Every owner of a car, garage or private home always tries to use the best wires in his electrical network, especially if it is necessary to transmit high current reliably and with minimal losses. The PV 3 wire was created precisely for these purposes. It acquired its designation back in the USSR, made in accordance with GOST 6323-79.
Today, PV-3 is still produced in modern factories according to the new GOST 31947-2012 and has its second name PuGV , but not only the name has changed, the conductors themselves have become more flexible, reliable and durable. learn more about the characteristics, main differences in colors, where you can buy them and much more from our article.
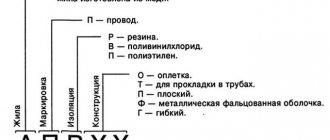
What does PV on the wire mean, decoding
According to the no longer valid GOST 6323-79, wires are marked by letter and color designations, the letter values are deciphered as follows:
- Letter P - wire
- Letter B – vinyl (polyvinyl chloride), insulation
- Number 3 – flexibility class from 1 to 6. (As the number increases, flexibility increases, pv1 has one core , and accordingly has the least flexibility)
For example, PV-3 1x0.75-0.38 says that this is a flexible wire in vinyl insulation, having one core with a cross-sectional area of 0.75 mm², capable of passing through itself up to 0.38 kV of electricity, for PuGV it is similar. Since this is a single-core wire, it is often designated as follows - PV-3-5 , this also means that it has one core with an area of 5 mm² (number 0.75, 1.5, 2.5, 3, 5, etc.) d – nominal cross-section, different for each wire, see table below).
Important! PV single-core, multi-core version of the wire is called PVS, PUGNP/PUGSP
According to GOST 31947-2012
- Letters PU – installation wire
- G – flexible
- B – vinyl or polyvinyl chloride, respectively
(PV, PuGV, puv same thing)
Fig. 1 – Explanation of wire designation
PV and PuGV wires according to the new GOST is that it cannot be used for installation work; its use is only possible in electrical installations.
Important! The main difference between PV 6 and PV 3 is increased flexibility, which is achieved due to a larger amount of copper wire in the cable cross-section. of the same cross-section are absolutely equal in conductivity. The resistance of thin-wire conductors nb 6 is slightly less, and accordingly there are fewer losses in the transmission of electricity.
The production of fine-wire products is more expensive than conventional ones, so the difference is also in cost.
PV 3 cable design, color marking
The design of the wire is quite simple (see the article “Colors of wires in a three-core cable”). The wire core consists of twisted thin copper wire wrapped in colored polyvinyl chloride insulation. Depending on the purpose, different colors are used:
- blue, cyan – neutral/zero
- yellow, yellow with green stripes – ground/earth
- black, white, red, brown, any color except blue and yellow – phase
The greater the amount of copper wire in the conductor, the more flexible the conductor. PV-6 is more flexible than PV 3.
Technical characteristics of wire PV 3 (Table), how to check and choose correctly
When choosing, you must first of all be guided by the characteristics of the cable; PV-3 has the following parameters:
- maximum length – depending on the purpose, limited to 100m
- resistance of the insulating layer – 2.25 – 13 kOhm/km
- core material – copper
- installation temperature – -15°C
- working temp. – -50 – +35gr.С
- minimum service life is 15 years. Actual up to 50 years.
