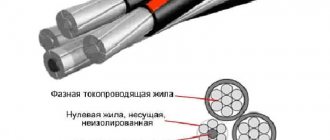
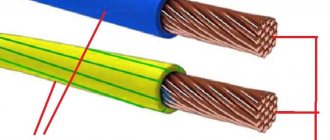
In order to understand the difference between PV-3 and PUGV, first of all you just need to understand what each wire is. After this, it will be possible to understand exactly what difference exists between them or whether there is one at all? Let's figure out what the wire is for, it essentially distributes electrical energy, which is laid in power and lighting networks.
Now let's try to start with PV-3. This is a power element that is used at rated voltage and constant current, best used in installations where increased flexibility is required. Installation is quite simple, it can be used with or without bends. It is best to trust the laying of the wire to real professionals who have experience in this matter, otherwise all this can lead to disastrous consequences. It is necessary to take care of this immediately so that there are no incidents.
Now let's say a little about isolation. The big advantage of cable insulation with the old markings is that it is not susceptible to combustion and the action of mold fungi. Such insulation can withstand temperatures up to 150 C, and will not stretch at temperatures up to 70 C, plus, it fits tightly to the cores and is easily separated from them. According to GOST, the insulation on PV-3 will be green. The PV-3 wire is marked using a stamp, printed and in relief.
Technical characteristics of wire PV-3
When operating the PV-3 cable, it must be taken into account that the temperature should be from -50 to 70 degrees Celsius. The humidity of its operation only at ambient or external temperatures can reach 100%. It is not recommended to carry out installation at temperatures below -10 -15 degrees Celsius. The heating temperature of the cores should not exceed 70 degrees Celsius. The ultimate insulation strength is 12.5 MPa, but no more! The wire can be bent at an angle of no more than 90 degrees. We can say that the minimum service life is 15 years. It undergoes thorough testing before it goes on sale.
Now let’s reveal a little secret: PV-3 and PUGV are practically no different from each other. GOST 6323 for vinyl cable was canceled on 01/01/2011. Instead, TU 16-705.501-2010 appeared. PUGV is an analogue of PV-3, its only difference is the number of cores is 5, that is, it is more flexible. Since 01/01/2001, GOST 6323-79 ceased to be valid on the territory of the Russian Federation, and GOST R 53768-2010 and TU 16-705.501-2010 were introduced in its place. In fact, wire PV-3 and PV-4 are PUGV, this change occurred due to changes in GOST.
I hope that thanks to this article you were able to understand the difference between the wires. We tried to describe the features of a vinyl conductor of the third class of flexibility specifically, since this cable is older and its characteristics are completely no different from the newer PUGV. Now, you will not be surprised when they offer you PUGV instead of the old name. I would like to believe that it will be much easier for you to select a wire, and that it will not be such a difficult task for you.
Every electrician must know the difference between these markings, but it will also come in handy for a novice entrepreneur. Let's take, for example, such a simple task as connecting cash register equipment (cash register or otherwise cash register), it is more convenient to connect using a PuGV wire. More in-depth knowledge about cash registers and their service can be obtained here.
What does PV on the wire mean, decoding
According to the no longer valid GOST 6323-79, wires are marked by letter and color designations, the letter values are deciphered as follows:
- Letter P - wire
- Letter B – vinyl (polyvinyl chloride), insulation
- Number 3 – flexibility class from 1 to 6. (As the number increases, flexibility increases, pv1 has one core , and accordingly has the least flexibility)
For example, PV-3 1x0.75-0.38 says that this is a flexible wire in vinyl insulation, having one core with a cross-sectional area of 0.75 mm², capable of passing through itself up to 0.38 kV of electricity, for PuGV it is similar. Since this is a single-core wire, it is often designated as follows - PV-3-5 , this also means that it has one core with an area of 5 mm² (number 0.75, 1.5, 2.5, 3, 5, etc.) d – nominal cross-section, different for each wire, see table below).
