A car battery is designed with a specific architecture so that it can be installed in different types of cars. Since manufacturers used the closest standards, two types of batteries appeared depending on the location of the pole terminals. What is direct and reverse polarity and what are the differences between batteries?
What it is?
When working with direct electric current, the electric welding process can be carried out using electric current with direct or reverse polarity.
When performing electric welding, the term “straight polarity” means that the electric current passes from the rectifier of the welding device to the surface of the workpiece with a positive charge. The positive terminal of the welding device is connected to the workpiece via a special electrical cable, and a negative electric charge passes through the electrode holder, which is connected to the negative terminal. Features of the electric welding process in this version are that the positive pole of the anode has a temperature significantly higher than the cathode, which serves as the negative pole. For this reason, the use of electric current with straight polarity is widespread when performing welding work on parts with thick walls. In addition, this method is also used for cutting metal, as well as in cases where the generation of a large volume of thermal energy is necessary to perform a particular process. As for performing the welding process using electric current of reverse polarity, to carry out welding work it will be necessary to change the connection order in the opposite direction. In this case, the negative charge of the terminal with the “-” sign will be applied to the working surface of the workpiece, and the positive charge from the terminal with the “+” sign will be directed to the welding electrode.
A feature of the reverse polarity of the welding electric current is that the entire potential of thermal energy falls on the electrode end of the rod, while the workpiece itself heats up much less. This version of electric welding allows you to carefully align the edges of the workpieces, minimizing the risk of through burning. Reverse polarity electric welding is used to work with alloyed or stainless steel grades of metal, with thin-walled parts, and in addition, it is suitable for those metals whose overheating during welding is extremely undesirable. Making a weld with electric current of reverse polarity is also effective for welding using flux or shielding gases.
What to do if the polarity is incorrect
If you still haven’t taken this parameter into account, and there is no opportunity to purchase a replacement analogue, you can connect the battery.
To do this, the equipment will have to be turned around and moved slightly to the side so that the positive terminal is placed as close as possible to the corresponding clamp.
In such a situation, the negative wire will not reach the corresponding socket, but this is not necessary. Next, you should take a long piece of cord with the largest possible cross-section. A model that is usually used for lighting a car is suitable.
The original wire is unscrewed from the car and replaced with a prepared section. A terminal is attached to its end for connection to the battery, which is placed over the terminal. This way you can connect a device in any location.
The positive cord cannot be extended. Therefore, your task is to position the battery in such a way that the positive clamp and terminal are connected efficiently using native devices.
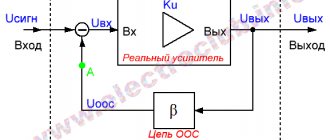
Battery polarity
Polarity refers to the arrangement of current-carrying elements on the top cover or front side of the battery. In other words, this is the position of the plus and minus. The current leads are also made of lead, as are the plates inside.
Direct and reverse polarity
There are two common layouts:
- straight polarity;
- reverse polarity.
Straight
During the Soviet period, all domestically produced batteries were with straight polarity. The pole terminals are arranged according to the diagram - plus (+) on the left and minus (-) on the right. Batteries with the same circuit are still produced in Russia and the post-Soviet space. Foreign-made batteries that are made in Russia also have this terminal arrangement.
Reverse
On such batteries, the minus is located on the left and the plus on the right. This arrangement is typical for European-made batteries and therefore this polarity is often called “Europolarity”.
Accumulator battery
The different position schemes do not provide any special advantages. It does not affect the design and operational features. Problems may arise when installing a new battery. A different polarity will force the battery to change position and the wire may not be long enough. Also, the driver can simply mix up the contacts, which will lead to a short circuit. Therefore, it is important to decide on the type of battery for your car when purchasing.
Design features of the battery
A car battery is a rechargeable DC source that is used to power the electrical system and start the engine. Cars have different layouts of components, so the polarity of the battery is as different as the type of terminals. In Europe, two types of cone-shaped batteries are used:
- Type A - 19.5 mm for positive and 17.9 mm for negative.
