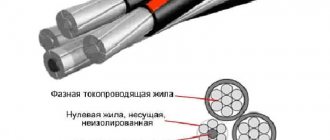
Choosing a PVS wire
PVA wire is a flexible copper wire with twisted conductors, having polyvinyl chloride insulation and the same sheath. Quite often it is confused with PVSP wire, which has the same structure, but a parallel arrangement of cores. In our article we will look at the main characteristics of PVA wire, as well as areas of application and properties.
Description of the PVS wire
PVS wire (also known as PVS cable) is one of the most common wires for household use.
It can be used to connect power tools (if the power consumption matches the wire cross-section), for laying lighting networks, and the like. As a rule, it is PVA wire or something similar that is used in household and industrial extension cords. Depending on the number and purpose of cores, this cable can be used in single-phase and three-phase networks.
Description
The design of this wiring is no different from the similar one. The conductors, made of copper, are protected by a polymer coating. PVA marking means the following:
- P – wire. It is indicated that the product belongs to the electrical wiring class and is intended to transmit electricity.
- B – vinyl. The insulating layer is made from this material. Moreover, it is used to protect each core and produce a common shell.
- C – connecting. Functional purpose.
The main characteristic of PVA is the diameter of the cores and their number. They are made of copper and can be solid or made up of several individual wires twisted around a base. To mark each core, it is customary to use standard colors:
- White - denotes the outer protective sheath, inside which there are insulated wires.
- Black, brown, red - this is how the phase conductor is usually marked.
- Blue – zero.
In some cases, green indicates a ground wire. When choosing, you should pay attention to the product labeling. It is carried out in accordance with GOST 7399-97. Let's look at the example of a typical designation - PVA 2×1.5. This means that the cable includes 2 insulated cores with a diameter of 1.5 mm each. In some cases, it is necessary to know the number of wire elements and their cross-section. Then you should use the table data. It also indicates the specific gravity of the cable and the possible outer diameter.
The technical characteristics of the PVS wire make it possible to use it in almost all areas where it is necessary to connect from a source of electricity to a consumer point.
Characteristics
When choosing a cable, you should pay attention to the number of conductors, their diameter and performance characteristics. The latter are an important point, since due to the properties of the vinyl sheath, it is possible to install the cable in damp rooms with the possibility of water getting on its surface
In this case, it is necessary to follow the rules for connecting individual sections of wiring. The joints are carefully isolated. It is best to use special heat-shrinkable tubes for this.
Technical characteristics of the PVS cable, common to all types of products:
- The maximum voltage is 450 V.
- Thermal stability belongs to class Y. It is characterized by limiting the heating temperature to +70°C.
- Standard fire resistance class. The insulation material is not flammable and does not support combustion when exposed to an external flame.
- The product has high mechanical strength and is characterized by good resistance to bending damage.
- Depending on the type of operation, the service life can range from 6 (mobile state) to 10 (stationary) years.
To all this I would like to add the affordable cost of PVS wire. Due to the above characteristics, the scope of application of this type of wiring is quite extensive.
Application
Most often, the cable is used as a current-carrying line to connect energy to device devices. It can be installed to create wiring in a house or apartment. But before this, the nominal and maximum network load indicators must be calculated. In accordance with the data obtained, a product with an optimal cross-section is selected. In household appliances, PVA is used to connect electrical appliances to sockets.
Generally speaking, PVA wire is one of the most common types of electrical wiring for household and industrial use. The choice of core cross-section should be based on the calculated data of the entire project or the parameters of the connected device. Only in this way will PVA be able to fulfill its functions as a conductor of electricity.
Purpose and use of PVS wire
The cable is often used:
- As an extension cord or carrying device for solving everyday problems;
- For external and internal connections of external electrical networks and devices;
- In gardening due to its flexibility and waterproofness;
- Inside electrical devices;
- For connecting any type of power tools (personal computer, lawn mower, electric kettle, TV, vacuum cleaner, etc.).
