The main element of any electrical wiring is cable products. Depending on the purpose, location and type of wiring, conductors of certain types are selected. In areas that consist of numerous irregularities, it is customary to lay the most flexible wires.
The PV wire is characterized by increased flexibility, which is its undoubted advantage compared to several foreign and domestic analogues. Another obvious advantage of this product is its versatility.
Marking designation
Let's start with deciphering the abbreviation. Questions may arise due to the additional numbers that are added after the two main capital letters. Let's get started:
- The letter “P” in the first place indicates that the product is a wire. In addition to wires, these products are divided into two categories - cords (W) and cables (C).
- The letter "B" in second place indicates the type of insulation used. In this case we are talking about a polyvinyl chloride shell, the positive quality of which is its resistance to many physical and chemical influences. This is one of the main materials used as a dielectric.
- The last digit indicates the cable flexibility class - from “1” to “5”. The higher this value, the more flexible the product will be.
Wires are divided into two main categories - installation and installation. The first category includes products that can be used for a long period of time in the same place. We are talking, for example, about installing a socket, switch, etc. The installation wire is intended for repeated use and temporary connection of various equipment.
It is logical that a more flexible cable should be called an installation cable, while a more rigid product should be called an installation cable. For example, PV1 is an installation wire, which is not recommended to be constantly moved and used in different places, PV3 is an installation wire.
Specifications
All characteristics of PV3 can be conditionally divided into mechanical, thermal and electrical, which determine its ability to fully solve the assigned tasks. Check them all out:
- Permissible wire bending radius – determines by what amount, depending on the parameters of the brand, a given conductor can be bent. This parameter is checked immediately after production and entered into the product passport. For PV3, the radius ratio is observed when laying at least 5 diameters of the outer part of the wire itself.
Rice. 4: bend radius - Permissible mechanical elongation of insulation - characterizes the ability of the polyvinyl chloride layer to change its geometric parameters, but not less than 50% of the existing length. So that the wire can be easily bent within a given range.
- Operating temperature is the permissible temperature limit at which normal operation of the wire is allowed without loss of its declared parameters. In relation to this brand, the nominal limits range from – 50°C to +70°C.
- Short-term overheating - exposure is allowed in an emergency or when the system is overloaded up to 150°C. At the same time, the insulation maintains dielectric and mechanical parameters.
- Resistance of the insulating layer to single impacts , acoustic and vibration influences. Due to its narrow specialization, such characteristics of PV3 are not relevant for the average consumer; they are important for communication lines and specific equipment.
- Electrical insulation resistance is tested at the manufacturing stage by immersing the wire in water and then applying a voltage of 2.5 kV for 5 minutes.
- Conductivity of the core is determined by the resistance of the copper conductor; this value is standardized for each brand separately and can vary depending on the temperature of the wire.
Table: dependence of PV-3 parameters on the number of wires and their cross-section.
| Nominal cross-section (mm2) | Minimum number of wires in the core (pcs) | Wire outer diameter (mm) | Maximum electrical resistance of the core at direct current and temperature 20°C. (MOhm/km) |
| 0,5 | 7 | 2,0 | 39,6 |
| 0,75 | 7 | 2,2 | 25,5 |
| 1,0 | 7 | 2,3 | 21,8 |
| 1,5 | 7 | 2,8 | 14,0 |
| 2,0 | 15 | 3,1 | 9,97 |
| 2,5 | 19 | 3,5 | 8,05 |
| 4,0 | 19 | 4 | 4,89 |
| 6,0 | 19 | 4,6 | 3,11 |
| 10 | 49 | 6,3 | 2,0 |
| 16 | 49 | 7,5 | 1,21 |
| 25 | 77 | 9,9 | 0,809 |
| 35 | 105 | 10,9 | 0,551 |
| 50 | 144 | 13,3 | 0,394 |
| 70 | 210 | 15,5 | 0,277 |
| 95 | 285 | 17,6 | 0,203 |
| 120 | 360 | 19,5 | 0,162 |
| 150 | 444 | 21,2 | 0,129 |
| 185 | 555 | 23,8 | 0,104 |
| 240 | 760 | 27,1 | 0,0808 |
It should be noted that despite the lower operating temperature limit of – 50°C, it is allowed to lay the wire in conditions not lower than – 15°C, since the insulation becomes fragile and can be easily damaged when bent. If you need to lay PV3 in a cold climate below – 15°C, it needs to be additionally heated.
