In order to connect stationary electrical equipment, wires and cables are used, performing installation on an ongoing basis. What should you do if you need to supply electricity to a device, installation or mechanism that is constantly changing its location? A conductor is needed that must be as flexible as possible without losing its physical and electrical properties. The power cable kg is designed specifically for such cases.
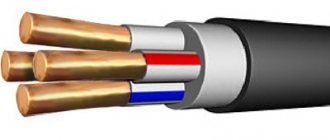
Flexible copper cable
Design
How is the kg wire structured, and what allows it to work for a long time without damaging the insulation or breaking the wires inside? Rubber insulation gives the product flexibility. If we compare it with paper or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulation, it is designed for several tens of thousands of flexion and extension cycles.
Important! The rubber insulation of flexible cables fails only when it self-destructs. This can occur as a result of aging under the influence of external causes. We are not talking about mechanical damage.
Impacts that influence the rate of aging include:
- long-term exposure of products to the sun (ultraviolet);
- high ambient temperature;
- increased content of ozone or oxygen in the air.
Over the years, the outer coating of the conductors becomes rougher and begins to crack. During long current loads, ionization of ozone inclusions in the rubber structure occurs. This can cause electrical breakdown, which also leads to cable failure.
For your information. The use of butyl rubber (BR) or ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) in the production eliminates the presence of ozone inserts. The linear structure of the molecules of such compounds allows almost no (BC) or no (EPC) ozone in the insulating layer.
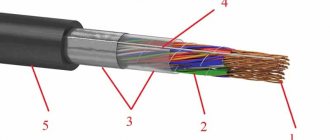
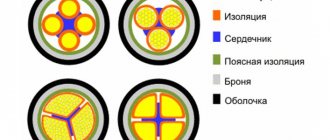
The design of the CG includes the following positions:
- core - stranded, copper;
- core insulation – rubber (RTI-1, RTI-2-HL);
- rubber sheath RTSh-2, RTShM-2, RTISH (for single-core cables).
The number of cores can vary from 1 to 5. The cross-section of the current conductors lies in the range of 1-240 mm2.
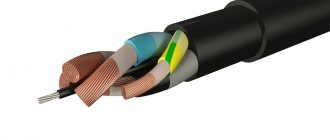
KG cable structure
Interesting. In the single-core version, PET-E (this is a synthetic film) is used as a covering for the cores, on top of which a rubber sheath is applied. This is true for conductors with a large cross-section.
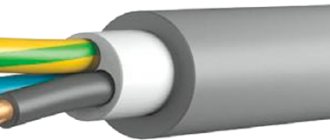
KG single-core large section
Application area
KG cables are used to connect mobile mechanisms to electrical networks. They are suitable for indoor and outdoor use. Installation underground, as well as use as a permanent connection for installations, is not allowed. The wire insulation is not designed to withstand mechanical loads. It can be damaged even from the pressure of hard soil. However, cable installation in pipes is permitted.
Subject to safety precautions, it is permissible to lay the conductor outdoors. It is able to withstand sub-zero temperatures.
KG wire is often used to connect taps, submersible pumps and welding machines.
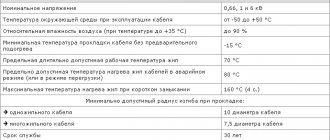
Technical characteristics of the KG cable
The main document regulating the parameters of flexible cable products is GOST 24334-80. According to this regulation, the kg cable has the following technical characteristics:
- core flexibility class – 5;
- the cable is designed to work with time-invariant current (with voltage up to 1 kV) and alternating current (with voltage 0.66 kV);
- maximum relative humidity of the ambient air – 98% (at Tamb = 350C);
- resistance to bending for any number of cores;
- minimum bending radius – not less than 8 D (external);
- insulation resistance (Rizol) – 50 MOhm/km;
- resistance to solar radiation;
- tensile forces (relative to the full cross-section of the cores) – up to 19.6 N/mm2;
- duration of work – 4 years or more.
SIP cable 2: technical characteristics
The number of flexion-extension cycles is from 30,000 to 40,000 (depending on the section S).
Important! When temperature conditions change (from -600C to +250C) for cables kg chl (UHL), the coefficient indicating a decrease in flexibility should not exceed a value of 10.