Important! PVS has a huge number of appointments. It is used even where no one expects to find it. All thanks to its flexible structure and performance characteristics. It is because of this that such a huge production of PVA has been established in the world by manufacturers from different countries.
PVA based carrier
Wire structure
PVA is a cable consisting of two or more strands of conductor material insulated from each other, which are intertwined (round cross-section) or lie parallel (oval cross-section) in an outer insulating sheath. According to the same regulatory document GOST 7399 - 97, it is allowed to use any material as pre-insulating material so that there are no voids between the cores. At the same time, they must be freely separated from the outer and inner shells. The overall structure of the cable is flexible, which allows it to be used in many industries.
The photo shows the PSVP wire
Decoding the PVS wire
For PVC wires, the decoding is quite simple - “P” means wire, “B” means the presence of vinyl insulation (this is an abbreviation for PVC) and “C” means the connection of all cores in a single sheath. In this case, the wire has a circular cross-section. The addition of the symbol “P” indicates a parallel arrangement of cores. In this case, the wire has an oval shape.
Decoding of PVS wires
So:
- The marking on the wire is applied to its outer surface . In addition to the designation of the wire brand, it also contains a number of numbers. Let's look at their meaning. And the video presented on the site will help us in this.
- The first digit after the letter marking is “2”, “3”, “4” or “5”. This number indicates the number of cores in the cable.
- After this comes the “×” sign and the second number, which can be “0.75”, “1.00”, “1.50”, “2.50” . This number means the cross-section of all wire cores.
Note! According to GOST 22483 - 77, the nominal and actual cross-sections of the cores may differ. The main requirement is that the electrical resistance of the wire meets the standards.
- For example, we have a flexible wire PVA 3x1 5. This means that this wire has three cores with a nominal cross-section of 1.5 mm2 each.
Decoding of PVA markings
It is quite simple to decipher the PVA:
- the letter “P” indicates that this product is a “wire”;
- the letter “B” means that the cores and sheath are protected with “polyvinyl chloride” (vinyl) insulation;
- “C” – “connecting” cable (purpose).
There are other wire options. For example, you can often find the PVSP label on store shelves. Many people mistakenly believe that we are talking about an identical cable, although in fact the cores of this model are located parallel to each other. As a result, the wire turns out to be oval in cross-section, and installers call it “flat”.
Any cable/wire must be marked on the outer surface. In addition to letter designations, there may be various numbers on the PVA shell:
- the first digit is used to indicate the number of cores, so the number will always be an integer - 2, 4, 5, 8, etc.;
- the second number indicates the cross-sectional area of an individual core - 0.25, 0.75, etc. (measured in sq. mm).
It will be much easier to understand by looking at examples. Let's assume that you see a cable marked PVS 4×0.75. Deciphering the meaning, we get “a connecting wire with polyvinyl chloride insulation and four cores with a cross-section of 0.75 square meters. mm for each." If the product is marked as PVSP 2×2.5, then this cable is a flat type of PVSP with two cores and a cross-section of 2.5 square meters. mm each.
There is more complex marking when the cable indicates “PVS 4×0.5+1×1.0. This wire has four cores with a cross section of 0.5 square meters. mm and one additional – 1.0 sq. mm.
Important! In accordance with GOST, small deviations are allowed between the actual and nominal values of the cross-sectional area of the wire. Thus, this value may be less or more than declared, while the electrical resistance must be the same as indicated in the technical data sheet. This is the main technical parameter!
Technical characteristics and operating conditions
According to the current GOST, this type of wire must meet the following standards:
- The lower limit of the operating temperature range is 20°C below zero, permissible long-term heating is 40-50°C, short-term heating is not more than 70°C. Frost-resistant design is possible, in this case the lower threshold drops to -40°C.
- The rated voltage is 380 V, but the insulation must withstand a short-term increase of up to 2000 V (at least 5 minutes). It is under these conditions that tests should be carried out by the manufacturer.
- PVA insulation of any type should not spread fire if a single installation was carried out. When laying in groups, this requirement applies only to wires marked “ng” in the marking.