- Type B - 12.7 mm positive and 11.1 mm negative.
There are also other types - F, G, T, H, D, C, and E, but these are no longer cone-shaped, but in the form of threaded studs, terminals, lugs and other modifications. The terminals can be located on the top or on the front side wall.
Advantages and disadvantages of methods
Varying the polarity has different effects on the activity of the electrode. Thus, reverse polarity during welding has the following features:
- increased heat input to the workpiece;
- high-quality, deep penetration of the welded part;
- the electrode works longer (melts slowly);
- splashing of liquid metal from the workpiece is minimized.
Forward current has the following features:
- the heat flow to the workpiece is minimal;
- the penetration of the part is high, but lower than with reverse polarity;
- the working element quickly melts, requiring replacement;
- metal splashes with maximum probability.
Can we say with certainty that one method is preferable to the other? Welding with reverse polarity current has more obvious advantages, but the choice is not determined solely by the advantages. For most electrodes, the recommended polarity is indicated on the label.
general information
What is reverse polarity in welding? Reversing current polarity is the process of applying a positive electrical charge to the electrode and a negative electrical charge to the metal part being welded. In this case, the heat is distributed in the reverse order: the electrode significantly overheats, but the part, on the contrary, does not warm up at all. For this reason, reverse polarity in arc welding is used in special cases when there is a high chance of deforming the metal at high temperatures or a very neat seam is required. Due to exposure to high temperatures, the metal easily warms up, the seam is formed quickly and evenly.
Reverse polarity is simply necessary when welding stainless steel, thin metal, alloy and high-carbon steel, aluminum and other alloys that are easily subject to overheating. For example, a current of reverse polarity is a mandatory satellite of electric arc welding using flux or welding in an inert gas environment. You simply won’t be able to deposit metal well if you use, say, argon arc welding and set straight polarity.
Many beginners still wonder why some jobs use reverse or direct polarity when welding with an inverter? We will try to explain in more detail. Reverse polarity is used in work, since when the arc burns, areas with a high concentration of anodes and cathodes are formed at the end of the welding rod. In this case, the temperatures differ significantly; the anode region can be hotter than the cathode region by 700 degrees Celsius!
Based on this, it is not difficult to guess that with reverse polarity, a huge amount of heat is released, which contributes to high-quality welding of the metal. If this indicator is important for welding a particular metal, then reverse polarity is used. Direct current direction is used in all other cases.
By the way, when working with direct current of reverse polarity, the electrode burns out much faster than when working with direct polarity. This is again due to excessive heating of the rod. So be prepared to overuse components. If you are using alternating current, then the choice of polarity is not relevant at all, since the direction of the current will constantly change during operation.
So, let us repeat: polarity is set only when working with direct current. Reverse polarity is used when welding special, easily deformable metals, when the seam needs to be formed quickly and efficiently.
Welding with reverse polarity current cannot affect the properties of the electrode used in the work. A large amount of heat passes through the rod, which means that the part itself heats up very quickly, the metal is easily and deeply boiled, and there is practically no spattering (especially when welding with flux).
Is it possible to change the polarity directly during operation if the welding inverter (or any other type of equipment) has such an option? You can, of course, try this method as an experiment, but we will not recommend it to you. This is simply not necessary. But sometimes there are situations when you started working with the wrong polarity and suddenly discovered this, so you want to set other settings. Try to finish what you started without changing the polarity (unless the requirements for the weld are very high). Yes, the electrode will stick, but you have to live with it. If the seam should turn out to be of high quality and beautiful, then it is better to start the work again, setting a different polarity.
How to determine?
It's not that hard to find out. First you need to turn the battery with the front side facing you. It is located on the side where the stickers with characteristics and logo are located. Also, the pole terminals are located closer to the front side.
