general information
Cable marking makes it possible, when installing electrical networks, to find out such operating parameters of the conductor as core material, thickness, design voltage, functional purpose of the cable, material and flammable characteristics of the insulating sheath, and other features.
The designations “wire” and “cable” are, in principle, synonymous; the difference between them is determined only by the scope of application. Thus, wires are usually used to distribute electrical wiring under light load conditions, and cables are used to conduct electricity from power plants and in highly loaded networks; therefore, they are heavier, as they are equipped with good protection. There is also a category of “cords” - this is a flexible conductor with twisted conductors, used in the design of electrical appliances for mains power. Cords, as a rule, lack overall insulation.
Despite the fact that the marking of wires and cables may have different letter designations in alphabetical order and case, it is always carried out in accordance with the general principle. First comes a description of the functional and design features using letters. For example, PUNP - wire (P) universal (UN) flat, and then digital markings of the number of cores and cross-sectional area of the conductors. Here the decoding of PUNP 3×1.5 means that this flat universal wire consists of three current-carrying wires with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2. The order of letters in the abbreviation depends on the strictly established GOST standard, and the thickness and number of cores must always come after them. After these data there is a designation of the climatic operating conditions (if there are any special features), and then the specifications or GOST according to which the cable products were manufactured.
According to the conditions under which and for what purposes conductors are used, they are divided into:
- power – used when laying electrical wiring;
- control - installed in the wiring that serves to transmit signals;
- control cables – installed in systems and circuits that control the operation of automatic systems;
- radio engineering – used in radio engineering installation.
PGVA design
PGVA is a single-core copper wire intended for laying flexible electrical wiring in automotive equipment.
The copper core ( 1 ) is multi-wire, has a circular cross-section with an area of 0.5 to 95 sq. mm and is twisted longitudinally for a denser arrangement of threads. The core insulation ( 2 ) is made of PVC plastic, which is highly resistant to cracking and exposure to automotive fuel and oils. It is resistant to fire and can withstand large temperature changes.
For ease of installation and in accordance with the requirements of regulatory documents, the insulation coloring has 10 primary colors, however, upon customer request, it is possible to use a combined color consisting of two multi-colored longitudinal stripes
Tables
All photos are clickable. Click to enlarge.
- Power cables with PVC and rubber insulation.
- Control cables
- Cable with BPI - impregnated paper insulation
Domestic wires and cords:
- Explanation of markings and abbreviations of wires: KSPV, KPSVV, KPSVEV, PNSV, PV-1, PV-3, PVS, ShVVP, PUNP, PUGNP.
- Suspended wires: A, AC, SIP, Ng
- Power, installation wires and connecting cords.
- Installation wires
Marking of foreign cables:
- Power cable
- FROR Italian cables: Italian standard CEI UNEL 35011
- Control cable
- Halogen-free fire-resistant cable
- Cables with cross-linked polyethylene insulation
Mounting wires:
Installation wires from foreign manufacturers
Table 1
| Wire brand | Wire name | Preferred area of application | Temperature range of use, °C |
| PVA | High flexibility wire with copper core, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulation, single core, heat resistant | For connecting electrical equipment and devices operating at elevated temperatures requiring increased flexibility | from minus 40 to 105 |
| PVAE | Same, shielded | The same, in places where wire shielding is required | Same |
| PVAMDE | Highly flexible wire with two copper cores, PVC insulated, shielded, PVC sheathed, heat-resistant | Same | » |
| PVA1 | Wire with tinned copper single-wire core, with PVC insulation, single-core, heat-resistant | For fixed installation of electrical equipment and devices | » |
| PVA4 | Highly flexible wire with copper core, PVC insulation, single-core, heat-resistant | For connecting electrical equipment and devices operating at elevated temperatures | » |
| PGVA | Same, but not heat resistant | For connecting electrical equipment and devices | from minus 40 (from minus 60 for the HL version) to 70 |
| PGVAE | Same, shielded | The same, in places where wire shielding is required | Same |
| PGVAB | Same as PGVA, armored with copper, galvanized steel or aluminum wire | For laying in places where protection from mechanical damage is required | » |
| PGVAD | Same as PGVA, two-wire | For connecting electrical equipment and devices | » |
| PGVTA | Same as PGVA, heat resistant | Same | from minus 40 to 90 |
Examples of symbols when ordering and in the documentation of other products:
PVA wires with a conductor cross section of 1.0 mm2 with red insulation:
PVA wire -1.0-K TU16.K17-021-94;
wires of the PGVA brand with a conductor cross-section of 1.0 mm2, with a combined (white with black stripes) insulation color:
Wire PVA-1.0-BCh TU16.K17-021-94;
the same, execution HL:
Wire PGVA-HL-1.0-BCh TU 16.K17-021-94.
Purpose
The decoding of the PUNP wire is as follows:
- P – wire;
- UN – universal;
- P – flat.
This cable is copper, with PVC insulation. This material is used in networks with voltages up to 250 V. In addition, a less common one can also be found - APUNP. This is an aluminum wire that is rarely used due to the fact that the cores are made of fusible metal.
Photo – PUNP three-core
Despite these seemingly most common technical characteristics, the PUNP electrical wire is dangerous for use both in industrial and domestic conditions. Its use in 55% of installations caused a fire. The main reason for the occurrence of life-threatening situations is that the wire manufacturer indicates incorrect (untrue) data about its products. For example, consider the popular household cable VVGng-P 3 x 6-0.66. It is often used for wiring, but you need to know that in more than 80% of cases the insulation thickness does not meet state standards (GOST 22483-77). It should be noted that a quality certificate is present.