- Failure-free operating time in hours is at least 5000; when used in stationary installations, this parameter increases to 12000; in years this is 6 and 10 years, respectively.
- The threshold of permissible relative humidity should not be lower than 98%.
- Mandatory resistance to the destructive effects of fungi and mold.
The remaining parameters are shown in the table below.
Application
Actually, the scope of application is indicated in the name - “connecting wire”. Its main purpose is to connect to the network various stationary or mobile (portable) electrical equipment powered by a voltage of no more than 380 V.
Given the flexibility of this type of wire, it is excellent as a household extension cord.
Household extension cord
But it must be taken into account that PVA insulation is not designed for outdoor use. It breaks down under ultraviolet radiation and is susceptible to moisture.
Now let's move on to the question of using PVA when installing electrical wiring. This is not what you can do. To immediately exclude the argument, which indicates the absence of a direct prohibition in the PUE. Let us provide excerpts to put an end to this dispute.
Excerpts from SP and PUE
This alone is enough to cause problems when obtaining insurance in the event of a fire in an apartment or house.
Please note that according to the above excerpts, installation with PVS ng wire is allowed. But there are the following arguments against this option:
- Pay attention to the service life, even for stationary installations it is 12 years; further, the insulation’s preservation of its properties is not guaranteed. Wiring laid with VVG cable will last almost three times longer.
- PVS ng is more expensive than VVG.
The above arguments are quite sufficient to demonstrate the absurdity of such a decision.
Basic parameters of PVS wire
Now let's look at the main characteristics of the PVS wire. After all, it is on the basis of them that the choice of wire and location of its installation is made.
Technical characteristics of PVS wires
So:
- According to GOST 22483 - 77 cores of PVS wires belong to class 5. Based on this, the cross-section of individual wires in the total cross-section of the core is selected. For example, for a wire with a nominal core cross-section of 1.0 mm2, the cross-section of a single wire should be no more than 0.21 mm2. And for a core of 2.5 mm2, the value of a single wire should no longer be more than 0.26 mm2.
- As for insulation, GOST 7399 - 97 PVS sets values for wires that depend on the cross-section of the cores. So the thickness of the core insulation ranges from 0.6 to 0.8 mm. And the thickness of the shell ranges from 0.8 to 1.2 mm. In this case, the insulation must provide an insulation resistance not less than those given in this GOST.
Note! According to clause 4.1.1.6 of GOST 7399 - 97, the wire sheath should not have any bulges or dents. In addition, the shell must be made in such a way that there are no voids between the cores. It is allowed to use additional materials for this. But in any case, separating the cores from the shell should not cause difficulties.
- Operating temperatures for PVA wire are considered to range from - 25⁰С to +40⁰С. In this case, the maximum operating temperature should not exceed +70⁰С. And the minimum temperature for installation should not be lower than -20⁰С
- The instructions assume that the wire sheath does not spread fire. At the same time, it itself is exposed to temperatures.
- GOST measures the service life of PVA wires at 6 years. But usually this period is much longer, unless the wire is exposed to aggressive environments.
PVS
PVA cable is a flexible copper wire. Its flexibility is very good, so you can install any electrical systems without fear of breakage. According to the standard, the conductors in the wire are assigned the fifth class of flexibility, which is one of the best results, especially considering the excellent resistance to various mechanical loads and deformation. Plastic insulation reliably protects the copper base from corrosion and is resistant to the appearance of various fungi.
The name PVS stands for:
- P - belongs to electrical products that distribute electrical energy.
- B - for cable insulation, vinyl is used both externally and for insulating a separate core.
- C - designed for creating electrical networks.
If you look closely at the insulation, you will notice that it has an outer and an inner layer. The material used to create the insulation layers is polyvinyl chloride plastic. Thanks to it, the wire is not subject to combustion and can withstand elevated temperatures.
The cores are insulated from each other and twisted in a spiral. In accordance with the international standard, each cable core is painted in its own color so that the neutral and phase cores can be identified. If there is a zero phase, then it is painted blue, green or yellow-green corresponds to the ground wire, and the remaining colors mark the current-carrying conductors.
