Our organization is ready to offer you the most popular brand of cable in the country for a wide range of work - VVG, in an assortment from leading domestic manufacturers. Thanks to close cooperation with the largest manufacturers, we are ready to give a 100% guarantee of maximum reliability and quality of cable products.
You can find out any information you are interested in by calling in the corner of the screen, or in the specially designated “Contacts” section - there you will find addresses and maps.
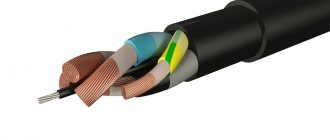
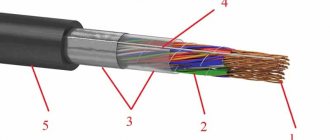
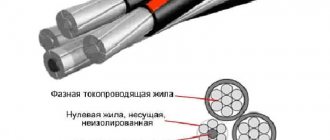
Design of the VVG cable product
The structural composition of the cable with the abbreviation VVG is the following device:
- In the center there is a metal core that carries current, the material of which is copper. The vein can be round or sectoral in shape. It is common for multi-core cables of these types to contain a grounding or neutral conductor;
- The conductors can be distinguished by the bright colors on the shells: the grounding conductors are contained in light blue or light blue shells, and the grounding conductors are yellow-gray.
- A twist is formed from several cores, the voids of which are filled with insulating material;
- This structure is placed in a surface shell, which is made of a similar polyvinyl chloride.
Decoding abbreviations and modifications
The abbreviation, which is applied to the outer surface of the cable's insulating sheath, denotes its design features and technical characteristics. The sequence of letters and numbers carries certain information. The first capital letters VVG indicate the following:
- B - the material from which the insulation of the current-carrying conductors under the outer sheath is made, in this case it is polyvinyl chloride. The letter "B" comes from the name of the main component of the vinyl insulating layer material;
- B is the outer shell material, the main composition of which is also vinyl. Such insulation is usually called PVC, it is a thermoplastic. 43% of its composition is a petrochemical product, ethylene and 57% combined chlorine. The compositions of plastic insulation may differ; some models use a PVC shell with impurities that block the spread of fire.
- G - indicates that the general sheath of the current-carrying wires does not have an armored layer; such a cable is called bare, which does not have protection from harsh mechanical influences.
All models have copper wires with a rigid monolithic or flexible multi-core structure.
There are a number of modifications of plastic insulation:
- VVGpng - in this version, the added letter designation “png” indicates that it can be laid as part of a group of cables of other brands. Its outer shell does not propagate combustion. (png – flat non-flammable)
- VVGng–ls means that the composition of the plastic insulation contains impurities that, during combustion, reduce the release of toxic gases and smoke;
- VVGng-hf, in case of strong fire in the environment and high temperature, the insulating layer burns out and does not emit corrosive gases;
- VVGng-fr indicates the presence of a mica tape in the insulating layer, which creates a thermal barrier between the environment and the current-carrying conductors.
If there are no such markings, they spread the combustion of the insulation; this is a regular VVG.
The marking of the VVG cable in the digital abbreviation designation indicates the number and cross-section of the current-carrying conductors.
Power cable VVG APG 3x2.5+1 in this version VVG, the labeling shows:
- PNG - flat, non-flammable;
- 3 – number of conductive cores;
- 2.5 – cross-sectional area of wires;
- +1 – additional ground wire in the cable.
For laying under plaster, it is most often convenient to use VVG wire of a flat design; it fits compactly into the grooves and is easily plastered without protruding on the surface.
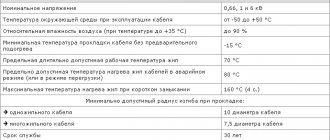
Specifications
Unom - from 0.66 to 1 kV; Frequency - 50 Hz; Operating temperatures, t - from -50 °C to +50 °C; Air humidity (at t0 +35 °C) – up to 98%; Working life: up to 30 years; Warranty from the date of purchase: 5 years; Installation without heating: at temperatures from -15 °C;
Maximum heating:
- In stable mode: +70 °C;
- In emergency situations: +80 °C;
- With one core - 10;
- With several cores - 7.5.
Minimum bend radius:
Construction length:
- from 1.5 mm2 to 16 mm2 - 450 m.
- from 25 mm2 to 70 mm2 - 300 m.
- from 95 mm2 and above - 200 m.
More clearly in the table:
Analogues of VVGng-LS
VVGng-LS-P is flat, with a copper core, insulation and PVC sheath of reduced fire hazard. VVGzng with filling, with copper core, PVC insulation, PVC sheath of reduced flammability. VVGng-P is flat, with a copper core, PVC insulation, and a PVC sheath of reduced flammability. VVGz with filling, with copper core, insulation and PVC sheath. VVG-P is flat, with a copper core, insulation and PVC sheath. VVGng-FRLS with copper core, insulation and PVC sheath of reduced fire hazard. Fire resistant. VVGng with copper core, PVC insulation, PVC sheath of reduced flammability. VVG with copper core, insulation and PVC sheath.
Estimated weight for VVG cable
| Core cross-section, mm., External ? cable, mm. | Weight of 1 km cable, kg. | ||
| With copper core | With aluminum core | ||
| 1.5 2.5 4 6 10 16 25 35 50 70 95 120 150 185 240 | 10.7 11.8 14.0 15.3 17.4 20.3 24.6 27.4 31.8 34.8 38.8 42.0 46.2 50.2 56.6 | 170 231 343 456 674 1007 1537 2035 2844 3811 5051 6246 7763 9472 12235 | — 151 216 265 356 499 743 940 1301 1625 2120 2544 3135 3765 4831 |
Types of cable markings
Due to its availability and reasonable price, the VVG brand conductor has become widespread in the installation of electrical wiring in private construction. The marking of this product is presented in several forms:
- A standard VVG cable consists of a round wire made of copper and protected by double insulation of PVC or plastic. Used in premises for permanent residence.
