Decoding
The definition of the abbreviation SHVVP is as follows:
- Ш – cord;
- B – polyvinyl chloride insulation of current-carrying conductors;
- B – similar outer covering of the wire;
- P – flat sectional shape.
ShVVP cable marking
According to the symbol, this type of product should not be classified as either a cable or a wire, if you take into account the meaning of the first letter in the marking. But in this case there is no big difference with the indicated types of materials.
Household wires
PBVVG, PBVV
PURPOSE
The wires are intended for installation in lighting networks, installation and connection of devices to an alternating current network with voltage up to 380 V alternating current with a frequency of 50 Hz.
DESIGN
CURRENT CONDUCT – single-wire copper, multi-wire copper.
INSULATION – PVC plastic. One of the isolated cores has a distinctive color. The insulation of the grounding conductor is green-yellow, the insulation of the neutral conductor is blue. Insulated cores are laid parallel.
SHELL – PVC plastic. The color of the shell is specified when ordering.
NUMBER OF CORES – 2, 3.
CORE SECTION, mm²: 1.0; 1.2; 1.5; 2.0; 2.5; 3.0; 4.0; 5.0; 6.0.
PBVV - wire with parallel laid conductors with polyvinyl chloride insulation and sheath.
PBVVG – wire with parallel laid conductors with polyvinyl chloride insulation and sheath, flexible.
SPECIFICATIONS
Type of climatic version U3 according to GOST 15150, but at the same time the lower operating value of the air temperature during operation is minus 40 °C, the upper operating value of the air during operation is plus 70 °C, and the upper operating value of the relative air humidity is 100% at 35 °C.
Electrical insulation resistance, recalculated per 1 km length and temperature 20˚C, must be no less than:
– 7 Mohm for a cross section of 0.75 mm²;
– 6 Mohm for sections 1.0 – 1.5 mm²;
– 5 Mohm for sections 2.0 – 4.0 mm²;
– 4 Mohm for section 5.0; 6.0 mm².
Operating temperature range – from -40˚С to +70˚С.
The wires do not spread flame when laid alone.
The established trouble-free operating time must be at least 12,000 hours.
Current-carrying conductors must be made of copper wire and comply with class 1 for PBVV wires and class 3 or 4 for PBVVG wires according to GOST 22483.
Polyvinyl chloride insulation and sheathing must be resistant to deformation at a temperature of (70±2) °C and resistant to cracking.
| Brand | Number and nominal core cross-section, mm | Maximum external dimensions, mm | Nominal radial insulation thickness, mm | Estimated weight, kg/km | |
| PBVV | PBVVG | ||||
| PBVV | 2×1,0 | 4,1×6,4 | 0,6 | 43,2 | ¾ |
| 2×1,2 | 4,2×6,5 | 0,6 | 47,4 | ¾ | |
| 2×1,5 | 4,3×6,9 | 0,6 | 53,2 | ¾ | |
| 2×2,0 | 4,5×7,3 | 0,6 | 61,7 | ¾ | |
| 2×2,5 | 4,7×7,7 | 0,6 | 74,3 | ¾ | |
| 2×3,0 | 5,0×8,4 | 0,6 | 86,3 | ¾ | |
| 2×4,0 | 5,4×10,0 | 0,7 | 108,6 | ¾ | |
| 3×1,0 | 4,1×8,9 | 0,6 | 61,8 | ¾ | |
| 3×1,2 | 4,2×9,2 | 0,6 | 65,4 | ¾ | |
| 3×1,5 | 4,3×9,6 | 0,6 | 76,7 | ¾ | |
| 3×2,0 | 4,5×10,2 | 0,6 | 89,9 | ¾ | |
| 3×2,5 | 4,7×10,7 | 0,6 | 108,0 | ¾ | |
| 3×3,0 | 5,0×11,6 | 0,6 | 121,1 | ¾ | |
| 3×4,0 | 5,4×12,7 | 0,7 | 159,1 | ¾ | |
| PBVVG | 2×1,0 | 4,2×6,6 | 0,6 | ¾ | 42,9 |
| 2×1,2 | 4,3×6,8 | 0,6 | ¾ | 47,0 | |
| 2×1,5 | 4,4×7,1 | 0,6 | ¾ | 52,6 | |
| 2×2,0 | 4,7×7,7 | 0,6 | ¾ | 61,1 | |
| 2×2,5 | 5,0×8,3 | 0,6 | ¾ | 75,9 | |
| 2×3,0 | 5,4×9,0 | 0,6 | ¾ | 86,6 | |
| 2×4,0 | 5,7×9,6 | 0,7 | ¾ | 111,6 | |
| 2×5,0 | 6,2×10,5 | 0,7 | ¾ | 136,6 | |
| 2×6,0 | 6,4×11,0 | 0,7 | ¾ | 161,7 | |
| 3×1,0 | 4,2×9,1 | 0,6 | ¾ | 61,2 | |
| 3×1,2 | 4,3×9,5 | 0,6 | ¾ | 65,2 | |
| 3×1,5 | 4,4×9,9 | 0,6 | ¾ | 75,7 | |
| 3×2,0 | 4,7×10,4 | 0,6 | ¾ | 88,9 | |
| 3×2,5 | 5,0×11,5 | 0,6 | ¾ | 110,3 | |
| 3×3,0 | 5,4×12,2 | 0,6 | ¾ | 123,1 | |
| 3×4,0 | 5,7×13,6 | 0,7 | ¾ | 163,4 | |
| 3×5,0 | 6,2×14,5 | 0,7 | ¾ | 201,9 | |
| 3×6,0 | 6,4×15,7 | 0,7 | ¾ | 238,0 |
The construction length of the wires is at least 100 m; supply lengths of at least 10 m are allowed in an amount of no more than 10% of the total length of the batch.