Cable Specifications
The technical characteristics of the PVS wire are determined by the state standard. But GOST only indicates a range of values, and the actual parameters may vary for different manufacturers. Therefore, to obtain accurate data for a specific cable, you need to look for the manufacturer’s documentation.
Description of technical features:
- The temperature range at which the wire must be operated is from -25 to 40 degrees Celsius. At the same time, the cable can withstand temperature increases of up to 70 degrees and even a short-term jump to 90.
- Suitable for use in rooms with high relative humidity and resistant to fire.
- The line voltage of the network should not exceed 660 volts.
- Resistance to deformation when bent in both directions is 30 thousand times.
- The number of cores can vary from 2 to 7.
- Manufacturers provide a 2-year warranty from the moment the wire is put into operation. In this case, the service life is at least 6 years. When used in stationary electrical devices, the service life can reach 10 years.
There are PVA made of aluminum. They are used in urban wiring and industry. Main differences from copper cables:
- When an electric current passes, aluminum heats up less than copper. This provides greater stability and power of the conducted flow of electricity.
- Wires made of aluminum that have undergone oxide treatment can be used in high-power facilities. Oxide treatment increases service life.
- Aluminum weighs less than copper. This property is useful for constructing high-voltage transmission lines and allows you to reduce the number of required supports.
- The cost of a cable made of aluminum is less than that of copper, and at the same time it has a service life no less and is not inferior in flexibility.
Application area
The PVS wire is used in the following:
- connecting power tools;
- various extension cords, carriers;
- lighting of residential buildings, outdoor lighting.
To protect against rust, some cables are coated with tar, for example, VVG, APPVS, KSVP.
The use of PVA wire for a hidden apartment wiring system is not recommended. Its purpose is only to connect and for the same price you can purchase a more suitable analogue. But there is no prohibition on this in the state standard, so you can use the cable for fixed wiring. When installing, remember to use clamps or crimp the cable.
Additional designations
The PVS cable may be marked with a number of additional letters and/or numbers indicating individual design features or functional properties. First of all, this is a 3x2.5 format code - a standard designation of the number of cores and their total (since they are multi-wire) cross-section.
Other possible designations:
- T - “tropical” version, increased resistance to humidity.
- Y - increased temperature range (up to –40 degrees).
- L - conductors made of tinned copper.
- A - conductors are made of aluminum, not copper.
- B - presence of armor.
- G - no insulation.
- PS is a shell made of a mixture of polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride.
- PV - shell and mixture of PVC with rubber mass.
Construction, appearance
The design of the PVA wire is clearly visible in the photo. Twisting the conductor from thin copper strands gives flexibility. The number and diameter of veins determine the total cross-section. Copper cores can be tinned or have a galvanic coating to prevent oxidation.
The twisted core is covered with an elastic layer of multi-colored vinyl insulation. Conducting insulated conductors (1-10 pieces) are twisted and filled with soft PVC outer shell, forming a monolith without voids. The shape is round in cross section. Models that increase tensile strength use a central dielectric rod.
The arrangement of conductors in one row forms a flat product of the PVSP brand.
The shell must be intact, without dents, bulges, or cracks. Separating the cores from the sheath is easy.
The letters indicate the brand, the numbers indicate the number of conductors (2-7), the cross section is written through X (0.5-10.0 mm²).
The designation PVA 3x4 shows Vinyl Insulated Connecting Wire, 3 conductors have a cross-section of 4.0 mm² each.
Types of insulation
Insulation types:
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVA). PVA is a relatively inexpensive and easy-to-use material that can be used in a variety of applications. The maximum temperature range is from minus 55 to 105 degrees Celsius. The polymer is resistant to flame, moisture and abrasion. It also resists gasoline, ozone, acids and solvents. It can also be used for medicinal and food purposes as it is odorless, tasteless and non-toxic. PVA shells can be used in heavy and thin-walled structures. PVA should not be used when flexibility and extended flex life are required at low temperatures. It also exhibits below-average flexibility when used in devices with retractable cords. PVA shells exhibit high attenuation and capacitance loss, meaning that power is lost when used in an electrical system.