Important! PV single-core, multi-core version of the wire is called PVS, PUGNP/PUGSP
According to GOST 31947-2012
- Letters PU – installation wire
- G – flexible
- B – vinyl or polyvinyl chloride, respectively
(PV, PuGV, puv same thing)
Fig. 1 – Explanation of wire designation
PV and PuGV wires according to the new GOST is that it cannot be used for installation work; its use is only possible in electrical installations.
Important! The main difference between PV 6 and PV 3 is increased flexibility, which is achieved due to a larger amount of copper wire in the cable cross-section. of the same cross-section are absolutely equal in conductivity. The resistance of thin-wire conductors nb 6 is slightly less, and accordingly there are fewer losses in the transmission of electricity.
The production of fine-wire products is more expensive than conventional ones, so the difference is also in cost.
The main advantages and disadvantages of PV-3 cable
Like all conductors, PV3 has a number of advantages over others, but unfortunately, it is not without its drawbacks.
pros
- flexibility due to the large number of wires
- resistance to the external environment due to vinyl insulation
- large diameter wire, over 15mm², can be used in car audio systems; PV-6 from the company zandz (zz)
- infusibility
- low price
- thinner insulation, and therefore its own weight (see table above)
Minuses
- With aging, the insulation becomes more rigid
- when applying high current, the conductive wires in the core may burn out
- with frequent bending, tears of individual veins are possible
Stages of selecting PuGV wires
It is also interesting that the standards provide for separate stages for wire acceptance.
These rules are quite simple and can be used by private individuals:
| First of all, the rules recommend that we inspect the wire. In this case, you should make sure that the wire cross-section is correct, its design is correct and there are no visible defects. |
| Scheme for measuring core resistance with a single bridge | The next step is to determine the electrical resistance of the conductive wires. Regulatory documents require this to be done using the above and similar diagrams. But in private, you can simply use an ohmmeter. |
| After this, electrical tests of the wire insulation are performed. To do this, insulation resistance is measured and high-voltage tests are carried out. As we noted above, the test voltage for the wire should be 2500V. |
| All wires must be marked accordingly. It must indicate the type of wire, manufacturer's mark, core cross-section and year of manufacture. In this case, this marking must be applied every 550 mm along the wire insulation. |
| But the price of a coil of wire should include the presence of a special label. It must indicate the manufacturer's mark, wire brand, date of manufacture, wire weight, length and conformity mark. |
Where to buy PV-3 wire: manufacturers, prices
Today there are a large number of companies on the market - manufacturers of wires of various brands, producing high-quality wire products in a wide range at the best prices. There are even more intermediary companies, especially on the Internet, for example, the ETM company (not advertising).
There are a huge number of places to buy, so first of all, pay attention to the manufacturer. The following Russian companies are considered among the industry leaders: Energokabel, TD Alliance Cable, NKZ Elektrokabel NN, Spetskabel, ROSSKAT, ALUR Cable Plant, Moskabelmet.
The foreign companies that distinguished themselves were Zandz (ZZ), which produces lightning protection, grounding, and Pride. They are usually sold by the meter, prices vary greatly depending on the brand and section. For example, PV3 1x0.75mm costs on average 4-5 rubles/m, the price of PV3 1 x 2.5mm for a heated floor is already 20rub/m, and PV3-150 is 959 rubles per meter.
Technical characteristics of PUNP wire
PUNP wires can be used in the temperature range from – 25 ̊С to + 45 ̊С with a humidity of 98%. When testing the voltage between the cores, the wire can withstand 1.5 thousand volts for 1 minute. A trouble-free operating time has been established, subject to the permissible operating conditions, of 5 thousand hours of continuous operation.