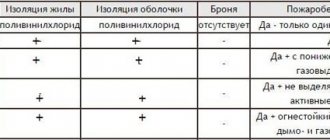
Table of characteristics of various brands of KG
Conditions for installation and operation of the KG cable
The cable in the standard version is intended for operation at ambient temperatures from minus 40°С to plus 50°С, in the tropical version – from minus 10°С to plus 55°С, in the cold-resistant version – from minus 60°С to plus 50° WITH. Can be laid without preheating at a temperature not lower than minus 40°C. The bending radius during installation and operation must be at least 8 outer diameters of the cable, tensile forces must not be more than 2 kgf per 1 mm2 of the total copper cross-section of all cores. Service life is 4 years from the date of manufacture of the cable.
Marking
Usually the abbreviation of the brand of cable products can tell you what kind of product it is, what it consists of and where it can be used. The main letter indices include:
- K – cable;
- G – flexible.
VVG cable - decoding and application
In addition, additional letters and numbers may follow, namely:
- T – tropical climatic version (heat and humidity);
- CL – cold climate with sub-zero temperatures (below -250C);
- N – non-flammable outer coating;
- 1st digit – number of cores (2-5);
- 2nd digit – S cores, mm2.
Attention! The symbol on the surface of the cable includes the plant logo and year of manufacture. Marking is applied along the entire length of the cable every 550 mm.
The conductors are wound on drums or twisted into coils. In this case, the label attached to the winding includes the following data:
- factory sign;
- cable name;
- length, m;
- weight, kg;
- certificate of conformity (if accompanied by a certificate);
- release date.
In the case of a paper label, it must be stamped by the technical control department.
Important! The core insulation is color coded. The “grounding” (green-yellow) and “grounding” (light blue) cores are highlighted in separate colors.
For example, a four-core CG may have the same color marking for three cores, and green-yellow for the fourth. In this case, the cross-section of the grounding conductor is allowed one step lower: KGng 3 * 2.5 + 1 * 1.5, but this is not necessary. Manufacturers produce products in which all four cores have the same cross-section.
Advantages
The main advantages of this brand of cable are:
It can be used at a humidity of 100%, no matter whether it is a damp room or outdoors. Highest flexibility. Recommended for use in installations with high vibration.
True, there are some restrictions. For example, to connect welding machines, mobile or portable tools, it is necessary to take into account the technical characteristics of consumers.
- Firstly, their voltage should not exceed 660 volts.
- Secondly, if an alternating current network is used, the oscillation frequency should not exceed 400 Hz.
- Thirdly, the power consumption in terms of current should not exceed 630 amperes.
We add that when connected to a DC network, its voltage should not exceed 1000 volts. If all these indicators are taken into account when operating the KG cable, then it is guaranteed to last four years.
Main technical and operational characteristics of KG cable
Dimensions
All cable products are divided according to the number of cores in the product. It was already mentioned above that the KG cable (with any technical characteristics) is subject to this classification. But there is one dimensional indicator that determines the power that this cable can withstand. This is the cross-section (area) of the core.
- In a single-core cable, the cross-section varies from 2.5 to 50 mm². There is a certain scale of standard values.
- In two- and three-core from 1.0 to 150 mm².
- In four-core from 1.0 to 95 mm².
- In a five-core cable from 1.0 to 25 mm².
As mentioned above, the grounding conductor is always one order of magnitude smaller than the phase conductor. For example, CG 3×6+1×4. That is, the decoding here is as follows - three phase conductors have a cross-section of 6 mm², the grounding conductor is 4 mm².
Temperature indicators
This is one of the important parameters that affects the service life of the cable itself. For the most part, KG cables can be operated in a temperature range from minus 40C to plus 50C. But there is a special abbreviation that helps you decide in which climate region which cable is best to use.
- If the operating conditions are sub-zero, then look for the letters “ХЛ” in the wire marking.
- If service conditions are tropical, then look for the letter “T”.
- If the insulation is made of non-combustible materials, then the brand will be designated as KGn cable.
As for resistance, the following are taken into account: wire length equal to 1 km, ambient temperature - +20C, transmitted current power 2.5 kW with an oscillation frequency of 50 Hz. And with all this, the resistance should be 50 mOhm. When testing single-core conductor material, it must be immersed in water. If all these parameters converge, then the maximum heating temperature will be +75C. If the temperature rises, then something is wrong in the cable: either the cores have broken, or the insulation has leaked.
And one more important addition is the length of the product depending on its cross-section
- The KG cable with a cross section of 1-35 mm² is available in lengths up to 150 m.
- Section 35-120 mm² – length up to 125 m.
- Cross section 150 mm² – cable length 100 m.