On many batteries you can immediately see the “+” and “−” signs, which accurately indicate the polarity of the contacts. Other manufacturers indicate information in the markings or highlight the current leads in color. Usually the plus is red and the minus is blue or black.
In the marking, reverse polarity is indicated by the letter “R” or “0”, and direct polarity by the letter “L” or “1”.
What are straight polarity batteries?
Polarity refers to the location of the current-carrying structural elements of the battery - the terminals - on its surface (for example, on the cover). It is considered straight if the “plus” of the battery is located on the left, and the “minus” is on the right. In this case, the battery should be facing the car owner (the terminals are in many cases closer to it, and if not, then it can be easily identified by the battery label).
The battery terminals are thus designated by “+” or “–” signs.
Basically, batteries with straight polarity are produced for Russian and Asian cars.
Which one should I use?
One of the important criteria on which the choice of electric welding polarity is based is the composition of the welding electrode coating. Depending on the electrode material, the electric welding mode is selected. For example, black carbon rods, which tend to heat up quickly, are not suitable for reverse polarity welding. Such electrodes will quickly collapse, and the electric welding process will be constantly interrupted; in addition, they are not suitable for thin metal.
The correct selection of the electrode in this case depends on the composition of the workpiece material. If you take an uncoated electrode, then when electric welding under conditions of direct polarity it will melt and burn well, but if you work with such wire under alternating electric current conditions, the uncoated electrode will not burn. The strength and appearance of the weld depends on the polarity of the poles. To obtain the deepest penetration of metal, you will need to use technology using direct current with reverse direction. With this arrangement of poles, the maximum gain of thermal energy will be in the anode region.
The use of electric welding with reverse current direction is considered the most popular. The welding machine can feed welding wire at a certain speed, which will determine the choice of certain welding technology options. Reverse polarity electric current is used for working in shielding gases, and forward polarity welding is used when working with flux-cored welding wire.
The direct direction of electric current is used to work with non-ferrous metals, when a tungsten electrode is used for welding metal.
The forward and reverse direction of the electric current is selected based on a number of factors, the main ones being the composition of consumables, the equipment used, the type of metal of the workpiece and its thickness. Regardless of which polarity of electric current is selected, there are certain nuances that are important to consider.
It is known that using constant electric current, it is possible to obtain a welded joint without the presence of large scale formation due to spatter. The cooled seam is neat and durable. Such characteristics of the seam are explained by the fact that when working with direct current, there is no frequent change of polarities, in contrast to working with an alternating type of electric current supply.
In the case when consumable-type electrodes are used for the welding process, due to the difference in heating between the cathode and anode, burn-through of the surfaces of the workpieces is possible. To avoid burning through the workpiece in the area where it is connected to the electrical cable, use a clamping clamp.
The charge carried by the cable does not play a role - in both cases, the clamp acts as additional protection for the workpiece.
Polarity when operating semi-automatically
A distinctive feature of semi-automatic devices is the supply of filler wire in automatic mode, at a fixed speed. It is clear that in this case the seam bead turns out neat and even, because the metal is melted evenly. To generate current, an inverter is used - a compact converter with electronic filling and additional functions that facilitate the welding process.
The specifics of automatic welding provide for several operating modes of the equipment:
- in the open air with an additive that forms a slag layer;
- using wire containing fluxes;
- in a protective gas environment covering the working area.
The connection of the terminals depends on the type of mode. Straight is suitable for ordinary cored wire. They switch to the reverse:
- using a protective gas, ionized molecules perfectly transmit electrons, the arc flares up quickly;
- Using a flux additive, heat is concentrated at the tip of the deposit, the flux burns out completely, and a homogeneous diffuse layer is formed.
Working with modern welding equipment, when connecting the terminals back, you can adjust the stability of the arc.
Knowing the features of working on alternating current, you can select the welding mode to suit the size of the workpiece and the type of metal. Direct current provides great opportunities; by changing the position of the poles, the welder controls the position of the high-temperature region of the arc. By shifting the position of the anode spot, strong connections are obtained on any workpiece.
