The main elements of overhead lines are wires, insulators, linear fittings, supports and foundations. On overhead lines of three-phase alternating current, at least three wires are suspended, constituting one circuit; on direct current overhead lines - at least two wires.
Based on the number of circuits, overhead lines are divided into single, double and multi-circuit. The number of circuits is determined by the power supply circuit and the need for its redundancy. If the power supply scheme requires two circuits, then these circuits can be suspended on two separate single-circuit overhead lines with single-circuit supports or on one double-circuit overhead line with double-circuit supports. The distance / between adjacent supports is called the span, and the distance between anchor-type supports is called the anchor section.
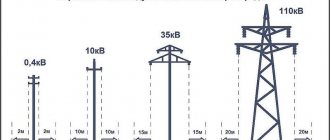
Wires suspended on insulators (A - the length of the garland) to the supports (Fig. 5.1, a) sag along the catenary line. The distance from the suspension point to the lowest point of the wire is called the sag /. It determines the size of the wire approaching the ground A, which for populated areas is equal to: to the surface of the earth up to 35 and PO kV - 7 m; 220 kV - 8 m; to buildings or structures up to 35 kV - 3 m; 110 kV - 4 m; 220 kV - 5 m. Span length / is determined by economic conditions. The span length up to 1 kV is usually 30...75 m; PO kV - 150...200 m; 220 kV - up to 400 m.
Wooden supports
They are usually made from pine logs with the bark removed. For power lines with supply voltages up to 1000 V, it is also possible to use other tree species, for example, fir, oak, cedar, spruce, and larch. Logs that will subsequently become power line supports must meet certain technical requirements. The natural taper of the trunk, in other words, the change in its diameter from the thick lower end (butt) to the upper cut should not exceed 8 mm per 1 meter of log length. The diameter of the log on the upper cut for lines with voltage up to 1000 V is taken to be at least 12 cm, for lines with voltage above 1000 V, but not higher than 35 kV - 16 cm, and for lines with higher voltage at least 18 cm.
Wooden supports can be used for the construction of overhead lines with a voltage not exceeding 110 kV inclusive. Wooden supports are most widely used in overhead lines with voltages up to 1000 V, as well as in communication lines. The advantage of wooden supports is their relatively low cost and ease of manufacture. However, there is a minus, a significant minus - they are susceptible to rotting and the service life of pine supports is about 4-5 years. To protect wood from rotting, it is impregnated with special antiseptics against rotting, for example anthracene or creosote oil. Those parts that will be dug into the ground, as well as cutting ends, braces and traverses, lend themselves to especially careful processing. Thanks to antiseptics, the service life increases by about 2-3 times. For the same purpose, quite often the legs of a wooden electrical support are made of two parts - the main stand and the chair (stepchild):
Where – 1) the main stand, and 2) a chair (stepchild)
If the lower part is severely rotted, it is enough to replace only the stepson.
Metal supports
Plus - durable and reliable in operation. Minus - a large consumption of metal is required, which entails a significant increase in cost (compared to wooden ones). Metal supports of overhead power lines are used, as a rule, at voltages from 110 kV, since the operation of metal supports involves high costs for performing very labor-intensive and expensive work on periodic painting, which protects against corrosion.
Reinforced concrete supports
In the industrial manufacturing process, they are the most optimal option for overhead lines both up to 1000 V and above 1000 V. The use of reinforced concrete supports dramatically reduces operating costs, since they practically do not require repairs. Currently, almost everywhere, reinforced concrete supports are used in the construction of overhead lines of 6-10 kV and up to 110 kV. They are especially widespread in urban networks up to and above 1000 V. Reinforced concrete supports can be made either monolithic (cast) or in the form of assemblies, which are assembled directly at the installation site. Their strength depends on the method of concrete compaction, of which there are two - centrifugation and vibration. When using the centrifugation method, a good density of concrete is obtained, which subsequently has a good effect on the finished product.
On overhead power lines, special anchor, corner, end, and intermediate supports are used.
