors, reliable insulation and a protective hose made of polyvinyl chloride plastic.
The AVBbShv cable meets all the requirements of regulatory documentation TU 16-705.4992010. OKPO code - 35 3771 5700.
Power cable with aluminum conductors AVBBShv
Purpose and scope of application of the AVBbShv cable:
- transmission/distribution of electricity in electrical installations designed for a rated voltage of 0.66/1 kV (at a rated frequency of 50 Hz);
- single installation (laying) in various cable systems and inside industrial premises;
- laying along the cable route (without limiting the difference in levels) and in sections of vertical configuration;
- use of alternating voltage in electrical networks with a grounded/insulated neutral (if the duration of operation in such networks during a single-phase short circuit to ground does not exceed 8 hours, and the total duration of operation in this mode for a year does not exceed 125 hours);
- air operation, if during operation there may be a real threat of mechanical damage;
- use of this cable in areas with cold/temperate/tropical climates;
- operation on land or bodies of water (rivers, lakes) located at an altitude of up to 4300 meters above sea level;
- installation in the ground (installation trenches), characterized by low to high corrosive activity, in the presence/absence of stray currents, provided that the cable is not subject to significant tensile loads;
- laying cable communications in rooms of any degree of humidity (technological tunnels), cable mezzanines, sewers, collectors, mine structures, industrial premises and structures (including partially flooded ones), if the laying environment is characterized by low/medium/high corrosive activity;
- installation of cable networks in rooms with a high fire hazard;
- laying in hazardous areas (classes B-Ib, B-Id, B-II and B-IIa);
- arrangement of horizontal/inclined routes.
Explanation of AVBbShv marking:
- A - the core is made of aluminum;
- B - the insulation material is PVC plastic;
- B - galvanized strips were used to make armor;
- b - without a protective cushion (represents the inner part of the protective layer and is placed under the armor coating to protect the element located under it from corrosion and mechanical damage that can be caused by tapes/wires of the armor layer);
- Shv - pressed hose (made of PVC plastic).
AVBBShv cable design
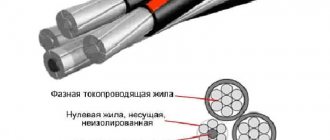
1. Current-carrying conductor - made of aluminum, single-wire/multi-wire configuration, round/sectoral shape, corresponds to classes 1-2 (according to GOST 22483). Possible number of cores - 1/2/3/3+1/4/5. 2. Insulation layer - made of PVC plastic. 3. Cordel - made of either PVC plastic or non-vulcanized rubber mixture. The internal and external gaps formed between the insulated conductors are completely filled, as a result of which the cable takes on a round shape. 4. Cable core - is a twist of insulated conductors. 5. Armor layer - consists of 2 galvanized steel strips. 6. Protective hose - made of PVC plastic.
Analogues of cable AVBBShv:
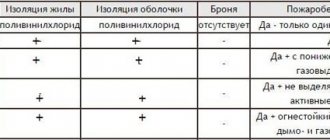
- AVBbShvng(A) - is distinguished by the presence of a protective hose made of polyvinyl chloride composite with reduced fire hazard indicators, and the ability to perform group installation.
- AVBbShvng(A)-LS - is characterized by the presence of a protective hose made of PVC composition and has reduced gas/smoke emission and fire hazard.
In some cases, the AVBbShv cable can be replaced with the following models:
- ApvBbShv - this cable uses a polyethylene sheath instead of a PVC sheath;
- AVBbShvz - here unvulcanized rubber mixture is used as a filler;
- AVVBG - this product is used without a protective shell.
When selecting optimal analogues, it is necessary to take into account the actual operating conditions of a given power cable. It should be borne in mind that it is not advisable to use these analogue cables in all situations.
Installation
When installed separately, the AVBbShv cable does not propagate fire (complies with IEC 60332-1 standards). Group installation of cables is allowed exclusively in outdoor electrical installations, as well as inside industrial premises, where maintenance personnel are present only periodically (with the mandatory use of fire protection equipment).
