- C - self-supporting;
- I - isolated;
- P - wire.
The letter at the end of the marking means:
- “A” - neutral core with insulation
- “H” - current-carrying conductors are made of aluminum alloy
- “T” - insulation resistant to elevated temperatures +90°C (short-term +120°C)
- “G” - sealed (moisture will not spread along the wire more than 3 meters from damage to the insulation)
In the marking of a SIP wire, a dash sign indicates the rated voltage for which the wire is intended. Sometimes two values can be indicated here separated by a slash. For example, 0.6/1. This means that the wire is designed for voltages of 660 or 1000V.
And the last thing in the marking is the technical condition according to which the wire is made. Usually this is a set of numbers after the abbreviation TU.
Cable marking, in addition to designating a specific group, also necessarily includes the wire cross-section, date of manufacture, batch number and additional information from the manufacturer.
Peculiarities
SIP is a self-supporting insulated wire, used for power supply in power networks. The SIP electric cable is used in a network with voltage: SIP-1, SIP-2, SIP-4 and SIP-5 are designed for a rated voltage of up to 1 kV, SIP-3 up to 35 kV.
Most SIP wires produced in Russia are color-coded in accordance with the PUE (Electrical Installation Rules) and the new GOST 50462-2009. The insulation of phase conductors and the supporting neutral conductor is made of thermoplastic polyethylene or silanol-cross-linked (light-stabilized) polyethylene, which can withstand temperatures of about 80-90°C for a long time
The technical characteristics of the SIP cable are regulated by GOST R 52373-2005 / GOST 31946-2012 / TU 16-705.500-2006, according to which self-supporting insulated wires include products for overhead lines with voltages up to 0.6/1 kV inclusive, and protected wires, products for the same lines, but with voltage up to 10 kV; from 10 to 20 kV; 20 kV and 35 kV. There are different types of SIP wire. Most often, SIP type cables are classified by cross-section: 4x16, 2x16, 4x50, 4x25, 4x35, etc. Also, the brand of wire is divided according to the type of core insulation and technical characteristics:
- SIPT-1, also known as SIP-1 - except for the zero core, all the rest are insulated with special polyethylene. SIP-1 is produced for 380 V networks. This is a four-wire cable made of aluminum or aluminum alloy, three cores are covered with light-resistant polyethylene, resistant to ultraviolet radiation, and the fourth without braid with a steel core acts as a carrier and neutral.
- SIPT-2 and SIPT-1A - all threads are isolated;
- SIP-2 - all cores (except for the zero wire) are insulated with cross-linked polyethylene;
- SIP-2A - all conductors, including neutral, are covered with a layer of cross-linked polyethylene;
- SIP-3 - a wire consisting of one conductive core, made of a dense alloy or steel-aluminum wire structure, the insulating layer is made of cross-linked light-stabilized polyethylene. SIP-3 is used for transmitting electrical energy with voltages up to 20 kV;
- SIP-4 - all four cores are insulated with thermoplastic polyethylene, but there is no separate load-bearing core. When laying and tensioning the line, all conductors carry the load, i.e. fastening is carried out immediately for all conductors;
- SIP-5 - does not have a separate load-bearing core, the rest are covered with a sheath of cross-linked (light-stabilized) polyethylene, the number of cores is two or more. They are used mainly in enterprises or for extending electrical networks in the city or between populated areas. It consists of insulated strands coated with polyethylene, where each strand is wrapped in a separate sheath. Types of wire SIP-4 and SIP-5 do not have a supporting zero core and can consist of two or more threads (most often 2 or 3).
Explanation of SIP markings
In comparison with other brands, SIP wire is a current-carrying element for transmitting electricity, which is deciphered by the three letters of the name:
- C – means that the wire is self-supporting;
- And - indicates the presence of insulation around current-carrying conductors;
- P - indicates that this is a wire, despite the presence of an insulating coating and branching along the cores, which is why it can be equated to a cable.
