Many people don't even think about this question. After all, most often the average citizen is interested in electricity inside the house, and external lines (power lines), as he thinks, should be handled by specialists...
Ability to recognize power line voltage
Many people don't even think about this question. After all, most often the average citizen is interested in electricity inside the house, and external lines (power lines), as he thinks, should be handled by specialists. But it is important for everyone to take into account that ignorance of simple differences between overhead power lines (OHTs) can cause injury or even death to a person.
Types and types
Power lines can be divided into two large groups - overhead and underground. They are classified according to many criteria, ranging from purpose to current parameters. Different types of devices are used for different purposes. They conduct electricity to homes, businesses, streetlights, stores, billboards and other structures.
What types of power lines are there?
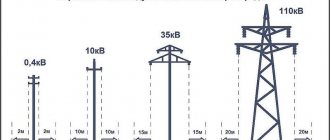
It is useful to know what voltage is transmitted along power lines, since each voltage has its own safe zone from wires. Let me give an example of the relationship between voltage and safe distance to it:
- For power lines 0.4 kV – 2 meters
- Power lines 1 - 20 kV - 10 meters
- Power line 35 kV – 15 meters
- Power line 110 kV – 20 meters
- Power lines 150 - 220 kV - 25 meters
- Power lines 220 - 500 kV - 30 meters
- Power line 750 kV – 40 meters
- Power line 1150 kV – 55 meters
Knowing the safe distance to power lines, you need to learn how to visually determine the voltage.
Power lines 220 kV
In appearance they resemble 110 kV, but larger, higher, and have longer strings of insulators - about 10-20 pieces, you’ll hesitate to count. There is an opinion that there is no phase splitting on such power lines, there is still 1 phase, this is 1 wire, but this opinion is inaccurate. The supports are also made of metal structures, much less often of concrete.
220 kV lines are found much less frequently than 110 kV lines. As a rule, they connect different settlements, regions, districts, and can have a significant length of up to several tens or even hundreds of kilometers. Like 110 kV lines, they usually run in two circuits, but single-circuit options also exist. Being near such lines, you can already hear a distinct crackling sound - corona discharges are taking their toll.
The security zone of a 220 kV cable line is 25 meters.
220 kV power line support - Dagomys substation
Double circuit tower 220 kV
HF suppressors 220 kV
Sign on the support
Supports of a two-tier structure
Power line supports and other visible elements
To ensure that the wire is securely held, supports are used. In the simplest case, these are wooden poles. But this design is applicable only to lines up to 35 kV. And with the increase in the value of wood, reinforced concrete supports are increasingly used in this stress class. As the voltage increases, the wires must be raised higher and the distance between phases greater. In comparison, the supports look like this:
Power line supports
In general, supports are a separate topic, which is quite extensive. For this reason, we will not delve into the details of the topic of power transmission line supports here. But in order to briefly and succinctly show the reader its basis, we will show the image:
Support Attributes
To conclude the information about overhead power lines, we will mention those additional elements that are found on the supports and are clearly visible. This
- lightning protection systems,
- as well as reactors.
The first ones contain a special cable, which is located above the wires, and pin lightning rods. The latter are designed to limit the rate of current rise during a short circuit. The reactor is essentially a choke.
Reactors on power transmission towers
In addition to the listed elements, several more are used in power transmission lines. But let’s leave them outside the scope of the article and move on to cables.
Power lines 1150 kV
I haven’t seen it live yet, perhaps because there is only one line for such voltage in our country. More precisely, two ends enter our country from Kazakhstan: one can be found somewhere in Chelyabinsk, the second near Barnaul, near the village of Ozerki, in the form of the Altai substation 500/110/10. This line, by the way, now operates at a voltage of 500 kV - the project for the highest-voltage power line in the Soviet Union never took off...
What can you say about such a power line? Enormous dimensions of the supports, 8 wires per phase, and incredibly long garlands of insulators. I think this cannot be confused with anything...
By the way, there are pieces of power lines that look similar near the Bely Rast substation, and somewhere near Kaluga. But even if they work, they also operate at 500 kV.
