Most industrial and household electrical equipment is designed to work with electrical networks up to 1000V. To distribute electricity in networks of this level, reliable power cables are needed. VVG fully meets such tasks; it is widely used in wiring and lighting lines.
Many types of VVG are produced, differing in their main characteristics, which allows you to choose the most optimal option for a particular task.
Variety of VVG types
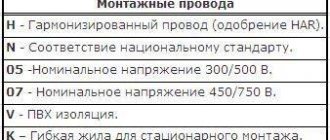
To accurately determine the type of cable product, it is marked in accordance with the national standard GOST 53769–2010.
How the marking is deciphered
Since 2010, a unified system has been used in the Russian Federation for marking cable products (660V, 1000V and 3000V), its principle is shown in the figure.
What do the fields on a marking record mean?
Below is a table that explains the VVG markings (first and second fields).
| A | B | B | G |
| If it is present in the designation, it means the wires are made of aluminum; when there is no letter, the wires are made of copper. | Type of wire insulation, “B” - means polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is used | Outer shell material, “B” - PVC | There is no protective layer (armor) |
After an abbreviation of three or four letters (VVG or AVVG), the marking indicates how many wires and their cross-section (in mm2). Next come the letters characterizing the type of core:
- “O” - indicates that monolithic conductors (single-wire) are used;
- “M” – wires consist of several cores (multi-core wires);
- After which the shape of the wires is indicated: “C” - sector or “K” - round.
If, in addition to the main wires, there are conductors with a smaller cross-section (PE and (or) N wire), a + sign is placed, after which the number of such wires and their cross-section are indicated. After this, the purpose of such conductors is given in parentheses (PE - grounding, N - zero).
The marking is completed by indicating the rated voltage (kV), optimal climatic conditions (optional) and specifications or GOST.
Let us decipher the VVG marking 3x25ms+1x16ms(N)-1 as an example. From the designation it becomes clear that this electrical cable does not have armor (letter “G”), the sheath and insulation of the wires is made of polyvinyl chloride (designation “BB”).
It has four sector stranded conductors, three of them with a cross-section of 25 mm2 (3x25ms) and one used as a zero - 16 mm2 (1x16ms(N)). This type of cable product can be used in electrical networks up to 1000 V (last parameter “1”).
Technical characteristics of VVG cable
To correctly determine the purpose of the wire, you need to clarify its technical and operational characteristics, which relate to design features, dimensions and weight, and physical characteristics. Let's consider the main selection criteria.
#1 – design features
Considering the many modifications, you should choose the most successful one from all the options presented on the market. And to do this you need to compare the characteristics of different products.
Suppose the choice is between VVG and VVGng - which one is better suited for kitchen electrical wiring? Both are copper, three-core, “sealed” in a PVC sheath. It is impossible to tell the difference by appearance.
The secret of the VVGng cable’s resistance to fire lies in the composition of the protective sheath. Under any operating conditions, it is less susceptible to combustion than VVG insulation
Considering that the kitchen is usually crammed with electrical household appliances, it is better to play it safe and choose an option with a non-flammable braid. Although for single wires with a small load a standard 3-core VVG 2-2.5 mm cable is suitable, but for group installation it is better to take a product in non-flammable insulation.
Is it possible to use other types of wires, for example, VVGng LS? Yes, but this is not always advisable. Cables with reduced smoke emission are more complex in design: they are multi-core, consist of twisted round or segment conductors, filled with plastic, one wire may have a smaller cross-section.
The option marked LS is usually used in industrial workshops or other premises where there is a real risk of accidental fire.
#2 – cross section
For domestic use, a cable with a cross-section of each core from 1.5 to 3.5 mm² is used, for industrial purposes - up to 250 mm². Products with a small cross-section are always on sale; modifications with parameters above 35 mm² are usually delivered to order.
The number of cores and their cross-section are usually written immediately after the name of the cable, for example: VVG 3x1.5 or VVGng 4x2.5. This is a common marking
If you are offered a cable with one conductor smaller in diameter, that’s okay. Most likely, this is a grounding conductor, which is usually enclosed in a yellow-green sheath.
Whether there is a core with a smaller diameter than the rest inside the outer sheath can also be determined by the markings. Usually the digital designation “+1” is assigned to the name. Example of a name: VVGng 3x2.5 mm²+1 – that is, 3 cores with a cross-section of 2.5 mm² plus one step smaller, 1.5 mm².