- Elongation – up to 50%
- Heat resistance – up to 150°C (short-term)
- Conductivity – depending on diameter (see table below)
Table - technical characteristics of PV 3 wire (diameter, mass - weight, core and insulation resistance)
| Nominal cross-section pvz (mm²) | Number of wires (pcs) | Outer diameter(mm) | Maximum electrical resistance in accordance with GOST 22483 (Ohm/km) no more | Reference mass/weight of 1km wire, (kg) | Electrical insulation resistance, kOhm/km, at +70°C, not less |
| PV 3 | |||||
| 1x0.5 | 7 | 2,1 | 39,5 | 8 | 13 |
| 1x0.75 | 7 | 2,3 | 25,6 | 11 | 11 |
| 1x1.0 | 7 | 2,5 | 21,7 | 14 | 10 |
| 1x1.5 | 7 | 3,1 | 14,1 | 21 | 10 |
| 1x2.5 | 19 | 3,7 | 8,01 | 34 | 9 |
| 1x4.0 | 19 | 4,3 | 4,8 | 49 | 7 |
| 1x6.0 | 19 | 4,7 | 3,1 | 70 | 6 |
| 1x10 | 49 | 6,5 | 2 | 116 | 5,6 |
| 1x16 | 49 | 8,1 | 1,2 | 182 | 4,6 |
| 1x25 | 65 | 10,5 | 0,81 | 272 | 4,4 |
| 1x35 | 105 | 11,4 | 0,55 | 365 | 3,8 |
| 1x50 | 144 | 13,3 | 0,4 | 540 | 3,7 |
| 1x70 | 210 | 15 | 0,28 | 706 | 3,2 |
| 1x95 | 285 | 18,1 | 0,21 | 1004 | 2,9 |
| 1x120 | 360 | 19,5 | 0,163 | 1245 | 2,7 |
| 1x150 | 444 | 21,2 | 0,128 | 1410 | 2,4 |
| 1x185 | 555 | 23,8 | 0,105 | 1650 | 2,25 |
more in GOST 22483 “Current-carrying conductors for cables, wires and cords” - link to GOST
Table 2 - maximum permissible current for wire Pv-3 (at voltage 220 V)
| One wire Pv 3 | ||
| Section mm² | Core diameter, mm | Power/current (kW/A, ampere) |
| 0,5 | 0,79 | 2,2/10 |
| 0,75 | 0,97 | 2,86/13 |
| 1 | 1,13 | 3,3/15 |
| 1,5 | 1,38 | 4,4/20 |
| 2,5 | 1,78 | 5,94/27 |
| 4 | 2,25 | 7,92/36 |
| 6 | 2,76 | 10,12/46 |
| 10 | 3,57 | 15,4/70 |
| 16 | 4,51 | 19,8/90 |
| 25 | 5,64 | 27,5/125 |
| 35 | 6,67 | 33/150 |
| 50 | 7,98 | 41,8/190 |
| 70 | 9,44 | 52,8/240 |
| 95 | 11 | 63,8/290 |
| 120 | 12,36 | 74,8/340 |
| 150 | 14,2 | 85,6/390 |
| 185 | 15,34 | 93,1/450 |
Important points when checking in a store
- Pay attention to whether the wire is made according to GOST or TU; GOST is preferable because TU is set by the manufacturer; there may be deviations in parameters from the standard.
- There must be a label on the packaging and markings on the cable itself
- Read reviews, choose only trusted manufacturers (about manufacturers , see below ↓ )
Important! Although this does not happen often, defects sometimes occur, especially if the product is Chinese. Before purchasing, be sure to look at the description on the package, pay attention to the cross-sectional diameter of the core, take a caliper with you to measure the diameter of the copper wire mm², count the number of wires.
Description of wire PV-3 0.75
| Parameter | Description |
| Number of cores Material Class | Four Copper Stranded |
| Insulation material | PVC plastic |
| Insulation resistance (Mohm\km) Cores, (Mom\km) | 24,5 |
| Dimensions: | |
| Cable D (mm) | 2,8 |
| Section (mm2) | 0,75 |
| Weight (kg/km) | 12 |
| Copper weight (kg/km) | 6,7 |
Application of copper wire PV-3 0.75
This cable is intended for stationary use, in electrical networks of lighting and power type with a nominal alternating voltage of 450 Volts (in electrical networks - 450-750 Volts with a frequency not exceeding 40 Hertz, or at a constant voltage of 1000 Volts). Copper wire PV3 is used to power power assemblies and switchboards, machine tools, various mechanisms, non-mobile machines, mechanisms and lighting equipment, lamps, and voltage stabilizers. The advantage of this cable is its flexibility, so it can easily withstand bends. It tolerates acoustic noise, vibration loads, mechanical damage, and linear acceleration well. The permanent laying of cables of type PV-3 occurs using trays, metal, PVC-plastic, technical pipes, along cable overpasses and bridges, in hollow channels, in building structures - blocks and beams, laid individually and in bundles. An important reminder from the manufacturer is that this type of wire should not be subjected to mechanical stress or strong stretching. If you plan to lay the cable in the soil, it is necessary to provide its protection in the form of polyethylene pipes or a special two-layer corrugated pipe. It is also not recommended to lay the cable in the open air; PV-3 0.75 is not intended to be used in conditions of constant temperature changes, low temperatures, or prolonged destructive effects of sunlight. The best installation method is under plaster, in pipes and other suitable structures.