In addition, on any wire of this type there is no marking, which should determine not only which cores a particular wire has, but also whose manufacturer it is and other technical operating parameters; Another significant drawback is that the cross-section of the individual cores is significantly smaller than the declared size: depending on the type of cable - from 20 to 30% of the total size. Because of this, the required resistance is not provided; When electric current flows through the wires, the wire heats up. If power analogues are manufactured with dense non-flammable insulation, then the PUNP can catch fire even from normal operation;
Manufacturing method and technical parameters of the wire
First, let's decipher its name. P is a wire, G is increased flexibility, B is the conductor insulation, which is made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic, and A means the automotive purpose of the wire.
Wire manufacturing method
The production of PGVA wire is organized only in a single-core version. The material used for making current-carrying conductors is copper.
PGVA wiring diagram
- One of the main advantages of wire is its flexibility. To do this, a current-carrying core is created by twisting several wires of smaller diameter.
- For example, to create a wire with a cross-section of 0.5 mm2, at least seven wires with a diameter of no more than 0.31 mm are used. And to create a wire with a cross-section of 95 mm2, at least 19 wires with a diameter of up to 0.83 mm are twisted.
The photo shows wire layers twisted in different directions
- In accordance with clause 2.3 of GOST 22483, these wires, depending on the cross-section, can have several layers. Usually these layers are twisted in opposite directions. But at the request of the customer, unilateral twisting of the layers is possible.
- As the instructions say, the break of several wires in a layer is also not a violation. The main thing is that the residual resistance of the cores complies with GOST 22483.
- The shape of the wire is usually round. But at the request of the customer, the manufacturer can produce PGVA and oval-shaped wires. In some cases, this may be a good solution for a more hidden installation.
PGVA wire insulation
- Polyvinyl chloride insulation is poured over the current-carrying part. The insulation must be applied tightly and without air pockets. Its thickness is standardized by GOST 23286-78 and varies from 0.6 to 1.6 mm.
- The insulation resistance of the wire is subjected to verification tests. The test voltage is at least 1.5 kV, and the time during which the wire insulation must withstand this voltage is at least 5 minutes.
Wire technical parameters
Automotive wire PGVA has a number of advantages, including over its counterpart - PVA wire. Therefore, for clarity, let's look at their technical characteristics in comparison.
Characteristics of PGVA wires
So:
- One of the main characteristics is the rated voltage for which the wire is designed. For wires of both brands it is 48V.
Comparative characteristics of PVA and PGVA wires
- The second important parameter is the electrical resistance of the wire . It is also practically the same and, depending on the cross-section of the wire, it may be better for one or another type of wire. For example, for a wire cross-section of 1 mm2, the resistance of PVA is 19.5 Ohms, and for PGVA - 19.8 Ohms.
But the nominal characteristics for bending conditions of PGVA wires compare favorably. Such a wire can be bent with a radius that is a multiple of 10 of its diameters. At the same time, PVA wire can only be bent with a radius that is a multiple of 20 of its diameters.
Flexibility of PGVA wires
- According to environmental conditions, PGVA also has certain advantages . The fact is that PVA wire is produced only for temperate and tropical climates. With temperature indicators from -40⁰С to +105⁰С. But PGVA can be manufactured in a climatic design for arctic zones. In this case, its minimum temperature is up to -60⁰С.
Otherwise the wires are quite similar. Both types are quite easy to install with your own hands, are designed to work with relative humidity up to 90%, are resistant to cracking and fungus formation, and do not support combustion when installed alone.
Note! The nominal relative humidity parameters for the work in which the wire is intended are measured for a temperature of 27⁰C. Some sellers use tricks and indicate relative humidity for higher temperatures.
Is it possible to use it at work?
If possible, it is better, of course, to use other types of cable, for example the same VVG or, for temporary work, PVS
But in austerity mode or the absence of other wires, you can, of course, use PUNP, taking reasonable precautions
Firstly, you should always measure the cross-section of this cable, for example, with a caliper. In his case, the labeling cannot be trusted at all. Or assume that PUNP with a cross-section of 2.5 mm corresponds to VVG with a cross-section of 1.5 mm. Thus, if you connect a floor lamp or lamp with this cable, nothing bad will happen. A low-power consumer like a modern TV or computer, which has low power consumption, will also withstand PUNP.
The main thing: you CANNOT connect any heating devices with this cable. Powerful ones are completely excluded - electric stove, boiler and the like. Microwaves, toasters and kettles are not recommended. And, of course, it is absolutely unacceptable to simultaneously connect several powerful devices to the network via this cable.
The wire must be laid on a non-flammable surface - concrete, tile or plaster. You cannot embed this wire into a wall without a corrugated pipe, from which it can be easily pulled out if necessary. Cannot be used outdoors without a protective cover. You can’t lay it in the ground, for example in a country house - cutting it with a shovel costs nothing. This wire cannot be laid in bundles, since due to the thin insulation it easily “breaks through”, and when laid in a bundle, it burns well. It cannot be mounted by twisting, that is, not on terminal blocks. It cannot be connected to aluminum except through a terminal block. It is not recommended to make homemade extension cords based on it.
But with carefully calibrated current loads, good quality connections and a proven cross-section, the PUNP wire can serve you well.
Description of characteristics
The KRPT cable has wide application and can be used to connect the load to electrical networks. Let's look at the main technical characteristics of the conductor:
- Voltage 660/1000V AC or DC respectively.
- The permissible current load (current density) is in the range of 3-20 A/mm2.
- The typical operating temperature range for cables with rubber insulation is from -60 to +50 degrees Celsius. It can briefly reach 75 degrees Celsius.
- Depending on the cross-sectional area of the cores and their number, the outer diameter ranges from 8 to 69 mm.
- A number of sections of cores - from 0.75 sq. mm. up to 400 sq. mm.
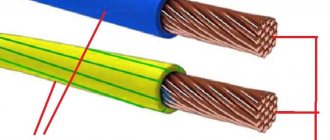
- The number of cores is from 1 to 4. The protective or neutral conductor is marked in yellow-green or blue, which corresponds to the international marking system. The “earth” core can be thinner than the others, for example 3x2.5 + 1x1.5 - there are three cores of 2.5 square meters each. mm and 1 with a cross section of 1.5 sq. mm.