Consider an example of such a designation - SIP-1-3×20+1×25-0.4, here SIP-1 indicates the brand, 3×20 indicates that three insulated conductors have a cross-section of 20 mm2 each, 1×25 means that the neutral core has a cross-section of 25 mm2, 0.4 is the rated voltage for this model.
Depending on the specific brand, there are five main types of SIP wire, designated by the corresponding numbers after the letter designation. There may be one letter at the end, indicating design differences and operational features. These differences in SIP brands are determined by design parameters, so it would be more appropriate to consider them using specific examples.
Application of SIP wire:
SIP-1 For mains of overhead power lines (OHT) and linear branches from OHL for rated voltage up to 0.6/1 kV inclusive, with a nominal frequency of 50 Hz in an air atmosphere of types I and II according to GOST 15150.
SIP-2 For mains of overhead power lines (OHT) and linear branches from OHL for rated voltage up to 0.6/1 kV inclusive with a rated frequency of 50 Hz in an air atmosphere of types II and III according to GOST 15150, including on the coasts of seas, salty lakes, industrial areas and areas of saline sands.
SIP-3 - For overhead power lines with a rated voltage of 20 kV (for networks with voltages of 10, 15, 20 kV) and 35 kV (for networks with 35 kV) with a nominal frequency of 50 Hz in air atmosphere II and III according to GOST 15150, including including on the coasts of seas, salt lakes, in industrial areas and areas of saline sands.
SIP-4 Designed for branches from overhead lines to the input and for laying along the walls of buildings and engineering structures for rated voltage up to 0.6/1 kV inclusive, with a nominal frequency of 50 Hz in air atmosphere II and III according to GOST 15150.
Table of differences between SIP wires 1,2,3,4
Below we provide a table with the main technical parameters of the wires, from which it is easy to understand what exactly are the differences between the brands of SIP.
| Brand | SIP 1 | SIP 2 | SIP 3 | SIP 4 | SIP 5 |
| Number of conductors, pcs. | 1-4 | 1-4 | 1 | 2-4 | 2-4 |
| Conductor material | aluminum | aluminum | Aluminium alloy | aluminum | aluminum |
| Section, mm2 | 16-120 | 16-120 | 35-240 | 16-120 | 16-120 |
| Null carrier | Aluminium alloy | Aluminium alloy | No | No | No |
| Electrical voltage, kV | 0,38-1 | 0,38-1 | 10-35 | 0,38-1 | 0,38-1 |
| Insulator material | thermoplastic XPE | light-stabilized XPE | light-stabilized XPE | thermoplastic XLPE | light-stabilized XPE |
| Operating temperature, C | -60/+50 | -60/+50 | -60/+50 | -60/+50 | -60/+50 |
| Ultimate heating, C | +70 | +90 | +70 | +90 | +90 |
| Min bending radius, D (outer diameter) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Operating period, years | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Scope of use | — overhead power lines; — branches from overhead lines | — overhead power lines; — branches from overhead lines | overhead power transmission lines 10-35 kV | branches from power lines to private houses and other consumers of electric current | branches from power lines to private houses and other consumers of electricity |
To correctly select the required SIP wire, you need to clearly understand its electrical characteristics.
The table shows the value of permissible current loads, depending on the nominal cross-section of SIP wires of various classes.
There are 2 more important indicators: the electrical resistance of the cores and the insulating layer.