Dimensions
When supplied to consumers, cable products of the KG brand are measured in meters, indicating the number of kilograms in the coil. Winding on drums and coils depends on the cross-section of the cores and their number. The most popular windings have the following parameters:
- 150 m at S = 1-35 mm2;
- 125 m at S = 35-120 mm2;
- 100 m at S = 150 mm2.
By the way. When purchasing a cable at retail, the seller measures the required length.
Cable diameters KG
Available methods for quality control of KG cable
Control methods are presented that, although not strictly corresponding to the specifications, allow making preliminary conclusions about the quality of the cable if the measured values differ significantly from the regulated ones. The final conclusion about the compliance of the cable with the specifications can be made only after testing the cable in a specialized laboratory using strict methods and in the volumes specified in the technical specifications.
Visual inspection The following can be checked: the number and color of cores, the integrity of the insulation and sheathing and the ability to separate them without damage.
Measurement of structural dimensions Can be checked using suitable measuring instruments: thickness of insulation and sheath, diameter of wires in the core dpr. Calculating the cross-section of the core using the formula 0.785dpr2N (where N is the number of wires in the core) is not a strict method for controlling the cross-section of the cores, because confirmation of cross-section compliance is electrical resistance, however, a significant deviation of the calculated cross-section from the nominal (more than 15%) may serve as a basis for doubts about the quality.
Measurement of the electrical resistance of current-carrying conductors Can be carried out on a finished cable with an ohmmeter with a suitable measurement limit (for cables with a small cross-section at a normal length in a coil or on a drum, it can be several Ohms) and recalculated for a length of 1 km. If the cable has twisted cores, the obtained values should be reduced by 1.02 times. Particular attention should be paid to making good contact with the test leads.
Temperature indicators
The main points characterizing the temperature dependence of various cable parameters include:
- maximum permissible operating temperature – 750C;
- temperature range for operation – from – 400С to +500С;
- insulation resistance - its value (50MΩ/km) is measured strictly at T = +200C.
Additional designations indicate the peculiarities of the temperature climate regime. For example, the conductor’s kg chl decoding indicates the permissibility of operation in cold climates.
Interesting. Tests of single-core CG cables require immersing the product in water. When current is passed through it, its maximum heating should be no more than 750C for a working cable.
Modifications
There are several models from this category of flexible conductors: KGVV and RKGM. They are designed for specific applications. The KGVV cable has polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulation in its structure, not rubber. This increases the service life to 25 years. It is used to connect mechanisms operating in quarries: these are excavators, cranes and other large mechanisms that consume alternating and direct current.
Important! KGVV allows the supply of current with a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage from 660 to 1000 V. The operating voltage range at direct current is from 1000 to 1500 V.
Decoding of KGVV markings
The RKGM modification cable has silicone insulation in its structure. He is not afraid of practically anything except oils and chemically aggressive substances. Temperature range – from -600С to +1800С. Available with core cross-sections from 0.75 to 120 mm2. Used in alternating current networks with a voltage of 0.66 kV and a frequency of 50 Hz.
Explanation of the RKGM designation
Explanation of markings
Let's decipher the possible letter designations for the KG cable and its modifications:
- “K” – cable;
- “G” – flexible type;
- “N” – there is an additional protective layer that prevents combustion;
- “T” – can be successfully used in tropical climates with a minimum permissible air temperature of -10 degrees. Celsius;
- “HL” – intended for use in cold climates with a minimum permissible temperature of -60 degrees. Celsius.
Modifications
The KG cable is available in various modifications. Two of them, KGVV and RKGM, will be discussed below. The KGVV wire is characterized by the presence of polymer insulation (instead of rubber as in the standard one). It could be polyvinyl chloride. Thanks to this, the service life of the product increases significantly (25 years). Using KGVV, they switch bulky and high-power equipment, devices connected to AC and DC sources. Examples include excavators working in a quarry, cranes, etc.
The polyvinyl chloride insulating layer significantly expands the operating temperature range, which ranges from -50 to +50 degrees. Celsius. Thanks to this, the KGVV cable does not have climatic modifications, since it can be used under any conditions.
When connecting the KGVV to an AC electrical network, you need to monitor the maximum voltage and frequency - up to 660/1000 V and 60 Hz, respectively. When switching with DC networks, the voltage should be in the range of 1000-1500 V. The non-flammable properties of KGVV are manifested exclusively when installed alone. Group installation of a cable with other wires does not provide such protection.
Another modification of the CG is RKGM. This abbreviation stands for as follows:
- “R” – rubber insulation;
- “K” – layer of organosilicon;
- “G” – bare;
- “M” – copper conductors.