Source: svarkaprosto.ru
Rules for choosing polarity
The main criterion for choosing direct or reverse polarity when welding is the electrode coating material. For example, carbon consumables heat up very quickly when the elements are connected in the opposite way and, as a result, are destroyed. A wire that does not have any coating burns well with straight polarity, but does not burn at all when using alternating current.
The dimensions and shape of the resulting seam also depend on the location of the poles. For example, deeper penetration is possible with a constant reverse current, which is due to increased heat generation at the anode and cathode.
It is important to remember that the faster the welding process is carried out, the smaller the width of the seam and the depth of penetration become.
Sheet metal thickness
Parts whose thickness does not exceed 3 mm are often burned through. To weld such workpieces, a reverse-polar scheme is used, providing an anode thermal spot at the edge of the electrode. This approach is appropriate when processing non-ferrous, alloyed materials.
Types of metals
The positive terminal is responsible for the final heating of the products and the holder. The cathode generates less heat than the anode. When machining refractory steels, it is better to use direct connection when the temperature reaches 4000 °C. For metals that change characteristics when overheated, connect the negative terminal. With direct-polar processing, the seam deepens; with “reverse” processing, it concentrates on the surface.
Types of electrodes
When choosing the brand of electrodes, take into account the type of current. Any variety is suitable for alternating voltage, since polarity does not play any role in this case. For varieties OK, OZS, MR, reverse connection is recommended. UONII and similar modifications are designed for a direct circuit. Manufacturers' recommendations are indicated on the packaging. Many welders prefer universal analogs to other options.
Additives and other consumables
Refractory electrodes used to create an arc are often used with straight polarity. Working with surfacing wire involves the use of only tungsten elements. Coal analogues are unstable to high temperatures, become brittle and crumble.
Type of metal
Here, moving the thermal anode spot will help us: what metals will it not harm, but, on the contrary, will help? The correct thing to do would be to carefully read the instructions for electrical settings of the welding machine, which accompany any modern alloy.
But now you can remember the fact that aluminum, along with alloys, welcomes heat; it helps reduce the amount of oxides formed during the process. So welding of aluminum with direct current is carried out only with a direct connection. Officially, this will be called DC welding of aluminum in an argon environment.
But steel, cast iron with various steel alloys require reverse connection of direct welding current: they do not need any additional heat due to the risk of the formation of refractory compounds.
Non-ferrous metals, like aluminum, are welded with non-consumable tungsten electrodes only when directly connected, without any exceptions.
Type of electrode
You know that modern electrodes are divided according to a huge number of criteria; they are produced in an incredible variety. Electrical parameters are also included in the description of each type of electrode. It never hurt anyone to read the instructions most carefully.
But here we can very well reason logically to choose the correct polarity for each type of electrode. The choice depends on the same thing - the warm anode spot, that is, the temperature regime. And such modes of electrodes depend on the type of flux and many other factors.
It is impossible to give short recommendations on current polarity for different welding consumables - there are too many of them. The only practical advice in this case is to read the instructions and not neglect them.
But what should you do if the instructions for the metal or alloy require the same electrical parameters, but the selected electrode requires completely different welding current settings? This happens, in this case there is only one answer: try and look for the best option experimentally.
Current strength, duty cycles, connection to poles - everything will have to be adjusted manually. But we are given a head to think, right?
How to buy the right battery
When buying a battery in a store or at a car market, the car owner needs to select it according to the main parameters:
- sizes;
- polarity;
- containers;
- starting current.
If the battery is too large, it will not be possible to fix it on the battery platform, and you need to be aware that the plates of an unsecured battery will quickly fall off due to vibration. The polarity of the new battery must correspond to the type of car, and if the driver is not at all versed in cars, he must at least remember how the terminals of the old battery are located, or sketch, so as not to forget, the location of the terminal pins. It is also important to choose the same polarity as it was, so as not to get confused - if the battery is connected incorrectly, a short circuit occurs with unpleasant consequences for the car owner.