Kinds
Power lines are used to move and distribute electricity. Types of lines can be divided:
- by type of cable arrangement - aerial (located in the open air) and closed (in cable ducts);
- by function - ultra-long-distance, for highways, distribution.
Overhead power lines can also be divided into subtypes, which depend on the conductors, type of current, power, and raw materials used. These classifications are described in detail below.
Alternating current
Based on the type of current, power lines can be divided into two groups. The first of them is DC power lines. Such installations help to minimize losses when moving energy, and therefore are used to transmit current over long distances. This type of power line is quite popular in European countries, but in Russia such power lines can be counted on one hand. Many railroads operate on alternating current.
Power transfer circuit
Direct current
The second group is DC power lines, in which the energy is always the same regardless of direction and resistance. Almost all installations in Russia are powered by direct current. They are easier to produce and operate, but losses when moving current very often reach 10 kW/km in six months on a power line with a voltage of 450 kV.
Types of power lines by voltage
All electrical installations and power lines have an electromagnetic impact on the environment. The main impact parameter is the electric field strength, which shows the level of force around the wires in the power line area. Due to electromagnetic radiation, lines of force arise in the space around power lines, which, when crossing any conducting medium, can induce an EMF in it. As a result, an unusual potential appears on any object, and in the presence of a closed circuit, electric current will flow.
However, the electromagnetic field strength is not uniform in space - the intensity decreases as one moves away from the power line. In addition, the gradation of harmful effects largely depends on the rating of the transmission line.
Therefore, all power lines are divided into the following categories:
- Low voltage – supply voltage in which is up to 1 kV;
- Medium level – for lines from 1 to 35 kV;
- High voltage – ratings for 110, 154, 220 kV;
- Ultra-high – for ratings from 330 to 500 kV;
- Ultra-high – power lines with voltages of 750 and 1150 kV.
It should be noted that the effect of electromagnetic waves depends not only on the voltage level, but also on the strength of the electric current flowing through the wires. Therefore, the generally accepted standard establishes the optimal distance to live parts, which will be safe [ ].
Classification
Electrical energy is transmitted through metal wires, where the conductor is copper or aluminum. The method of laying wires differs:
- By air - by air lines;
- In soil (water) - cable lines;
- Gas-insulated lines.
The listed types of power lines are the main ones. Experiments are being conducted on wireless energy transfer, but at present this method is not widespread in practice, with the exception of low-power devices.
Wireless charger
By type of current
Most existing power lines are designed to operate with alternating current, which is due to the ease of voltage conversion.
Certain types of lines operate with direct current. They are intended for some applications (power supply of contact networks, powerful DC consumers), but the overall length is small, despite lower losses on the capacitive and inductive components.
According to the operating mode of neutrals in electrical installations
- Networks with solidly grounded neutral;
- Networks with isolated neutral;
- With resonant grounded neutral;
- With effectively grounded neutral.
According to the operating mode depending on the mechanical condition
The main operating mode of the overhead line is normal, when all wires and cables are in good condition. There may be cases when some of the wires are missing, but the power line is in operation:
- In case of a complete or partial break - emergency mode;
- During installation of wires and supports, use installation mode.
By purpose
- Intersystem (long-distance) – for combining several energy systems. This includes overhead lines 500 kV and above;
- Trunk – for connecting power plants into a network within one power system and supplying electricity to central substations;
- Distribution - for connecting large enterprises and settlements with central substations;
- overhead lines of agricultural consumers;
- Urban and rural distribution network.
Installation method
The main criterion by which power lines are classified is the constructive method of transmitting energy. Lines are divided into the following types:
- aerial - electric current is transmitted through wires suspended on special supports;
- cable - transmission of electric current is carried out through power cables laid in the ground, cable ducts or other types of engineering structures.
Power lines 500 kV
Three pyramidal supports of a 500 kV power line and interesting graffiti
This is where the real monsters begin, their very appearance inspiring greatness and awe. 500 kV power lines are large lines that usually connect power systems of different regions; the typical line length is about 200-300 km, although they can be longer.