Mechanical characteristics of SIP wire
| Estimated outer diameter of the wire, mm" | Estimated weight of 1 km of wire, kg | ||
| SIP-1-0.6/1 | 1×16+1×25 | 15 | 135 |
| 3×16+1×25 | 22 | 270 | |
| 3×25+1x35 | 26 | 390 | |
| 3×35+1×50 | 30 | 530 | |
| 3×50+1×50 | 32 | 685 | |
| 3×50+1×70 | 35 | 740 | |
| 3×70+1×70 | 37 | 930 | |
| 3×70+1×95 | 41 | 990 | |
| 3×95+1×70 | 41 | 1190 | |
| 3×95+1×95 | 43 | 1255 | |
| 3×120+1×95 | 46 | 1480 | |
| 3x150+1x95 | 48 | 1715 | |
| 3×185+1×95 | 52 | 2330 | |
| 3×240+1×95 | 56 | 2895 | |
| SIP-2-0.6/1 | 3×16+1×25 | 24 | 308 |
| 3×16+1×54.6 | 28 | 427 | |
| 3×25+1×35 | 27 | 424 | |
| 3x25+1x54.6 | 30 | 512 | |
| 3×35+1×50 | 31 | 571 | |
| 3×35+1×54.6 | 32 | 606 | |
| 3×50+1×50 | 34 | 727 | |
| 3×50+1×54.6 | 35 | 762 | |
| 3×50+1×70 | 36 | 798 | |
| 3×70+1×54.6 | 39 | 973 | |
| 3×70+1×70 | 40 | 1010 | |
| 3×70+1×95 | 41 | 1087 | |
| 3×95+1×70 | 43 | 1240 | |
| 3×95+1×95 | 45 | 1319 | |
| 3×120+1×95 | 48 | 1553 | |
| 3×150+1×95 | 50 | 1787 | |
| 3×185+1×95 | 55 | 2403 | |
| 3×240+1×95 | 60 | 2968 | |
| SIP-3 -20 | 1×35 | 12 | 165 |
| 1×50 | 13 | 215 | |
| 1×70 | 15 | 282 | |
| 1×95 | 16 | 364 | |
| 1×120 | 18 | 445 | |
| 1×150 | 19 | 540 | |
| 1×185 | 21 | 722 | |
| 1×240 | 24 | 950 | |
| SIP-3-35 | 1×35 | 14 | 209 |
| 1×50 | 16 | 263 | |
| 1×70 | 17 | 334 | |
| 1×95 | 19 | 421 | |
| 1×120 | 20 | 518 | |
| 1×150 | 22 | 618 | |
| 1×185 | 24 | 808 | |
| 1×240 | 26 | 1045 | |
| SIP -4 0.6/1 kV | 2x16 | 15 | 139 |
| 4x16 | 18 | 278 | |
| 2x25 | 17 | 196 | |
| 4x25 | 21 | 392 |
How it differs from bare wires: main advantages
Electrical products with this marking have many positive qualities, which include:
- high tensile strength, which allows the wire to withstand wind loads and the fall of massive branches from trees;
- ease of tension;
- the insulating layer is made of a safe modern material that does not allow the wires to rust, it also protects the wires from the influence of moisture, ice formation and minimizes the likelihood of a short circuit among the phases;
- SIP-4 can be operated in adverse conditions - the network will operate uninterruptedly at temperatures from -60 to +50 degrees C;
- Good flexibility - the smallest bending radius is 10 outer diameters of the wire, making it easy to create various turns during stretching;
- increasing the reliability of power supply - even if the insulation is broken, the design of the wire prevents the spread of moisture;
- reduction of commercial electricity losses - it is much more difficult to connect to an isolated line based on SIP-4, unauthorized electricity supply becomes much more difficult or is completely blocked;
- branches and branches to connect subscribers are created using special piercing fittings so that installation does not require de-energizing the main line.
Another advantage of SIP-4 wires is their long service life, amounting to several decades.
Permissible current loads of insulated wires for overhead transmission lines (SIP)
| Nominal cross-section of main cores, mm2 | Permissible load current, A, no more | Permissible one-second short circuit current, kA, no more | |||
| Self-supporting insulated wires | Protected wires | Self-supporting insulated wires | Protected wires | ||
| 20kV | 35kV | ||||
| 16 | 100 | — | — | 1,5 | — |
| 25 | 130 | — | — | 2,3 | — |
| 35 | 160 | 200 | 220 | 3,2 | 3,0 |
| 50 | 195 | 245 | 270 | 4,6 | 4,3 |
| 70 | 240 | 310 | 340 | 6,5 | 6,0 |
| 95 | 300 | 370 | 400 | 8,8 | 8,2 |
| 120 | 340 | 430 | 460 | 10,9 | 10,3 |
| 150 | 380 | 485 | 520 | 13,2 | 12,9 |
| 185 | 436 | 560 | 600 | 16,5 | 15,9 |
| 240 | 515 | 600 | 670 | 22,0 | 20,6 |
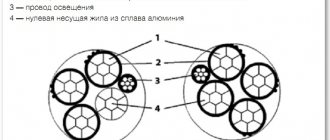
Decoding SIP wires
The abbreviation of wire brands of the SIP group stands for:
- C - self-supporting (usually a separate core is the carrier);
- I - insulated (the insulating layer is made of thermoplastic/light-stabilized cross-linked polyethylene XLPE);
- P - wire (the product is sometimes mistakenly called a cable).