The average service life of wires is 8 years.
Design
The design of the cord includes the following components:
- current-carrying conductors with a round cross-section, made of solid copper wire or twisted wires;
- insulating coating of each core;
- external insulation material.
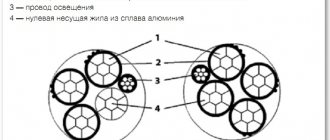
Structurally, the number of cores can be 2 or 3. To identify conductors, their insulation is made in the following colors:
- yellow-green - for the grounding wire of a three-wire cord;
- blue – zero;
- brown – phase.
The outer covering is most often made white in contrast to make it easier to distinguish its color from the insulation of the current-carrying conductors. A designation with a wire marking indicating the corresponding abbreviation, number of cores and cross-sectional area is applied to the outer insulating coating at certain intervals.
Copper wire in vinyl insulation - PVA
In PVA cords, both internal and external insulation is made of polyvinyl chloride. The internal conductor insulation has standard markings. However, the PVA cores themselves are multi-wire, so the cable is very flexible. The PVA cord must be tinned or banded during installation. The outer vinyl layer of these types of cables is several millimeters thick. Due to its characteristics, the PVA cable is ideal for connecting to a network of electrical receivers. This type of cord perfectly withstands various mechanical loads. The cross-section of the veins in it can vary from 0.75 to 16 sq. mm. The cable is suitable for making various extension cords and carriers that are not used at low temperatures. In the cold, the PVA shell simply bursts. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6utEHsfjf40
Purpose and application
Due to the specific technical parameters, this material is not suitable for connecting high-power industrial installations. This cord is most often used in domestic conditions for the following purposes:
- performing home wiring;
- connecting household electrical appliances;
- making carriers and for other household needs.
Also read: Why are electrical insulators needed?
Taking into account the characteristics of the wire, when using it as wiring, it is recommended to use this product only for supplying lighting. If you need to connect powerful household appliances, it is better to use a cable that can withstand heavy loads.
SHVVP can be used externally, but appropriate protection must be used for this.
Operational and technical characteristics
The recommended scope of use of PVA cables is various connections of electrical equipment: moving and fixed. A distinctive feature is its excellent flexibility, which allows use in conditions of repeated bends.
- P – wire (although it can also be called a cable);
- B – the wire cores are covered with polyvinyl chloride, as is the outer sheath;
- C – connecting – this letter shows where it is recommended to use the wire.
The purpose of this cable precludes its use when installing internal electrical wiring, although such a prohibition is not directly stated in GOSTs or the requirements of the PUE.
What does the marking say?
- The outer shell is most often white, but there are no obstacles to making it in other colors - black, red, gray, blue, etc.
- The grounding conductor is connected to the yellow-green wire.
- Blue color is used to connect the neutral wire.
- All other colors are used to connect a phase - one or more.
The manufacturer marks the outer sheath in the following form: PVA X*Y, where X indicates the number of cores in the cable, and Y is the size of their cross-section in mm².
- Two-core – PVA 2*(0.5-6)
- Three-core – PVA 3*(0.75-10)
- Four-core – PVS 4*(0.75-10)
- Five-core – PVS 5*(0.75-10)
- Seven-core – PVS 7*(1-2.5)
Other physical characteristics are shown in the table in the figure:
Technical characteristics of PVA
- Operating voltage – 660 Volts.