In emergency operation mode, heating of current-carrying conductors above +80 degrees Celsius is not allowed. In this case, the duration of cable operation in emergency mode cannot exceed 8 hours per day (but not more than 1000 hours over the entire service life).
The AVBBShV model has a design that provides complete reliable protection of the product from possible damage caused by external mechanical loads. This circumstance makes it possible to lay the specified cable in soils even in an open way, but provided that there are no tensile loads on the cable at the installation site.
To effectively protect current-carrying cable cores from damage that may occur during excavation work, steel spiral armor is provided inside the plastic hose.
The disadvantages of the AVBBShV cable include the presence of significant bends and deformations. The reason for this weak point is the use of aluminum in the design - by definition, a fairly brittle metal.
The AVBbShv model can be used for single installation in rooms with a high fire hazard. Especially for such cases, a modification was developed, the name of which contains an additional letter index “LS”. It indicates the use in the design of a protective hose made of polyvinyl chloride, which has a reduced level of flammability.
A special feature of this model is the different cross-section of all current-carrying conductors, which fully complies with the standards of TU 16-705.499-2010. At the same time, a 4-core cable (with a conductor cross-section from 25 mm2) may have a core for “zero” or phase, which is thinner than the rest of the cores.
The high demand for AVBbShV cable is explained not only by its high reliability, but also by its affordable price. In particular, it is approximately 4 times cheaper than its high-voltage copper analogue.
Specifications
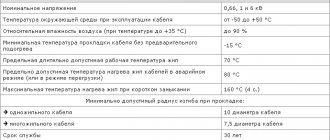
| Rated AC voltage | 0.66/1 kV frequency 50 Hz |
| Rated DC Voltage | 1.4 kV for single-core cables |
| AC test voltage | 3.5 kV frequency 50 Hz |
| DC test voltage | 8.4 kV for single-core cables |
| Test holding time | 10 minutes |
| Electrical resistance of the conductor | 0.46 Ohm/km |
| Insulation resistance at 20 °C | not less than 2.5-12.3 MOhm*km |
| Construction length, not less | for sections 6-16 - 450 meters for sections 25-70 - 300 meters for sections 95 and above - 200 meters |
| Minimum bend radius | for single-core cables - 10 outer diameters for multi-core cables - 7.5 outer diameters |
| Permissible forces when pulling the cable along the laying route | 50 N/mm2 |
| Operating temperature range | from -50°С to +50°С |
| Minimum temperature for cable installation without preheating | -15°С |
| Type of climate control | UHL (operating temperature up to -60°C) T (resistance to mold fungi) |
| Accommodation category | 1 and 5 according to GOST 15150-69 |
| Resistance to high relative humidity at ambient temperatures up to +35°C | 98% |
| Fire safety class | according to GOST 31565-2012: O1.8.2.5.4 |
| Permissible core heating temperature | +70°C long-term permissible +90°C in overload mode +140°C limit in case of short circuit +350°C under the condition of non-ignition in case of short circuit |
| Warranty period | 5 years |
| Life time | at least 30 years |
Insulation and Sheath Comparison Chart
