The PV-3 cable is used in electrical equipment for special industrial purposes such as machine tools, electrical machines, and electrical mechanisms. In such devices, kinks in wires often occur, shock impacts occur when laying cables, vibrations, noise, and pressure drops occur. It is used in any temperature conditions, and is also used in the electrical systems of marine vessels. In the article we will talk about the PV-3 wire and consider its characteristics.
Appearance of the PV-3 cable, used as a copper conductor when laying industrial electrical networks
Purpose of wire model PV-3
Model PV-3 1x4 is produced for alternating current networks used at a voltage of 450-500 V, with a frequency of 90 – 100 Hz. In DC networks it uses a voltage of 900 -1000 V. The base conductor conducts current and passes a current signal of 41 A. Possibility of operation at temperatures -60 - +60 ° C and humidity 90-100%.
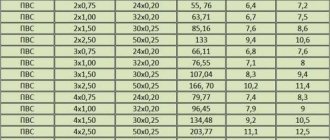
The main core heats up to +65 - +70 °C under standard conditions, passing the rated current. The cable consists of a copper core, intertwined wires and polyvinyl chloride insulation. The outer diameter is 4.0-4.1 mm and the insulation is more than 0.7-0.8 mm. This modification uses a Class 4 cable with a resistance of 4.89Ω. The cable parameters are shown in the table.
Table 1. Resistance of class 4 cable cores. (Tinned - multi-core cables, most often used in electrical circuits).
Mechanical properties
Determine the scope of application and operating conditions:
- Flexibility. A remarkable property that increases operational value and efficiency of use. The cross-section of each wire is the same, the number in the set determines the degree of flexibility. According to GOST 22483-77 for PV 3 wire, the wire diameter is 0.79 mm. For small cross-section cables, the wire diameter can be 0.53 mm and the minimum number of cores is 7, which corresponds to the fourth class of flexibility. The sum of the cut areas of the cores is the nominal cross-section of the cable, indicated in the technical specifications. The permissible bending radius is at least five outer diameters;
- Strength. The concept of the conductor design in the form of a cable provides, in addition to flexibility, increased mechanical strength and increases the ability to bear loads. The insulation material, which can be two-layer, can successfully withstand various mechanical influences without loss of useful properties and destruction. Linear tension until the moment of failure is 150% of the original length, that is, it lengthens one and a half times. The thickness of the insulation depends on the diameter of the core;
| Nominal core cross-section, mm | Nominal insulation thickness, mm |
| From 0.5 to 1.0 incl. | 0.6 |
| 1.5 | 0.7 |
| from 2.5 to 6 | 0.8 |
| 10.0 and 16.0 | 1.0 |
| 25.0 and 35.0 | 1.2 |
| 50.0 and 70.0 | 1.4 |
| 95.0 and 120.0 | 1.6 |
| 150 | 1.8 |
| 185 | 2.0 |
| 240 | 2.2 |
- Colors. Using the right color is very important and must comply with generally accepted standards. Creates convenience, reduces labor costs for dialing, troubleshooting for installers and repairmen, and promotes the creation of safe conditions for handling electricity. The colors are determined by the PUE and the European standard: o Yellow-green, yellow or green - intended for connection to the ground contact, the international designation of the contact is “PE”; o Blue or cyan connects the neutral, or “zero” (“N”); o The remaining colors are designated by “phase” (“L”) and are chosen arbitrarily.
In three-phase versions, it is customary to mark the phases:
- A – white;
- B – black;
- C – red.
DC circuits use different markings. Here white, black is “plus”, red is always, the rest are, as necessary, “minus”;
- Temperature. High electrical safety indicators are ensured by the presence of two layers of elastic insulation made of polyvinyl chloride modifier. Allows flawless operation in the ambient temperature range -50⁰С - +35⁰С, allowing long-term operation when the core is heated to +70⁰С. Installation, to prevent the formation of shell cracks, is prohibited when the air is cooled below -15⁰С.
Cable brands
Copper cables have varieties:
- PV-3 x 2.5;
- PV-3 x 1.5;
- PV-3 x 0.75.
They are made with one core made of copper. Has high strength and flexibility coefficients. The multi-wire structure of the core guarantees a long service life and good current conductivity.
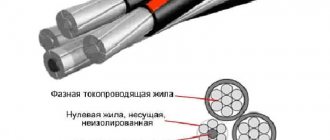
Image of cable PV-3. Legend: 1 – conductive core, 2 – insulation shell
The wires of these models are used in industrial and household installations. They do not heat up when exposed to current. Models also often used:
- PV 3 16;
- PV 3 10.