Execution of PV-3 0.75
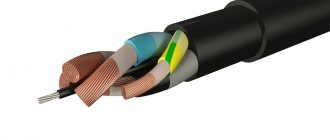
The design of the PV-3 power cable is represented by a conductive core and an insulating sheath. The conductor is made of copper, multi-wire. Stranded conductor class 2.3 or 4 for sections from 0.5 to 1.5 mm2 incl., class 4 for sections from 2.5 to 4 mm2 incl., class 3 for sections from 6 to 95 mm2 incl. according to GOST 22483-77. But the insulating layer is represented by polyvinyl chloride plastic compound in one layer. This type of insulation is not subject to combustion and is not affected by mold fungi. The insulating layer fits tightly into the current-carrying core, but is easily separated and has a different color. The power copper cable is also marked in a certain way: the marking is applied to the insulation in relief, printed and stamped. Or the marking can be colored in the form of a solid longitudinal line or distinctive stripes.
Characteristics of wire PV-3 0.75
Installation of this wire must take place at a temperature not lower than -15°C. PV-3 is resistant to mold fungi. Operating temperature ranges from -50°C to +70°C. The cable lasts 15 years. Type of climatic modification OM and HL, placement category 2 according to GOST 15150-69. This wire, when laid alone, will not spread combustion, and the permissible (long-term) heating temperature of the conductors should not exceed +70°C. The wire is resistant to mechanical stress.
PV-3 wire of other sections is here! <<
You can calculate the wire cross-section PV3 0.75 or select a wire for the required load using a calculator or by calling our managers
Author: MEGA CABLE
The main advantages and disadvantages of PV-3 cable
Like all conductors, PV3 has a number of advantages over others, but unfortunately, it is not without its drawbacks.
pros
- flexibility due to the large number of wires
- resistance to the external environment due to vinyl insulation
- large diameter wire, over 15mm², can be used in car audio systems; PV-6 from the company zandz (zz)
- infusibility
- low price
- thinner insulation, and therefore its own weight (see table above)
Minuses
- With aging, the insulation becomes more rigid
- when applying high current, the conductive wires in the core may burn out
- with frequent bending, tears of individual veins are possible
Where are PV brand wires used? Can they be used in cars for sound?
Due to the large number of current-carrying wires in the conductor cross-section, PV-3 (PUgV) have proven themselves well in moving elements of electrical installations, especially where increased flexibility is required, they are used literally everywhere:
- in everyday life - when laying in an apartment, house, garage, use as portable and temporary connections, extension cords (carriers), grounding
- in industry - special. equipment, moving consumers in workshops, powerful current consumers, in outdoor installations pvz are especially good to use
- for power lines - with a frequency of up to 400 Hz, communication lines
- for audio systems - for example, as power cables for car audio in a car. For such purposes, wires with a cross section of 1x25mm², 50mm², 70mm² are well suited, depending on the power of the installation. With the correct selection of the cross-section, you can get a high-quality and stable acoustic system. wire from the Zendz or Pride company is capable of transmitting up to 290A of current, let alone 70mm². Please note that in order to transmit such a powerful current without loss or interference, the ends of the wire must be crimped with lugs (sleeved) - more details.
PV 3 for sound into a car 50mm2
Application area of the wire
The cable markings cover a fairly wide range of applications. The wire can be used for laying wiring, connecting electrical appliances, power networks and automation.
However, it is not advisable to use PG3 for power cables. Two-core and stranded wires are much better suited (depending on the number of phases of alternating current, i.e., a two-core wire is convenient to use for laying two-phase power lines). For wiring in a house or apartment, wires with more sophisticated insulation that protect the cable from mechanical damage are much better suited. In addition, there are models of materials that serve perfectly as screeds.