You should not buy a battery with a reduced capacity; for a standard passenger car without air conditioning and other additional electrical equipment, the battery must have a capacity of at least 55 Ampere-hours. If there are many consumers in the electrical circuit, you can purchase a 60 Ah battery.
When purchasing a new battery, you should try to purchase a battery with the maximum starting current. There will be no harm to the engine from such a battery, but the starter will be able to crank the engine in frosty weather without problems. It would also be a good idea to take a voltmeter (multimeter) with you and check the voltage at the battery terminals - for a normally charged battery it should be about 12.5 Volts.
We recommend: Intercooler - what is it in a car
What equipment to use
The reverse direction is required in work with special installations. The specificity is that the machine feeds the wire at a certain speed to the workpiece, so several types of welding can be selected.
For example, in a protective gas environment (when argon or carbon dioxide is used), or using powder-treated wire. Reverse direction of current is applicable when working with gases, direct - when the process is performed with cored wire (also known as flux-cored wire).
Semi-automatic welding involves a number of process changes. Firstly, the connection of the “holder” and “ground” changes - on the first “plus”, on the second “minus” (reverse). This is done so that the flux burns out completely, and the welding process occurs inside the resulting gaseous cloud. The metal will heat up less, and the splashing of droplets will be minimized.
The straight line is used for welding non-ferrous metals, when the working consumable element is a tungsten electrode. In this way, an increase in temperature in the heating zone is achieved, which can be critical for, for example, aluminum.
When working with alternating current, the user’s task is to change consumables in a timely manner. Professionals or advanced amateurs prefer direct current as a reliable guarantee of high-quality welding. Working with an inverter allows you to choose one of two known options. Direct and reverse polarity when welding are used in methods, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of direction is dictated by a number of factors, the main of which are the material of consumables and the equipment used.
Type of current
The peculiarity of welding with alternating current is that when the sinusoid passes through zero, the arc goes out and then flares up again. The human eye does not detect this at high current frequencies. The conclusion immediately suggests itself: the type of current affects the stability of the arc. It is no coincidence that high frequency alternating current is used for welding.
When the device produces direct current, welding capabilities increase, you can change the direction of the flow of electrons, and influence the density of the electric arc. The strength of the connections formed ultimately depends on the type and polarity of the current.
Let me clarify: the polarity changes only when working with direct current.
For alternating current generators, the wires can be connected in any order; this does not affect the welding process.
When choosing electrodes, it is important to consider the type of current. When buying consumables, you need to carefully study the instructions; the necessary instructions are always given there. Electrodes are available for direct or alternating current and are universal. For example, UONII - for permanent. But it is most convenient to work with universal rods; there are fewer problems with them. Prepared the required amount, heated it to the specified temperature, and got to work.
What does direct and reverse polarity give when welding with an inverter?
When welding metal with direct current, the temperature at the end of the electrode depends entirely on which pole will be connected to it. With reverse polarity, when a plus is connected to the electrode, the temperature at the end of the electrode reaches 4000 degrees. When the inverter is switched to direct polarity, when minus is applied to the electrode, this temperature is significantly lower, almost 1000 degrees.
Thus, by changing the forward and reverse polarity of the inverter, you can more finely control the welding process.
First of all, this applies to welding thin and thick metals, when it is necessary either not to burn through the metal, or, on the contrary, to achieve a high-quality and reliable connection.
What does changing the polarity on the inverter give?
From all of the above, it becomes clear what welding in direct and reverse sequence gives:
In general, welding in reverse polarity with an inverter is recommended when welding thin metals and stainless steel. In other words, those types of metal that are very sensitive to overheating.
In this case, it is worth considering one important nuance, which is associated with the consumption of electrodes. When welding with an inverter on direct and reverse polarity, the rate of electrode combustion will be different. When welding with an inverter at reverse polarity, due to strong heating, the consumption of electrodes will be much higher than at direct polarity.