Weight and dimensions of different types of PUNP:
| Brand | Weight kg/1km | External dimensions in, mm |
| PUNP 2x0.75 | 34 | 3,4:5,1 |
| 2x1 | 38 | 3,5:5,3 |
| 2x1.5 | 53 | 4,0:6,4 |
| 2x2.5 | 74 | 4,4:7,1 |
| 2x4 | 110 | 5,1:8,4 |
| 2x6 | 151,2 | 5,6:9,4 |
| 3x0.75 | 44,2 | 3,4:7,1 |
| 3x1 | 55,3 | 3,5:7,5 |
| 3x1.5 | 73,5 | 4,0:8,7 |
| 3x2.5 | 107,6 | 4,4:10 |
| 3x4 | 160,8 | 5,1:12 |
| 3x6 | 223,1 | 5,6:13,5 |
If we compare the characteristics of PUNP with the characteristics of PUGNP, which it is often replaced with, we can see that the dimensions of the wire do not differ significantly, but the weight is significantly greater.
Appearance of PUGNP
The cross-section and number of wires are the same, the weight increases due to denser insulation, which ensures reliable tightness. Weight and dimensions of different types of PUGNP:
| Brand PUGNP | Weight kg per 1 km | External dimensions in mm |
| 2x0.75 | 34,5 | 3,5:5,5 |
| 2x1 | 40,1 | 3,6:5,5 |
| 2x1.5 | 54,8 | 4,1:6,5 |
| 2x2.5 | 81,1 | 4,6:7,5 |
| 2x4 | 116,1 | 5,3:9 |
| 2x6 | 159,5 | 5,8:10 |
| 3x0.75 | 47,4 | 3,5:7,5 |
| 3x1 | 57,4 | 3,6:7,5 |
| 3x1.5 | 79,1 | 4,1:9 |
| 3x2.5 | 118,5 | 4,6:10,4 |
| 3x4 | 170 | 5,3:12,4 |
| 3x6 | 235 | 5,8:14,1 |
Application area:
- lighting networks;
- installation of electrical equipment, machines, mechanisms and machine tools for rated alternating voltage up to 450/750V with a frequency of up to 400Hz or direct voltage up to 1000V.
Cables and wires are intended for stationary installation indoors and outdoors, for laying electrical wiring under plaster, in concrete, brickwork, in the voids of building structures, as well as openly along the surface of walls and ceilings and in other structures, including where increased flexibility is required . Cables and wires can be used in all classes of hazardous areas (taking into account the requirements of GOST IEC 60079-14). Fire-resistant cables and wires can be used in all electrical installations that are subject to fire resistance requirements in accordance with Federal Law No. 123 “Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements” and GOST 31565-2012 “Cable Products. Fire safety requirements."
Technical specifications (brief)
- Wire and cable cores of increased flexibility - stranded copper, class 5 according to GOST 22483, cores of regular flexibility - class 1 or 2
- Wires and cables can have: a screen made of copper wires or aluminum flex
- armor made of galvanized steel wires
Wide temp. application range:
- from –60° to +70°C with the designation “ХЛ”
from –60° to +125°C with “T” material from –50° to +200°C with “T-T” material — in a shell from –50° to +150°C with “T-T” material — single-core wires without sheath from –50° to +70°C all other types Minimum installation temperature, not lower:
- –30°С with the designation “HL” or material “T”
–15°С for other types of wires and cables Shock resistance at low temperatures:
- “HL” – up to minus 30°С
others - up to minus 15°C Bending radius during installation, not less than: 5D - wires and cables with flexible conductors, 10D - with ordinary conductors (D - outer diameter of the cable or wire) Climatic version B, placement category 1-5 "UV" — resistant to solar radiation “v” — protection against the spread of moisture under the shell “M” — oil and petrol resistant shell Rated voltage
- for wires: ~450/750V up to 400Hz or –1000V
for cables: ~300/500V with a frequency of up to 400Hz The DC resistance of the conductors complies with GOST 22483 El. insulation resistance at temperature t = +20°C no less than 5 MOhm over a length of 1 km Voltage test according to GOST 23286-78:
- insulated conductors for passage according to category EI-2
wires ~2500V 50Hz for 5 minutes according to EI-1 cables ~2000V 50Hz for 5 minutes according to EI-1 Fire-resistant wires and cables, remain operational in fire conditions for at least 90 minutes (PO4 according to GOST 31565-2012) “LTx” - low toxicity of combustion products Service life of at least 20 years
Modifications
In the “PV” category there is a fairly large model range, where there are both installation cables and mounting cables, which are used even in low-voltage systems.