- Manufacturer's warranty – 2 years from the date of use.
- The temperature of use at which the wire insulation retains its properties is from -25 to +40C°. There is a frost-resistant type of cable, marked “Y”, which can function at -40C°
. The insulation must withstand long-term heating up to +70C° and short-term heating up to +80. Since the cable can be used on moving mechanisms, all this also applies to the permitted installation temperature. - Number of cores – 2-7.
- The humidity level at which the wire can be used is 98%.
- Service life - 2022 hours when installed as electrical wiring and 12,000 hours when used to connect electrical equipment.
- Resistance to deformation, when bent in both directions with a radius of 6 cm - 30,000 cycles.
- The length of the wire coil for sale is 30 and 200 meters.
- Dielectric tests are carried out with an alternating voltage of 2019 Volts - the cable must withstand it for 5 minutes.
As you can see, all technical characteristics of the PVS wire are designed for fairly large loads, electrical and mechanical. This is more than enough for domestic use, but when choosing a suitable wire, you still always need to make careful calculations of the cross-section of the cores.
What is the PVS wire used for, see this video:
additional characteristics
In addition to the standard version of the PVS cable, it has varieties for use in conditions of increased fire hazard with the corresponding marking PVSng-LS:
- ng in the marking determines the non-flammable type of insulation;
- LS - indicates that insulation with reduced smoke emission during combustion is used.
Sometimes the abbreviation PVS can be confused with the consonant one - PPS, but apart from the similar-sounding names, these cables are nothing alike. High-voltage electricians know well what a PPS wire is - according to its technical characteristics, this wire is designed for transposition of cable screens and the cross-section of the smallest of them is 70 mm²
. They are used by the relay protection service of distribution substations and such wires do not intersect with household needs.
Briefly about the main thing
Proper use of cables and wires is the key to the safety of you and your home. And not only. This also means trouble-free operation of electrical appliances.
.
Therefore, you need to select cables and wires exactly in accordance with their purpose, not rely on “maybe” and not save money
.
Electrics are the last place where it makes sense to save money
.
For example, PVS wire is sometimes used for internal hidden wiring, but it is not intended for this. Its characteristics and properties are not the same
. Read the article about where it is best to use it and why.
Classification and price
This type of cable and wire products does not have a wide variety of designs, and is produced with the following differences:
- by the number of cores - 2 or 3;
- according to the cross-section of wires - ranging from 0.5 to 6 square meters. mm.
It should be taken into account that GOST requirements do not apply to wires with a cross-section of more than 0.75 square meters. mm. Therefore, for large cable sizes, the performance cannot be guaranteed to comply with the standards prescribed by the standards.
The cost is determined by the pricing policy of the company selling the product and the characteristics of the cable. The price ranges from 8 to 50 rubles, depending on the specified features.
Characteristics of SHVVP wire
The technical characteristics of any wire can be divided into mechanical and electrical. And they should be considered separately.
Mechanical characteristics of SHVVP wire
Let's start our analysis with mechanical characteristics. It was they who ensured wide distribution of wires of this brand. Therefore, increased demands are placed on them.
Wire bending radius
So:
- One of the main advantages of the ball screw is its flexibility. The minimum bending radius is 5 cable diameters. Moreover, considering that our cable’s flat diameter is determined by its smallest value. This is a fairly high figure.
- In addition, the production of SHVVP wire must ensure its high resistance to repeated bending and extension. Typically, these figures fluctuate within 30 thousand cycles.
Test stand for wear resistance of SHVVP braid
- But of course, bending the wire negatively affects its performance. In this regard, the warranty period for wires subject to constant bending is only two years. At the same time, for SHVVP wire not subject to operational bending, this period is more than 10 years.
- In addition to bending tests, wires of this brand undergo a tension test. According to table. 10 GOST 7399 – 97 the cord must withstand tension up to 9.8 N (1 kgf) without visible damage. Moreover, the tests are carried out without an outer shell.
- The production of ball-type wires must also provide temperature protection for the wire. To do this, I place the cord in a chamber with a temperature of 80⁰C for 90 hours. Two hours after it has cooled, it is inspected for external damage.
Installation for testing wires for low temperatures
- The test for low temperatures is even more stringent. At subzero temperatures, the cord is passed through a roller, the cross-section of which is equal to four outer diameters of the wire. And after this, the wire is also subjected to impact testing. If there is no damage on the surface, then the wire is considered to have passed the test.
- In general, the nominal temperatures for wires are considered to be - 25⁰С - +40⁰С. Although, with special climatic modifications, it is possible to operate the wire at temperatures of -40⁰С - +40⁰С. But in any case, the core temperature should not rise above +70⁰С.