- Accordingly, the cable weight is from 90 to 9900 kg/km.
- 8 outer diameters – minimum bending radius.
- Service life – 4 years.
- The insulation composition does not allow the spread of fire and allows the cable to be used for outdoor installation without additional protection.
KRPT is most often supplied in drums with a diameter of 10 to 22 cm, its minimum construction length is 100 m. For small batches of cable up to 100 m, coiled packaging is used. The cable complies with: GOST 13497-77 and OST 16 0.505.003-77.
Below is a table of typical conductor cross-sections:
Wire supply options
The price of the wire may differ depending on the method of its delivery to the end user. This depends on the wire cross-section and agreements between the manufacturer and the buyer.
| Usually the wire is supplied in coils. Their length for a wire with a cross-section from 0.2 to 25 mm2 is up to 100 meters. For wires with a cross-section of up to 95 mm2, the wire length is usually at least 50 meters. |
| PGVA wire supply options | The weight of the coil usually does not exceed 25 kg. In some cases, the bay may contain wires longer than 10 meters, but less than standard. But the total mass of such wires cannot exceed 5% of the total volume of supplies. |
| Color palette of PGVA wires | A separate issue is the color of the wire. As you can see in the video, it can vary within quite a wide range. This depends on the agreements between the manufacturer and the buyer. |
| The guaranteed service life of such a wire is at least 3-3 years. At the same time, the service life for the wire is 10 years. In practice, it lasts much longer. |
Note! According to the PUE standards, each conductor must have a color marking corresponding to the scope of its application. So, according to clause 1.1.30 of the PUE, red should be used to mark the positive wire in a DC network. To mark the negative conductor - blue. Due to the fact that PGVA is an automotive wire, this color is predominantly used.
What is PUGNP used for?
Before deciding to use a conductor when switching electrical equipment or laying wiring, it is recommended to take into account the technical characteristics and level of protection, then create a work plan and calculate the future load on the line. PUGNP, despite the prohibitions, is used in several areas:
- Arrangement of lighting systems by switching the current source and electrical devices using this wire. The cable is run from the distribution board to the light sources, breaking the circuit with a switch. The maximum permissible voltage in the AC network should be no more than 250 V, otherwise the conductors will begin to get very hot, a short circuit or fire will occur.
- Connecting components inside lighting fixtures, including chandeliers and fixtures. We are talking about creating conductor fittings. Single- or double-core products with a cross-sectional area of 1.5 square meters are used. mm. With their help, distribution between lamps is organized.
- At your own peril and risk, you can use a conductor to install electrical wiring inside an apartment or rooms of a private house. However, in this case, only low-power household appliances can be connected to the network.
- To organize temporary wiring during repair work.
Technical characteristics of PGVA
The operational and technical characteristics of the wire are determined by the requirements of regulatory documents TU 16.K17-021-94, GOST 15150-69, ST TOO 06:
- Operating temperature range - from -40°С to +70°С
- The wire is not subject to combustion, fireproof
- The wire is resistant to mechanical stress and vibration
- The permissible bending radius when installing the wire is 10d, where d is the outer diameter of the wire
- The resistivity of a wire with a cross-sectional area from 0.5 to 95 mm2 ranges from 40.5 to 0.203 Ohm/km, respectively
- Dielectric insulation resistance more than 3 MOhm
- Operating voltage: no more than 48V.
The technical life of the wire at an operating temperature of 70°C is at least 20,000 hours. Calendar service life is 10 years. PGVA wire can be produced for use in areas with temperate, tropical and cold climates. U ”, “ T ”, “ HL can be added to the wire designation , respectively.
Purpose of the PUNGP wire
Wire PUGNP
An electric cable is a type of PUNP with flexible conductors. It is cheaper in comparison with NYM or VVG and until 2007 it was manufactured according to TU 16.K13-020-93. The low quality of products for organizing the electrical network was the reason for the ban on production. Currently, some manufacturers produce PUNGP, so after purchasing it you need to check it:
- put in a freezer at a temperature of -15 degrees and inspect the shell for cracking;
- After keeping the twist in the freezer for about 2 hours, warm it up for 60 minutes at room temperature and wind it onto a cylinder 10 times longer.
If the cable housing remains intact, it can be used for its intended purpose - for arranging interior lighting, power supply to small household appliances and industrial units.
Main variety
Today, cords, cables and wires are used for electrical installation work. Before deciphering the markings, it is necessary to understand what these products are and what their differences are.
Wires
A wire is an electrical product consisting of one or more wires twisted together, without insulation or insulated. The core sheath is usually light and not made of metal (although wire wrapping is also common).
Such products can be used in electrical installation work (for example, installing electrical wiring in a wooden house), as well as in the manufacture of electric motor windings. Today there are wires with copper and aluminum conductors. The copper version quickly oxidizes in open space and has a high price, but at the same time it is capable of passing through higher current loads. In addition, copper is more elastic, which means it will not break as quickly. Aluminum ones are more fragile and are not connected to copper ones (except perhaps through terminals), but for that they have a low cost. Today, aluminum wiring is used less and less.
It should also be noted that the contacts may be insulated or bare. The latter option is used for power lines. An insulated wire can be protected or unprotected. Protection is provided by another layer of insulation (made of plastic or rubber), which covers the sheath of the cores.
The last classification is carried out depending on the purpose: mounting, power and installation. The mounting wire must be copper; it is used, as a rule, to connect elements of an electrical circuit in a switchboard, as well as to connect circuits in radio equipment. Power (as well as installation) is better known to us, because used outdoors and indoors.
Cables
An electrical cable is a product made up of several wires that are located under one insulating sheath (PVC, rubber, plastic). In addition to this shell, there may be additional protection - an armored shell made of wire or steel tape, which must be indicated in the marking.