Classification of supports by functional purpose
According to their design and technological purpose, power transmission line supports are divided into the following types:
- intermediate – the most popular and widely demanded type of product, which is designed to maintain conductors at the design height. When designing and building high-voltage lines, intermediate support elements make up 80–90% of the total number of products used. In this case, the intermediate supports are intended solely to support the wires and do not bear the load from the tension of the wires. The amount of permissible load depends on the model of the supporting elements, which are accepted for installation during individual calculations. Installation of intermediate supports is carried out on straight sections of the line. Steel and reinforced concrete products can be used at low temperatures of negative temperatures down to – 65 ºС, allowing the use of elements in the northern regions of the country;
- transitional or anchor - are used at points, network nodes, where the presence of barriers of natural origin or engineering structures requires a change in topology. These may include reservoirs, rivers, ravines, hills, infrastructure facilities, etc. The supports have increased dimensions, which allow them to withstand significant loads caused by the tension of the wires. The design of such products is characterized by increased rigidity;
- corner – products which are installed at the turning points of the high-voltage line. Angular intermediate elements are used for small rotation angles - up to 30 degrees. Above that, full-fledged corner anchor structures of supporting products are used, allowing them to withstand the forces of constant tension of wires and cables of adjacent spans;
- end - products, the installation of which is carried out at the starting and ending points according to the power line installation project. The wires from them go to the substation portals. Elements of this type, as a rule, perceive a one-sided load from the tension of the conductors;
- transpositional - supports of a special type, which are used if there is a need to organize branches or change the order of conductors running as part of an overhead line. Also, special products are used in cases where the line needs to be strengthened to increase the anti-wind load or when two or more cross power lines intersect.
Anchor supports
Their purpose is to rigidly secure wires and lines to them. The location for their installation is determined by the project. By design, the anchor support must be strong, since if a wire breaks on one side, it must withstand the mechanical load of the wires on the other side of the line.
Anchor spans are the distance between anchor supports. On straight sections (depending on the cross-section of the wires), anchor spans are up to 10 km long.
General structure of power lines
Externally, a power line, regardless of category, looks like a support on which a power cable is suspended. Fastening is carried out using special insulators that prevent leakage even in heavy rain. They allow you to hang wires on various engineering structures without the risk of electric shock to service personnel, other people, and animals. All elements are made of durable materials (concrete, stainless steel, etc.).
More details about the main parts of power lines:
- Supports are the basis of the entire structure; they are responsible for hanging wires at a certain level and holding them, regardless of climatic conditions.
- Wires - transmit electric current over a given distance in accordance with the design.
- Linear reinforcement – performs the functions of fastening individual elements to each other.
- Insulators are used to “separate” live parts of an overhead line from all other elements (supports, fittings).
It is also worth noting such an element as security cables. They are mounted in the upper part of the supports and perform the functions of protection against atmospheric (lightning) surges and lightning during thunderstorms. Structurally, the supports are divided according to the number of circuits located on them - 1 or two lines (3 wires of one three-phase network). On the anchor supports, which are the end points, the cable is rigidly fixed and tensioned to the tension specified by the design.
Intermediate supports only support it in order to prevent it from sagging below the limit, when there is a risk of contact with living objects. It is not possible to completely eliminate sagging, because a powerful, large-section cable with thick insulation is used. The same applies to security cables; they are quite strong, but because of this they have a considerable mass, making it difficult to tighten to the “string” state.
Special supports
They are electric poles of increased height and are used at intersections of power transmission lines with highways and railways, rivers, intersections between power lines themselves, and in other cases when the standard height of electric poles is not enough to ensure the required distance to the wires. Intermediate electrical supports for lines with voltages up to 10 kV are made single-post (candle-shaped). In low-voltage networks, single-post supports perform the functions of corner or end supports, and are also equipped additionally with guy wires attached to the side opposite to the tension of the wires, or with struts (supports) that are installed on the side of the tension of the wires:
For lines with a voltage of 6-10 kV, electrical supports are made A-shaped:
Air lines are also characterized by their main dimensions and dimensions.
Overhead line dimension is the vertical distance from the lowest point of the wire to the ground or water.
The sag is the distance between the imaginary straight line between the wire attachment points on the support and the lowest point of the wire in the span:
All dimensions of power lines are strictly regulated by the PUE and directly depend on the value of the supply voltage, as well as the terrain through which the route passes.
The PUE also regulates other dimensions when crossing and approaching power lines, both among themselves and between communication lines, highways and railways, overhead pipelines, and cable cars.
To check the designed power line to the requirements of the PUE, mechanical strength calculations are performed, the methods of which are given in special courses on electrical networks.
Terms and Definitions
Power line support (PTL) is a structure designed to hold wires and, if available, lightning protection cables for overhead power lines and fiber-optic communication lines at a given distance from the surface of the earth and from each other.
Intermediate power line supports are structures installed on straight sections of power lines and designed only to support wires and cables at a certain level. Not designed for loads directed along the route.
Intermediate straight power line supports are structures installed on straight sections of overhead lines to support the wire in the anchor span.
Intermediate corner power line supports are structures installed at the turning points of the line, used to compensate for the total lateral loads from the tension of the wires when the route turns .