- VVGP cable is a copper wire (“P” stands for flat), which is used in places with variable temperature conditions. It has a flat cross-sectional shape and is equipped with an additional insulating layer, and is also more durable in use.
- Copper cable VVGng is a wire with a round cross-section. The central core has a special flexible mesh winding. The outer insulating layer is made of polyvinyl chloride. Even large industrial enterprises do not refuse to use this product, since it is made of materials that are not subject to combustion and, due to its flexibility, is less susceptible to fractures.
- Features of flat copper wire, denoted by the abbreviation VVGP ng, are the presence of double insulating protection, which uses polymers. Polymers play a protective role and ensure extended cable life.
- The VVGng-ls marking indicates that it prevents combustion and does not emit soot and smoke during an open flame. The presence of plastic in the winding does not allow installation outdoors or in rooms with temperatures below +5 °C.
- For industrial use, a product with the abbreviation VVGP ng-ls is suitable, which has increased strength and flexibility, the outer insulating layer of which is made of non-flammable polymers with a high degree of wear resistance.
This will be interesting to you Electrical wiring diagram: design features
Non-flammable conductors also include the VVGng-LSLTx and VVGng-HF products.
In these subtypes, external and internal insulation is made using a plasticizer with reduced flammability and smoke toxicity.
Main settings
Sip cable: decoding
Depending on the nature of use and operating conditions, the cable is selected according to the most suitable parameters. They directly depend on the properties and shape of the material from which it is made.
One of the most important parameters of the material being described is the cross-sectional area of the core. The calculation formulas are shown in the figure.
Formula for calculating the cross-sectional area, where S is the cross-sectional area of the conductor core, N is the number of conductors in the core (for stranded ones), D is the diameter of the wire, π – 3.14
The resistivity and, consequently, the limiting current value at which the conductor is heated depends on the cross-sectional area. This parameter is usually determined for each cable individually, since different manufacturers may use different grades of copper. When choosing a cable, they are guided by such a parameter as the long-term permissible current.
Shell modifications
An important parameter is the technical characteristics of the insulation; the specifics of its properties are reflected in the name of the product and technical documentation for it.
The properties of the shell material mainly determine the temperature characteristics, as well as the strength and chemical resistance of the insulation. If the product shell differs from the standards in terms of the insulation characteristics of the VVG cable, this is indicated in the documentation for it.
Important! Installation must be carried out at ambient temperatures below -15°C.
Number of cores and cable shape
The VVG p cable has numbers after all letter abbreviations. The first, from 2 to 5, means the number of cores, the second - a fractional figure means the cross-sectional area in mm². If after the second digit there is a + sign and another digit, then this indicates the number of wires in the core and the diameter of these wires. For example, the description of VVGng 5×22+1.2 has the designation that it is non-flammable and has 5 wires, each of which consists of 22 wires, with a cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200beach wire 1.2 mm².
Some manufacturers may have different cross-sections to save copper and reduce the cost of the cable. The neutral conductor, with blue insulation, has a smaller area than the main conductor (yellow-green conductor), and the grounding conductor is even thinner. According to the standard, the ratio of cross-sectional area S is indicated in the table.
Differences in diameters of some cable types
Continuous current
When choosing the required material, they are guided by the value of the maximum current at which it will be operated. This value is called the long-term permissible load current. The dependence of the load current on the cross-sectional area and cable type is shown in the table.
Dependence of maximum current on S, mm
The fields highlighted in blue and green contain values calculated from the power law along the trend line of the graph in Excel.
For four or five-core cables operated in three-phase networks, the current value is calculated as follows: to do this, multiply the value indicated for a cable of 3 cores by a factor of 0.93.
What to look for when purchasing
With a large selection of products, it will not be difficult to more accurately select the wiring of the required diameter to ensure the operation of electrical appliances of a certain power, which will save money when designing and installing wiring.
When purchasing a product, you should carefully check the quality of the product's insulation. The cable must have a smooth cut with insulation that securely wraps around the cores. The shell material should not have any smudges or signs of drying out, that is, it should be elastic without cracks.
You may be interested in: Types and types of electrical wires
To obtain complete information about the product, you should read the certificate of conformity and then rely on the technical data. Based on the operating conditions, along with the wires, you should also purchase the necessary accessories that provide additional protection when laying the cable.
Areas of use
Due to its technical characteristics, the VVG cable is actively used when installing wiring outdoors, as well as in wet rooms, and the humidity level is allowed at 98%. It can be used in industrial premises, power plants, distribution and lighting devices, residential premises (as wiring).
In premises intended for living , it is recommended to lay VVGng or VVGng-ls grades; when installing under plaster, it will be more convenient to use a flat cable. In an open manner, the product is mounted on surfaces made of non-combustible materials (brick, concrete, plasterboard). On wooden walls, protection in the form of special channels and corrugated sleeves is required.
You may be interested in this Features designation of phase and zero
A similar cable is used when installing wiring in tunnels, collectors, channels and similar places. It is not recommended to lay it in the ground without special protection, as it will be subject to mechanical and corrosive influences.
It is also considered advisable to use such wiring in rooms where there is a risk of fire or explosion (armored cable is installed in explosive areas).