Varieties
PV is the general name for wires with high-quality polyvinyl chloride insulation. If we look deeper, there are a huge number of varieties of this product: there are both installation and installation products. All of the wires listed below are successfully used in AC electrical networks with voltages up to 450 V:
- PV1 is an installation wire used in an electrical network with a voltage of 450 V and a frequency not exceeding 100 Hz. In the case of DC networks, PV1 can be used at voltages up to 1000 V. The maximum permissible current value is 41 A. The cores are made of tinned copper. Any PV1 is single-core, and the conductor consists of several small wires.
- PV3 is an analogue of PV of the first class of flexibility. In terms of basic technical and operational parameters, it is in no way inferior to PV1, but it can be used as an installation product.
- BPVL – on-board wire. Its name is due to its original purpose: the cable was used in aircraft construction. Over time, it began to be used when switching stationary equipment. The maximum permissible voltage in AC networks is 250 V at a frequency of 2000 Hz, DC - 500 V.
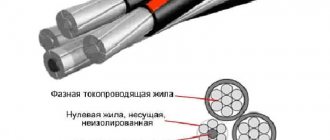
- APVBBShv is a power wire whose cores are made of aluminum. The main purpose is to transport energy through stationary electrical installations in alternating current power networks with voltage and frequency not exceeding 1000 V and 50 Hz, respectively. A cable with a similar marking, but without the letter “A” is in first place - the same product, but made of copper conductors.
- APV is an aluminum installation wire with parameters similar to copper products. The main difference between aluminum products is that the maximum permissible voltage at alternating current is 400 V (instead of 450) at a frequency of 50 Hz (instead of 100).
- KSPV is a high-quality wire that is used in the installation of alarm and video surveillance systems. Contains two-layer insulation: the inner shell is made of polyethylene, the outer shell is made of polyvinyl chloride. Often the outer insulation is white.
Design
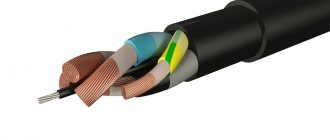
Structurally, this brand of wire is a single core made of several copper wires, which is covered with a layer of polyvinyl chloride insulation. An example of the design of PV3 is shown in Figure 1:
Rice. 1: PV3 wire design
The color coding of the insulation may vary depending on the specific purpose for which the wire itself is used. For example, when installing PV3 for a PE conductor in the grounding circuit, the insulation color should be yellow-green. If PV3 is installed as a neutral conductor, then blue insulation color is selected. In practice, there is a huge selection of colors for PV3.
Rice. 2: color marking PV3
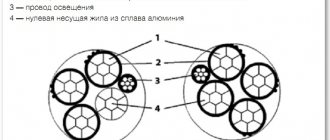
The core can use several wires of a certain cross-section, the ratio of which determines the flexibility of the entire product. The figure below shows various brands of PV, which differ in exactly this ratio:
Rice. 3: dependence of flexibility on the number of wires
The PV3 core can contain at least 7 wires; the maximum limit on their number and thickness is limited only by the manufacturer’s model range, since most often it varies up to 50 wires in the core.
Nomenclature of wires PV1
Next, we will consider the main types of PV1 wires (first class of flexibility), which are produced by domestic manufacturers. All products comply with GOST.