Anchor supports for power lines are structures on straight sections of power lines at places of transition through engineering structures or natural barriers to limit the anchor span, as well as in places where the number, grades and cross-sections of wires change.
Anchor-corner power transmission line supports are structures used for the construction of overhead lines in areas with various ice and wind loads and designed for small rotation angles and small grades of wires.
Power line end support is a structure that is a type of anchor support and is installed at the end and beginning of a power transmission line. Designed to withstand the load from one-sided tension of all wires and cables.
Lattice power line supports are structures used in the construction of overhead lines with a voltage of 35-1150 kV and intended for installation in populated and uninhabited areas in IV climatic icy and windy regions, where the ambient temperature does not fall below -65°C.
Anchor-corner metal supports for 35 kV overhead lines are single-column free-standing structures used for the construction of 35 kV overhead lines in areas with various ice and wind loads.
Anchor-angle steel power transmission line supports are special steel structures with horizontal wires, designed for use in urban environments.
Transition metal supports for power transmission lines of 110 kW overhead lines are single-column, free-standing structures used for the construction of overhead lines up to 110 kV in areas with various ice and wind loads.
Metal lattice transmission line supports are structures used in the construction of overhead lines with a voltage of 35-1150 kV and are intended for installation in populated and uninhabited areas in IV climatic icy and windy regions, where the ambient temperature does not fall below -65°C.
Unified lattice transmission line supports are structures used in the construction of overhead lines, which are made in the form of spatial lattice structures and are assembled from a large number of elements made of rolled angle steel.
Transient power line supports are structures used to cross overhead lines through natural barriers and engineering structures.
Transposition transmission line supports are structures used to change the order of arrangement of wires on the supports.
Branch power line supports are structures used to make branches from the main overhead line.
Power transmission line supports for large crossings are structures used in the construction of overhead lines across rivers and water bodies, etc.
Cross power transmission line supports are structures used to implement the intersection of two overhead lines.
Overhead line supports with guy wires are structures used to compensate for the forces arising from the tension of wires when turning and ending the power line route.
Free-standing single-post metal power transmission line supports are structures based on steel polyhedral posts and have a flange connection to the foundation.
Steel multifaceted power transmission line supports are structures used for the construction of overhead power lines and designed to support overhead power line wires with a voltage of 10-500 kV. Installed in populated and uninhabited areas in IV icy and windy areas, where the air temperature can drop to -65°C.
Steel lattice transmission line supports are spatial lattice structures made of low-alloy rolled steel grade 09G2S or carbon steel grade St3 with anti-corrosion treatment by hot-dip galvanizing or coating with a special zinc-filled composite.
Steel transmission line supports made of bent profile are spatial structures used when laying overhead lines to increase reliability, reliability, durability and reduce operating costs, especially in hard-to-reach areas with severe climatic conditions.
Single-circuit power transmission tower supports are T-shaped structures tapering upward with one traverse, used for the construction of high-voltage direct current lines.
Portal power line supports are structures made of metal, wood or reinforced concrete, resembling the letter “P” or the letter “N”. They are widely used on 330-750 kV power lines. As a rule, single-chain.
AP-shaped power transmission line supports are single-circuit spatial structures created using welded metal pipes, MGS or wood, resembling the letter “A” in profile and the letter “P” in front. The cross-section of pipes in these supports can reach 1300 mm, and the height can be over 80 m.
Three-post separate lattice power line supports are spatial metal structures used as anchor supports for the construction of overhead lines at turns and transitions.
L-shaped power transmission line supports are flat L-shaped lattice structures, articulated with two foundations, used as transition lines for two 110 kV or 220 kV overhead line circuits.
Y-shaped single-chain supports are metal spatial lattice-type structures. Used as transitional supports for overhead lines.
V-shaped intermediate pores of power lines are spatial structures of the “Nabla” type with guys, used on power line routes of 330-1150 kV. Exclusively single-chain.
Power transmission line poles are spatial structures of a non-lattice type, based on wooden, metal or reinforced concrete poles. There are single-post and portal ones. structures that serve to support live wires and lightning protection cables above the earth's surface.
Portal pole supports for power transmission lines are spatial structures consisting of two poles (wooden, reinforced concrete or MGS) connected by a common traverse.
Intermediate supports with internal connections are structures used in the construction of overhead lines that have internal fixed connections connecting several support elements to each other.
Intermediate transitional power transmission line supports are steel structures for the construction of overhead lines up to 330 kV in areas with various ice and wind loads. These supports are produced as single-column free-standing ones.
Multifaceted supports of a closed profile - steel structures of a closed profile (six-, eight-, etc. edges), galvanized by hot-dip galvanizing, with bored and sheet-pile foundations.