| Characteristic name | Value for PVC Insulation | Value for PVC outer sheath and hose |
| Before aging | ||
| Tensile strength, not less | 12.5 N/mm | 12.5 N/mm |
| Elongation at break, not less | 150% | 150% |
| After aging | ||
| Tensile strength, not less | 12.5 N/mm | 12.5 N/mm |
| Deviation* of tensile strength value, no more | ±25% | ±25% |
| Elongation at break, not less | 150% | 150% |
| Deviation of elongation at break value, no more | ±25% | ±25% |
| Punching depth at high temperatures, no more | 50% | 50% |
| Water absorption - increase in mass, no more | 10 mg/cm2 | — |
| Resistance to low temperatures - deviation of elongation at break, no more | — | 20% |
Comparative table of cross-sections and dimensions of the AVBbShv power cable:
| Number of current-carrying cores and their nominal cross-section, mm2 | Design outer diameter, mm | Estimated weight, kg/km |
| 1x1.5 | 6,33 | 60 |
| 1x2.5 | 6,77 | 80 |
| 1x4 | 7,75 | 90 |
| 1x6 | 8,3 | 110 |
| 1x10 | 9,17 | 140 |
| 1x16 | 10,38 | 180 |
| 1x25 | 12,88 | 280 |
| 1x35 | 14,09 | 340 |
| 1x50 | 16,05 | 440 |
| 1x70 | 16,81 | 510 |
| 1x95 | 19 | 680 |
| 1x120 | 21,18 | 810 |
| 1x150 | 23,36 | 990 |
| 1x185 | 25,98 | 1240 |
| 1x240 | 28,82 | 1540 |
| 1x300 | 31,66 | 1850 |
| 1x400 | 35,59 | 2340 |
| 1x500 | 39,41 | 2900 |
| 1x625 | 49,7 | 3856,48 |
| 1x630 | 43,01 | 3480 |
| 1x800 | 47,05 | 4200 |
| 1x1000 | 52,18 | 5190 |
| 2x1.5 | 12,67 | 260 |
| 2x2.5 | 13,54 | 300 |
| 2x4 | 15,39 | 400 |
| 2x6 | 16,48 | 450 |
| 2x10 | 18,23 | 560 |
| 2x16 | 21,31 | 710 |
| 2x25 | 25,22 | 1060 |
| 2x35 | 27,95 | 1310 |
| 2x50 | 24,24 | 990 |
| 2x70 | 26,86 | 1210 |
| 2x95 | 29,91 | 1540 |
| 2x120 | 32,1 | 1790 |
| 2x150 | 35,59 | 2210 |
| 2x185 | 39,08 | 2690 |
| 2x240 | 43,24 | 3310 |
| 2x300 | 23,1 | |
| 2x400 | 26,1 | |
| 3x1.5 | 13,1 | 290 |
| 3x2.5 | 14,09 | 330 |
| 3x4 | 16,15 | 430 |
| 3x6 | 17,25 | 500 |
| 3x10 | 19,22 | 630 |
| 3x16 | 21,4 | 790 |
| 3x25 | 26,86 | 1210 |
| 3x35 | 29,58 | 1460 |
| 3x50 | 28,72 | 1410 |
| 3x70 | 31,33 | 1730 |
| 3x95 | 35,49 | 2250 |
| 3x120 | 38,44 | 2680 |
| 3x150 | 42,15 | 3250 |
| 3x185 | 46,51 | 3950 |
| 3x240 | 51,97 | 4960 |
| 3x300 | 55,1 | 4286 |
| 3x400 | 61,8 | 5311 |
| 3x2.5+1x1.5 | 20 | 562 |
| 3x4+1x2.5 | 16,8 | 409 |
| 3x6+1x4 | 19,2 | 549 |
| 3x10+1x6 | 20,9 | 562 |
| 3x16+1x10 | 23,1 | 684 |
| 3x25+1x10 | 25,3 | 892 |
| 3x25+1x16 | 29,37 | 1410 |
| 3x35+1x16 | 32,43 | 1730 |
| 3x50+1x16 | 31,5 | 1512 |
| 3x50+1x25 | 31,77 | 1750 |
| 3x70+1x35 | 35,49 | 2230 |
| 3x95+1x35 | 39,9 | 2419 |
| 3x95+1x50 | 40,5 | 2930 |
| 3x120+1x70 | 43,67 | 3430 |
| 3x150+1x50 | 50 | 3602 |
| 3x150+1x70 | 48,7 | 4290 |
| 3x185+1x95 | 53,28 | 5140 |
| 3x240+1x120 | 59,61 | 6460 |
| 3x300+1x150 | 60,5 | 4934 |
| 3x400+1x185 | 68,7 | 6264 |
| 4x1.5 | 13,97 | 310 |
| 4x2.5 | 15,06 | 380 |
| 4x4 | 17,36 | 490 |
| 4x6 | 18,67 | 580 |
| 4x10 | 20,74 | 730 |
| 4x16 | 22,3 | 752 |
| 4x25 | 27,3 | 1115 |
| 4x35 | 27 | 1111 |
| 4x50 | 30,2 | 1379 |
| 4x70 | 33,5 | 1745 |
| 4x95 | 38,9 | 2367 |
| 4x120 | 41,8 | 2770 |
| 4x150 | 45,7 | 3350 |
| 4x185 | 50,4 | 4054 |
| 4x240 | 56,4 | 5170 |
| 4x300 | 65,73 | 7900 |
| 4x400 | 72,5 | 8882 |
| 5x1.5 | 14,96 | 350 |
| 5x2.5 | 16,05 | 400 |
| 5x4 | 18,67 | 540 |
| 5x6 | 16,6 | 330 |
| 5x10 | 18,7 | 433 |
| 5x16 | 24,6 | 902 |
| 5x25 | 29,8 | 1274 |
| 5x35 | 33 | 1600 |
| 5x50 | 33,8 | 1697 |
| 5x70 | 38 | 2227 |