The supports are very high, usually U-shaped or glass-shaped, always single-chain. Corner and tension supports are usually made of three separate pyramidal supports and have 3 garlands of insulators. There is phase splitting - 3 wires per phase, insulators consist of an average of 30 plates per garland. In the south of Moscow, by the way, in Butovo, you can find a 500 kV power line with a vertical phase arrangement and splitting into 4 wires.
In our country, not many facilities can operate at a voltage of 500 kV. Often (but not always), one such substation powers one large city, for example, Novosibirsk. Around the harsh Chelyabinsk you can count as many as 3 such substations, and near the vast Moscow there are already 10 of them.
Under the 500 kV lines there is a devilish crackling sound, the grass begins to beat with electricity and fluorescent lamps glow. Which, however, does not prevent people from building summer cottages in clearings for such power lines...
The security zone of a 500 kV power line is 30 meters.
Intermediate U-shaped support
Tension pyramid supports
Corner supports with surge arrester
Sign on one of the supports
Building directly under power lines
Composition of power lines
The composition of cable and overhead lines is different. For differentiation, we will consider each type of power line separately.
Components of an overhead power line
Overhead lines include many devices and structures. We list the main ones:
- supports;
- fittings and insulators;
- grounding devices;
- wires and cables;
- discharge devices;
- markers for identifying wires;
- substations.
In addition to their direct purpose, overhead lines are used as engineering structures for suspending fiber-optic communication cables. In this regard, on some lines the number of constituent elements is constantly growing.
Components of a cable power line
Cable lines are used to transmit electrical energy in places inaccessible for suspension along overhead line supports. The structure includes a power cable and input units at the substation and to end consumers.
Power line insulator design
Insulators are the main protective device that prevents short circuits and leakage of electric current in wet weather. Such products are produced in accordance with standards such as GOST 27611-88, 6490-93, 30531-97, 18328-73 (the application of standards depends on the material). Structurally, they are divided into categories: pin, suspended, rod, support-rod. The first are used on lines up to 1000V, the rest are intended for power lines of 110 kV and above.
Difference in material:
- Porcelain - used 100 years ago, is now considered obsolete. And all because of their mechanical fragility, the difficulty of finding microcracks, and breakdown. This disadvantage is partly compensated for in ceramic insulators (analogous to porcelain).
- Glass is also fragile, with low impact strength, but the place where the breakdown occurred is clearly visible on them. Like porcelain, they require care during transportation, storage or installation.
- Polymer - this material is lighter and stronger than glass and porcelain, so it is cheaper both in transportation and during installation and operation. With them there is no longer a risk of damage by vandals, the plastic is not so easy to break.
The only drawback of polymer insulators is the lack of objective data on the durability of the structure. Plastic began to be used in the construction of power line insulators quite recently. Plus, it is difficult to see electrical damage on it, even if a breakdown occurs. Otherwise, plastic insulators are noticeably superior to porcelain (ceramic) and glass.
All materials can withstand severe frosts and heat well, so when choosing an option, they usually focus on cost, ease of transportation, installation, and upcoming working conditions. Thus, polymer products in the heat are capable of bending under longitudinal loads. How critical this is, you need to check with the specialists servicing a particular route. Because it is one thing to install insulators on 10 kV power lines and quite another to work with 110 kV.
Rationale for high voltage
It is customary to deliver electric current to consumers at 220 and 380 volts. However, in conditions of long lines this is not beneficial, since losses in sections longer than 2 km may not be comparable with the required power consumption.
In order to reduce losses over long distances, the power is increased and high voltage current is transmitted. To do this, step-up substations are used before transmission, and step-down transformers are placed in front of the consumer. So the transmission line looks like this:
Structural diagram of power lines
Voltage danger
High-voltage lines differ in dangerous and safe voltages. The higher the power of the line, the greater the distance the electric field operates.
There is a direct relationship between these values. To accurately calculate the voltage, it is necessary to take into account that the connecting phase of one phase may have a different number of wires. For example, 2 wires typically correspond to a voltage of 330 kV, 3 wires to 500 kV, and 4 wires to 750 kV.
Power line supports and pond Source energybase.ru
Purpose of overhead power lines
Such overhead lines are called installations that are used to move and distribute electrical energy along cables located in the open air and held using special racks. Overhead lines are installed and used in a wide variety of weather conditions and geographic areas, and are prone to atmospheric influences (precipitation, temperature changes, winds).