Multifaceted open profile supports are open profile steel structures (triangular and square cross-section), galvanized by hot-dip galvanizing, used for the construction of overhead lines.
Wooden power line poles are pine and larch round logs impregnated with an anti-rot compound (antiseptic), used for lines with voltages up to 220/380 V.
Composite power line supports are building structures made of reinforced polymer composite materials, designed to hold wires and lightning protection cables at a given distance from the ground and from each other.
Cable-stayed emergency reserve supports are V-shaped structures on guys with a cable-stayed polymer traverse, used for the prompt elimination of technological violations on power lines.
Mobile power transmission line supports are prefabricated structures for the construction of overhead lines, which can be assembled without the involvement of teams of workers and without preparing the foundation.
Narrow-base power transmission line supports are a structure no more than 4 meters high for laying overhead lines, installed in the foundation with fastening to a steel pipe or steel screw or reinforced concrete pile.
Power transmission line branch supports are metal structures used to organize branches from overhead lines.
Vibrated reinforced concrete posts for power transmission line supports are elements of power transmission line supports that are made from both prestressed and non-stressed reinforced concrete in multi-place rectangular formwork using vibration and heat treatment.
Centrifuged reinforced concrete racks for power transmission line supports - conical with a slope or cylindrical reinforced concrete structures of annular cross-section, manufactured by rotation in special forms.
Swinging transition supports for power transmission lines are flat L-shaped structures, hingedly connected to two foundations, used for laying overhead lines.
Classic tower supports for power transmission lines are spatial structures used on both single-circuit, double-circuit and multi-circuit crossings of lines.
Elevated linear power line supports are structures that have special supports at the base. Used for short transitions.
Three-post power transmission line supports are structures that have three posts, each of which is designed for hanging wires of one phase.
Power line supports based on polyhedral bent posts (MGS) are spatial structures of a transitional type, made of multifaceted bent posts. Can be U-shaped or tower.
High-voltage cross-beams are gripping devices used for installing pin and suspension insulators and fastening insulated and non-insulated wires, installing disconnectors on 6-10 kV overhead lines and switchgear in populated and uninhabited areas.
Low-voltage traverses TM are the main load-bearing elements of overhead line supports, used for installing pin and suspension insulators and fastening insulated and non-insulated wires, installing disconnectors on overhead lines and switchgear 6-10 kV in populated and uninhabited areas.
High-voltage crossbeams TV, V, B - steel elements in the supports of 35 kV and 110-220 kV overhead lines.
High-voltage extensions TS are devices intended for use in transition supports for 6-10 kW overhead lines. They allow you to increase the height of standard reinforced concrete racks to organize the safe passage of power lines through various engineering structures, including other overhead lines with insulated and non-insulated wires.
Exhaust overlays and headbands in power transmission line supports are devices designed for installing insulators of the upper single or double wire or insulating pendants on reinforced concrete supports of 6-10 kV overhead lines in populated and uninhabited areas.
Brackets and assemblies for fastening slopes in power transmission line supports are connecting elements used in the construction of corner, transition, branch and end supports with struts based on reinforced concrete racks of trapezoidal cross-section and serve for reliable fastening of the strut to the support rack, transmission and distribution of existing horizontal loads between the connected load-bearers designs.
Power line support tie-downs are elements used for the installation of corner, transition and end supports based on SV164 reinforced concrete pillars, to compensate for the forces arising from the tension of wires when turning and ending the power line route.
Pins for supports are connecting elements used to attach pin insulators to the cross-arms of power transmission line supports.
Support clamps are metal elements for power transmission line supports, made of carbon steel with corrosion protection and galvanized or painted.
An A-frame drop boom is a structure used to lift and install assembled power transmission towers from a horizontal to a vertical position by rotating around the hinge of the mounting boom connected to the poles being mounted.
Reinforced concrete foundations for power transmission line supports are standardized foundations used when installing power line supports with voltages of 35-500 kV.
Unified foundations for 35-500 kV transmission line supports are a mushroom-shaped monolithic foundation with a vertical or inclined post or with hanging slabs.
The foundations of metal supports for overhead lines are monolithic footboards in formwork. They can have a vertical or inclined stand.
Crossbars for overhead line supports are structural elements of power transmission line supports used to improve the ability of the foundation to withstand horizontal loads.
Wire sag - vertical distance from the line connecting the wire suspension points on adjacent air supports. Power lines, to the lowest point of the wire. If the suspension points have different heights, then two S. points f1 and f2 are determined. For air lines with a voltage of 35-110 kV S.p. is 3 - 4 m, for lines 500 - 750 kV - 7 - 8 m.