The presented models have high strength, better conductivity and a large variation in cross-sectional dimensions. An overview of prices for cities of the Russian Federation is shown in the table.
Table 2. Prices by region of the Russian Federation:
Positive qualities, features
PV 3 has undoubted advantages, expressed in the efficiency of the design and the materials used in its manufacture. This:
- A sufficiently large selection of the cross-section of the current-carrying conductor, correspondingly wide limits for connecting power;
- High flexibility provided by the design and materials used. Significantly facilitates the work;
- The insulation material contains substances that make wire products “unpalatable” to rodents and repel them. Limits the harm of exposure to mold and mildew;
- The use of special plastic modifiers in some brands of wire makes it possible to obtain products that do not support combustion when laid alone, self-extinguishing or with insignificant smoke emission;
- The ability of insulation does not deteriorate during long-term heating (+70⁰С) makes it possible to use PV 3 for heating pipes by winding around them, passing a sufficiently large one;
- The ability to operate at 100% ambient humidity at a sufficiently high temperature makes it possible to use it in the lighting network of baths and saunas, and to use it in the electrical systems of ships;
- Durability - almost 15-20 years, lack of contact with aggressive environments increases service life.
Manufacturers of wires of this model
JSC ELKAb produces the following types of wires:
- PV-1;
- PV-3;
- PV-4.
Cable products are reproduced with aluminum and copper screens with 100% overlap. All products have an international quality certificate.
SARANSKKABEL is one of the leading enterprises in the cable industry. In 2022 it produces:
- Flexible power cables with thermoplastic elastomer insulation sheath;
- bare wires;
- tinned;
- for electrical equipment;
- household use.
The company already has extensive experience and a reputation as a high-quality manufacturer of electrical goods.
Concord LLC is a company with experience in the production of wires from conductive copper conductors. Their products are manufactured with modernized fire protection parameters:
- VVGng – reduced flammability;
- VVGng-LS – reduced fire hazard.
The company's products are ISO 9001 certified.
EM-CABLE LLC – produces:
- heat-resistant uninsulated cables;
- isolated;
- power;
- with reduced gas emission;
- with reduced smoke emission.
Certified products according to ISO 9001 guarantee quality for various applications.
Suggested wire analogues
- VVG wire. This type of wire is applicable in both wet and dry areas. Poor stretchability. Its main variety is VVGng.
The prefix “ng” means that in the event of a short circuit, fire will occur only on one conductor, without spreading to the entire cross-sectional area. Its advantages include:
- configuration variations;
- Various cross-section geometries.
Disadvantages: the design is not designed for excessive stretching. These types are produced by MARPOSADKABEL.
- Images of NYM electrical cable produced according to the German standard DIN 572250
NYM wire. Its distinctive feature is the use of German production standards.
The cable is used on high-rise structures, provided that it is not exposed to direct sunlight.
Consists of copper conductors and a non-flammable insulating sheath. Its advantages:
- flexibility;
- low degree of smoke emission;
- high fire hazard.
Disadvantages: cannot be used in the open sun. Cables of this type are produced by.
- Flat wire PUNP. The main feature is low cost compared to other models.
Such conductors are used exclusively flat in light and power networks. This variety is offered with 2 or 3 copper cores. Often used for installing electrical wiring in domestic conditions. Advantages: used in open wiring.
Flaws:
- materials are not of high quality;
- instant loss of its properties when heated.
A large selection can be found in the online store “All Instruments.ru”
- Appearance of a single-core copper cable with PV insulation in different color variations
Single-core cable PV1. There are multi-wire and single-wire varieties.
Single-core cable is used in potential equalization systems. For installation in electrical panels, models with a large number of cores are used, which are more expensive varieties. Advantages: flexible shell for models with 2 or more cores.
Flaws:
- single-core cables are less flexible;
- multi-core cables are more expensive.
A large selection of PV-1 wires is offered at KabelTransService LLC.
Application area
Where is the conductor used? Due to the fact that PV-3 has a wide range of core sections and simple technical characteristics, it is used in almost all areas of production and industry: the formation of an individual electrical network, installation of electrical wiring in an apartment, connection of electrical appliances and much more.
The areas of application of the product can be divided into the following sections:
- communication systems;
- residential, non-residential and industrial premises;
- electrical wiring, both indoors and outdoors.
Double layer of insulation ensures maximum safety. The insulation is made from special advanced PVC plastic, which is not able to heat up from current. Due to this, it is used in high-voltage production. In addition, the material in its composition has a special substance that reduces the likelihood of combustion to a minimum.