First, pay attention to the table, which shows the relationship between the cross-sectional area of PV1 and mass:
| Section, sq. mm | Maximum outer diameter, mm | Weight of 1 km cable, kg |
| 0,5 | 2,4 | 8 |
| 0,75 | 2,6 | 10 |
| 1,0 | 2,8 | 13 |
| 1,5 | 3,3 | 19 |
| 2,0 | 3,3 | 26,2 |
| 2,5 | 3,9 | 30 |
| 3,0 | 3,9 | 37,7 |
| 4,0 | 4,4 | 45 |
| 5,0 | 4,4 | 54,8 |
| 6,0 | 4,9 | 65 |
| 8,0 | 4,9 | 80,2 |
| 10 | 6,4 | 107 |
| 16 | 8 | 172 |
| *** | *** | *** |
| 120 | 17,5 | 1060 |
The first thing you must remember: any PV1 wire is a single-core product. Unfortunately, this fact overshadows its domestic use, since the presence of only one core is in itself a limiting factor and determines the following conditions:
- The range of permissible wire cross-section is 0.5-120 sq. mm. Depending on the specific value, the structure of the core and its technical and operational parameters may change.
- In accordance with GOST for wires with a cross-sectional area of 0.5-10 sq. mm can be produced as a single core. Only such products belong to the first class of flexibility.
- For the production of cable cores with a cross-section of 16-35 sq. mm should be used from seven wires and above. This results in increased flexibility. The wires, in fact, belong to the first class, but according to the instructions they are called PV2.
- Products with a cross-sectional area of 50-95 sq. mm are made of 19 or more wires. PV 1×120 must be made from 37, and in accordance with GOST, such a wire belongs to the second class of flexibility.
Another equally important factor is the thickness of the insulating layer. It is selected depending on the cross-section of the product: as this parameter increases, the requirements for insulation strength increase. In accordance with GOST rules, PV1 insulation can be two-layer. It is important to follow the general rule: the thickness of the first insulating layer should be less than 70% of the size of the second.
Next, you should take into account the colors of the cores in the wire. According to GOST, the color of the cores in PV1 is selected depending on the customer’s preferences. However, there is a general concept for the ground wire: such a conductor is colored yellow-green. When considering a piece of wire 15 mm long, one color should occupy at least 70%, the other the remaining 30% or lower.
Modifications PV-1
Wire PV 3 1x6
According to the current GOST, it is permissible to create improved modifications with a double protective shell. In these products, the first layer must be at least 70% of the total insulation thickness.
Color coding simplifies the installation of PV 1 and troubleshooting when performing repair work. To connect the ground loop, a yellow-green sheath is provided. Blue color indicates the neutral conductor. Red, brown and others - phases. For large orders, it is possible to manufacture products with unique aesthetic parameters.
Design Features
PV1 is a single-core wire, so it can be used to connect only one equipment. The cable is made from copper, which first goes through a tinning process (coated with flux).
The PV wire is simple in design. It consists of the following structural elements:
- A current-carrying copper conductor, which may consist of one solid wire or several small wires. The structure of a particular product depends on the cable cross-section. As stated above, for the range of 0.5-10 square meters. mm core can be solid, from 16 sq. mm and more - stranded.
- An insulation layer made from polyvinyl chloride. Has color marking chosen by the customer (if it is not a grounding cable).
Features of the PV-1 design
PuGV wire
With a cross-sectional area in the range of 0.5-10 mm sq. a single-core conductor is used. This is quite consistent with the basic class (1) in terms of permissible radius and flexibility. However, in the nomenclature 16-35 mm sq. at least seven wires are provided (50-95 mm sq. - no less than 19, 120 mm sq. - 37 wires, respectively).
It should be emphasized! In these modifications, the digital symbol does not change. However, in reality such products are more resistant to deformation. They meet the standard requirements of class No. 2 for flexibility.
As the conductor cross-section increases, larger current loads are implied. Therefore, the requirements for the insulating capacity of the PV 1 cable are increasing. The problem is solved by adjusting the thickness of the protective sheath, for the range of 0.5-1 mm2. – not less than 0.6 mm. Other denominations:
- 1.5 mm sq. – 0.7 mm;
- 2.5-6 mm sq. – 0.8 mm;
- 10-16 mm sq. – 1 mm;
- 50-70 mm sq. – 1.4 mm.
Application area
There are no strict restrictions on the scope of application. It is successfully used when switching lighting systems or stationary electrical installations. PV3 is often used on machines that require reliable connection of several electrical components and mechanisms.