But more often than not, everyone selects conductors of the same cross-section, which is convenient for connecting them to electromechanical installations and to each other in junction boxes
Both “single-gauge” products and wires with a core of unequal cross-section are classified as standard and are manufactured in accordance with GOST.
#3 – parameters of long-term permissible current
When choosing a cross-section, the main role is played not so much by the resistance of the conductors, but by the magnitude of the electric current, the maximum permissible in the circuit.
It depends on the following factors:
- installation method;
- number of cores;
- cross section of each core.
The installation method means open or closed (in grooves) installation.
The table shows the dependence of the value of the continuous permissible current on the number of conductors in the cable and their cross-section - from 1.5 to 35 mm²
We remind you that VVG wires are used for AC electrical wiring from 0.66 to 1 kW.
#4 – VVG cable weight
The cable is sold by manufacturers and intermediary companies, which are construction and electrical materials stores and specialized companies. Various modifications with a cross-section of 1.5-2.5 mm² are sold in coils and sections from 10 to 100 m.
It is clear that the weight will directly depend on both the cross-section and the footage. It is calculated that the mass of a coil of VVGng wire 1 km long, depending on the cross-section, can weigh 30, 10, or 250 kg.
A 100-meter bay of 3-core VVG cable with a cross-section of 2.5 mm² weighs a little more than 13.5 kg.
#5 – other operational and physical indicators
When purchasing a coil or a piece of cable, you can inquire about other technical characteristics, which are necessarily indicated in the accompanying documentation.
The following values are typical for VVG cable:
- operating temperature – -50°С – +50°С; max temperature – up to +70 °C (with long-term use); emergency temperature – +80 °C (during short-term overheating);
- the minimum temperature value for installation is -15 °C or higher;
- relative air humidity – 98% (at t +35 °C);
- climatic version - T/UHL (tropical or moderately cold climate, respectively);
- service life – 30 years, warranty – up to 5 years;
- bending radius - at least 7.5 outer diameters for multi-core products, 10 outer diameters for single-core products.
Coils should be stored indoors for a maximum of 10 years, outdoors (under a canopy) for no more than 5 years. The absence of a canopy reduces the shelf life to 2 years.
In the tables you can familiarize yourself with the remaining parameters: insulation thickness and core resistance. Standard values for cables of various sizes are indicated.
Recommendations for using VVGng at home:
- lighting contours – 3x1.5;
- socket groups – 3x2.5;
- connection of powerful equipment (boiler, stove, dishwasher) - 3x4.
The latest version of the cable can withstand a load of up to 8 kW - this is enough to build the most energy-intensive kitchen network.
Device
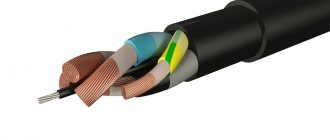
Let's look at how a regular two-core VVG and its modification VVGng (flame retardant) are constructed.
Main components of VVG
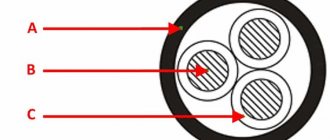
As can be seen from the figure, the design of a two-core VVG is quite simple; it includes two copper wires “C”, each of which is covered with a layer of polyvinyl chloride insulation “B”. The conductors are placed in a protective PVC sheath “A”.
Now let's see how the three-core VVGng, shown in the figure below, is constructed.
Installation of VVGng electrical cable (flame retardant)
Designations:
- A – copper conductors;
- B – heat-resistant barrier;
- C – polyvinyl chloride insulating coating;
- D – heat-resistant filler;
- E – protective shell made of polyvinyl chloride.
As you can see, the main difference between the two types of electrical cables is the presence of thermal protection in the latter (not taking into account the number of wires).
Marking of power cables
Chapter 4 GOST regulates the classification of cables. It contains a description of the abbreviations used and defines the order of their use in the symbols.
Let's see what the abbreviation VVG shows, deciphered in accordance with the standard:
- In the first place is the material used in the conductive conductors. The letter "A" indicates the use of aluminum. When using copper, the designation is put on. Accordingly, we have a copper wire;
- In second place, the insulation material is indicated. The letter “B” denotes polyvinyl chloride plastic;
- Another letter “B” indicates the wire sheath material. In our case, it is the same with insulation;
- The last letter - “G”, indicates the absence of armoring of the conductive core.
