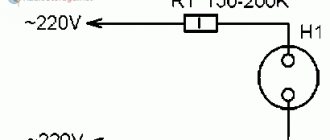
Schematic diagram of the attachment for the ability to measure high voltages (many thousands of volts) using a multimeter. In some cases, it is necessary to measure very high voltages (tens of kilovolts). For such purposes, there are special devices - “kilovoltmeters”.
It makes sense to buy a special kilovoltmeter only when you need to measure “kilovolts” quite often. In everyday amateur radio practice, such measurements have to be carried out extremely rarely.
And in this case, you can get by with a simple multimeter. But the upper limit of voltage measurement for a standard multimeter usually does not exceed 2000V.
In order for a multimeter to be able to measure significantly higher voltages, it must be supplemented with an attachment in the form of a high-resistance and high-voltage voltage divider.
Voltage: what is it?
First, let's remember the definition. Voltage is the pressure from a circuit's power source that causes charged electrons to move through a conductive circuit, causing these particles to perform useful work for people, such as making a lamp glow.
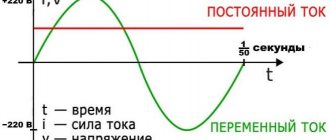
When we talk about voltage, we are talking about two types of current:
- Alternating current. It is found in our sockets, supplies energy to household electrical appliances, and lights with its help. Produced in power plants, alternating current consists of electrons constantly moving through cables. This movement creates the necessary tension. For ordinary sockets, the frequency of movement is equal to 50Hz, and their voltage is 220V. In a second, the flow of electrons changes direction 50 times, which leads to a change in charge: “+” changes to “-”. This process is called alternating current: it powers everything connected to this outlet.
- D.C. It is inherent in all batteries, be it a car, a telephone or a simple AA battery. When the electrical charge runs out, the mains connection is made and the alternating current is converted to direct current. This way the battery again accumulates a voltage reserve if we are talking about reusable batteries.
This means that the process of checking voltage with a multimeter must be separate for each type of current, that is, each device has its own method, in particular for the socket and battery.
Units for measuring the power of electric current.
In addition to Amperes, we often come across the concept of electric current power. This value shows the work done by the current per unit time.
Power is equal to the ratio of the work done to the time during which it was done. Power is measured in Watts and denoted by the letter P. It is calculated using the formula P = A x B, i.e., in order to find out the power, it is necessary to multiply the voltage of the electrical network by the current consumed by the electrical appliances connected to it, household appliances, lighting, etc. d.
On electrical consumers, the plates or passports often only indicate the power consumption, knowing which you can easily calculate the current. For example, the power consumption of a TV is 110 watts. To find out the amount of current consumed, divide the power by a voltage of 220 Volts and get 0.5 A. But keep in mind that this is the maximum value, in reality it may be less because the TV at low brightness and under other conditions will consume less electricity .
Instructions: how to measure voltage with a multimeter
Measuring voltage is quite easy: you just need to select a certain mode, measurement limit and connect the probes. But each stage has its own nuances. Be sure to read your tester's manual for the exact symbols. And to make sure you do everything correctly, read the article on how to use a multimeter.
Mode selection
In the question of how to measure volts with a multimeter, first of all it is important to decide on the tester mode.
The switch handle must be switched to the voltage change mode, and the abbreviation should be selected depending on what will be measured:
- ACV - alternating voltage.
- DCV - constant.
There are also other symbols that also indicate voltage:
- V is voltage, V~ is alternating voltage.
- V with a horizontal dash with three short ones under it - constant voltage.
On some models, only V may appear, which indicates that the tester automatically determines the type of voltage.
Selecting the measurement limit
If you want to figure out how to check voltage with a multimeter, you need to learn how to determine the range of values.
You need to find it on the case in the voltage switching area. For most models, the maximum limit is 750V for AC voltage and 1000V for DC.
If you measure the voltage in an outlet, turn the switch knob to a value of 750 ACV, but if you test a car battery, you can set, for example, 200 DCV.
Remember the rule: the measurement limit of various parameters is set higher than the expected value. Otherwise, there is a high risk that the multimeter will burn out.
The tester will display voltage values in the range you set. Having set the limit to 750V, you may well see a value of 230V on the screen, more or less. There will definitely not be a figure above 750. If you set a limit, for example, at 200V, then if the actual value is greater, the number 1 will appear on the display.
If you measure the voltage in a regular outlet, it does not have to be 220V. 10-15V less or more is quite normal.
Connecting probes
Now, in how to measure voltage with a multimeter, you need to understand how to correctly place the probes, of which there are two - black and red. First, they need to be inserted into the sockets on the case, of which there are often two, but there can be three or even four.