The wide range of applications of PV3 is due to the following advantages:
- the installation wire is durable and therefore can easily withstand numerous mechanical loads;
- no microorganisms appear on it, which could negatively affect the quality of data transmission and service life;
- the polyvinyl chloride from which the insulation is made is a self-extinguishing material;
- PV3 and PV1 have minimal linear expansion.
The wire can be placed inside cable trays, metal or plastic pipes, cable ducts, or inside equipment. Yellow-green conductors are used to connect grounding loops.
Application
Thanks to a wide range of models with different cross-sections and numbers of wires in the core, PV3 is excellent for various fields of industry and the national economy. In general, the installation PV-3 is used for:
- Domestic needs - when installing electrical wiring in an apartment, garage, moving connection points, making extension cords and for other purposes.
- Industrial - for making wiring in enterprises, connecting lighting equipment, special equipment, powerful consumers, etc.
- For communication lines with an operating frequency in the network of no more than 400 Hz.
A distinctive feature of this wire is its high resistance to atmospheric and other types of influence, due to which it is also used for external installation.
Wire PV 3, PV 1, PuGV: technical characteristics
Now let’s look at the main technical and operational characteristics of the PV wire. All of them can be divided into two categories - mechanical and electrical, so we will consider them separately.
Mechanical characteristics
Mechanical parameters include tensile strength, flexibility, compression resistance, insulation and conductor strength before weathering.
Let's talk about each parameter separately:
- The main characteristic of PV is its ability to bend. From the name it becomes clear that not everything is going smoothly with this parameter for the product. On average, PV1 can be bent at a radius equal to no more than ten outer diameters.
- The lack of flexibility of PV1 is compensated by other useful properties. The operating temperature range during product operation is from -50 to +70 degrees. Celsius. For comparison, the same parameter for a flexible SHVVP cord ranges from -25 to +40 deg. Celsius, while exposure to temperatures exceeding 70 degrees. leads to destruction of the product. In the case of PV1, it will not deform under short-term exposure to temperatures up to 150 degrees. Celsius.
- Another advantage is resistance to moisture. At an air temperature of +30 degrees. Celsius it must work with 100% humidity.
- The wire easily withstands vibrations, acoustic shocks, etc.
- Another advantage is that the cable insulation does not support combustion and is resistant to aggressive environments.
- PVV1 is a high-voltage cable created on the basis of conventional PV1. It is used in mechanical engineering.
- The cable service life is at least 15 years. For many processes this is more than enough.
Electrical characteristics
However, the electrical characteristics of any wire are considered more important. And if the PV1 is not so good in terms of mechanical parameters, then in terms of electrical parameters it shows its best side.
The cable is used in AC electrical networks at voltages up to 450 V and frequency 400 Hz. For DC networks, the voltage can reach 1000 V.
Other characteristics:
- The resistance of the wire directly depends on the cross-sectional area. For example, for a conductor of 0.5 sq. mm resistance is up to 15 kOhm, 5 kV. mm – 11 kOhm, PV1-120 – 3.5 kOhm.
- The above values are relevant for a piece of wire 1 km long and an operating temperature of 70-90 degrees. Celsius. If the conditions are different from those indicated, then the values will be different.
- The test voltage is much higher than stated in the technical documentation and is 2500 V. The cable testing process itself is of interest. To do this, take a length of 5 m or more. It is placed in water for 24 hours. A test voltage is applied to its ends. As a result, the PV1 wire must withstand such loads for 15 minutes.
- PV1 is characterized by stable parameters. During operation, its resistance differs from the nominal value by a maximum of 120%. And this is a good indicator.
Advantages and disadvantages
Compared to other options for cable and wire products, PV3 wire has a number of significant advantages:
- The average level of flexibility - provides a fairly wide scope for the use of PV3 - can be used as an installation wire for installing electrical systems, connecting equipment, for power supply to lighting devices and various household needs.
- It has good resistance to external factors - copes well with atmospheric conditions, temperature changes, mechanical shocks, moisture, prevents the occurrence and development of mold, etc.
- The insulation contains fire retardants - substances that lead to self-extinguishing. Due to this, in the event of sparking, the PV3 wire will not light up, but will only melt. In case of exposure to open sources of fire, the insulation will also not support combustion, which ensures the possibility of its use in fire hazardous areas.
