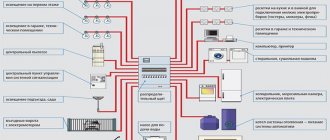
To properly organize the supply of electricity during construction or renovation, you need to know which wire to use for wiring in the house. It is better to entrust the installation of the power supply network to a specialist, but you can purchase materials yourself. To do this, you need to remember the basic rules for choosing a cable correctly.
What are electrical cables made of?
The main conductor of electric current is aluminum or copper conductors. The larger their diameter, the higher the cable's capabilities.
Aluminum wires are cheaper, but they are more likely to deteriorate and have a lower electrical conductivity coefficient.
Copper cable is durable, does not break at bends and is capable of carrying more current than aluminum cable with the same diameter.
It is recommended that all wiring in the house be of the same type. This is due to the fact that to connect products from different materials, a special adapter will be required so as not to create a galvanic couple. In this case, oxidation and destruction of the wires occurs, which can lead to a short circuit.
The main cores are covered in braids made of rubber, polyethylene or PVC. Often several of these insulated conductors are combined into a bundle, which in turn is covered with a protective sheath.
Cables for laying in the ground
If on your site there is no possibility of laying a cable from the power line to the house over the air, you should consider the possibility of laying it underground. This technology is more labor-intensive, you have to dig a trench and the price of cables is significantly more expensive.
It is not allowed to cross cable lines with gas water mains under the foundations of buildings. The trench must run parallel to the foundation at a distance of at least 0.6 m. In normal places, the depth of the trench should be 0.8 -09 m, under the road of vehicles 1.25 m the cable should be in a pipe.
Tip #2. Take a photo or video of laying a trench, where long-term landmarks will be visible (a tree, preferably a corner of a building, and others), it is advisable to measure the distance to them and put it on the photo.
Save the materials electronically on a flash drive or on the cloud on social networks. If necessary, after many years you will be able to accurately determine where the cable lies. To lay cables from power lines to the distribution board at home, two types of AVBbShV are most often used - aluminum wires and VBBShV copper wires.
Main technical characteristics of the AVBBShv cable
- A – aluminum wires;
- B – heat-resistant PVC insulation on the conductors;
- B – presence of protection, two steel strips;
- B - indicates the absence of a protective cushion between the conductors and the armored tape.
- Shv – material of the outer shell of the hose is polyvinyl chloride.
This structure reliably protects the product from hard soil elements and rodents.
Design and technical characteristics of the VBBShV cable
This cable is similar in design to the AVBbShV structure, except that the conductor cores are copper. It is used for external wiring along the walls of buildings and concrete fences, and other structures.
Types of wiring
The choice of the required wire depends on the type of installation, because The installation method affects the requirements.
Open
Open cabling is the laying of cables directly along building structures. It is produced where there is no possibility or need to hide wiring in the wall or ceiling.
Since an openly laid cable is not protected by anything, it is necessary to protect it from mechanical damage. In addition, for safety reasons, it is recommended to use a wire with a core cross-section of at least 4 mm².
Hidden
To install hidden wiring, a groove is punched in the wall in which the cable is laid, and then it is sealed and covered with plaster. With this method of power supply, less stringent requirements are imposed on the wire, because it is isolated both from external influences and from the effects of overheating.
The requirements for the home electrical network are regulated by the PUE clause 7.1.34.
Selecting an electrical wire
Before starting work, you need to decide which wire to use for wiring. In most cases, it is better to install copper wiring. Such a cable will be more durable, reliable and immune to external negative factors. Aluminum is less resistant to mechanical damage and is brittle. Also, copper conducts current more efficiently and has less resistance, so a copper cable will have a smaller cross-sectional area of the current-carrying core, which will significantly reduce the mass of the line.
Important!
- avoid second-rate products;
- buy wires from well-known manufacturers with certificates;
- select the cross section depending on the load.
To select the required wire cross-section for home wiring, you need to know the strength of the current passing, as well as the degree of insulation intensification during the supply of electricity. If rubber insulation is used, the maximum heating temperature should not exceed 65 degrees Celsius. If the cable is insulated with plastic, then the temperature limit for the cord is 70 degrees.