- Semi-rigid PVC (SR-PVC). Mainly used as primary insulation and very resistant to abrasion. (For thicknesses 30-16, 10mm wall is UL 1061 style, 80 degrees Celsius, 300 volts.) Semi-rigid PVA is fire resistant and also resistant to heat, water, acids and alkalis.
- Plenum Polyvinyl Chloride (Plenum PVC). Plenum PVC is suitable for use in areas behind drop ceilings or raised floors that are left open to allow air circulation. Standard PVA is considered a non-film insulation option because it does not have the qualities required for safe indoor use. To achieve rated density, insulation must meet more stringent fire codes.
- Polyethylene (PE). This connection is used most often in coaxial and low capacitance cables due to its typical electrical properties. Many times it is used in these applications because it is affordable and can be foamed to reduce the dielectric constant to 1.50, making it an attractive option for cables requiring high speed transmission. Polyethylene can also be cross-linked to provide high resistance to cracking, cutting, soldering and solvents. Polyethylene can be used at temperatures from minus 65 to 80 degrees Celsius. All densities of polyethylene are rigid, hard and inflexible. The material is also flammable. Additives can be used to provide fire resistance, but this will sacrifice dielectric constant and increase power loss.
- Polypropylene (PP). This material is very similar to polyethylene, but has a wider temperature range from minus 30 to 105 degrees Celsius. It is mainly used for thin-walled primary insulations. Polypropylene can be foamed to improve its electrical properties.
- Polyurethane (PUR). Polyurethane is known for its extreme strength, flexibility and flexural life, even at low temperatures. This material also has excellent ratings for chemical, water and abrasion inertness. This material works well when used with a retractable cord and can be an excellent option for salt spray and low-temperature military applications. Polyurethane is a flammable material. The fire-resistant version sacrifices durability and surface finish. However, the main disadvantage of polyurethane is its poor electrical properties, which makes it only suitable for jackets.
- Chlorinated polyethylene (CPE). CPE has very good resistance to heat, oil and weathering. Many times CPE serves as a cheaper, environmentally friendly alternative to CSPE. Its reliable performance under fire also makes it an advantageous replacement for PVA insulation. Chlorinated polyethylene is commonly used in power and control cables and in industrial power plants.
- Nylon. Nylon is usually extruded over softer insulating compounds. It serves as a tough shell exhibiting high abrasion, cut-through and chemical resistance, especially in thin-walled applications. It is also an extremely flexible material. One of the disadvantages of nylon is its ability to absorb moisture. This degrades some of its electrical properties.
Design
Modern PVA wire consists of several intertwined copper wires with separate insulation made of high-quality polyvinyl chloride. Additionally, all conductors are protected by a PVC sheath. The standard cable has a round cross-section, although the PVSP model, as described above, will have an oval cross-section. Insulating materials may include various additives that give them additional protective functions (for example, the product does not support the combustion process).
Each copper core contains a large number of copper wires. When twisting each one, a dense rope is formed. In accordance with GOST, the class of lived in PVA must be at least fifth. Such a standard automatically regulates the minimum thickness of the wires from which a separate core is formed.
If the cross-section of each core in the cable is 1 sq. mm, then the diameter of the wires used should not be lower than 0.21 mm.
According to the standards specified in GOST, the wire can be produced in the following versions: with two, three, four or five cores. The cross-sectional area varies between 0.75-16 square meters. mm. Thicker types of cable are produced in specialized factories and are necessary for industrial use.
Analyzing GOST, you can discover another important rule: in PVA, the cores are twisted in the left direction, but the density is so high that filler is not used.
When choosing an insulating shell, manufacturers try to use materials of different colors, which simplifies installation tasks. Individual wires can be colored blue, brown, red, yellow or even yellow-green. The phase conductor is usually marked brown or red, the neutral conductor is blue or cyan, the ground conductor is double, yellow-green. The common sheath, under which all the cores are located, can have an arbitrary color (for example, black).