Wire for overhead power lines - self-supporting insulated and protected wires for overhead power lines.
Lightning protection cable is a cable lightning rod, a grounded wire in overhead power lines, used to protect current-carrying wires from direct lightning strikes.
A power line arrester is a device for closing electrical circuits by means of an electrical discharge in a gas, vacuum or (less commonly) a solid dielectric; contains 2 (or more) electrodes separated (respectively by one or more) discharge gap, the conductivity of which changes sharply when the potential difference between the electrodes becomes equal to a certain value determined under given conditions - the breakdown voltage, or ignition potential.
Overhead power lines are spatial structures in which wires are suspended above the ground or above water.
Overhead line (OL) is a device for transmitting electricity through wires located in the open air and attached to supports using insulators and fittings.
An anchor span is the distance between two overhead line anchor supports on which the wires are rigidly fixed.
Wire is an overhead line element designed to transmit electric current.
Wire (cable) tension is the force directed along the axis of the wire (cable), with which it is stretched and secured to the overhead line anchor supports.
The dimension of the overhead line is the distance from the lowest point of the wire sag to the surface of the earth.
Wire sag (f) is the vertical distance between the straight line connecting the wire suspension points and the lowest point of its sag.
Overall wire sag (fgab) – the largest wire sag in the overall span.
Overhead line span is the distance between adjacent supports of overhead power lines.
Overall span (lgab) – a span, the length of which is determined by the normalized vertical distance from the wires to the ground when installing supports on a perfectly flat surface.
Weight span (lweight) is the length of the overhead line section, the weight of the wires (cables) of which is perceived by the support.
Wind span (lwind) is the length of the overhead line section from which the wind pressure on the wires and lightning protection cables is perceived by the support.
Vibration of wires (cables) - periodic vibrations of a wire (cable) in a span with a frequency from 3 to 150 Hz, occurring in a vertical plane in the wind and forming standing waves with a swing (double amplitude) that can exceed the diameter of the wire (cable).
Dance of wires (cables ) - stable periodic low-frequency (0.2 - 2 Hz) oscillations of a wire (cable) in a span with one-sided or asymmetrical deposition of ice (wet snow, frost, mixture), caused by wind speeds of 3 - 25 m/s and forming standing waves (sometimes in combination with traveling ones) with the number of half-waves from one to twenty and an amplitude of 0.3.
A garland of insulators is a device consisting of several suspended insulators and linear fittings, movably connected to each other.
Linear fittings for overhead lines are, in particular, elements for fastening insulators, protective equipment, clamps, and spiral ties.
Normal overhead line mode is the state of the overhead line with intact wires or cables.
Emergency mode of an overhead line is the state of an overhead line with broken wires or cables.
Installation mode of overhead lines - the state of overhead lines when installing supports, wires or cables.
The overhead line route is the position of the overhead line axis on the earth’s surface.
Cable fastening is a device for attaching lightning protection cables to an overhead line support; if the cable fastening includes one or more insulators, then it is called insulated.
An electrical network is a set of overhead and cable power lines and substations operating in a certain area.
Electrical installation work during the construction of power lines is a complex of works related to the installation of electrical networks and electrical equipment. Electrical installation work is carried out in stages following a certain sequence of actions.
Reinforced concrete support - a short support post made of reinforced concrete or steel, fixed in the ground and used to secure a wooden power line support or a wooden lighting pole.
Anchor clamp is a device used for end anchoring of insulated and unprotected conductors with a voltage of 6-35 kV. The body of the end anchor clamps is made of aluminum alloy, resistant to corrosion.
Wedge-type end clamps are devices used for anchoring protected wires in power line supports. The clamp is easily mounted on wires, as it does not require stripping of insulation.
Supporting clamps - devices for power transmission line supports, which make up a wide range of fittings for insulated power supply, are used for bare and protected wires with a voltage of 6-35 kV.
Suspension clamp is a device designed for fastening tension and suspension clamps to the support post on straight sections and at internal angles of rotation of the line.
Emergency mode of an overhead line is the state of an overhead line when one or more cables are broken.
Fiber-optic communication line on overhead power lines - a communication line through which an optical cable placed on overhead power line supports is used to transmit information.
Vibration dampers for power transmission towers are devices installed on power lines to limit vibration of wires and lightning protection cables and prevent fatigue damage caused by vibration.
The foundation of a power transmission line support is a structure embedded in the ground or laid directly on the ground without deepening and transferring loads from the support, insulators, wires and external influences (ice, wind) to it.