At average temperatures (20–25 °C), the insulation should not overheat by more than 50 °C. You should also take into account the load that goes on the wiring depending on the material, area and type of section (see tables 1, 2).
In case you do not know the cross-sectional area of your cable, determine its diameter (D), and then calculate the area using the formula:
Sectional area = 0.785 × D²;
T-1. Maximum current loads for copper electrical wires with rubber or PVC insulating coating
T-2. Maximum current loads for aluminum electrical wires with rubber or PVC insulating coating
Which wire to choose in the end?
Ideally, it should be a stranded copper wire with a correctly calculated cross-section. For correct calculation, you need to calculate the total power of all devices and add 20–25% to this value. And then select the appropriate option from the tables above.
Which cable is suitable for hidden wiring?
Concealed wiring will function better with the following types of electrical wires:
- VVG is a copper electrical wire with 1–4 cores. It has a round or flat shape. It has good fire protection. You can also use its subtypes: VVGng and VVGng-LS - even more fire-resistant wires.
- NYM - German high-quality cable with functionality similar to VVG;
- PVA - made of copper, has stranded conductors.
Properties of VVG wire: can be used in wiring with operating voltages up to 1000 V. Has 1–5 cores. The cable is capable of operating in a wide temperature range: from –50 to +50 °C. VVG copes well in conditions of high humidity (up to 98 percent) and also has high tensile strength. Typically, a cross-section of one and a half square millimeters is used; in open wiring, a cross-section of at least 6 mm² is recommended. The bending radius is 10 sections.
VVG cable
NYM cable properties : operates in networks with voltages up to 660 V. Consists of copper, stranded conductors (from 1 to 5). Section: from 1.5 to 16 mm². The bending radius is 4 sections. A distinctive feature of German wire is double insulation. The outer shell consists of standard PVC, and the inner shell is made of non-flammable material. The space between the outer and inner insulation layers is filled with rubber, making the cable more durable and resistant to temperatures. NYM is a moisture-resistant and heat-resistant wire that can withstand temperatures from –40 to +70 °C. However, NYM is afraid of ultraviolet rays and must be masked in open areas.
If you need to save money, you can use a budget option - PUNP wire. This is a flat electrical wire of 2 or 3 cores with a cross-section from 1.5 to 6 mm². The conductors are copper, single-wire.
If your budget allows, then it is better to take NYM; many professional electricians give it preference. Also an excellent option would be the VVG electrical cable.
Which cable is suitable for open wiring?
In the private sector or villages, open wiring is most often done. The best and most convenient cable for an outdoor line is an electrical cord. It looks like two insulated cables twisted together. The cord is woven from multi-core electrical wires. It is most convenient to install electrical wires along the ceiling or walls using special porcelain rollers. At the ends and corners the cable is fixed on rollers using tape.
Recommended brands of cords for home use:
Bath cable
In places where wiring is forced to function in conditions of high humidity, increased requirements are placed on it:
- it must be resistant to wet environments;
- must withstand high temperatures (bath wiring up to 190 degrees Celsius).
In such conditions, it is best to use cables: RKGM and PVKV, equipped with silicon-containing protection.
Cable for lighting in an apartment
For lighting in an average apartment (3 rooms), it is recommended to use a flexible electrical wire with a cross-section of 1.5 mm², capable of withstanding a load of 4000 Watts. If the cable is laid in an apartment where there is no grounding, then you need to install a two-core wire with a phase and a neutral.
In apartments and houses with grounding, when using fluorescent lighting fixtures, it is recommended to install a three-core cable. Also, lighting lines should be connected to separate boxes. This will improve safety and convenience during the debugging process.
Difference between cable and wire
The wire is a lightweight structure consisting of 1-3 insulated cores. It is less secure than cable and has a simpler internal structure.
A cable is a wire of a more complex structure. In addition to several cores separated from each other, it has a double layer of insulation, a gasket, a screen and is recommended for use in residential areas.