There are 5 main types of electrical cables:
- power;
- control;
- For driving;
- for communication;
- radiofrequency.
Let us briefly consider the conditions of use of each product.
Power is used to transmit electricity in power and lighting electrical appliances. There are products of various types and purposes. Power cables are mainly used for external (both overhead and underground) and internal electrical wiring (in residential and non-residential premises). Power cables can have both aluminum and copper conductors. It is recommended to give preference to the latter option. The insulating layer can be PVC, paper, rubber, polyethylene, etc.
The control is used for the operation of electrical devices that transmit an information signal to control any devices. This type can also be with aluminum and copper conductors.
The control cable is a copper electrical conductor with a protective shield. Used in various automation systems. The protective screen serves to remove interference and also protect against mechanical damage.
A communication cable is used to transmit information using currents of various frequencies. Transmission of local communication lines is carried out by low-frequency conductors, and long-distance lines - by high-frequency ones.
RF cable is used in radio engineering devices. The main purpose is the transmission of video and radio signals.
Cords
Cord for household electrical appliances
So we have figured out the main differences between all three types of electrical products. We hope that the information was accessible to you. We also recommend watching the video, which provides this information more clearly:
Main characteristics and differences of conductors
General Differences
All conductors may differ in the following ways:
- Cross section. There are cores with a cross section of 0.35 mm2. up to 240 mm.sq.
- Manufacturing material: copper, aluminum, aluminum-copper (a special composite of two metals).
- Rated voltage (for example, can withstand 220 or 380V).
- Number of cores (single-core or stranded).
- Insulation material (PVC, rubber, paper).
- Protective shell material (rubber, plastic, metal).
Installation and operating conditions
Climatic modification according to GOST 15150 - 69, placement categories 1, 2:
— for wires of the PGVA brand, versions U, T, HL.
Temperature range of use:
— for PGVA brand wires from -40°С (for HL from -60°С) to +70°С
Wires are resistant to cracking, exposure to diesel fuel, oil and gasoline
T-type wires are resistant to mold damage
Wires of the PGVA grades in the KhL version are resistant to multiple impacts with an acceleration of 1470 m/s with an impact duration of 1-5 ms at a temperature of -60°C, resistant to punching at a temperature of +110°C for 8 hours
Wires of the PGVA grades in the KHL version are resistant to installation and operational bending with a bending radius of at least ten maximum outer diameters of the wire at a temperature not lower than -60°C (wires of the PGVA grades in the T and U versions, PVA in the U version - at temperatures not below -30°C).
The flexibility coefficient of PGVA brand wires in the HL design when the ambient temperature changes from -60°C to +(25±10)°C is no more than 10.
Construction length of wires:
— for sections from 0.5 to 25 mm2 not less than 100 m — for sections from 35 to 95 mm2 not less than 50 m
Minimum operating time of wires in modes and conditions allowed by technical specifications:
— at 70°C for at least 20,000 hours.
Construction length:
- for a section of 0.20-25.0 mm2 - at least 100 m; - for section 35.0-95.0.0 mm2 - at least 50 m.
The wires do not spread flame when laid alone.
Why is marking needed?
Wire and cable markings are specific markings on the outer sheath. Using a short code allows you to distinguish one type of wire from another without violating its integrity. The marking is strictly standardized; all electrical manufacturers must produce cables with the appropriate marking on the outer insulation. Wire markings are a special sequence of letters and numbers. The decoding of symbols is the same for all electrical manufacturers. This method is intended to display all the important characteristics of a particular cord.
Material. First of all, there is a need to determine the material from which a particular cable was produced. Since upon purchase this indicator is immediately clarified. The most common materials are aluminum and copper. Purpose. The next indicator is for what purpose the wire was made. It can be used to connect powerful electrical equipment, to lay an electrical network in buildings for various purposes (residential, industrial, public) or for standard household appliances. If the purpose of a certain type of wire does not match, its service life is reduced and there is a possibility of phase breakdown, which can lead to dangerous consequences.
Insulation. Further, the marking should briefly indicate what type of insulation was used for this power cable. After determining the type and material of the insulating winding, you can understand what properties and characteristics it has (increased strength, fire resistance, moisture resistance, etc.). Design feature. This parameter is also very important, since the layout of the entire wiring and house will depend on it. Based on the cable design, it will be necessary to determine what types of protective devices can be connected to the electrical network, whether a ground loop, lightning rod and other equipment will be connected. So in their design there can be one, two or more phase conductors, a neutral, as well as a grounding conductor, which is used for grounding.
Section
It is very important to know what cross-section the cable used for installation work in the house is. The material and thickness of the section will allow you to find out what load the electrical network can withstand in a given section. Voltage
The marking also allows you to determine the rated voltage that will pass through the power line.
By decoding these characteristics from the markings, you can understand whether a particular type of power cable is suitable for installation work. These designations should be able to be deciphered by a specialist in the field of electrical engineering, as well as a sales assistant in a store. The buyer can give the parameters he is interested in, and the seller, based on them, must select the appropriate type of wire with the required characteristics.
Marking
The general insulation and shell of phase conductors are marked in accordance with the PVA color marking standard:
- The overall insulating sheath is always painted white. Sometimes there are two diametrically located stripes of a different color.
- Black, red, yellow, gray and brown colors are used to mark conductive wires.
- If there is a “zero” phase, it is indicated in blue.
- Green or yellow-green color is reserved for the ground wire, but it is rarely found in PVA.
Marking of PVS wires is carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST 7399-97. Decoding the notation is very simple:
- the presence of the letter “l” indicates that the phase wires are made of tinned copper (PVC);
- the capital letter “T” indicates the climatic design of the cable;
- “A” in the marking means that the cable uses aluminum conductors;
- “B” - armored wire;
- PS - the cable insulating sheath is made of a mixture of self-extinguishing polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride;
- G – cable without insulation;
- ШВ – outer insulating shell made of flat polyvinyl chloride;
- PV - the outer insulating shell is made of a mixture of PVC and vulcanized rubber;
- the first number following the letter designations indicates the number of cores inside the cable;
- the number following it is the cross-sectional area of the conductive conductors.