Thus, it is possible to decipher any symbol used in the marking. The VVG wire, considered as an example, has copper, unarmored conductors, sheathed in polyvinyl chloride plastic and insulated from the same material.
By analogy, it can be determined that for the VVG brand with the index “P” the decoding will correspond to that already given, with the exception of the geometric shape. The letter “P” gives an additional characteristic regarding the cross section. The wire marked with this index is flat, and the wires in it are arranged in one row.
Scope of application
The scope of application of VVG electrical cables is regulated by the national standard - GOST R53769–2010, the main criterion of which is to ensure the required degree of PB. According to the specified requirements, these cable products can be used when organizing single-type lines for power supply and lighting. VVG can be laid in a damp room.
It is allowed to use this type of cable product for group installation, but only in cases where the line is equipped with all the necessary fire protection equipment.
Decoding the abbreviation
The VVGN cable must comply with GOST 31996-2012. In the name, each letter stands for:
- B – the first letter in the name means vinyl (more precisely polyvinyl chloride);
- B – the second letter means that the cable has a second layer of insulation, which is also made of vinyl;
- G - the third letter indicates that the cable has no armor. This provides flexibility although it is less stable. This characteristic makes conductors of this type widely popular.
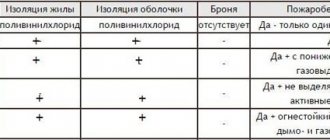
- NG - the presence of these letters in the name indicates that the cable is resistant to fire when laid together. When laid alone, almost all wires do not ignite. And to ensure this property during group installation, the cable is coated with a special solution.
Modern VVGng GOST cable may also have modifications:
- LS – gas and smoke are released in reduced quantities;
- HF – no gaseous products are released during combustion.
Main characteristics
One of the main characteristics indicates the nominal and minimum thickness of the insulating coating; it depends on the voltage and cross-section of the wires.
| Threshold voltage value (V) | Ø wires (mm2) | Nominal layer of insulation coating (mm) | Minimum permissible layer of insulating coating (mm) |
| 660 | From 1.00 to 2.50 | 0,62 | 0,46 |
| From 4.00 to 6.00 | 0,71 | 0,54 | |
| From 10.00 to 16.00 | 0,93 | 0,72 | |
| From 25.00 to 35.00 | 1,12 | 0,90 | |
| 50,00 | 1,32 | 1,08 | |
| 1000,0-2500,0 | 0,80 | 0,64 | 0,54 |
| From 4.00 to 16.00 | 1,10 | 0,82 | |
| From 25.00 to 35.00 | 1,22 | 1,02 | |
| 50,00 | 1,44 | 1,18 |
The next most important parameter is the characteristics of the insulating layer of the sheath; they depend on the total cross-section of all the wires of the electrical cable.
| Overall Ø (mm2) | Nominal layer of insulating sheath (mm) | Minimum insulation layer (mm) |
| Until 6.00 | 1,22 | 0,94 |
| From 6.00 to 15.00 | 1,54 | 1,20 |
| From 15.00 to 20.00 | 1,72 | 1,36 |
| From 20.00 to 30.00 | 1,92 | 1,54 |
| From 30.00 to 40.00 | 2,14 | 1,70 |
The threshold electric current strength, this indicator may depend on how many wires are in the cable and what their cross-section is. In addition, the location of the electrical cable (overhead line or underground wiring) influences. We recommend that you check this specification when purchasing cable products. Below is a table showing the threshold electric current for overhead lines.