Copper conductors
The big disadvantage of using cable in home wiring is the risk of burnout if the load is too heavy. It will not cause a fire, but it will easily ruin the fruits of the work of electricians in equipping the home.
But this is not a reason to put a cross on the wire. After all, for some reason they are still releasing it. PV3 has found the widest application in automation. Thus, it is often used in fire extinguishing systems. The wire is indispensable in automation systems of boiler rooms, ventilation, and car power supply.
Using PV3 in the automation panel of a ventilation unit
Note! PV3 is often used in domestic brands of cars and when repairing door locking elements, power supply to interior lamps and dashboard. In this regard, the wire compares favorably with foreign analogues, which are several times more expensive.
It is in car automation and power supply systems that the main property of wire is used - flexibility. With a huge number of wires and technologically important design details, the wire easily passes through any bends, connecting different models together.
If the load on the automation system is too high, the wire burns out, which triggers the alarm. Just what you need for fire alarm systems and any other automation.
Table of technical characteristics of PV cables
During home repairs, the wire is ideal for arranging grounding. You can ground the panel of a private house or any part of the apartment without any problems using any cable, but PV3 is inexpensive. At the same time, the model will do an excellent job of removing stray currents.
You might be interested in Description of the VVGng-LS cable
Where to buy PV-3 wire: manufacturers, prices
Today there are a large number of companies on the market - manufacturers of wires of various brands, producing high-quality wire products in a wide range at the best prices. There are even more intermediary companies, especially on the Internet, for example, the ETM company (not advertising).
There are a huge number of places to buy, so first of all, pay attention to the manufacturer. The following Russian companies are considered among the industry leaders: Energokabel, TD Alliance Cable, NKZ Elektrokabel NN, Spetskabel, ROSSKAT, ALUR Cable Plant, Moskabelmet.
The foreign companies that distinguished themselves were Zandz (ZZ), which produces lightning protection, grounding, and Pride. They are usually sold by the meter, prices vary greatly depending on the brand and section. For example, PV3 1x0.75mm costs on average 4-5 rubles/m, the price of PV3 1 x 2.5mm for a heated floor is already 20rub/m, and PV3-150 is 959 rubles per meter.
Manufacturers of wire PV-3 1×6
PV3 is produced only in Russia; analogues can be imported. Below are the main suppliers of products to the market.
LLC "Bikonnekt (Stinkab)"
Stinkab is a fairly young manufacturer of cable products. But maybe that’s why it’s worth choosing it, because the company has managed to establish itself in such a short period of time. The plant's office is located in Moscow, warehouses with products are located in Klimovsk.
Note! For large orders, it is possible to pick up the cable at your own expense.
CJSC "EnergoMaximum"
Unlike the previous company, this is a supplier that works with the largest domestic cable manufacturing plants. The company has a fairly long history and established traditions of quality. The supplier positions itself as the largest company in the Volga region.
Important! When working with a company, you need to pay attention to the absence of the name PV3. The company works with names according to the updated GOST for 2010, so the material here is labeled PuGV.
Elkom-Eletro LLC
This is a real giant in the distribution of cable products. Like EnergoMaximum CJSC, the company deals only with the sale of cables. The company has been on the market since 1992, has a convenient website and a huge number of items. PV3 is also present, like the rest of the PV marking positions, adjusted for the new name.
PV cable cross-section
You shouldn’t give up the idea of using PV3 immediately after reading the list of limitations and disadvantages. The cable perfectly fulfills its role - a flexible single-core conductor of automation and grounding loops. There are no perfect cables, and if they exist, they cost exorbitant amounts of money. The PV3 1×6 grounding cable is cheap and perfectly suited for its field of use.
You might be interested in Tee for TV cable
GOST for electrical wires
- GOST 6323-79 (ST SEV 587-87) “Wires with polyvinyl chloride insulation for electrical installations”
- GOST 31947-2012 “Wires and cables for electrical installations for rated voltage up to 450/750V inclusive”
- GOST 22483-2012 “Current-carrying conductors for cables, wires and cords”