In order to find out the exact physical characteristics of the PVA cable, you should refer to the following table:
| The wire | Number of cores/sectional area of each (mm2) | Number of wires in phase conductors/diameter | Weight of 1km cable (kg) | Outer diameter (mm) | Max Diameter(mm) |
| PVS | 2×0,75 | 24×0,2 | 55,8 | 6,4 | 7,2 |
| 2×1,00 | 32×0,2 | 63,7 | 6,7 | 7,5 | |
| 2×1,50 | 30×0,25 | 85,15 | 7,6 | 8,6 | |
| 2×2,50 | 50×0,25 | 133 | 9,4 | 10,6 | |
| 3×0,75 | 24×0,2 | 66,1 | 6,8 | 7,6 | |
| 3×1,00 | 32×0,2 | 76,5 | 7,1 | 8 | |
| 3×1,50 | 30×0,25 | 107 | 8,3 | 9,4 | |
| 3×2,50 | 50×0,25 | 166,7 | 10,2 | 11,4 | |
| 4×0,75 | 24×0,2 | 79,8 | 7,4 | 8,3 | |
| 4×1,00 | 32×0,2 | 96,5 | 7,9 | 9 | |
| 4×1,50 | 30×0,25 | 134,5 | 9,2 | 10,5 | |
| 4×2,50 | 50×0,25 | 203,8 | 11,1 | 12,5 | |
| 5×0,75 | 24×0,2 | 102 | 8,3 | 9,3 | |
| 5×1,00 | 32×0,2 | 118,4 | 8,7 | 9,8 | |
| 5×1,50 | 30×0,25 | 170,6 | 10,3 | 11,6 | |
| 5×2,50 | 50×0,25 | 257,6 | 12,4 | 13,9 |
In this article we want to talk about a special type of wires, the main purpose and scope of which is automobile and tractor construction. The PGVA wire is used to connect various electrical equipment and devices with a rated voltage of up to 48 V. The marking of the PGVA wire is deciphered as: automotive wire. It is produced according to specifications. PGVA: OKP 35 521201.
Based on the technical characteristics, which you can see at the end of this article, of the specified type of wires, their use can be carried out in almost any temperature conditions of various climatic zones. Unless in conditions of ultra-low Arctic temperatures, without additional automotive equipment, they can fail.
The marking of PGVA wire classically consists of an abbreviation of the first letters of the words characterizing this type of product:
P – Wire
G – Flexible
B — PVC insulation
A – Automotive
If we consider the design of this wire, we note that it is a stranded copper wire in plastic insulation. It has good resistance to cracking, diesel fuel, gasoline and oils. Accordingly, exposure to sunlight also has minimal impact on it. It can be bent many times without damaging the insulation and, most importantly, the conductors.
Also, when laid alone, the PGVA wire does not spread fire. The plastic from which the insulation of this wire is made does not support combustion and in case of fire the open fire goes out. Like many materials for electrical equipment, including wires, PGVA has modifications. This is PGVAE - the same wire, but with shielding, as well as PGVTA - a wire with increased flexibility, single-core, heat-resistant. Their individual characteristics are much superior to the base wire and are used in particularly difficult operating conditions.
For the convenience of auto mechanics, PGVA wire is available in insulation of various colors and different sections.
The industry produces PGVA wire in coils 100 meters long, if the cross-section is no more than 6 mm. Moreover, the weight of such a skein is no more than 25 kg. If the wire cross-section is more than 6 mm, it is wound on special coils with a diameter of up to 400 mm, or wooden drums.
Depending on the cross-section of the current-carrying wires, the weight of the PGVA wire can be from 1.5 kg per 1000 meters (core cross-section 0.2 mm) to more than 1000 kg per 1000 meters (core cross-section 95 mm).
Technical characteristics of PGVA wire
Core – stranded copper made of soft wire;
Insulation – PVC plastic compound (GOST 5960-77);
Length – with a cross-section from 2.5 to 25 mm2: 100 meters, with a cross-section from 35 to 95 mm2: 50 meters;
Operating voltage – 48 V;
Temperature range of application – from – 40 to + 105 °C;
Service life – 10 years;
Warranty period – 3 years;
The minimum bending radius is 10 diameters;
Insulation color – white, orange, yellow, red, black, brown, green, blue, light blue, pink, burgundy, violet (two-color insulation in the form of longitudinal stripes is possible);
Core resistance with a length of 1 km (no more) - 0.5 mm2 - 37.1 Ohm; 0.75 mm2 - 24.7 Ohm; 1.0 mm2 - 18.5 Ohm; 1.5 mm2 - 12.7 Ohm; 2.0 mm2 - 9.4 Ohm;
Minimum operating time at 70°C – no less than 20,000 hours.
Other types of wires
Features of application
According to the current rules of electrical installations (PUE), the PUGNP wire in domestic and industrial premises can only be used to supply electricity to devices, and the rated parameters of the supplied current must correspond to the tolerances of the conductor. However, in reality, this wire can often be found as a power cable. In Soviet times, it was quietly used for installing electrical networks in houses and apartments. Today, professional organizations are prohibited from doing this, but independent electricians continue to use PUGNP for these purposes.
The ban on the use of PUGNP is due to the fact that this wire is not produced in accordance with state standards. TU 16.K13-020-93, to which the conductor characteristics correspond, allows the manufacturer to make wires with a tolerance for cross-sectional area of up to 30%. Manufacturers take advantage of this, trying to reduce the selling price of the product by reducing production costs. As a result, a person buys a PUGNP with a nominal cross-sectional area of 2.5 mm2, but in reality it does not exceed 2 mm2. A good electrician, of course, will measure the wire before purchasing and refuse a thin conductor, but an inexperienced person will install the wire in a network where the load may be critical for a cable of such thickness.