In the marking of SIP wires, the letters A, N and T are sometimes found, for example, SIP-1A. Here's what they mean:
- A - the null core is insulated;
- N - conductors carrying electric current are made of aluminum alloy;
- T - the insulating layer can withstand increased heat, up to +90 C (up to +120 C for a short time).
How many kilowatts can a SIP withstand?
| SIP section | voltage 380V (3-phase load) | voltage 220V (1 phase load) |
| SIP 4x16 | 62 kW | 22 kW |
| SIP 4x25 | 80 kW | 29 kW |
| SIP 4x35 | 99 kW | 35 kW |
| SIP 4x50 | 121 kW | 43 kW |
| SIP 4x70 | 149 kW | 53 kW |
| SIP 4x95 | 186 kW | 66 kW |
| SIP 4x120 | 211 kW | 75 kW |
| SIP 4x150 | 236 kW | 84 kW |
| SIP 4x185 | 270 kW | 96 kW |
| SIP 4x240 | 320 kW | 113 kW |
Product marking
SIP cables are marked according to their type and cross-section, type of insulation, and technical properties. Manufacturers sometimes do not insulate the neutral core in some types of products: 1. SIP-1. The cable of this brand has 3 aluminum cores, for the insulation of which PET is used. This is the name of thermoplastic polyester - a synthetic film or fabric. The neutral core can be with or without insulation. If the letter “A” is present in the marking, the product is insulated. 2. SIP-2. This type of SIP cable has the same design as in the previous version with the difference that the neutral core is necessarily closed. This type of product is intended for installation on power lines whose voltage does not exceed 1000 V. Suitable for use in the northern regions of the country with a temperate climate. You can use a SIP cable for installation in summer cottages if the voltage does not exceed 380V.
3. SIP-3. This model differs significantly from previous product versions in its design - its core is made of steel and has an aluminum braid consisting of an alloy of silicon, magnesium, and aluminum. Single-core SIP wire is used when installing 20 kilovolt overhead lines. Manufacturers recommend using products of this type in areas with any climate, except sharply continental and arctic. According to the standards, this type of SIP wire can maintain its performance at temperatures from +90 to -20° C. 4. SIP-4. This type of product does not have a neutral wire. The design consists of several pairs of cores (two or four). If the marking contains the designation “H”, an alloy was used for their manufacture. If there is no letter designation, the cores are made of aluminum. Thermoplastic polyvinyl chloride is used for external insulation. 5. SIP-5. Products of this brand are similar in design to SIP-4 wires. The difference is the thermal insulation material - PET is used here. Thanks to this, the duration of exposure to permissible temperatures increases by 30%. SIP wires of this type are used for installation on 2.5 kilovolt power line supports. The installation of self-supporting insulated SIP-5 wires is allowed in areas with moderate and cold climates. What are the cross-sections of SIP cable? Phase conductors can have a cross-section with a diameter of 16 to 120 mm², and a zero-carrying conductor - from 25 to 95 mm².
Types of wires
Today, four main SIP systems can be distinguished, and wire sizing tables can be easily found on the Internet:
Finnish, whose modern designation is SIP-1. Among the cores there is one non-isolated one, which takes on the role of a carrier. A variety of the specified brand SIP-1A, which has a significant distinctive feature. More on this a little further.