Cable or wire
The first step is to deal with the question in the title. At the everyday level, these concepts are approximately equivalent. Those who are close to electrical engineering and have a superficial knowledge of regulatory documents often claim that a wire contains one conductor, and a cable contains two or more (referring to GOST 15845-80). In fact, there are cables with one conductor (for example, PvPu 1x95), and there is a wire consisting of several conductive elements. Thus, a self-supporting insulated wire (SIP) consists of three conductors in separate insulation, twisted around a supporting cable.
Self-supporting insulated wire.
In reality, the difference between a cable and a sheathed wire . The wire has light single-layer insulation. If a cable consists of several wires that have independent insulation, then they are enclosed in one common sheath. This shell can have a reinforced structure, even armored. This allows wiring products to be laid in any way, including underground (wires cannot be laid underground without additional protection). The same applies to single-core cables. Thus, the APvPug cable has a multi-core conductor, cross-linked polyethylene insulation and a multi-layer additional sheath, including an armor layer.
Installation of single-core cable APvPug.
Rules for choosing a cable for wiring in the house
The selected cable must comply with the following rules:
- Ensure the required level of electrical and fire safety.
- Provide the ability to simultaneously turn on several household appliances and lighting.
- Allow quick and convenient installation.
Initially, the rules of the PUE, clause 7.1.34, allowed the use of only cables with copper conductors in residential premises, except for houses whose construction began before 2001. However, later these requirements were excluded.
However, when choosing home electrical wiring, you must remember that to combine aluminum and copper conductors, you need special adapter clamps that prevent contact of dissimilar metals.
When choosing means for home electrical wiring, it is necessary to determine the material of the cores and their cross-section. When purchasing, first of all, check the labeling and availability of certificates. The quality of the cable products offered does not always meet the standards, so it is better to purchase them from reputable manufacturers.
Marking
The wires are marked on the braid. The letter designation is followed by a series of numbers.
If the cable brand begins with the letter A (for example, AVVG), then its cores are made of aluminum. Otherwise, the conductors are copper. The following letters indicate the material from which the outer and inner braids are made:
- B (Вр) - polyvinyl chloride;
- P (Ps) - polyethylene;
- C - lead.
The numbers indicate the number of cores and the cross-sectional area of each of them.
For example, the name of the most common cable for internal wiring VVG-0.66 kV 3x1.5 means the presence of 3 cores with a cross-section of 1.5 mm² each, enclosed in a polyvinyl chloride sheath, with the same external insulation.
The designation 0.66 kV indicates that the product is used in networks up to 660 V.
If the marking has the letters “ozh”, the conductors are single-wire, i.e. whole.
Section calculation
To determine the required wire cross-section, you should estimate the maximum load of the electrical network. This can be done by knowing the power consumption of the connected devices. It is indicated in the instructions, passports or on the housing of the devices themselves.
Construction and section
Cable products are distinguished by cross-section, type of insulation, presence of armor, number of cores and their flexibility class. If we talk about lighting, then for stationary lamps, such as a chandelier or sconce, they require stationary (fixed) installation; a rigid wire or cable with a single-wire (monolithic) core is suitable for this. To connect a table lamp or a lamp that can change its position, you need a flexible core.
Let us immediately make a reservation that in home electrical wiring, including for lighting, the use of wires with aluminum conductors is prohibited by the requirements of the PUE. Therefore, modern electricians always use copper wires and cables for these purposes. It is also worth remembering that in a wooden house it is recommended to lay external wiring in corrugated pipes, pipes or cable ducts.
The cross-section of the core is selected based on the load connected to it. First, let's look at the table of permissible long-term currents through conductors:
Typically, electricians use a simplified rule: for sockets, use a cable with a cross-section of 2.5 square meters. mm. and more, for lighting circuits 1.5 sq. mm.
Why is it not advisable to use thick-section cores for all consumers? The fact is that the difference in cost is between 1.5 and 2.5 square meters. mm. approximately 1.3 times, in some cases even more. Accordingly, the cost of electrical wiring will be unreasonable and excessive.