Therefore, overhead lines must be installed taking into account weather factors, air pollution, installation requirements (for a city, field, village), etc. The installation must comply with a number of rules and regulations:
- economical cost;
- high electrical conductivity, strength of the ropes and racks used;
- resistance to mechanical damage and corrosion;
- be safe for nature and people, do not occupy a lot of free territory.
What do insulators look like?
Protective devices
Lightning protection conductors, arresters and grounding devices are used as protection. Grounding of metal supports is carried out by mechanically attaching the supporting structure to the ground loop. Grounding of reinforced concrete supports is especially important, since when current leaks, it begins to flow through the concrete reinforcement, having a destructive effect. The damage caused to the support will not be visually visible.
Important! For best protection, the security wire is placed above all others.
Determination of power line voltage
Of course, cable power lines are mostly hidden, and those located in the open air cannot always be distinguished visually.
But air lines can be identified by:
- The type of supports used in power transmission lines;
- The appearance and number of insulators;
- Seeing off;
- The size of the security zone;
- Letter marking on the supports (T – 35 kV, S – 110 kV, D – 220 kV).
Therefore, next we will consider a system for determining the voltage value of power lines using basic visual criteria.
Power lines 330 kV
It must be said that this is not a very common type of power transmission lines, and they can only be found in St. Petersburg, where the entire energy ring operates at a voltage of 330 kV, and, perhaps, even in Crimea.
Outwardly, they strongly resemble 220 kV lines, but they look somewhat larger, and have a clear splitting of the phase wires into 2 wires. There are also about 20 insulators in the garlands.
I was lucky enough to visit St. Petersburg once, so, in fact, here it is:
330 kV power line (left)
Impact on human health
Thanks to research by scientists, it was found that exposure to electromagnetic fields has a negative impact on human health. Currents are formed in his body. This is explained by the conductivity of organs and tissues through which blood and lymph circulate.
An analysis of the studies showed that residents of houses located near power lines or substations developed cancer twice as often as residents of other areas. The field had an even stronger effect on the child’s health. Children fell ill with leukemia 4 times more often.
The negative impact of high-voltage lines on the following body systems has been recorded:
- cardiovascular,
- hematological,
- nervous,
- sexual,
- endocrine,
- immune.
It has been established that the health of people living near power lines gradually deteriorates over time. They are more likely to experience headaches, memory problems, muscle pain, and dizziness. The number of strokes and heart attacks is increasing. I am worried about insomnia and weakness. Women have problems bearing and giving birth to children. The health of newborns is weakened.
The harm a person receives when exposed to an electric field depends on the intensity and the duration of the effect on the body.
Valid values:
- in populated areas – 5 kV/m;
- when crossing roads – 10 kV/m;
- outside populated areas – 15 kV/m;
- in hard-to-reach places - 20 kV/m.
A person can be exposed to an electric field of 0.5 kV/m for a long time, without any negative impact on health.
If a person is required to stay in places of high tension, one must be guided by the following standards according to which the time of stay in the zone is:
- not limited at 5 kV/m;
- no more than 180 minutes at 10 kV/m;
- 90 minutes at 15 kV/m;
- 10 minutes at 20 kV/m;
- 5 minutes at 25 kV/m.
If these conditions are met, human health is restored within 24 hours.
If it is impossible to limit the time spent by working personnel at hazardous objects, workplaces are shielded with metal sheets, nets and other devices. Shrubs with a height of 3 meters and 6-meter trees planted under overhead lines give a good effect.
When exposed to electromagnetic fields in residential buildings, it is important to preserve the health of the people living there. For this purpose, sanitary standards have been developed (SanPiN 2971-84), regulating the minimum safe distance, the protective zone, from the power line to the nearest buildings.
Increased demands are placed on the location of ultra-high voltage routes. The distance from the overhead line to the populated area should be:
- at 750 kV not less than 250 m,
- at 1150 kV not less than 300 m.