In addition, PUGNP does not meet current requirements for electrical conductors in terms of insulation thickness. According to current standards, the thickness of the insulating sheath of the entire wire and conductive cores separately must be at least 0.4-0.5 mm, and in the specifications according to which PUGNP are produced, a PVC layer of 0.3 mm is allowed. The answer to the question of why the cable can still be found on the shelves of large construction hypermarkets is quite simple - a ban on use does not mean a ban on production, and the installation of wires that are unsuitable for specific conditions is a risk and the responsibility of the one who carries it out.
For these reasons, PUGNP, like PUNP, is not recommended for use in wiring the electrical network in domestic conditions. A good alternative for this material is NYC cables - this is a European analogue of our PUNP, which undergoes modern certification according to European standards. Among domestic brands, the best alternative is VVG, which is produced according to GOST.
Despite all that has been said, it is neither possible nor advisable to categorically ban the PUGNP wire. Essentially, any cable, no matter how standardized it may be, will not be safe if used in the wrong conditions. This wire can be used, but only in conditions where you are completely sure that even an increased work load will not cause a fire. For example, to connect electrical appliances or supply light to a garage, cellar or bathhouse, when there are no plans to connect high-power devices to the network, such a cable will do. True, in this case it is advisable to lay it in corrugation. And you most likely won’t want to use such a weak material to power an electric stove or washing machine yourself, or the electrician doing the work will tell you that this is contrary to basic safety.
Wires PUNP
The PUNP wire has been discontinued due to the cancellation of TU 16.K13-020-93 from 06/01/2007.
All products supplied by us comply with the requirements of regulatory documents of the Russian Federation (GOST R, OST, TU), which is confirmed by the presence of Certificates (declarations) of quality and fire safety, as well as quality passports.
All products are covered by the manufacturer's warranty, subject to compliance with the rules of transportation, storage, installation and operation.
We guarantee the return or exchange of products of inadequate quality in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
If you receive products of inadequate quality, you have the right, at your discretion, to demand: replacement, a proportionate reduction in the purchase price, or payment of the cost of the defective product. Replacement or payment for low-quality products is made only after they are returned to the supplier.
Replacement, refund or price reduction is made if the products are not damaged or destroyed as a result of damage, improper or careless handling, storage, or use. The Kabel.RF company guarantees its customers not only the quality of products sold, but also transparent pricing
The Kabel.RF company guarantees its customers not only the quality of the products sold, but also transparent pricing.
We cooperate directly with Russian and foreign manufacturers, which allows us to offer the buyer the lowest possible prices.
With us you can be sure that your finances will not suffer!
We make sure that the cargo arrives on time and in complete safety, therefore we work only with reliable insurance partners, leaders in their segment.
When delivering products worth more than RUB 300,000. insurance against all risks is carried out at our expense. If you need to insure cargo worth less than 300,000 rubles, be sure to inform your personal manager at Kabel.RF, he will select the most suitable insurance conditions for this case.
Delivering cargo throughout Russia, it is important for us to guarantee safe transportation to each client. Of course, we are confident in our transport partners, but it would be unprofessional to exclude even the most unlikely risks
Payment
Payment for ordered products can be made in the following ways:
- Non-cash payment to the supplier's bank account (for legal entities)
- Online payment by bank card on the website (for individuals)
- Payment by receipt (for individuals)
All payment documents are sent to you by email by your personal manager.
Delivery
The Kabel.RF company has an extensive warehouse network. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the possible methods of delivering paid goods to your address.
- Pickup
- Our delivery
- Transport companies
- Delivery to the countries of the Customs Union
You will be informed about each stage of delivery (documentation, order formation, shipment) by an employee of the logistics department of our company.
The warranty period and service life of the cable is established; the warranty period for the products sold is established by the manufacturer. Detailed information about warranty periods is provided upon purchase of a specific product.
The warranty period for a cable is the period of time during which the manufacturer guarantees and ensures compliance with the established requirements for the cable, subject to the consumer's compliance with the rules of transportation, storage, installation, installation and operation. The warranty period is calculated from the moment of commissioning or production.
The service life of a cable is the calendar duration of its operation until a limit state occurs, i.e., the impossibility of its further operation. The service life is calculated from the day the cable is received by the consumer, subject to the conditions of transportation, storage, laying, installation and operation.
All images posted on the site are registered with the Russian Copyright Society.
Alphanumeric marking structure
Marking wires and cables in accordance with GOST allows you to quickly find the desired wire among similar products that have the same type and color.
At large industrial facilities, where the number of installed communications is in the thousands, tags are used.
An experienced installer just needs to look at the markings and find out the size of the cross-section of the cores; cross-sectional area, which ranges from 0.35 to 70 square meters. mm; the number of cores and the metal from which they are made.
SIP wires are made from aluminum billets. The VVG cable, according to the marking, is made of copper wire.
Cable marking according to GOST indicates data on the rated voltage for which this product is designed. The marking also contains information about the insulating material.
According to GOST, the list of such materials is strictly limited. Among the most well-known are rubber, paper, PVC and other plastics.
And one more important parameter that is important when choosing a cable is the material of the protective sheath. The outer shell is made of metal, plastic, rubber.
Tags with information about the purpose of the product are attached during the installation process. Decoding the markings on the cable, according to GOST, is inherently simple.
The initial letter in the marking code characterizes the metal from which the core is made. For aluminum conductors, the letter “A” is used. There are no letters for copper.
The same materials are used here, vinyl and rubber.
The fourth letter characterizes the cable design. “A” indicates that the wire is covered with an asphalt coating. "B" - armored with metal. “G” - has no protective cover or, as installers say, naked.
The first number indicates the number of cores. The second is about the cross-sectional area. The third is about the operating voltage for which the cable is designed.
If you quote the marking VVG -3x1.5-380, then everything will be clear to a specialist. Since the letter “A” is missing at the beginning, it means the vein is copper.