- The relatively low cost of the PV3 brand on the market, which makes it much more attractive in comparison with other wires and cables.
- Not afraid of rodents - due to treatment with repellent impregnation, it is practically not subject to destruction by pests.
Among the disadvantages of the PV3 wire, only one layer of insulation should be highlighted, which is often insufficient under certain installation conditions. In such situations, in addition to the existing dielectric, it is necessary to adapt additional corrugations, tubes or cable channels.
The second disadvantage of PV3 is the mechanical “memory” of the core itself. If you give it a shape when connecting, then after some period of operation it is extremely undesirable to twist the ends and change their position, since the wire becomes fragile.
Analogues and manufacturers
In accordance with the technical characteristics, PV3 and PV4 can be considered analogues of each other (like PV1 and PV2). Among foreign products with flexibility class 5, cables H05V-K and H07V-K can be distinguished.
PV wires of various brands are produced at several factories:
- "Belaruskabel";
- "Tomskkabel";
- "Rybinskkabel";
- "Kavkazkabel";
- "Sevkabel".
Main manufacturers
When purchasing cable and wire products, it is important to obtain specified parameters that can ensure the nominal operating conditions of the system. Otherwise, you may encounter the problem of insufficient cross-section or inappropriate climatic design, when the connected wire or cable begins to overheat and lead to a line burnout. Therefore, it is so important to purchase PV3 only from trusted manufacturers. Among the well-established factories, the following should be highlighted:
- TD Alliance Cable;
- Special cable;
- Moskabelmet;
- Interregional trade and industrial company.
If you are just going to buy PV3 wire, pay attention to the products of the above-mentioned factories. If you already have a brand of PV3 wire from some other manufacturer, and you want to use it in electrical work, it is better to check its cross-section and the quality of the insulation. You can learn how to check the cross-section of a core at home from the corresponding article on our website:.
Basic performance characteristics and design
The PV-3 cable has the following technical characteristics:
- construction length - 100 m;
- insulation resistance - 1 MOhm;
- conductor material - copper;
- minimum gasket temperature - minus 15 degrees Celsius;
- operating temperature range - from –50 to +35 degrees;
- maximum permissible humidity - 100% at a temperature of +35 degrees;
- standard service life is 15 years, warranty is 2 years.
Structurally, the PuGV is a single stranded conductor enclosed in a dielectric shell. GOST allows that this wire can be single-core, but in practice you will not find this, since the single-core design deprives the cable of its main advantage - flexibility. Therefore, the norm is a multi-core design with a number of wires of at least 7. The smaller the wire diameter, the better the flexibility. So, for class 3, copper wire with a diameter of up to 0.79 mm is used, if the total cross-section does not reach 50 mm. As the cross-sectional diameter increases, the number of wire strands also increases.
Please note: when purchasing a PV-3 wire, it is recommended to measure its diameter D with a caliper (the cross-sectional area can then be calculated using the formula S = 0.785 × D² ), since many unscrupulous manufacturers tend to save copper by underestimating this extremely important parameter.
The maximum diameter of the PV-3 wire can be 95 mm.
Manufacturers of PV-3 brand wire
Many companies produce high-end cable products. Among them are the most popular manufacturers who guarantee a long service life of the purchased product.
The best companies manufacturing PV-Z brand products
TD "Alliance Cable"
Alliance Cable Holding is one of the three leaders in the cable industry in Russia and the CIS countries. The well-known company produces dozens of types of cables for industrial and domestic needs, made of high-quality copper from the Ural Mining and Metallurgical Company.
This is a guarantee of high quality products, confirmed by relevant certificates. LLC Trading House "Alliance Cable" makes it possible to purchase cable products for the needs of aviation and instrument making, installation of communication and alarm systems, repair of rolling stock and laying of power lines.
Note! Products are supplied to the facilities of Gazprom, Transneft, FGC UES and other large Russian companies.
Consumers choose products from this manufacturer because of:
- prices corresponding to the quality of the products;
- prompt delivery of products;
- product compliance with international quality standards;
- large selection of items.