The second is called Torsada, the more common version in Russia is SIP-2. In this system, the supporting conductor is covered with an insulating layer. This is done to protect the zero core in areas where there is a polluted climate. Another name (outdated version) is SIP-2A.
The third involves a power line with a power rating of up to 35 kW (inclusive). The wires do not form a twisted bundle, each goes to its own phase. As the load increases, installation of SIP-3 is required.
The fourth has such a feature that all four conductors carry the load - it is distributed equally between the neutral and phase conductors, and all conductive conductors are covered with an insulating protective layer. The markings are different - SIP-4, SIPs-4, SIPt-4, etc.
If you look at the photo of the sip wires, it becomes clear that the specified conductor is insulated with thermoplastic polyethylene, which is considered a cheaper protective layer. The other two conductors are covered with cross-linked polyethylene, due to which they have improved heat resistance.
Brand SIP-4
One of the modifications of a self-supporting wire, devoid of an additional power element. The product is supplied in coils (in the case of a cross-section up to 25 mm2), weighing up to 25 kg. If the specified values are exceeded, winding on drums is applied. Short cables (up to 100 m) can be untwisted manually; in other cases, a winch and rollers are used.
SIP-4 cable design
The cable consists of stranded aluminum conductors for primary and secondary purposes. On the outside there is a coating of light-stabilized polyethylene (cross-linked), having a thickness of 1.3-1.9 mm (depending on the cross-section of the cores). The veins are twisted together in the right direction, and with a large cross-section - in the left direction. An example of a cable is the products SIP-4 2*50 or SIP-4 4*120.
Various cable options SIP-4 (for single-phase and three-phase connection)
Features of the SIP-4 cable
A design feature of SIP-4 is the absence of a power core. Because of this, the strength of the product is reduced; it is used for arranging short highways. For example, to make a connection to a private building or between rooms. The interlacing pattern of the cable cores provides improved self-cleaning from adhering snow and ice.
Scope of application of SIP-4 cable
The wire is used for arranging overhead power transmission lines, as well as for forming branches. The cable is connected to residential buildings or outbuildings. The product can be used in lighting networks operating under voltages up to 1000 V (at a frequency of 50 Hz).
Scope of application of cables SIP-4 2x16 and 4x16
This type of wiring has the lowest cost among SIP-4, which makes it popular for connecting country houses and dachas. The wiring characteristics allow the transmission of electric current with a force of up to 16A, which is quite enough for a living space.
SIP cable structure
Structurally, the SIP wire consists of individual aluminum conductors covered with an insulating layer on top, which is reflected in the designation diagram. For the manufacture of the protective shell, light-stabilized polyethylene with improved strength characteristics is used. The structure of the material does not change its parameters under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, which increases the service life of the wire.
As part of a cable with a cross-section of the main conductors of more than 50 mm2, auxiliary conductors (from one to three) for the following purposes can be used:
- For connecting lighting circuits. The cross-section is selected from three possible options - 16/25/35 mm2.
- For operation of control devices. Three versions of this wire are allowed - 1.5/2.5/4 mm2.
In a number of publications there are references to SIP-6 cables, supposedly slightly different from other products. Such products are not specified in the standard; this designation is erroneous. There is no mention in the standard and cable SIP-7, which, nevertheless, is produced by a number of enterprises (for example, Sevkabel). The wire has improved insulation and provides transmission of electric current with voltages up to 110 kV.
Cable design SIP-7
Installation. Video
Tips for installing SIP wires to your home are presented in this video.
It can be concluded that SIP cables have a number of advantages over older models of aluminum cables that do not have insulation. The cable is reliably protected from short circuits when laid in tree branches and other difficult operating conditions. It can be laid on the walls of buildings, structures, along fences, and does not require highly qualified workers. The absence of special supports and insulators reduces installation time and costs. Thanks to insulation and other design features, the scope of application of SIP cables has expanded significantly.