Video:
The letter “B” indicates that the cable insulation is vinyl. Just like the vein, this is indicated by the second “B”.
The letter “G” means that there is no protective cover. The first number is 3 wires. The second number is the wire cross-section of 1.5 square meters. mm. And the last number is the operating voltage 380 V.
This is how the cable marking is deciphered according to GOST.
1.1. INSTALLATION AND POWER CABLES
Installation and power wires are intended for the distribution of electricity in power and lighting installations when they are fixedly installed outdoors, indoors, in pipes, under plaster, and also as flexible output ends for electrical machines.
Installation and power wires are produced with rubber and plastic insulation for voltages of 380, 660, 300 V, 50 Hz. Installation of wires is allowed at a temperature not lower than 15°C.
Wires with plastic insulation allow long-term heating of cores up to 70°C, with rubber insulation up to 65°C, with heat-resistant rubber - up to 85°C, with silicone rubber insulation - up to 180°C.
Information on the nomenclature of installation and power wires, their design and areas of application is given in Table 1.1.
Table 11.1. Brands, design elements and areas of application of installation and power wires
| Brand | GOST or TU Name of wire elements | Advantageous Applications |
| Wires with rubber insulation | ||
| PRTO | TU 16-705.465-87. Wire with copper core, rubber insulation, braided with cotton yarn, impregnated with anti-rot compound | For installation in fireproof pipes |
| APRTO | Same. With aluminum core | Same |
| PRN | GOST 20520-75. Wire with a copper core with rubber insulation in a non-flammable rubber sheath, flame retardant | For installation in dry and damp rooms, in hollow channels of fireproof building structures and in the open air |
| APRN | Same. With aluminum shell | Same |
| PRGN | Same. With copper flexible conductor | For installation with increased flexibility during installation and for connecting moving parts of electrical machines in dry and damp rooms, as well as in the open air |
| APRN | Same. With aluminum core | Same |
| APPR | GOST 20520-75. Wire with aluminum core, rubber insulation, flame retardant, with separating base | For laying on wooden surfaces and structures of residential, industrial and agricultural premises |
| PRD | TU 16.505.904-75. Flexible wire with copper core, rubber insulation, unimpregnated braid, two-core, twisted | In lighting networks of dry rooms |
| PRVD | Same. Flexible wire with copper core, rubber insulation, two-core, twisted, in a polyvinyl chloride sheath | In lighting networks of dry and damp rooms |
| ART | GOST 14175-69. Wire with aluminum core, rubber insulation, with support cable | Indoor installation in 660 V networks where increased mechanical strength is required |
| Shielded rubber insulated wires | ||
| PRP | GOST 1843-69. Wire with copper core, rubber insulation, braided with galvanized steel wires | In lighting and power circuits, secondary networks of stationary installations and mechanisms in the presence of light mechanical stress on the wire and the absence of exposure to oils and emulsions |
| PRRP | Same. In a rubber shell | In lighting and power circuits, secondary networks, in excavators, machines and mechanisms in the presence of mechanical stress on the wire, exposure to oils, emulsions |
| PRF | GOST 1843-69. Wire with a copper core, in rubber insulation, in a folded sheath made of AMC alloy | In lighting and power networks in dry rooms in the presence of light mechanical stress on the wire (wiring in staircases, clubs, theaters, etc.) |
| APRF | Same. With aluminum core | Same |
| PRFl | Same. Encased in brass | Same |
| Wires with plastic insulation | ||
| PV1 | GOST 6223-79. Wire with copper core and polyvinyl chloride insulation | For installation of secondary circuits, installation in pipes, hollow channels of fireproof building structures and for installation of lighting and power circuits in machines and machines |
| PV2 | Same. Same, flexible | The same for mounting circuits where bends in the wire are possible |
| PV3 | Same. The same, increased flexibility | Same |
| PV4 | Same. Also particularly flexible | Same |
| Automatic reclosing | Same. Wire with aluminum core and polyvinyl chloride insulation | Same |
| PP | TU 16-K17.021-94. Wire with copper core and self-extinguishing polyethylene insulation | Same |
| AMS | Same. Wire with aluminum core and self-extinguishing polyethylene insulation | Same |
| PGV | TU 16-K17.021-94. Wire with flexible copper core and polyvinyl chloride insulation | For mounting secondary circuits, for flexible installation with hidden or exposed installations |
| PGVA | TU 16-K17.021-94. Same | The same applies to connecting automotive and tractor electrical equipment. |
| PPV | GOST 6223-79. Wire with copper cores and polyvinyl chloride insulation | For installation of power and lighting circuits in machines and machines and for fixed open installation |
| APPV | Same. The same with aluminum conductors | Same |
| PPP | Same. The same with copper conductors and polyethylene insulation | Same |
| APPP | Same. The same with aluminum conductors and polyethylene insulation | Same |
| PPVS | Same. Wire with copper cores and PVC insulation, flat, without separating base | For fixed hidden installation under plaster, for installation in pipes and hollow channels of fireproof building structures |
| APPVS | Same. The same with aluminum conductors | Same |
| PPPP | Same. The same with copper conductors and polyethylene insulation | Same |
| APPS | Same. The same with aluminum conductors and polyethylene insulation | Same |
| AVT | TU 16.K71-051-87. Wire with aluminum conductors, insulated with polyvinyl chloride plastic, with supporting cable | Same |