| Ø(mm2) | Permissible electric current threshold (A) | ||
| two-wire | three-wire | four-wire | |
| 1,50 | 24,00 | 21,00 | 19,00 |
| 2,50 | 33,00 | 28,00 | 26,00 |
| 4,00 | 44,00 | 37,00 | 34,00 |
| 6,00 | 56,00 | 49,00 | 45,00 |
| 10,00 | 76,00 | 66,00 | 61,00 |
| 16,00 | 101,00 | 87,00 | 81,00 |
| 25,00 | 134,00 | 115,00 | 107,00 |
| 35,00 | 166,00 | 141,00 | 131,00 |
| 50,00 | 208,00 | 177,00 | 165,00 |
The resistance of the wire depends on its cross-section; this parameter is given in the table below (the values are indicated for direct electric current)
| Ø (mm2) | 1.50 | 2.50 | 4.00 | 6.00 | 10.00 | 16.00 | 25.00 | 35.00 | 50.00 |
| Resistance value of one wire (Ohm/km) | 12.0 | 7.40 | 4.60 | 3.10 | 1.80 | 1.20 | 0.73 | 0.52 | 0.39 |
Section and dimensions
Multi-core products must be produced with conductors of the same cross-section. Cables with several conductors, if the cross-section of each is greater than 25 mm2, can be equipped with a neutral or grounding conductor of reduced cross-section.
Ratio of values for conductor cross-sections of 25 mm2 and larger:
- main conductors (in mm2): 25, 35, 50, 70, 95, 120, 150, 185, 240, 300, 400;
- respectively, the cross-section of the grounding conductor or neutral (in mm2): 16, 16, 25, 35, 50, 70, 70, 95, 120, 150, 185.
Single-wire cables are produced with a conductor cross-section of 1.5 to 50 mm2; they do not come in a segment (sector) design. Stranded ones have a cross-section of 16 - 1000 mm2, if they are produced in sector, then the cross-section is in the range of 25 - 40 mm2. Cables are manufactured from 200 to 450 meters in length.
How to store
The power cable must be stored indoors, where there is no access to weather conditions, or under a canopy. Storage in an open-air area is allowed, provided that the cable is in a lined drum.
Covered Drums
Acceptable storage period:
- indoors (where there is no access to atmospheric influences) no more than 10 years;
- area covered with a canopy – 5 years;
- open area – 2 years.
How to choose a wire cross-section?
There is a table of correspondence between wire cross-section and load (shown below). It indicates what maximum load corresponds to what cross-section of copper conductor.
| Core cross-section, mm2 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 10.0 | 16.0 | 25.0 | 35.0 | 50.0 |
| Current load, A | 19 | 27 | 38 | 50 | 70 | 90 | 115 | 140 | 175 |
So, suppose you need to select a wire for wiring in the kitchen. For example, the kitchen has a 1.6 kW boiler, a 0.4 kW refrigerator, a 1.8 kW microwave and a 1.2 kW toaster. In this case, the total current load will be as follows:
(1600+400+1800+1200)/220=22.7 A
It is also necessary to multiply the current load by a power reserve factor of 1.5, since the number of electrical appliances may increase in the future. In total we get:
22.7x1.5=34.05 A
Now we look at the plate and see that our load corresponds to a wire with a cross section of 4 mm2 .
Using the same principle, the wire cross-section is selected for all other rooms and for the input cable.
Weight and dimensions of the packaged electrical cable
The dimensions of the drum or coil, as well as their weight, depend on the purpose of packaging (storage or transportation). These parameters can be found on the websites of cable manufacturers or their regional dealers. As practice shows, the declared dimensions and weight may have a deviation of around 10%.
Operating conditions:
- First of all, you need to adhere to the temperature regime. According to the technical characteristics, VVG can be operated in the temperature range from -50°C to 50°C. Short-term heating of the cable to a temperature of no more than 90°C is allowed.
- When laying an electrical cable, it is impossible for its temperature to drop below -15°C; this can lead to the “fragility” of the PVC material from which the protective sheath and insulation are made. In this case, heating will be necessary.
- Humidity threshold no more than 98%.
- When laying, bending less than ten diameters of the electrical cable is not allowed.
- Compliance with operating conditions guarantees the service life of VVG cable products up to 30 years.
Use and laying rules
The main area in which VVG cable is used is electrical networks with voltages up to 1 kV. Recommended for single installation of lighting and power lines. Subject to meeting additional requirements in the field of fire protection, its use for group installation is permitted.
The lack of protection imposes certain restrictions on the conditions under which the VVG cable must be laid. According to general recommendations, it can be performed on surfaces made of non-combustible or low-combustible materials. It is possible to lay cables on suspended structures. In this case, it is necessary to ensure the required structural rigidity to exclude mechanical damage. Taking into account the weight of the VVG cable, when laying externally, free sagging, causing uncontrolled stretching of the cores, must be excluded.