The top, outer layer is a polyvinyl chloride shell, which is applied using the extrusion method. During the single installation process, the protective layer does not support combustion. Due to its plasticity, the sheath fills any gaps formed between the cores, making the wire round in shape. The maximum eccentricity value is 10%.
Characteristics
PVS wires have the following technical characteristics:
- Depending on the cross-section of the phase elements, the product can withstand current up to 2 kW;
- When stretched, rupture occurs after the length has increased by one and a half times;
- The optimal operating temperature ranges from plus 40˚C to minus 25˚C;
- Frost-resistant grades of PVA are marked with a special symbol “Y”. It indicates a lower temperature threshold of up to - 40 ˚C;
- The warranty period is usually 2 years;
- When laid alone, the shell of the product does not support combustion. In case of fire during prolonged contact with an open flame, it has the property of self-extinguishing;
- PVA-T has a coating that has a number of special properties that increase service life in hot and humid climates;
- Can be used at high air humidity (up to 98%);
- The safe bend radius is at least 4 cm;
- The resource of uninterrupted operation when used as a temporary wiring or carrying element is 5000 hours. When used as stationary and permanent wiring - 12,000 hours.
A PVS cable from different manufacturers may have different technical characteristics, even if the markings are the same. Differences may relate to parameters such as:
- Thickness of the insulating layer;
- Conductor cross-section;
- The number of copper wires in the strand.
An exact description of the properties of a particular PVA can be found in the supplier's documentation.
Watch this video on YouTube
Colors
The above GOST does not impose any special requirements for the coloring of external insulation; 10 color options are allowed: white, black, gray, etc.
As for the color of the core insulation, it must correspond to the table below.
The color chart for insulation is live depending on their purpose and quantity:
| Number of cores | Accepted color standard | |
| there is a grounding conductor | No grounding conductor | |
| 2 | brown, blue | |
| 3 | yellow-green, brown, blue | black, brown and blue |
| 4 | yellow-green, black, brown, blue | blue, black, brown, black or brown |
| 5 | yellow-green, blue, black, brown and black or brown | blue, black, brown, black or brown, black or brown |
The purpose depending on the color of the insulation is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Colors according to GOST for neutral, protective and phase conductors
Please note that sometimes the insulation of the phase conductor is also white, which is acceptable according to the international standard.
Having finished with the design features and color designation, let's move on to the description of the main parameters.
Decoding
The abbreviation PVS 3x1.5 stands for as follows:
- P – wire,
- B – polyvinyl chloride insulating coating,
- C – connecting,
- 3 – number of cores,
- 1.5 – core cross-section, mm².
Also in the marking of this product, after the given letter designation, the number of cores and the cross-sectional area of each of them are indicated, separated by a dash.
Service life of PVS wire
The service life should be indicated on the cable label when purchasing the cable. On average, the service life of such a carrier is stated to be up to 5 years, but in fact, under the right operating conditions in a normal environment, the cable can operate smoothly for more than 10 years. If the environment in which the wire is used is aggressive or humid (hot), then the service life will naturally be reduced.
Having studied the description of PVS cable, what it is, what types it comes in and what technical and operational characteristics it has, it is clear why it is used not only by electricians, but also by a huge number of people around the world to solve various problems.
Wire or cable
The scope of application of this type of electrical product overlaps with areas in which similar cables are used. Therefore, the question may arise - is it a wire or is it a cable, and if the areas of application and technical capabilities are related, then how do a wire and a cable differ?
From a technical point of view, it is still a wire. Even the labeling (discussed in the article below) indicates this. To match the cable's rank, the PVS does not have the same technical characteristics.
A cable is, first of all, a rather complex composite system of several conductors, each of which has its own insulation, supplemented (in various versions) with intermediate insulating layers, armor, one or more layers of protective sheaths, and so on. The design of the wire is much simpler - one or several cores in individual insulation, a common sheath that protects from external influences and at the same time serves as an additional insulator. All.