But this is true for laying a line from the input circuit breaker to the distribution box. Further wiring can be done with a thinner wire. For example:
- You are going to connect a chandelier with five arms and install 100 W incandescent lamps in them. Then the current will be equal to 5*100/220=2.2 A.
- You need to connect a wall lamp, for example, a sconce with one light bulb. It will be used to create diffuse, dim lighting and you will install a 7W LED bulb. The current in this case will be extremely weak 0.03 A.
In both cases, a wire with a core cross-section of 1.5 square meters. mm is excessive, based on the table of permissible currents. It is also undesirable to choose a wire that is too thin, since in this case it is difficult to obtain reliable contact in screw and clamp terminal blocks. Therefore, in most cases, a 0.75 square meter wire is sufficient to connect lighting. mm. It will withstand current up to 14 A (more than 3 kW), and costs less than 1.5 sq. mm.
Cables for underground input
To supply electricity to a detached house, a cable is often laid by digging a trench in the ground. The following must be taken into account:
- The cross-section of the conductors must provide a general house load for both devices plugged into sockets and for lighting. The thickness of the cores in this case is at least 6 mm².
- For underground input, you need a shielded cable, which is designed for installation in a trench. Otherwise, use a metal pipe (corrugation) of the PND type.
- When calculating the depth of the trench, soil freezing must be taken into account.
- Sometimes rodents damage wiring.
Cable calculation
You need to know what cross-section is needed for 15 kW and 380 for input into the house, since with an aluminum and copper core it has different characteristics, and also differs with different connection methods. For open introduction at a voltage of 380 V and a power of 15 kW, a copper conductor with a cross-section of 4 mm² and capable of withstanding a current of 41 A is required, and for an aluminum wire - from 10 mm² and a current of 60 A.
For cables laid in a pipe, copper conductors must have a cross-section of 10 mm², and for aluminum conductors - from 16 mm². The length of the cable depends on the distance of the entry point to the pole, as well as the presence of additional fasteners or supports.
Cable laid over the air
Often, to organize power supply in outbuildings, sheds, garages, and local areas, the cable is pulled through the air. If the wiring distance is more than 25 m, install additional support.
When laying a cable through the air, it is important to protect it from external influences: ultraviolet radiation, temperature changes, and precipitation. These factors negatively affect the most commonly used PVC braid, causing it to crack. To extend the service life of the cable when laid overhead, it is enclosed in a corrugated metal or polyethylene pipe.
Why do you need to consider the cable cross-section for electrical wiring?
When installing cable lines in a private home, it is necessary to solve several problems:
- selection of cable cross-section for electrical wiring;
- determining the number of cores for the cable;
- method of laying conductors;
- selection of cable type.
Particular attention should be paid to the choice of cross-section, since the performance of future electrical wiring, as well as the safety of the entire home and the people living in it, depends on this.
Any cable consists of two or more conductors insulated from each other. You can also remember from the school physics course that when current passes through a conductor, it generates heat. The amount of heat is equal to the product of the square of the current strength and the resistance and the time spent under current:
Q = (I x I) x R xt , where
I – the magnitude of the current arising in the conductor when the load is switched on,
R – conductor resistance,
t is the time during which the conductor is under electrical load.
It follows that when the current increases, for example, three times, the conductor will heat up nine times more. Resistance depends on the material from which the conductors are made and on their cross-sectional area. Copper wire has less resistance than aluminum, and the thicker the conductor, the lower this parameter.
If the cross-sectional area of the wire is not sufficient to pass a given current, it will begin to heat up. And since a thin wire has a smaller side surface area, it will become so hot that it will begin to melt and burn out. In this case, the current supply will stop. And sometimes the insulation can catch fire, which often leads to a fire in the house.
When, due to the connection of powerful electrical appliances, the current strength exceeds the design value, an overload occurs in the wiring. Even if it is small and does not lead to heating and subsequent fire, the service life of the cable during such work is reduced hundreds of times.