| AVTU | Same. With reinforced support cable | The same in regions III and IV of ice conditions |
| ABTV | Same. Wire with aluminum conductors, with polyvinyl chloride insulation, with support cable | Installation indoors (including livestock) in networks with a voltage of 380 V |
| AVTVU | Same. With reinforced support cable | The same, but where increased mechanical strength is required |
| runway | TU 16.705.077-79. Copper core, twisted from soft wire, insulation from low-density polyethylene, sheath from thermo-light-stabilized polyethylene | For connecting water-submersible electric motors to the network |
| ERW | Same. The same with a shell made of polyvinyl chloride plastic. | Same |
| PVVZ | TU 16.K01.03-93. Wire with PVC insulation, PVC sheath and round protective wire | For powering electrical installations with stationary installation and electric lighting, installation of machines, machine tools |
| Wires for electrical machine terminals and heat-resistant | ||
| PRKA | TU 16.505.317-76. Heat-resistant wire, with a copper core, in an insulating and protective sheath made of silicone rubber of increased hardness, single-core | For fixed installation inside lighting equipment and devices with temperatures up to 180°C |
| PVBL | Same. Wire with copper core, rubber insulation based on butyl rubber, braided with Mylar thread | For electric motor leads at temperatures up to 105°C |
| RKGM | Same. Wire with copper core, silicone rubber insulation, fiberglass braided, impregnated with enamel or heat-resistant varnish | In electrical installations for a voltage of 600 V with a frequency of up to 400 Hz in the absence of aggressive environments and operating temperatures from -60 to +180°C |
| PAL | Same. Wire with copper core, with asbestos film insulation, varnished | For stationary installation in electrical installations, lighting devices with a rated voltage of 600 V, 50 Hz, for operation at temperatures from -50 to +200°C |
| PALO | Same, lightweight | Same |
| PVVT | TU 16.K80-09-90. Output wire with PVC insulation, heat-resistant | For operation in electrical installations with a voltage of 380 V with a frequency of up to 400 Hz in conditions of aggressive media and oils at temperatures from -40 to +105 ° C |
| PVKF | Same. Output wire with two-layer insulation made of organosilicon and fluorosiloxane rubber | The same, for voltage 380 and 660 V at operating temperatures from -60 to +180deg; C, heat resistance class H |
| PVFS | TU 16.K80-09-90. Output wire with fluorosiloxane rubber insulation | For operation in electrical installations with a voltage of 600 V with a frequency of up to 400 Hz and 1140 V with a frequency of 60 Hz in conditions of aggressive media and oils at temperatures from -60 to +180 ° C, heat resistance class H |
| PVKV | Same. Output wire with two-layer silicone rubber insulation | For operation in electrical installations at voltages of 380 and 660 V with a frequency of up to 400 Hz in the absence of aggressive media and oils at temperatures from -60 to +180 ° C, heat resistance class H |
| RKGN | Same. Output wire with silicone rubber insulation, fiberglass braided, impregnated with silicone enamel or varnish | For operation in electrical installations at voltages of 380 and 660 V with a frequency of up to 400 Hz in the absence of aggressive media and oils at temperatures from -60 to +180 ° C, heat resistance class H |
| RKGMPT | Same. Output wire with insulation made of silicone rubber of increased heat resistance, in a fiberglass braid, impregnated with silicone enamel or heat-resistant varnish | For operation in electrical installations at voltages of 380 and 660 V with a frequency of up to 400 Hz in the absence of aggressive media and oils at temperatures from -60 to +200 ° C, heat resistance class C |
Table 1.2. Number of cores and nominal cross-section of installation wires
| Brand | Number of main cores | Nominal core cross-section, mm2 |
| PRTO | 1 | 0,75…120 |
| 2; 3 | 1…120 | |
| 4; 7 | 1,5…10 | |
| 10 | 1,5; 2,5 | |
| 14 | 1,5; 2,5 | |
| APRTO | 1, 2, 3 | 2,5…120 |
| 7 | 2,5…10 | |
| PRN, PRGN | 1 | 1,5…120 |
| APRN | 1 | 2,5…120 |
| APRL | 1 | 2,5…120 |
| PRGL | 1 | 0,75…120 |
| APPR | 2; 4 | 2,5…10 |
| 3 | 2,5 | |
| AVTU | 2, 3, 4 | 4 |
| PV1 | 1 | 0.5…10 and 16…95 |
| PV2 | 1 | 2,5…95 |
| PV3 | 1 | 0,5…95 |
| PV4 | 1 | 0,…10 |
| PBPP | 2; 3 | 1,5…2,5 |
| Nominal core cross-section, mm2 | ||
| PBPPz | 3 | 1,0…2,5 |
| PRP | 1, 2, 3 | 1,0…95 |
| 4…30 | 1,0…2,5 | |
| PRRP | 1, 2, 3 | 1,0…95 |
| 4…30 | 1,0…2,5 | |
| APRF | 1, 2, 3 | 2,5…4 |
| PRF | 1, 2, 3 | 1,0…4 |
| PRFl | 1, 2, 3 | 1,0…4 |
| PRD | 1 | 0,75…6 |
| PRVD | 2 | 1,0…6 |
| 3 | 4; 6 | |
| 4 | 4…35 | |
| AVT | 2, 3, 4 | 2,5 |
| 4 | 6; 10; 16 | |
| ABTV | 2, 3, 4 | 2,5 |
| AVTVU | 2, 3, 4 | 4 |
| 4 | 6; 10; 16 | |
| PUNP | 2; 3 | 1,0; 1,5…6,0 |
| PRKA | 1 | 0,5…2,5 |
Permissible long-term current loads of installation and power wires are given in tables 1.10-1.12.
Selection of wire PUNP / PUGNP (main parameters)
The choice of wire of the PUNP / PUGNP series depends on the individual conditions of the room, the number of connection points to consumers. Only copper wires should be used for internal wiring.
The number of cores depends on the grounding requirements of certain devices that consume electricity. In a three-core cable, two wires represent the power branch, the third wire is connected to ground.
To power equipment with a three-phase current of 380 volts, two wires carry two-phase current, the third wire is neutral.
Three-core cable coil
For household electrical networks inside buildings and houses, choose a copper cable PUNPBM or PUGNPBM with a cross-section of 1.5-2 mm². For supply to sockets, a wire with a cross section of 2.5 mm² is used.