Electrical characteristics of the SHVVP wire
But mechanical characteristics alone cannot become decisive when choosing wires. After all, be that as it may, the cord is designed to pass current and it is the electrical parameters that determine this ability.
In the photo you can see the electrical resistance of the ball valve cores
- For any wire, the determining factor is the resistance of the wire. So, according to Table 2 of GOST 7399 - 97, the resistance of a wire with a cross section of 0.5 mm2 at a temperature of 70⁰C should be at least 0.012 MOhm. And for a wire with a cross-section of 0.75 mm2 this parameter is 0.01 Mohm. For some, these values will seem large, but if you consider that they are given for a wire 1 km long, then this is a fairly good result.
- The next critical parameter of the SHVVP wire brand is the insulation resistance of the wire. It is measured in relation to one core to the ground and between two cores.
- The insulation resistance test of one core is carried out on a piece of core at least 5 meters long, which is placed in water. A voltage of 2 kV is applied to the current-carrying part and leakage currents are checked.
- The insulation resistance between the two cores is made using a piece of wire at least 2 meters long. In this case, the sheath between the cores should be cut. Otherwise, the test is identical and it is quite difficult to do it yourself.
Advantages and disadvantages of wire
ShVVP are distinguished by the following positive qualities:
- greater flexibility, with the ability to withstand several alternating deformations without consequences for integrity;
- high conductive properties;
- the presence of a reliable insulating coating;
- color marking of cores, facilitating wire installation.
The disadvantages include insufficient power, and therefore the cable is not suitable for connecting powerful electrical appliances, and the need for additional protection when used outdoors.
How to choose a high-quality VVG and AVVG cable?
Nowadays, finding a high-quality cable is quite difficult, because there are a lot of small companies selling cheap cables under the guise of high-quality products. In this regard, craftsmen have to be vigilant and carefully inspect the cable before purchasing and installing.
The first thing you need to check before purchasing a cable is the tag and certificate for the cable. The tag of a quality product from a trusted manufacturer will necessarily indicate the name of the manufacturer or its trademark, the length of the product and the date of its manufacture, a technical control stamp and a mark of conformity. The highest quality products are made according to GOST standards.
When inspecting the certificate, be sure to pay attention to the name of the manufacturer, which must be in full, as well as the expiration date of the certificate. Do not forget to study the names, signatures of managers and the seal of the company.
If the tag and certificate are in order, then half the battle is already done, and we are dealing with a company that has the right to produce VVG and AVVG cables
Unfortunately, even the most famous manufacturers in one batch or another decide to save on material and make a product of poorer quality. Therefore, it is necessary to study the cable itself.
If the tag and certificate are in order, then half the battle is already done, and we are dealing with a company that has the right to produce VVG and AVVG cables. Unfortunately, even the most famous manufacturers in one batch or another decide to save on material and make a product of poorer quality. Therefore, it is necessary to study the cable itself.
The main quality criterion, which can be checked directly at the point of sale, is the actual cross-sectional area of the cable core. Often, saving on materials, the manufacturer greatly underestimates this value, which significantly worsens the electrical resistance of both the VVG and AVVG cables. Therefore, when choosing a product, you often have to arm yourself with a caliper and calculate the cross-sectional area of the core using the formula for determining the area of a circle:
S=π*R2 or S=(π*D2)/4, where D is the diameter of the core, measured using a caliper, and R is the radius of the core, i.e. the same value halved. Well, π = 3.14.
The resulting value should be compared with the value indicated on the packaging. A slight difference is completely acceptable, since the nominal value is indicated on the package, but if the value is more than 25% less than declared, the cable should be discarded.
Choosing the right VVG and AVVG cable is a serious matter, which in the future will allow you to get rid of a bunch of unnecessary problems. Of course, in addition to the steps described, before installation it is advisable to check the quality of the cable insulation, as well as the presence of breaks and short circuits, however, this is impossible to do in a store. Therefore, you should be content with what is already known about the product.
Cables of the VVG and AVVG brands are among the most common, which is why there are many low-quality products. The main thing to remember is that you should not skimp on wiring and trust incomprehensible, uncertified manufacturers. It is better to turn to those who are not afraid to put their name on the product, like the participants in the project “Against counterfeiting in the cable market.”
We sell only high-quality cables, wires and couplings from reliable manufacturers. Call +375 17 207-24-16 (17,18,19).