Connectivity differences
Anyone who has used electric arc welding machines understands that we are talking about the distribution of poles between the holder and the workpiece. There are two types of polarity when welding:
- Direct, when electrons move towards the workpiece (minus on the electrode). The arc turns out compact and dense.
- Reverse, when a plus is connected to the holder. A diffuse area of contact between the arc and the metal is formed.
The main difference between direct and reverse polarity welding is the localization of the point of maximum heating. With direct heat, the metal heats up more, and with reverse heat, the consumables heat up more. The method of connecting the poles depends on the thickness and physical properties of the metal.
How to properly connect a welding inverter
Many novice welders do not know that an inverter can be used to weld in different ways. They still use it this way, the standard connection is positive to the electrode and negative to the metal.
However, if you connect the inverter differently, the electrode to the minus, and the metal to the plus, you can achieve better deepening of the weld. In simple words, with this connection of the inverter, the main temperature will fall on the metal, as a result of which the workpiece will warm up better.
Well, and, on the contrary, with a “standard” connection of the inverter, when the electrode is connected to the plus and the metal to the minus, it will be possible not to burn through the thin workpiece. How does it work and what is the point? How to connect the inverter correctly, positive to electrode or negative? Read in this review.
What are the consequences if the terminals are mixed up?
The consequences may be different, depending on the situation in which the terminals were mixed up.
When installed on a vehicle
In the event that the plus “+” with the minus “-” on the battery were mixed up at the time when the battery was installed on a car with a running engine, then the owner of the vehicle will receive a fairly large number of troubles, ranging from the fact that it may fail generator diode bridge, as well as other electronic devices in the car.
Most often, this situation happens with old vehicles, where there was no protection against incorrect battery connection.
Important! A battery that has been connected incorrectly and left in the vehicle for a long time can cause a short circuit and fire.
In the event that the terminals are mixed up and the car does not start at this moment, then the owner will face much less problems.
In such a situation, only devices that were turned on earlier, for example, a radio, clock, etc., can fail. Sometimes, the situation is saved by blown fuses that are installed in the power circuit, naturally, if they meet the requirements of the maximum current in the circuit.
Features of welding with reverse polarity current
When carrying out welding work to connect metal products of small thickness, there is always a high probability of so-called burn-throughs. Therefore, to perform such complex, labor-intensive work, as a rule, the welding machine holder is connected to the plus, and the product being welded to the minus. When using this mode, welding of metal structures, as well as workpieces, is carried out using an intermittent seam. Simply put, when joining them, first a small section is welded at the beginning of the seam, and then its central part is welded.
For correct, reliable welding of products made of thin metal, during welding work, the arc must be periodically interrupted. Simply put, the welding electrode needs to be pulled out of the welding area, and then quickly ignited again.
If it is necessary to do overlap welding, then the metal parts to be joined should be securely, hermetically and tightly pressed against each other. Otherwise, even if there is a small air gap, a burn will appear on the top of the part being welded. In order to securely secure the workpieces together, it is recommended to use clamps or a large load before performing overlap welding.
The choice of welding mode primarily depends on the tasks assigned to the welder. When it is necessary to weld non-ferrous metals together, as a rule, direct polarity is used. In addition, it is more expedient to use it for working with massive, thick workpieces, since the metal will be melted much deeper, which will ensure good quality of the seam. It is also more suitable for cutting metal structures. Reverse polarity is recommended for use in cases where it is necessary to weld high-alloy steel or thin sheet metal.
What can you do?
Despite all the precautions, problems with battery installation due to its polarity still arise quite often. To avoid them, it is necessary not only to determine the polarity of the battery, but also to see how it is located in the seat. And this is very important.