The dark wire of the multimeter is called negative and must be connected to the COM socket. The scarlet wire is positive or phase. If there are two holes on the tester, it is logical that the second one is for this probe. If more, read the instruction manual for where to connect the red wire to measure voltage. This is usually a nest with the letter V next to it.
To measure voltage with a multimeter, other probe tips are connected to the measuring element. Everything is simple here, because the voltage is checked by parallel connection, that is, no load is needed. All you need to do is insert the probes into the socket and look at the display.
Three-phase testing is performed by connecting two tester wires to two buses. The norm between them is 380 V, between one bus and the ground - 220 V (maybe a little more or less).
Tester operating modes
The operation of the multimeter and its modes is regulated using a switch. Its upper vertical position indicates that the device is turned off. A turn in any other direction indicates a change in mode and is indicated as follows:
- DCV or V with a straight line displays the constant voltage;
- ACV or V with wave indicates that alternating voltage is being measured;
- Ω - symbols of this kind indicate resistance;
- And with a straight line or a combination of letters DCA is an indicator of direct current (amps);
- And with a wave indicates that the multimeter measures the strength of alternating current, which not all devices have;
- the sign indicating a diode indicates that the diodes can be ringed;
- hFE shows that it is possible to measure the characteristics of transistors.
All results are displayed on the tester screen in a matter of seconds, reporting the value of the selected indicator with an accuracy of hundredths.
The designation of alternating current on any multimeter can be depicted in the form of AC symbols (alternating current). Accordingly, ACA is alternating current strength, ACV is alternating current voltage. This is a current that changes direction a huge but constant number of times in 1 second. In home networks, the variation frequency is 50 Hz.
How to measure voltage with a multimeter in a socket
Now let’s look step by step at how to measure voltage with a multimeter in an outlet:
- Select the multimeter's AC voltage measurement function by setting the maximum measurement range.
- Attach the probe tips to the socket, feeling the wire inside. In the case of alternating current, we do not need to figure out where the “+” and “-” are.
- Look at the result shown on the display. Don't forget to turn on your multimeter to do this.
Video on how to find out the voltage in a socket with a multimeter:
How can you measure current?
To determine power consumption and current, an electrical meter is required that can measure these parameters taking into account the characteristics of alternating and direct current. There are only two types of such devices:
- An ammeter is a special device for measuring exclusively the current in a circuit. The ammeter is connected to the circuit under test in series with electric current consumers. On the device scale, in addition to the main values, milliamps are also used in amperes. You need to pay special attention to amperage. There are electronic and mechanical versions of the device.
How to measure battery voltage with a multimeter
Measuring the DC voltage of a battery with a multimeter is carried out as follows:
- Select the DC voltage measurement mode on the tester, as well as the measurement range higher than expected. You can start with the maximum and gradually decrease. For home batteries, 20 DCV is enough.
- Connect the tip of the dark wire of the meter to the minus.
- Connect the tip of the scarlet wire to the positive.
- Look at the numbers on the display. If there is a minus sign in front of them, then you have reversed the polarity, but the value itself reflects the real voltage.
Compare the resulting value with the standard that may be indicated on the device body.
Video on how to check the volts on a multimeter for a AA battery:
Now you know how to check voltage using a multimeter. Share your experience in the comments.
We wish you safe and accurate measurements!
A little theory - how measuring instruments are connected
To use it correctly, you need to know how voltage is measured, and how current is measured, and connect the device correctly. When the wires are simply connected to a working power source, an electrical voltage appears on them, which can be measured between plus and minus (phase and zero). This means that the voltage can be measured both with a load (operating device) connected to the network and without it.
Electric current appears in the wires only when the circuit is closed - only then does it begin to flow from one pole to the other. In this case, current measurements are carried out when the measuring device is connected in series. This means that the current must pass through the device and only in this case will it be able to measure its value.
Of course, in order for the measuring device not to influence the current it measures, the resistance of the multimeter should be as low as possible. Accordingly, if the device is configured to measure current, and you mistakenly try to measure voltage with it, a short circuit will occur. True, not everything is clear here either - current and voltage measurements with modern electronic multimeters are carried out with the same connection of the terminals to the device.
If you recall at least superficial school knowledge about electrical circuits, then you can formulate the rules for measuring voltage and current as follows: the voltage is the same on parallel-connected sections of the circuit, and the current is the same when the conductors are connected in series.
To avoid errors, before taking measurements, be sure to check the markings located near the contacts of the multimeter and its mode switch.