To ensure normal conditions for cable operation, it is necessary that the cross-section of the conductors corresponds to the rated current value. That is, for a given current value, it is necessary to use a cable with certain parameters and characteristics.
Which wire is better to choose for wiring in a private house?
Taking into account modern loads on the electrical network due to the inclusion of powerful household appliances, it is recommended to use a multi-core copper cable when installing or replacing wiring.
For sockets, VVG 3x2.5 is most often used. Even when all household devices are turned on simultaneously, it can withstand a load of 27 A with a power of 5.9 kW.
Lighting requires less energy consumption, so electric current is supplied to the switches using VVG 3x1.5.
A wooden house must have an increased level of fire safety. According to the rules of the PUE, in this case the cable is laid in metal pipes. It is unacceptable to use a plastic box.
Standard wire and cable sizes
This parameter is taken into account when designing various electrical wiring in all areas of human activity. In this article we will look at standard wire cross-sections, and also give examples where different cross-sections are used. Standard range of wire and cable core sections: 0.5; 0.75 1; 1.5; 2.5; 4; 6; 10; 16; 25; 35; 50; 70; 95; 120; 150; 185; 240; 300; 400; 500; 625; 800; 1000; 1200; 1600 sq. mm. This range is relevant for both copper and aluminum conductors, with the exception of the minimum cross-section - for an aluminum cable the minimum cross-section is 2.5 square meters. mm. Aluminum wire of a lower cross-section is not produced due to its low strength - aluminum breaks easily and “floats” at the contact connection.
For wiring lighting devices in everyday life, copper wire with a cross-section of 1-1.5 square meters is used. mm or aluminum wire with a cross section of 2.5 sq. mm, since this is the minimum cross-section of aluminum.
To power individual sockets, use copper or aluminum wire with a cross-section of 2.5 square meters. mm.
Cable cross section 4-10 sq. mm in everyday life is used to power powerful household electrical appliances, which require a separate line with a large load capacity, and to power distribution boxes that supply power to several outlets in a given room.
A large cross-section cable in the home can only be used to supply electricity to the home distribution panel.
Wires with a cross section of 0.5-2.5 square meters. mm are used as power cords for most household electrical appliances.
Industrial enterprises, energy enterprises
Wires of small sections 1-6 sq. mm are used to connect secondary switching circuits of various protection, automation and control devices for various equipment at industrial enterprises, power plants, distribution substations.
To control powerful equipment, high-voltage switches, a large cross-section cable is used, up to 120 kW. mm, which feeds powerful control solenoids.
In power circuits with a voltage class of up to 1000 V, powering various equipment, a cable with a cross-section from 2.5 to 50 kV is used. mm. A cable with a larger cross-section is used as an input cable from transformers to switchgears or switchboards for various purposes.
In high-voltage networks 6-750 kV, cables, busbars, and busbars with a cross-section of 35 square meters are used. mm up to 1600 sq. mm.
If you liked this article, share a link to it on social networks. This will greatly help the development of our site!
Subscribe to our channel on Telegram!
Just follow the link and connect to the channel.
Don't miss updates, subscribe to our social networks:
Which wires are not suitable?
PVA wire cannot be used in residential premises, despite its low cost, for the following reasons:
- Its conductors are multi-wire, so when connecting the segments you will have to tin and solder each conductor. Because of this, installation takes a long time.
- Multiple wires cannot be laid in the same groove, unlike other cables. Each line will have to be grooved separately.
Products branded PVVP and ShVVP also cannot cope with modern loads. For apartment wiring, the PUNP cable is outdated.
Applications in lighting systems
To organize lighting, you can use both wires and cables, depending on the conditions:
- It is convenient to use cables for indoor wiring - three conductors (phase, neutral, ground) are laid simultaneously;
- Wires can be used for installation in distribution panels or wiring where it is difficult to lay cables;
- outdoors, for the most part, cables are used - due to increased mechanical strength, protection of current-carrying conductors, and also because of the aforementioned convenience;
- When laying overhead (overhead lines, etc.), it is convenient to use SIP - no additional cable is required.