"Special cable"
Cable was founded in 1997. The company has specialized cable production, modern scientific, technical and testing facilities.
Wire production at
The main range of products developed by the enterprise include:
- fire-resistant cables for fire protection systems (addressed SPS, SOUE);
- cables for industrial automation (RS-485, Profibus, LonWork);
- fire-resistant cables for security systems;
- cables for local computer networks (non-standard installation conditions);
- cables for digital telephony (E1 stream);
- radio frequency cables (cable TV networks, radio-cellular communications);
- triboelectric products (for vibration security systems);
- combined wires (including for video surveillance systems).
For your information! The company produces radio-frequency cable assemblies (cable sections complete with connectors) for radio-electronic equipment and antenna-feeder paths with normalized transmission parameters in the frequency band up to 20 GHz.
An accredited testing laboratory and quality control system guarantee a high level of work performed. The company has copyrights to almost all mass-produced products, most of which are certified in the GOST R and Fire Safety systems. Certificates of type approval from the Russian Maritime Register of Shipping and licenses from the Federal Service for Environmental and Technological Supervision for the manufacture of equipment for nuclear power plants were obtained.
You may be interested in Description of wire PV3
"Moskabel"
Moscow Cable has been operating since 1878. Initially, the plant had a different name - “Partnership for the exploitation of electricity M. M. Podobedov and Co.” However, over time, the owners of the plant renamed it.
Note! The group's subsidiary, Moskabel Plant LLC, is engaged in the production of power cables, Moskabelmet LLC. The company produces a wide range of power cables with impregnated paper or plastic insulation, including armored type and self-supporting insulated SIP wires.
Successful competition in the market for medium-voltage cables up to 10 kV allows Moskabel Plant LLC to supply RAO UES structures, metro services, and construction sites throughout Russia with its products for decades.
Production of cable products at the Moskabel enterprise
“The interregional trade and industrial enterprise has been operating since 2005. The main feature of this enterprise is the production of power cables of various modifications. Some models have copper conductors, which can be used for permanent installation in certain enclosed areas. No less popular are installation and connecting wires for household use.
The products of this manufacturer are presented throughout Russia. Mezhregionprom LLC is a young company producing high-quality cable products that meet all international standards.
If the manufacturer complies with GOST, then the PV-3 wire is the best solution for performing certain electrical tasks. Due to its temperature characteristics, use of this product in hot areas should be avoided.
Features of installation and operation
The main purpose of the PPV is to connect fixed wiring at industrial or residential facilities
In addition to practicality and versatility, the product attracts attention with its low cost
During operation of the PPV, several important features must be taken into account:
The rigidity of the product is associated with the monolithic design of the cores. The bending radius during installation should not exceed ten outer diameters. Ten cycles - exactly this number of bends is permissible at right angles with a return to the original position. These values must be taken into account when designing the cable route. Try to eliminate unnecessary bends and kinks. Polyvinyl chloride is a chemically resistant material. It is laid along a brick or concrete base, and can subsequently be hidden under a layer of plaster or putty. There is no need to use additional protective equipment. Modern building mixtures contain various additives and additives, which, when exposed to a single insulating layer, destroy it over time. If you do not know the composition of the solution, then it is still better to use additional protection in the form of corrugated pipes and boxes. When laying PPV under plasterboard or plastic boards, MDF, the presence of corrugation or cable duct is mandatory. Installation in the open air is possible, but many experts recommend using canopies or other devices that protect the product from direct sunlight. Hygroscopicity allows the PPV to be used in damp and warm rooms (for example, in a bathhouse)
In this case, it is important to use plastic protection (metal is not suitable). The route should be located at the bottom or mid-height
Choose a three-wire wire with an RCD connection.
Scope of application PV1
Taking into account all the characteristics presented above, it is necessary to emphasize high insulation parameters and low resistance. Wires of this type can be used for laying power lines and connecting a ground loop.
It is necessary to prevent the conductor from moving during use. The absence of an armor layer implies limited resistance to mechanical damage. There is no shielding layer, so sometimes electromagnetic noise may occur.