Open installation on wooden structures is not recommended due to possible mechanical damage. This problem is eliminated by the use of additional external protection in the form of a pipe, metallized or corrugated hose with sufficient strength characteristics.
Hidden gasket is widely used in construction. If the requirements for the non-combustibility of the underlying surface are met, it is allowed to be laid under plaster, in special niches or prepared cable routes.
Concealed installation outside of building structures, carried out directly in the ground, is not recommended. In this case, the VVG cable may be exposed to dangerous external influences, both man-made and natural. Lack of protection in the form of armor can lead to destruction of the insulating layer or damage to current-carrying conductors.
As with gaskets in wooden structures, additional methods of protection come to the rescue. The use of pipes, concrete or composite cable trays will allow installation in the ground. At the same time, the integrity of the building structure protecting the cable must be ensured.
Review of manufacturers
From the city of Elektrougli, it produces products for various purposes, including power cables of the VVG type. Founded in 2000, the production allows us to produce products of excellent quality at the most modern level. The main direction is power, non-flammable cables with insulation and an outer sheath made of polymer composites, designed for voltages of 0.66 and 1 kV.
Price for VVG cables:
- brand 2x1.5(P) – 11.24 rubles;
- brand 2x2.5 (P) – 18.44 rubles;
- brand 2x4.0(P) – 28.72 rubles;
- brand 2x6.0 – 41.97 rubles;
CJSC Cable
Since 2004, it has continued the traditions of the Kavkazkabel trademark, which has been producing products since 1958. The main product samples are wires and power cables for various areas of use - power, ships, for pumps and alarms.
Production Association LLC "Rybinskkabel"
City of Rybinsk. Since the founding of the plant in 1949, it has been producing the entire range of cable products and wires for the electrical industry. But the main direction is wires for various electrical machines and devices. It is worth noting that this company represents the largest range of VVG brand products, both in names and dimensional lengths.
Prices for three-core conductors:
- 3x1.5 (P/cr) – 16.76-16.97 rubles;
- 3x2.5 (P/kr) – 27.57-28.02 rubles;
- 3x4.0 (P/kr) – 42.82-43.56 rubles;
- 3x6.0 (P/kr) – 62.70-63.92 rubles;
JSC "PODOLSKKABEL"
Leader of cable industry enterprises in the Moscow region. The plant ranks first among mechanical engineering enterprises in the Moscow region. “Podolskkabel” is an enterprise that is dynamically developing its production based on the introduction of new high-tech production facilities.
Four-core wires are sold at prices:
- 4x1.5 – 22.34 rubles;
- 4x2.5 – 37.05 rub;
- 4x4.0 – 58.26 rubles;
- 4x6.0 – 85.41 rub;
- 4x6.0 – 85.41 rub;
- 4x10.0 – 159.03 rub;
- 4x16.0 – 255.43 rubles;
"Amur Cable Plant"
This is the only plant producing cable and wire products in the Far East , the main direction is the production of high-tech power cables for various industries both in Russia and abroad. In total, the plant has about 8,000 macro-sizes in its arsenal, and all manufactured goods are certified both for the domestic market and for supplies abroad.
VVG stranded wires in 5-core version:
- 5x1.5 – 27.75 rubles;
- 5x2.5 – 47.39 rubles;
- 5x4.0 – 72.40 rubles;
- 5x6.0 – 106.27 rubles;
- 5x10.0 – 198.94 rubles;
- VVG 5x16.0 – 318.10 rubles;
Description and technical documentation
The main document defining the technical parameters and conditions for the production of cable and conductor products of this class is the Russian standard of 2010 GOST 53769 - 2010 “Power cables with plastic insulation...”. This standard contains all the general requirements for products of this type, namely, for conductor cable products used for voltage 0.66; 1.0 and 3 kV.
This state standard also normalizes a unified marking system for this type of cable products. It should be especially noted that the technical specifications of the plants producing cable and wire products are developed on the basis of this GOST. In addition, any products manufactured by enterprises are subject to mandatory certification, this is another one of the requirements of this GOST.
One of the main parameters of power supply cables in accordance with GOST 53769 - 2010 is the degree of its fire safety , namely, laying conditions, temperature conditions of operation, necessary fire protection measures.