Health hazards from power lines
A voltage of 10 kV is considered safe for humans. It creates a background density not exceeding 10 μT - microtesla. For comparison, the Earth's magnetic field is 30–50 μT.
Standard support drawing
It differs from the radiation generated by overhead lines in that it has a constant or smoothly varying value. A current with a frequency of 50 Hz passes through the power line - this means that per second the current changes its direction 50 times, a complete oscillation occurs - an alternating current wave. The value of the emitted magnetic field also changes with this frequency.
The highest value of natural vibrations reaches 40 Hz. When constantly in the zone of magnetic waves with high values, malfunctions occur in the human body. This is possible not only when standing under power lines for a long time, but also next to household electrical appliances, especially thermal ones. The damage from the close proximity of overhead lines is commensurate with the harm to health caused by an iron, refrigerator, washing machine, or computer.
Types of supports
In the European Union, it is generally accepted that if the voltage in the power line wires is higher than 35 kV and the apartment is located closer than the standard interval of the security zone plus 20 m, then, according to the health standards of the United Europe, such proximity can cause a number of diseases of the nervous, cardiovascular and immune systems. systems
The distance from power lines and possible harm to health in this case have a direct relationship. Construction of housing in the European Union is permitted at a distance of 20 meters from the sanitary protection zone, if we take its value from our PUE standards. Russian standards for distance to residential buildings are described above.
Table of European standards.
| Voltage, kV | Security zone according to PUE, m | EU norm for construction, m |
| 35 | 15 | 35 |
| 110 | 20 | 40 |
Impact on the environment and ecology
Electromagnetic fields have a strong influence on all biological objects located near air routes: insects, plants, animals.
The proximity to high-voltage lines has a detrimental effect on bees. Insects become aggressive, restless, lose their working capacity and flight activity. There is a threat of death of queens and families.
Flying insects - beetles, mosquitoes, butterflies - tend to an area with a lower level of tension.
Plants change the shape of leaves, stems, flowers, extra petals and other developmental anomalies appear. According to some data, the electromagnetic field has a positive effect on the yield of agricultural crops, on the fruiting of berries and vegetables. Experiments have shown that after exposure to a high-intensity field, the seeds began to produce a higher percentage of germination and rapid germination.
The impact of overhead power lines on animals is just as negative as on people. Artiodactyls are the most sensitive. If the pasture is located in an area adjacent to an overhead line, a potential of 10 kV can be induced in the body of the animal, isolated from the ground by its hooves. When you touch grounded objects (grass, bush branches), a current pulse of 100 - 200 μA occurs. This value is not life-threatening. The health of the artiodactyl will not deteriorate, but it will experience unpleasant sensations. If wooden overhead line supports are treated with creosote, then contact with this substance can have adverse consequences for the animal.
Birds become victims of electrical discharges through direct contact with live parts and when touching the insulating parts of the wire suspension.
To minimize the harm caused to the environment by high-risk objects, it is necessary to use special protective devices.
High-voltage power lines are capable of locally affecting even the weather. It was recorded how power lines affect air flows. The cold air, having reached the high-voltage route (800 kV), began to flow around it.
In his work on the theory of atmospheric electricity, Russian scientist Lev Aleksandrovich Pokhmelnykh put forward the hypothesis that high-voltage power lines have an adverse effect on the environment. According to the scientist, global warming and the formation of an arid climate occur due to the ionization of the atmosphere by power lines, so the greenhouse effect has nothing to do with it.
Voltage in residential areas
Within cities, there are numerous power lines on the streets, the voltage of which usually does not exceed 10 kV. Such values do not pose a risk to human health. The wires provide electricity to homes; they pass over residential areas and fenced areas.
Mountain and power line supports Source neftegaz.ru
Standards for safe use are also taken into account here. Buildings and structures are located at a distance from power lines of at least 5 meters. This line is the front boundary along which all communications pass. All wires are within this zone, except for the cable connected to the house itself.
An insulator with a fixed wire is placed at a height of 275 cm on the wall of the building. It should not enter the building in the areas of bedrooms, children's rooms and living rooms. The use of storage rooms, utility rooms and corridors is allowed.