When laying a path, it is advisable to place the wires in cable ducts or corrugations. This will further protect them. If there is a need for air laying, then it is imperative to use supports that will protect the product from sagging. Also, the conductor is used when laying lines for alarms or CCTV cameras.
Important! The scope of application of PV1 is extensive - from residential premises to heavy industrial enterprises.
Protective corrugation
PV wire decoding and application
The PV cord is a copper conductor for transmitting electricity over distances from the source to the recipient. It is protected by a special layer - insulation made of polyvinyl chloride. It is used for connecting electrical devices and mechanisms, as well as for grounding lighting paths.
According to generally accepted standards, the abbreviation PV means the following:
The letter P stands for wire. The designation K is also possible - cable. The letter B indicates that the insulating layer consists of polyvinyl chloride or vinyl.
If there is no letter A in front of the PV, this indicates that copper conductors are used as a conductive element.
As a rule, after the abbreviation PV a number from 1 to 6 is indicated, each of which is responsible for the flexibility class of the wire. Remember - the first class is the least flexible, but the sixth is the most flexible of all the types presented. The level of flexibility directly depends on the design of the wire itself and its characteristic features.
PV wires are very resistant to mechanical damage, mold damage and are quite wear-resistant in their parameters. A special feature of this product is its self-extinguishing insulation, which protects the wire from overheating.
The PV wire is used in the following cases:
- for connecting electrical devices to a current source;
- for grounding stationary and power lighting networks;
- for connecting electrical devices and devices.
Let's consider each type of cable: their features and scope of application.
Conditions for storage and transportation of PUV wires
In factories, wires are wound into coils or onto wooden drums; the coils can have different lengths and weights, this depends on the cross-section of the wire, the norms determined by the standards and the manufacturers:
| Designation of passages | Ø mm2 | Length, in industrial spools km. |
| PV - 1 | 0,75 | 1,2 |
| 1,00 | 1 | |
| 1,50 | 08 | |
| 2,50 | 05 | |
| 4,00 | 04 | |
| 6,00 | 03 | |
| PV - 1 | 10,00 | 02 |
Coil of wire PV-1 in plastic packaging
It is not practical to reel in a length greater than 1200 m; the bobbins will have a large volume and weight, which is inconvenient for loading and transportation. To make the packaging more durable, the spools are packaged partially or completely in plastic film. According to generally accepted requirements for manufacturers, a wire in one package can consist of three parts, each of which is at least 20 meters. Wires with a larger cross-section of class 2 or 3 are usually wound onto wooden drums. But sometimes a core with a cross-section of 10 mm2 is packaged on drums.
What are the mistakes when laying
Many people, when installing a product in a wall, neglect to use corrugation. Since the cable is not fire resistant, in the event of a fire the fire may spread to it. The corrugation will protect the conductor from fire or mechanical damage.
Also, errors include incorrect selection of wire cross-section. If it is not enough for the network, the cable will overheat and a short circuit will occur. To select the correct wire cross-section, you need to calculate the load of all devices that will be connected to the network. This can be done using a multimeter or calculating the power of each device and then summing these values.
The result of contact between copper and aluminum
If a mixed type of conductors is used (copper and aluminum), then they should not be allowed to come into contact, because after a short period of time they will oxidize and the devices connected to them will fail, and a fire will occur at the point of contact.
Cable storage and transportation conditions
For any cable products, you must follow a number of rules for storage and transportation. Store wires only in a dry room with low humidity. Otherwise, mold or mildew may form on the product. It is advisable to make sure that there are no rodents in the warehouse that could damage the insulating layer. Storage is allowed at temperatures from 15 to 25 degrees. It is allowed to place cable reels outdoors, but away from direct sunlight.
Important! Cable drums must not be placed on their sides.
What are the problems when using
During operation, the wire often breaks. This may occur due to improper installation. Other problems are short circuits, power surges, which can be caused due to atmospheric phenomena.
You may be interested in Description of the PVS cable
Are there any problems when using the wire?
Note! To avoid this problem, experts recommend using aluminum material for cable insulation, since the tape has good adhesion to the conductor materials.