In difficult cases, you need to look at the situation, but it is always better to focus on the cable - for reasons of reliability.
Useful tips
Tips for purchasing electrical cables:
- Carefully inspect the appearance of the cable. Even small bends, dents, or scratches can cause wiring to malfunction.
- The lack of packaging and its poor appearance may indicate poor quality storage of the cable. It is better to refuse such a purchase.
- In order to save money, the lighting can be made with aluminum wires, and a cable with copper conductors can be connected to the sockets.
- To reduce the reserve cross-sectional area to 30%, it is recommended to leave terminals in the apartment panel for connecting additional lines if necessary (for example, purchasing energy-intensive equipment).
The costs of properly installing the electrical network are fully compensated by the durability and reliability of the wiring.
Cable for street (outdoor) lighting
There are 2 main ways to lay cables for street (outdoor) lighting : underground and over the air.
Underground installation of a cable line requires the presence of strong armor made of special wire or galvanized steel tape in the wire structure to prevent mechanical damage or flooding with groundwater. Examples of underground cable grades are VBShv and PvBShv, incl. designed with aluminum cores. If the conditions and standards for a given case allow the use of protective structures, such as pipes, trays, boxes, curbs with an electrical gutter, then it is possible to use unarmored power cables for lighting, for example, VVG, PV, PPV, PUGNP, NYM and others. Laying by air requires the brand to have a self-supporting element, otherwise the cable will have to be suspended on a special steel cable. For aerial installation of lighting systems, the most commonly used brands are AVT, SIP-2, SIP-4.
For more information about installing street lighting, watch the video:
Cable brand
To know which cable to choose for wiring in the house, you need to determine its operating conditions. The brand of wire will depend on this. For a private house, three main zones can be distinguished: interior, street, bathhouse. In this case, you need to take into account whether the wiring is mounted hidden or open.
For hidden wiring
The following brands of cable are suitable for the kitchen, bedroom and other rooms:
- VVG is a single-core copper conductor or cable with up to four cores. Manufactured in round or flat form. A subtype of the VVGng brand prevents the spread of flame along the wiring, and a conductor marked as VVGng-LS does not burn and emits almost no smoke. Russian production;
- AVVG is a single-core aluminum wire or cable with up to four cores. Can be round or flat. The protective shell is unable to burn. Russian production;
- NYM – German analogue of VVGng, does not burn. Only round. The workmanship is high;
- PVS – multi-strand copper conductor of round cross-section;
- SHVVP is a thin flat multi-hair conductor made of copper. Suitable for household electrical and electronic equipment only.
There are no special rules for selection. Take what you think is best. But electricians prefer the German NYM cable. It costs more, but the quality of the wiring will be higher.
For open wiring
In wooden houses, wiring is desired to be of an open type, although no one forbids using it for stone buildings. In this case, the choice of cable determines only its color:
- VVG is painted black;
- NYM gray;
- PVA is available in white or orange;
- ShVVP is standard white, although other colors are rare. Ask the seller about them.
What kind of wiring is best done in a wooden house? It is not the color that is important here, but the fire protection. There are only three options here: Russian VVGng-LS or VVGng, as well as German NYM conductors.
For wiring outside the home
If electricity is supplied to the house not by air, but by ground, then you need to take AVBBSHV cables if you have aluminum wiring, and VBBSHV cables if you have copper wiring. This grade is armored with steel tape, which is applied after the insulating layer. The steel is protected by rubber from the effects of groundwater. This design resists mechanical damage that is possible due to careless trench digging and soil movement.
What cable should I use for wiring outdoors, where precipitation, large temperature changes, sun and wind are possible? VVG and AVVG cables are not afraid of this. They can be laid on the roof and wall.
For the bath
It is forbidden to install sockets and switches in the steam room. The wire in the bathhouse is needed only to provide light. But high demands are placed on him:
- Moisture resistance;
- Ability to withstand temperatures up to 180 degrees.
Russian brands RKGM and PVKV, which are protected by a silicon-containing organic shell, meet these requirements.