City and power line pylons Source fadedead.org
The wires can hang over the tracks no more than 350 cm. Moreover, this distance should be more than 6 meters above the tracks for cars.
In single-story residential areas, power lines are usually located on one side of the road. On the plan this place is marked with a red line. The distance from the power line support to residential buildings must fully comply with PUE standards. To connect the building from the opposite side to the wire, it is necessary to use additional poles. Insulators should be located at a height of 620 cm. The shortest distance from a 6 kV line to vegetation is 2 meters.
Harm to technology and means of communication
The increase in the length of electricity transmission routes across the country has led to the fact that the electromagnetic field of power lines began to affect the reception of television signals and radio communications.
What are the causes of radio interference from overhead lines, and why do they affect TV reception? As a result of a corona discharge in space, electromagnetic disturbances arise near the wires, which cause interference for radio receiving devices.
How does weather affect radio interference? Depending on meteorological conditions, interference may decrease, increase, or disappear temporarily. For example, when rain washes away contaminants from wires, the level of interference on radio channels and communication lines also decreases. They do not increase during fog or dew. But in rainy weather, the increase in interference on terrestrial television occurs in proportion to the intensity of the rain.
When using overhead line supports for the installation of fiber-optic communication lines, it is necessary to take into account that the fiber-optic line will be subject to an electromagnetic field. The potential induced in this case will cause its premature failure. To avoid this moment, you need to find the point of zero potential and attach the optical cable to it.
High-voltage power lines have an unsafe effect on steel main pipelines, including gas pipelines in the following cases:
- parallel running of the pipeline and power lines;
- at the places of their intersection;
- in places of approaching and moving away from each other.
The danger lies in the fact that the alternating electromagnetic field created by the overhead electric line affects the pipeline located in the ground. The induction that appears in this case leads to the formation of a longitudinal EMF in the pipeline. The health and life of service personnel is at risk.
How does this process affect the pipeline itself? Due to alternating current, electrolytic corrosion of the metal occurs. Electrical devices associated with the pipeline may fail. In addition, if a power line breaks, the pipeline may be under high voltage.
To ensure safety, pipeline protection devices (PPD) are used:
Does the magnetic field of overhead lines affect mobile communications and phones? Much depends on the operator, on the technical capabilities of the phone, on the distance to the power lines. At high humidity, when corona discharges are clearly audible, the connection at the support may be weak or even absent. But, in general, overhead lines do not have a significant impact on cellular communications.
The same can be said about the effect of overhead lines on drones and other radio-controlled models. Interference occurring on power lines can interfere with the control of these devices. But, basically, nothing interferes with the movement of quadcopters. They are even planned to be used for technological inspections of overhead electrical routes.
Definition of remoteness
The size of sanitary zones along power lines depends on the voltage level. To determine their boundaries, draw a conditional line along the projection of the wires onto the earth's surface. For even greater security, these values should be multiplied by 10.
Power lines against the backdrop of sunset Source elektrovesti.net
A distance of 100 meters from power lines can be considered completely safe for humans. During rainy weather, a large number of oppositely charged ions are released into the atmosphere, which leads to an increase in the area of electric fields and their spread to adjacent areas.
Not only residential and industrial buildings, but also garages, fences and other structures cannot be located on the territory of the sanitary zone. It is also prohibited to plant trees in these areas.
Residential buildings, children's and educational institutions should not be located under the wires. In this case, it is allowed to build production structures of the first and second levels of fire resistance in accordance with fire safety standards.
Wires with birds Source birdsandpowerlines.blogspot.com
The distance from power lines is a conditional value that provides for the safe functioning of people at a sufficient distance from wires and supports. Such a distance cannot guarantee the complete absence of any exposure to the residents of the house.
Underground installation significantly reduces the size of the danger zone, which is no more than 1 meter on each side of the electrical cable. At the same time, moving power lines underground requires investing a significant amount of money. Compared to the air type, the cost of underground installation increases several times. Therefore, this solution is still rarely used in practice.
For large urban settlements, underground cable laying is more typical. In this case, the wires are placed in special trenches, which are laid in blocks or tunnels. The depth of installation is about 1 meter. In this case, it is necessary to organize quick access to the lines during an emergency.