When examining the design of the RKGM, one can find strands of copper wires, an insulating layer of silicone rubber and a high-quality braid of glass fiber impregnated with varnish.
For other technical and operational parameters, we highlight the following:
- The cross-sectional area of the cores is in the range of 0.75-120 square meters. mm;
- bending radius – from two outer diameters;
- operating temperature range – from -60 to +180 degrees. Celsius;
- withstands operation in conditions of 100% humidity at a temperature of +35 degrees. Celsius;
- It is possible to connect to an alternating current source at a voltage of 660 V and a frequency of 40 Hz.
Often, electrical products are used to connect equipment and electrical appliances to AC and DC networks. It is possible to install the cable by air, which is due to increased resistance to precipitation, mechanical and wind loads, and ultraviolet rays of the sun.
The main requirement is related to the absence of contact area with a chemically aggressive environment, mineral or natural oils. Thus, before connecting the RKGM, make sure in advance that there are no oil stains indicating equipment leakage. If there are any, then you must first eliminate any leaks by cleaning the surface. Similar to other types of cables, RKGM is selected depending on the load.
Difference between cables KG, KG-HL and KGN
Regardless of the type of cable, it is suitable for all areas of operation listed in the first section of the article. Any CG is resistant to ultraviolet radiation, and is also used for switching mobile units.
Structurally, the cores of each wire consist of copper wires, have insulation and a separating layer of polyethylene terephthalate. Manufacturers choose natural or vulcanized rubber to insulate the cores, while the sheath is made of isoprene synthetic rubber.
There are several types of cable depending on the climatic version. Let's look at the main differences:
- KG is a standard wire with an operating temperature range from -40 to +50 degrees. Celsius;
- KG-HL – modification for cold climates (from -60 to +50 degrees Celsius);
- KG-T – for tropical climates (from -10 to +55 degrees Celsius);
- KGN is a product characterized by resistance to oils, having a fireproof shell (from -30 to +50 degrees Celsius) and intended for use in aggressive environments.
KG-T stands out from the rest in that the current-carrying copper conductors are additionally coated with tin or its alloy with lead (40/60 ratio). The insulation of such a wire, which can be used in tropical areas with a hot and humid climate, must meet special requirements. Fungicides are added to butadiene rubber to prevent the formation and spread of mold or mildew. These substances are not used in other modifications of CG.
The KG-HL cable is used in low temperature conditions (for example, in the Arctic and Antarctic). To create such a product, new technologies for protecting insulation and rubber were required. The latter must withstand extremely low temperatures. To do this, organosilicon substances are added to the composition of butadiene or natural rubber. Thanks to this approach, the minimum permissible temperature was increased to -60 degrees. Celsius.
KGN contains chloroprene rubber, which makes it possible to increase resistance to oil and make the rubber less flammable. Such products are successfully used in mines and quarries.
A regular KG can be easily replaced with other modifications - KG-HL and KGN. On the other hand, reverse replacement can lead to dire consequences. The situation is similar with wires intended for use in networks with voltages of 380 and 660 V. Direct replacement is acceptable, reverse replacement is not.
Laying methods
Such flexible power cables are not installed permanently. They usually roll out on the ground or hang in the air. Large lengths of cable for moving devices (telphers and talcs, hoists) are hung on cables along which they are fed or collected depending on the direction of movement.
By the way. It is permissible to cover them with temporary covers, lay them in channels and corrugated sleeves or HDPE pipes, but it is unacceptable to lay them in the ground. They are not designed for this.
Cable suspension KG
Flexible power cables will last longer than the period stated by the manufacturer if all the necessary technical conditions for their operation are met. A CG conductor of sufficient cross-section will ensure uninterrupted operation of mobile electrical objects.
Color designation of cores of power cable KG
The outer insulating layer of a single core is painted in the desired color or has a blue stripe along its entire length. Most often, the grounding circuit is made yellow-green, the neutral conductor is blue or cyan (or with the symbol “0”).
When designating the cores of a KG cable, it is prohibited to use three colors - red, white and gray. Other shades are acceptable, but the designation is not important. Depending on the individual preferences of the customer, the cores can be painted in certain colors, have stripes, or be produced without colors.
Depending on the number of cores, the colors may be as follows:
- three veins - yellow-green, blue and brown;
- four – yellow-green, blue, black and brown;
- five – yellow-green, blue, brown and two black;
- six – yellow-green, blue, brown and three black.