| 5x95 | 43,4 | 2909 |
| 5x120 | 46,9 | 3435 |
| 5x150 | 50,6 | 4058 |
| 5x185 | 56,7 | 5029 |
| 5x240 | 62,5 | 6201 |
| 5x300 | 23,1 |
Current-carrying conductors must be single- or multi-wire with nominal cross-sections in accordance with the table:
| Core type | Nominal core cross-section, mm | |
| round | sectoral (segmental) | |
| Single wire | 2,5-300 | 25-400 |
| Stranded | 25-1000 | 25-400 |
Four-core cables with conductors with a nominal cross-section of 25 mm2 or more may have one conductor of a smaller cross-section (neutral or ground) in accordance with the table:
| Purpose of the core | Nominal core cross-section, mm | ||||||||||
| Main | 25 | 35 | 50 | 70 | 95 | 120 | 150 | 185 | 240 | 300 | 400 |
| Zero or grounding | 16 | 16 | 25 | 35 | 50 | 70 | 70 | 95 | 120 | 150 | 185 |
Explanation of the designations VBBbShv, VBBShvng, VBBShvng-FRLS and PvBbShv
So, the VBBShV cable marking consists of three groups of symbols: “V” - “BB” - “Shv”. Formally, there is also a fourth, hidden symbol, which is placed in the first position and this is the symbol responsible for the material of the core. Since at first we see the letter “B” and not “A”, this automatically means that the wire is copper. Further decryption proceeds as follows:
- B – core insulation made of PVC plastic,
- BB – two-ball armor made of galvanized steel strips. It is wound in the form of a spiral with the calculation of the mutual overlap of the joints,
- Shv – the outer layer of the hose type, made of PVC.
Next comes the VBBShvng cable, which, judging by the designation, is almost an analogue of the previous one, with the exception of the last pair of characters “ng”. It means that the materials used are non-flammable, that is, if a fire occurs in the wiring, they will prevent its spread.
The VBBShvng-FRLS cable is a partial analogue of the previous one. The symbols “FR” and “LS” after the dash mean high fire resistance and low smoke emission (Low Smoke). A fire on such wiring not only spreads poorly, but also creates optimal conditions for the evacuation of personnel due to the absence of smoke.
The last is the cable under the brand PvBbShV, which is an analogue of VBBShV, with the only exception that the basic core insulation is made of vulcanized polyethylene (“Pv”).
How to choose the right cable?
Before purchasing a cable for use at home, it is necessary to determine the required cross-section of the cores in accordance with the current power. In this case, you should also take into account the number and power of household electrical appliances and the total load on the network.
When choosing, you should take into account the fact that many manufacturers, to save money, reduce the cross-sectional area of the cores by 10% (which is allowed according to the specifications). Reducing the area reduces the technical characteristics of the wire, which can lead to an emergency situation, so products from trusted manufacturers should be preferred. You can check the cross-section using a special tool or by visual inspection of the casing.
Understanding the rules for deciphering the name abbreviation will also greatly help when selecting a cable. By marking you can determine the internal structure and types of materials used in manufacturing.
AVBbShv 4x16 - reliable, high-quality and time-tested power cable