Cable selection instructions
Choice of material. The most common are copper and aluminum. Copper has better conductivity and is also non-corrosive. Aluminum is a soft material; cables bend quickly and break quickly. When aluminum comes into contact with air, it quickly oxidizes and an oxide film forms on the surface. Such a film does not transmit current signals well and provides unreliable contact.
Section size. The defining parameter of the section is diameter (d). At low current values, a copper core is used with a diameter of more than 1 mm2, and an aluminum core - 2 mm2. When working with large current values, the diameter is selected based on the power of the network. Diameter selection is made according to table. 3, taking into account the cable laying through a pipe or openly.
Table 4. Cable size selection for various types of cable installations
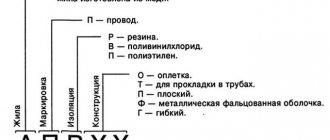
Brand samples. The marking characterizes the property of the cable, namely:
- material of conductors;
- level of flexibility;
- isolation.
Tip #1. When installing permanent wiring, use a wire with current-carrying cores consisting of single wires.
The following notations are used:
- The first symbol is the material of the core; if this symbol is absent, then the core is made of copper.
- The second symbol is wire;
- The third indicates insulating material.
FAQ
Question No. 1. How is the cable cross-section selected?
The cross-sectional size is proportional to the properties of the wire to withstand given loads. The most popular varieties are sections: 0.75; 1.5; 2.5; 4.0; 6.0; 10. It is also worth paying attention to the material of the core. Aluminum cable has low conductivity compared to copper, so the cross-section is chosen one unit larger than for copper.
Question No. 2. What's better? Aluminum or copper based wire?
Aluminum is cheaper compared to copper. Aluminum cables have weak electrical conductivity, less strength, and quickly break when bent. Also, aluminum quickly oxidizes when exposed to air. Copper is considered a structurally sound and reliable solution compared to aluminum.
Question No. 3. Which wire is better: flexible or rigid?
- Rigid wire is a monocore cable.
- Flexible wire – multi-core cable.
The rigid variety of cables is usually used for laying in the ground and installation in walls. Flexible is applicable when working with mechanisms, instruments, and machines that can move. The ends of the flexible cable require special crimping and installation of pipe connectors before connection. Rigid ones do not require such a procedure. To connect lighting devices, it is recommended to use hard wires. Lighting equipment can be replaced frequently, and flexible cable is not as prone to fractures as rigid cable.
Question No. 4. What kind of insulation should there be?
The amount of insulation affects the service life of the cable. Single insulation will allow the wire to last 10-15 years, double insulation - about 30. The protective coating is made of various materials, such as:
- plastic;
- glass;
- steel.
Specialists who service and repair cables share the concepts of sheath and insulation.
- Insulation is a protective coating on live parts of a cable.
- Sheathing is a protective coating applied on top of the insulation.
Marking designation
Let's start with deciphering the abbreviation. Questions may arise due to the additional numbers that are added after the two main capital letters. Let's get started:
- The letter “P” in the first place indicates that the product is a wire. In addition to wires, these products are divided into two categories - cords (W) and cables (C).
- The letter "B" in second place indicates the type of insulation used. In this case we are talking about a polyvinyl chloride shell, the positive quality of which is its resistance to many physical and chemical influences. This is one of the main materials used as a dielectric.
- The last digit indicates the cable flexibility class - from “1” to “5”. The higher this value, the more flexible the product will be.
Wires are divided into two main categories - installation and installation. The first category includes products that can be used for a long period of time in the same place. We are talking, for example, about installing a socket, switch, etc. The installation wire is intended for repeated use and temporary connection of various equipment.
It is logical that a more flexible cable should be called an installation cable, while a more rigid product should be called an installation cable. For example, PV1 is an installation wire, which is not recommended to be constantly moved and used in different places, PV3 is an installation wire.
This is interesting: Protection device for LED lamps - which one to choose
Errors when using PV-3 cable
- The size of the cores is less than the size of the entire cable cross-section. This factor will cause the wiring to burn out when connecting the load that the wire must withstand. The automatic switch will not operate when an overloaded signal is received.
- The veins joined each other. In the case of using a two-key switch, when one button is turned on, the contacts of the second will also close. Possible burnout of electrical appliances.
- Broken vein. An open circuit is formed and current flow is impossible.
- The insulation thickness is less than normal. Such insulation can be easily damaged:
- during installation of electrical equipment;
- when stepping on a cable;
- when hit or dropped by any object.
- Technical characteristics of PPV wire
- Technical characteristics of PRKA wire
- Do-it-yourself testing of wires and cables (device)