Wires, including PVS wire, are more flexible and lighter than (on average) cables. Therefore, they are more convenient for indoor wiring, but are never used for transmitting electricity over long distances.
Can PVS wire be used outdoors?
Flexible wire PVA (GOST 7399-97) is equipped with polyvinyl chloride insulation and consists of copper cores. It is intended for connecting to an electrical network with a voltage of up to 380/660 V household electrical appliances of various types and devices of similar applications (refrigerators, washing machines, microclimate devices). Including in small mechanization tools for gardening - in situations where the wire is subject to chafing and moisture.
There are no prohibitions on outdoor use, but it is worth considering that the wire has a multi-wire core, which is more susceptible to corrosion, unlike a monolith. Also, the PVA wire quickly picks up moisture, which remains inside.
Description of properties and decoding of PVA
PVA wires are used not only for connecting household appliances to a voltage of 220 V. Some varieties can be used to transmit voltages up to 660 V. The service life of the wire can also range from 2 to 10 years. It all depends on the operating conditions and the quality of the insulation material. The abbreviation for the name of the wire PVS means:
- “P” is a conductor.
- “B” - polyvinyl chloride insulation.
- “C” - “network”.
This abbreviation also indicates the method of packaging conductive wires into a single cylindrical PVC bag.
One of the purposes of PVA wire is the ability to be used outdoors. Therefore, the permissible operating temperature range for it is from -30° below zero to +45° above zero. The permissible heating temperature of the PVA wire is +80°, after which its shell begins to melt and collapse, which can lead to a short circuit. The PVS cable is considered a flexible conductor, but it has a bending strength of up to 50,000 in one section.
This is interesting: How to turn off the light in an apartment through a panel: this is useful to know
Features of installation of PVA for laying in the ground and outside
The first thing you should pay attention to is that PVA wire is not intended for underground installation. If this is absolutely necessary, then the product should ideally be hidden inside a double-walled pipe. When laying cables outdoors, it is necessary to use corrugated pipes attached to walls and other surfaces of stationary objects. In this case, grounding must be carried out.
If you need to create an overhead power line using a PVA wire, then choose a cable exclusively with copper conductors. In this case, the distance between the beginning and end of the route should be minimal. Hidden wiring from PVC cable is unacceptable (it cannot be hidden under plaster).
Despite the fact that the cable has a short service life (for electrical wiring in a house, six years is really not enough), it can be used when laying under a screed. This option is appropriate if you want to save money on purchasing a higher quality and more durable wire. Thanks to a set of unique properties and protection from dust and moisture, PVA can be used in rooms with high humidity levels.
Installation features
They are the same as those of other copper stranded conductors. When connecting to plugs, automatic machines or other devices, the insulation is removed from the ends of the wire, the wires are tinned or crimped with special lugs.
Tips and crimping tools
If you have the necessary tools, the crimping technology is quite simple, the algorithm of actions is as follows:
- A layer of external insulation will be removed (approximately 12-15 mm).
- The ends of the conductors are also freed from the insulating sheath at a distance of 10-13 mm from the edge.
- A ferrule is put on the end of the wire and crimped with press pliers (you can see what they look like above).
The procedure can be significantly speeded up if you use special pliers to remove the insulation.
With the help of these tools, the crimping process is done in a matter of minutes, quickly and in accordance with the standards. Just in case, we remind you that the PUE does not know what twisting is.
Advantages and disadvantages of PVA
The PVS cable is inconvenient when installing hidden wiring, as it has a round shape
The main advantage is the relatively light weight, softness and flexibility of the cord. This makes it possible to install in complex systems, structures with a steep transition radius, a large number of bends and turns.
Can be used in electrical networks of 220 and 380 volts. The wire has a standard fire resistance class. The insulation material does not ignite from an external flame and does not support combustion. It is not recommended to use it for hidden installation, since its service life is no more than 6 years. Having a round cross-section, it is inconvenient for installation under plaster.
PVA has found wide application and is in great demand among buyers. However, for electrical wiring it is better to choose the cable VVG, VVGng, or another analogue that is most suitable for this purpose.