Installation features
Considering the properties of the wire, it can be laid as follows:
- inside the plaster layer - when performing wiring;
- in the form of an open line - with fastening to a flat surface, which facilitates the shape of the cable.
Also read: How to Test Transformer Insulation
When making connections, conductors of the same name are twisted or connected with terminals, followed by insulation of the twist. If the cable is located outdoors, steel pipes or a corrugated sleeve are used as additional protection.
Species diversity
KVVG cable
The manufacturer can change the color marking, both external and the color of the core insulation. The designation SHVVP does not indicate a specific color, so black cord is also found. The manufacturer has the right, based on GOST-7399-97, to change the color scheme. But this does not in any way affect the quality and price.
Carefully. When purchasing this product, in which the cross-section of the current-carrying conductor is indicated as 3; 4; 6 mm2, you need to remember that it does not comply with this GOST. This means that the product is not certified.
Manufacturers
Among the most well-known manufacturers of ball screws in Russia are the following companies:
- Rybinskcable,
- SKK (Samara Cable Company),
- Electric cable,
- Parity and others.
ShVVP has become widespread in the domestic sphere. In industrial enterprises, this product is used to a limited extent, given its characteristics, and can be used to connect lighting devices and equipment of low power.
Video testing the cable for flammability
Where is it used?
The shvvp wire, the decoding of which speaks about its features, is used mainly for connecting to a 220 V AC network in everyday life. It is convenient to connect household electrical appliances (hair dryers, irons, refrigerators, TVs and much more) using a flexible conductor. Carrying cases and various extension cords are also made from a similar cord and are practical. It is not recommended to connect permanent electrical installations.
Wire Application Table
Main settings
The main operational indicators, and in other words, the technical characteristics of the ball screws are presented by the following values:
- rated voltage - 220/380 Volts;
- nominal frequency of alternating current oscillations is 50 Hz;
- peak voltage (up to 15 minutes) – 2000 Volts;
- core cross-section from 0.35 to 2.5 mm2;
- service life from 6 to 15 years;
- warranty period 2 years;
- specific electrical resistance per 1 km of cord – no more than 270 Ohms;
- operating temperature (working) – from -40 to +40оС;
- installation is allowed at ambient temperatures from -10 to +30°C;
- the minimum permissible bending radius of the cores is 30 mm2;
- permissible current load (long-term permissible current) - depends on the cross-section of the conductors (for example, for size 2 * 0.75 mm2 it is 6 Amperes).
- weight from 0.026 to 0.049 kg per 1 meter of length.
As you can see, the characteristics of the ShVVP make it possible to use this cord for electrical work, both outdoors and indoors. We will talk further about where this type of conductor is used in relation to the house.
Dangers of use
It is unacceptable to use the cord for several household appliances connected to it at the same time. Even if their individual power is small, it may turn out that the total power exceeds what is permissibly possible for ballast cables, the characteristics of which are not designed for a continuous current load exceeding 6 A.
For example, using such a cord, even with a cross-section of 0.75 mm2, we connected an outlet in the kitchen. Using a tee, a microwave oven, an electric kettle and an electric stove were simultaneously connected to it. The average power of connected consumers is:
- stove - 2.5 kW;
- microwave – 1.8 kW;
- electric kettle – 1.2 kW.
The total power of three household appliances will be 5.5 kW. With a network voltage of 220 V, the total current consumption will be equal to 25 A. This means that when the devices are turned on simultaneously, the current value will exceed the permissible value by 4 times. The wire will not hold up and will burn, which can cause a general fire.
There are several common reasons why the rule for using such a cord is violated, namely:
- imaginary ease of installation - flexibility;
- remnants of material that are a pity to throw away;
- double insulation.
Double insulation and temperature range (-25-+400C) are misleading to the average person, but should not confuse a specialist. The insulation is not thick enough, and moisture and temperature changes can damage it if the wiring is exposed. In any case, GOST-7399-97 and OKOF 143131040 prescribe not to use this electrical product to power stationary power units (PS).
Attention! For control systems, power cables and wires with conductors of a suitable cross-section, insulation of sufficient thickness and a large current reserve are used.
The flexible SHVVP cord will serve efficiently and for a long time if you do not violate the methods of its use. A correctly selected cross-section corresponding to the load power will ensure proper safety during its operation.
Prices from applications
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 8 500 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 10 000 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 10 000 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 10 800 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 10 800 | rub./km |
| show 10 more ↓ | ||
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 10 800 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 10 800 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 12 332 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 12 500 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 13 310 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 13 310 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 13 310 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 13 586 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 13 800 | rub./km |
| ShVVP 2x0.75 | 17 720 | rub./km |
View applications