Technical characteristics of SIP 2 cable
SIP 2 wire is produced with the following technical characteristics:
- the number of conductors can be from 1 to 4;
- the cross section is in the range of 16-120 mm2;
- the zero core is made of aluminum alloy and has a steel core;
- rated voltage – 0.6-1 kV;
- insulation material – light-stabilized silanol cross-linked polyethylene;
- relative humidity of the operating environment – up to 98%;
- the minimum bending radius is 10D, where D is the diameter of the wire;
- installation of the wire is allowed at a temperature of at least -20°C;
Temperature parameters:
- Operating temperature range – -60°С – +50°С. Thanks to these properties, the cable can be used when laying electrical networks in a cold climate zone;
- Heating up to +90°C for 8 hours is allowed;
- Short-term heating up to 130°C is allowed;
- The permissible short circuit temperature is +250°C.
Attention! During operation, heating up to 90°C is possible. It is allowed to be allowed for no more than 8 hours per day, no more than 100 hours per year and no more than 1000 hours for the entire period of work.
The warranty period is at least 3 years, the service life must be at least 40 years.
Strength characteristics of SIP 2
| Nominal cross-section of zero and main cores, mm2 | Core tensile strength, kN, not less |
| 25 | 7,4 |
| 35 | 10,3 |
| 50 | 14,2 |
| 70 | 20,6 |
| 95 | 27,9 |
| 120 | 35,2 |
| 150 | 43,4 |
| 185 | 53,5 |
| 240 | 69,5 |
Depending on the number of cores and their cross-section, cables have different weights and diameters.
Characteristics of the diameter and weight of SIP 2 wire
| Number and cross-section of cores | Outer diameter of wire, mm | Weight of 1 km of wire, kg |
| 1x16 + 1x25 | 16,4 | 167 |
| 3x16 + 1x25 | 24,1 | 307 |
| 3x25 + 1x35 | 27,1 | 424 |
| 3x35 + 1x50 | 30,8 | 570 |
| 3x50 + 1x50 | 34,1 | 729 |
| 3x50 + 1x70 | 36,1 | 799 |
| 3x70 + 1x70 | 40,0 | 1010 |
| 3x70 + 1x95 | 41,8 | 1086 |
| 3x95 + 1x70 | 44,2 | 1247 |
| 3x95 + 1x95 | 45,9 | 1323 |
| 3x120 + 1x95 | 48,1 | 1545 |
| 3x150 + 1x95 | 50,9 | 1812 |
| 3x185 + 1x95 | 55,0 | 2162 |
| 3x240 + 1x95 | 59,6 | 2652 |
| 4x16 + 1x25 | 24,1 | 377 |
| 4x25 + 1x25 | 27,1 | 522 |
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the products include the following characteristics: 1. There is no need to install powerful insulators on the line. 2. Security. Thanks to the insulation, there is no danger for specialists when servicing or installing self-supporting SIP wires. 3. Since the cores are connected by the same insulation, the width of the route is reduced. 4. Products can be used for regions with any weather conditions. 5. Eco-friendly. SIP cables do not affect people or animals. 6. Corrosion resistance. 7. Easy and simple installation of SIP wire. 8. Savings. To maintain and repair a line with exposed aluminum wires, you need to spend a lot of money, several times more than what is required for lines with SIP wires. Of course, there are also disadvantages, which include the large weight of wires of this type. Because of this, there is a need to more often install supports for installing the SIP cable to the house. If the products are used for installation in industrial enterprises, it will be necessary to perform reinforced insulation.
What are the features
Next, you should consider the technical characteristics of sip wires, which have many advantages:
- Safety both during installation and during operation due to the high insulation of conductors;
- Resistant to negative environmental influences, from high humidity to ultraviolet rays;
- Ease of installation, since there is no need to erect load-bearing installations and apply an insulating layer;
- Long service life, ranging from thirty to fifty years.
However, there are also disadvantages:
- High cost of wire;
- The need to lay SIP at temperatures above -20°C;
- Inability to cool conductors;
- Low current limits.
The listed advantages make this wire the most popular and in demand.