Cable characteristics
The key characteristic of PVA is the immediate diameter of the current-carrying cores (conductors) and their number. Copper conductors. They can be solid or can be represented by individual twisted wires.
Each conductor has its own color. Their decoding means:
- White is usually the color of the outer insulating sheath.
- Red, brown, black are the colors used to paint the insulating sheath under voltage.
- Blue represents the neutral wire.
- A green conductor with this is used for grounding.
Full cable marking is carried out in accordance with GOST and looks like this: ПВС Х*ХХ. Explanation of this abbreviation:
- X is the number of conductors,
- * - means a separating sign,
- XX is the diameter of the conductor.
PVS cable compared to VVG
In terms of technical and operational characteristics, VVG is superior to PVA wire, however, these models have different purposes.
When organizing electrical wiring in a house, apartment, or industrial facilities, it is best to use a VVG cable, since this is its main purpose.
PVA is used where VVG is inappropriate and can spoil the overall picture. Or in any other situations when it is inconvenient to operate the VVG cable due to its higher rigidity. For example, it would be difficult to imagine a VVG used to switch a microwave oven, iron or hair dryer. It looks ridiculous, extremely irrational, so in this case there is no alternative to PVA.
VVG also cannot be used when arranging temporary street lighting, constructing extension cords for connecting a lawn mower, cords for connecting boilers and expansion tanks. Thus, it is inappropriate to compare VVG and PVS in terms of technical parameters, since these conductors are designed to solve completely different problems.
Insulation material: description
The vinyl-sheathed connecting wire owes its name to the material used to insulate live parts—polyvinyl chloride resin. It does not burn in air, is frost-resistant and invulnerable to acids, alkalis, solvents and mineral oils.
All kinds of chemical elements: talc, calcium carbonate and kaolin, plasticizers and stabilizers are part of the plastic and improve its performance characteristics.
Dyes allow you to obtain insulation of different colors. PVC insulation is environmentally friendly and does not harm the environment. It is the main advantage of the cable, as it is made of fire-resistant material.
How to choose PVS wire
The first thing you should pay attention to when choosing any electrical cable or wire is the number and cross-section of cores, selected in accordance with operating conditions. You need to select a PVA depending on the power of the electrical appliances that will be switched to the network through it. The presence or absence of a grounding conductor, which allows connecting the electrical appliance and the ground loop, is important. For example, when laying an industrial network, you need to use a PVA with four cores. At least, this is how it is stated in the rules of the PUE.
When inspecting the product, make sure that there are no defects in the insulation and that it is of proper quality. Test it for strength, since the insulation should not be damaged or torn by touch. Otherwise, the cable will not last long and will also pose a danger.
Each manufacturer must submit a sample of their wire. While studying it, make sure that the individual core is twisted correctly. Poor quality can be judged by the presence of stains, breaks, different colors and other defects that are visible to your eye. On the marking you can see not only the number of cores and their cross-sectional area, but also find out about the percentage of copper content.
To ensure safe and energy-efficient operation of electrical equipment, it is important to select the appropriate PVS wire. If you encounter any difficulties in the process of choosing a product, then seek help from professional installers or store consultants. However, you should not believe every word of the latter. Ideally, you should study the basic information regarding PVA and, armed with knowledge, go shopping.
All about PVS wire in GOST 7399-97
Domestic manufacturers of PVS wire working for the Russian and CIS markets strive to comply with the requirements of GOST 7399-97, since it has interstate status. In addition, this facilitates export operations to non-CIS countries, since the content of the document is synchronized with the relevant parts of the international standards IEC 60227-1-93 (97) and IEC 60245-1-94 (97).
Sections of GOST 7399-97 contain all the most important information about the range, mechanical and electrical characteristics of PVA wire, as well as safety requirements, a list of tests, etc.
Marking example:
PVA 2x0.75+1x0.75 GOST 7399-97
The wire of the PVA brand is designated here; it has two main conductors with a cross-section of 0.75 mm2 and one grounding conductor with a cross-section of 0.75 mm2.