- For example, the KSPV 4×0.5 or 2×0.5 cable, which is most often used to power video surveillance and alarm systems. The KSPV 4×0.5 cable is a four-core wire with a cross-section of 0.5 mm², which has double insulation : the one closest to the core is polyethylene, the top one is polyvinyl chloride. Typically this wire is white. By the way, the KSPV 2×0.5 cable can have a cross-section not only of 0.5, but also of 0.4; 0.64 and 0.8 mm².
- The autoreclose wire is an aluminum installation cable that has the same technical characteristics as copper. The only difference is that the autoreclose wire can only be used in alternating current networks with a voltage of no more than 400 volts with an oscillation frequency of 50 Hz.
- APVBBShv – aluminum power cable. Designed for transmitting electricity in stationary installations with a voltage of 1000 volts and a frequency of 50 Hz. PVBbShv is a copper sample.
- BPVL – airborne. It was specially designed for aircraft, although it is also used to connect stationary installations. Can withstand AC voltage up to 250 volts at 2000 Hz, or DC voltage up to 500 volts.
PVZ is an installation wire that can withstand an alternating current voltage of no more than 450 volts with a frequency of 100 Hz and a direct current of 1000 volts. PVZ can conduct current with a force of up to 41 A. PVZ is a copper cable consisting of one core, which is woven from several thin wires. PVZ practically repeats the PV 1 brand.
Design
The structure of a flat flexible wire is clear from Fig. 1.
READ MORE: Vibration and dancing of wires on overhead power lines
Rice. 1. ShVVP cord design
Structurally, the flexible wire consists of copper conductors covered with polyvinyl chloride sheaths. They are located parallel in one plane, covered with individual multi-colored insulation. The flat profile of the cord is given by the shape of the outer shell, consisting of the same polyvinyl chloride, but with other additives.
ShVVP products use stranded copper conductors. The wires in the bundles are twisted to the left to enhance the strength of the core shape. This can be clearly seen in Figure 2.
Rice. 2. Type of copper conductors of the SHVVP wire
Please note: flat wires come in two-core and three-core types. Their PVC insulation has properties that are ideal for patch cords:
- significant resistivity;
- withstands short-term high temperatures generated by insulated conductors in critical situations. Rated operating temperature can reach 70ºC;
- the material of the insulating layer ensures high flexibility of the wire (limit – up to 30,000 bends);
- has a fairly long service life;
- polyvinyl chloride is environmentally safe;
Some parameters and properties of the outer sheath are slightly different from the qualities of the insulating materials that protect the inner cores. More plasticizers and stabilizers are added to their composition, providing aesthetic appeal, resistance to sunlight, and better mechanical strength. These qualities are important for cords used in connecting household appliances and in the manufacture of extension cords.
Specifications
Let's break down the characteristics into points, where first of all we highlight the main parameters of the product.
- This is an electrical product with copper conductors;
- insulation made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), here we mean external protection and individual cores;
- color marking fully complies with standards;
- such a wire can withstand a voltage of 250 volts, a frequency rating of up to 50 hertz;
- The PUNP cable can be operated in a temperature range from -15C to +50C, with maximum heating up to +70C;
- there are conductors with a cross section of 1.0-4.0 mm²;
- the number of cores in the cable is 2 or 3;
- service life – no more than 30 years.
There is one more parameter - this is the specific weight of the product per linear meter of its length. You can see it in the table below:
If we talk about the wire cross-section, the most popular models were 3x1.5, which was used to connect lamps, and 3x2.5, used to connect socket groups. But, as mentioned above, PUNP cable is banned today. Let's figure it out - why?