This is because it is enough to rotate the battery 180 degrees to get the correct position of the terminals on the battery. For example, a car uses a straight-polarity battery and it is installed “face-on” when looking at it (label facing forward). If you take a “reverse” battery and turn it 180 degrees, then the terminals will be as they should be, but the battery will be facing the back. And since the wires have a certain length, they may simply not reach the terminals or something will interfere with them.
Finally, let's consider what to do if you have a battery with the wrong polarity, but it is not possible to get another one. Here it is important to try to position the battery so that the “positive” wire reaches its terminal on the battery and can be secured. To do this, you can unfold the battery, try to move it to the side, etc.
But it will be much easier to deal with the “negative” wire. After all, it is a mass and is connected to the car body. Therefore, it can easily be increased. That is, we take a piece of large-section wire (bigger is better) of the required length. We unscrew the “original” wire, and fix the prepared one in its place. Then we flip the terminal and connect it to the battery.
But the “positive” wire cannot be extended or replaced, so it is important to do everything to connect it to the battery “as is”, without making modifications, especially since it is almost impossible to do this. After all, ordinary twisting to increase length is unsafe.
Is it possible to install a battery of a different polarity?
This question often arises among those who inadvertently bought a battery of a different type. Theoretically, this is possible, but it will require costs and unnecessary red tape with installation. The fact is that if you buy a battery with reverse polarity for a domestic car, then the length of the wires may simply not be enough. You can't just lengthen the wire. It is necessary to take into account the cross-section and diameter of the terminals. This may also affect the quality of current transmission from the battery.
The best option would be to replace the battery with another one with a suitable contact arrangement. You can try to sell the purchased battery so as not to be at a loss.
What are the consequences for a car owner when the polarity is reversed?
It is important to remember: the design of the car assumes the use of only batteries of a certain size and terminal location. It is possible to install a battery of similar capacity, but not the correct polarity, into the seat. But it will no longer be possible to connect it in standard mode. Because the wires simply won't reach.
It is no coincidence that such a difference between batteries is present: incorrect polarity will cause damage to the car’s electronics. The engine control unit may fail and a short circuit may occur. It is important to remember: not all electrical appliances fail when changing poles. But many will be damaged. Such situations should be avoided.
Moreover, in some cases, the holes in the terminals are even different. Usually the diameter of the positive one is slightly larger than the negative one. Therefore, it will be difficult to confuse them even by accident. Moreover, changing the poles can cause the starter to rotate in the other direction. Some engines may require major overhaul after this.
We recommend: Buying cars at AvtoRoom
Connecting a welding inverter - plus and minus
As mentioned above, many novice welders do not pay enough attention to polarity when welding with an inverter. And to be more precise, some have never heard anything about it.
As a result, a lot of problems arise - thin metal is quickly burned through, while thick metal, on the contrary, is not sufficiently fused. Just try experimenting when connecting the inverter.
To begin, connect the holder to the plus of the device, and start cooking, and then connect the inverter, on the contrary, with the holder to the minus. You will definitely feel the difference.
It's all about polarity, since a welding inverter, unlike an AC transformer, produces direct current. And if on transformer machines there is no such difference in connecting cables, then when welding on direct current, it is still the same, and, moreover, significant.
What are reverse polarity batteries?
The polarity is considered reversed if, in turn, the “plus” of the battery is located on the right, and the “minus” is on the left. Of course, also provided that the battery is facing the car owner.
As a rule, batteries with reverse polarity are produced for American and European cars.
The main difference between batteries with direct polarity and batteries with reverse polarity is, in fact, the location of the “positive” and “negative” terminals. The appearance of the devices, as well as their functionality, can be almost identical (especially if they are produced by the same brand for the same category of cars).
However, it is extremely undesirable to install batteries in which the terminals are located differently on a car designed for straight-polarity batteries. If the polarity is broken, the electronics in the car will not work, or even fail altogether. In addition, the design of many machines simply does not allow the correct connection of batteries that do not have the correct polarity.
When choosing a battery, you can focus on the country that owns the car manufacturer brand. If this is Russia or, for example, Japan, then the car most likely requires a straight polarity battery. If this is the USA or Germany, then you will probably need to use devices with terminals located in reverse.
Having determined what the difference is between batteries of direct and reverse polarity, we will record the conclusions in a small table.
Source: thedifference.ru
Direct and reverse polarity when welding
Thus, when connecting a DC welding machine, you can connect the electrode holder to the positive or negative terminal. If the holder with the electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the welding arc source, then we get reverse polarity.
Reverse polarity is characterized by greater heating of the electrode, since where there is plus, the temperature will always be higher. This connection will make it possible not to burn through metal of small thickness, since the main concentration of temperature during welding will be on the electrode, and not on the metal being welded.
And vice versa, if the holder with the electrode is connected to the negative terminal, and the ground holder to the positive terminal, then the metal will heat up the most. Straight polarity is used when welding metal workpieces of significant thickness. When welding, this mode allows the metal to melt well and sufficiently deepen the root of the weld.
Types of welds
Differences in welding modes
When welding with constant current, a thermal spot with a high temperature appears at the tip of the consumable. Depending on the pole connected to the electrode, the welding mode is selected. For example, if a positive terminal is connected to the electrode, an anode spot with a temperature of 3900 degrees Celsius will form at its end; if a negative terminal is connected, the spot will be cathode, and its temperature will reach 3200 degrees Celsius. This is the main difference between the two methods.
Connecting welding cables with different polarities.
When welding with direct polarity is used, the main part of the temperature load is received by the metal part. As a result, it is easy to deepen the weld seam. In the case of reverse polarity, the heat is concentrated at the end of the electrode. In this case, the parts at the joints heat up less, which is advisable for welding workpieces of small thickness.
The work involves heating the metal until it melts, that is, the formation of a weld pool, the state of which is influenced by the choice of welding mode with reverse or direct polarity:
- If the current is too high, the electric arc will begin to push away the heated metal. In this case, the parts cannot be connected;
- if the voltage is insufficient, the metal will not heat up to the desired state.
With straight polarity, a spreading medium is created in the bath, where you can guide the electrode, directing the weld and controlling its depth. The final result depends on the speed of the electrode. The smaller it is, the more heat enters the welding zone and the better the metal warms up. The depth and width of the weld depend on the mode used.
Diagram for connecting poles with reverse polarity.
Important! The higher the current and driving energy on the arc, the deeper the penetration. The greatest penetration depth can be achieved using the reverse polarity welding mode.
As for the choice of consumables, it is recommended to use clean uncoated metal rods for welding in reverse polarity mode, and carbon electrodes for direct welding.
Features of welding when using straight polarity
When working with a DC welding machine and using the method of connecting a straight polarity circuit, you should take into account the following features of the process:
- The seam of the welding joint is deeply penetrating, narrow in width, stronger in quality;
- Almost all types of steel can be welded, the thickness of which starts from three millimeters and above;
- When using tungsten rod for non-ferrous metals, only straight polarity welding method can be used;
- The welded arc is stable and resistant to breakdowns, making it easier to control the work process and get a beautiful seam;
- Electrodes designed for use in alternating current welding are not suitable for working with this method;
- When using a welding machine as a cutter, the workpiece is easier to cut.
Equipment
Welding with reverse direct current is carried out only on welding machines designed for such work. Choosing a welding machine is a very important topic, so in this article we will tell you only the most important things. First of all, your welding machine must be able to work with different modes and feed wire at different speeds. So you can weld with argon or carbon dioxide (this is very important when welding stainless steel), but you cannot weld with flux-cored wire, since this requires straight polarity.
With the help of reverse polarity, it becomes possible to use semi-automatic welding equipment in your work. Here the holder and ground are connected to “plus” and “minus”, respectively. Due to this, the flux burns out gradually and completely, and the welding itself occurs in the resulting gas cloud.