In everyday life, after repeated copying of an erroneous interpretation, the concepts of “single-core” and “multi-core” wires were established in the meaning of a single- and multi-wire conductor. In fact, the number of cores conditionally determines the number of functional wires enclosed under a common shell. The most famous example is a multi-core power cable with 5 cores: 3 phase, neutral and ground (L1, L2, L3, N, PE). More detailed characteristics and areas of application of the product are presented below.
Heating cable requirements
If you rely on state standards, it is important not to forget about the following general requirements for a heating cable:
- If a heated floor system is to be used in an apartment, then it should be an additional, and not the main, source of heating.
- In wooden houses with a wooden base, you need to install a wire whose power will not exceed 2 kW.
- To heat ramps or stairs located outside the premises, a wire with a rated power of 4 kW is used.
- To install one circuit, it is necessary to use a continuous piece of cable. It is advisable to install one circuit in one room if its area does not exceed 25 m2.
- The transition of a wire from one room to another is not allowed. In the transition area it may simply break.
- To install the product, you must use only those spare parts and accessories that are sold with it.
Materials for the production of stranded wires
Modern production of cable and wire products considers copper and aluminum as the main materials.
In some situations, an alloy of copper and aluminum is used, although the highest quality is considered to be stranded copper wires, which have proven their strength, reliability and increased functionality in relation to other materials.
The main advantages of multi-core copper cables:
- Excellent conductivity even after forming a film on the surface;
- Service life up to 50 years;
- Mechanical strength;
- Easy to install.
Chinese manufacturers, trying to save money, use a steel core, partially covering it with copper. This kind of wire is fragile, short-lived and practically impossible to solder.
Aluminum stranded wires were widespread during the Soviet era, which is explained by the low cost of the material, but aluminum lines carried the following negative features:
- Difficulty of installation;
- Service life no more than 25 years (which is 2 times lower than the service life of copper wires);
- Fragility of the material, fragility of wires under mechanical stress;
- Oxidation of aluminum, which led to an increase in resistance and a decrease in the useful cross-section of wires;
- Low electrical conductivity.
Installation methods
The heating cable must ultimately be covered on all sides with mortar/tile adhesive; this can be achieved in three ways:
Fill
. The most correct way in my opinion. It consists of pouring a 1-2 cm mini-screed over the mounted cable. The resulting screed will be suitable for any floor covering. To implement this option, when pouring the main screed, you should provide a couple of centimeters of height in places where there will be a warm floor. For work, mixtures are used that allow such thin layers to be poured. If the screed is initially poured at one level and raising the floor level is unacceptable, then this method is not suitable.
Glue layer
. When the tiles are laid, and in addition to everything else, it is permissible to raise the level of the subfloor by 1-2 cm (do not forget, the tiles themselves will add at least 1 cm), the tiles are placed on top of the cable on a thick layer of glue. This option should be considered last, because there will be a significant difference at the border of the warm zone.
Grilling
. The most difficult and tedious method, however, when raising the screed level is unacceptable, is the most correct. First you need to mark the lines where the heating cable will go. You also need to take into account the groove for the corrugation with a temperature sensor and the coupling with the cold connecting cable. After marking, you need to attach some kind of thread/rope to the lines to check the length of the grooves. You need to be sure that the entire cable will fit into the future groove, otherwise you need to change the markings.
After gating, the dust is carefully removed and the surface is primed. The wire is laid in a groove; the depth of the groove should allow 3-5 mm of caulking solution to be applied over the cable.
The temperature sensor in the corrugation is also mounted in the groove; the corrugation must be plugged at the end (wrap it with electrical tape). The end of the corrugation should be placed between the heating conductors, not far from the edge of the heating zone (but not on the edge). The optimal distance of the temperature sensor is 30-50 cm from the edge, deep into the warm area.
When the wire is laid, the grooves are sealed with tile adhesive or a self-leveling floor mixture. If you plan to lay linoleum, it would be a good idea to apply a finishing layer of 1-2 mm of self-leveling floor.
Floors should be checked or used no earlier than a month after completion of all wet processes with the floor (pouring, laying tiles). Switching on earlier will not damage the cable itself, but may cause the solution/adhesive to crack.
Conclusion
- Heating cable is recommended for use with heated floors. The most preferred method of application is a direct heating system or "thin floor".
- Among all the variety of heating cables, it is best in terms of price-quality ratio to use a two-core resistive cable.
- The selection of the required cable with the required power density, its length and laying pitch are obtained as a result of calculations.
- Changing the length of a resistive cable section (except for a zonal cable) is unacceptable.
Types of flexible cable
Flexible multi-core cable is available under various brands with different properties. The most popular ones can be identified:
KGVV is a product that can withstand temperatures from minus 50 to plus 50 degrees due to reliable insulation, which includes PVC, providing a service life of about 25 years. It is used to supply power to power plants, for example, excavators, electric hoists, etc. Designed for a voltage of about 1000-1500 Volts;
Flexible cable from the KGVV series
- RKGM is intended for power lines and mobile equipment, designed for temperatures from minus 60 to plus 180 degrees, resistant to high humidity due to reliable insulation made of silicon and rubber;
- VVG is intended for electrical wiring in residential and non-residential premises; the insulation contains polyvinyl chloride, which gives additional strength to the entire structure;
- KOG is designed for supplying power to welding machines of various powers; operation with high humidity is possible, as well as both indoors and outdoors;
- FRB is designed for installation directly in ground trenches, has good insulating properties due to armor, but at the same time its flexibility is not very high;
Flexible cable from the VRB series
SHIF has silicone insulation and is designed to operate in extremely high temperatures up to 220 degrees, and is resistant to various alkaline environments.
Due to its varieties, flexible cable requires various installations: both in specialized boxes and cable channels, and in earthen trenches. It can also be an air or even open gasket. The type of installation depends on the individual characteristics of the cable wiring, temperature conditions, crowds of people and operating conditions. Based on the required conditions of use, the necessary products are selected that meet the required technical characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages
When the functional cores are assembled under a single sheath, such a wire is more convenient to lay, especially in hard-to-reach trays and cable channels. Its shell protects all the cores at the same time, i.e. there is a clear saving in labor costs and in the consumption of insulation material. But there is one scourge of all multi-core wires - this is capillarity, i.e. drawing in moisture from the cut end through the cavities between the insulated conductors. For this purpose, the cavities are filled with rubber or similar non-flammable fillers.
Stranded and single-core cables
Single-core soft copper wires, for example, are widely used in the automotive industry, where the role of the “minus” is played by the car body itself, when distributing electrical wiring in rooms, assembling lighting panels and distribution cabinets, and acoustics.
Single-core copper wires are indispensable in electrical wiring to sockets and lighting fixtures. Every electrician is familiar with the procedure when, in the absence of a standard wire, he is forced to unravel a multi-core cable with a knife, removing individual insulated cores from there to perform the tasks of wiring groups of sockets.
You may be interested in Description of PRKA wire
Important! The insulation and copper conductor of the solid wire must be able to withstand repeated bending when the outlet module is seated in place.
What is a wire or cable made of?
Wire and cable within the scope of this article do not have significant differences, so we will omit them and equate these concepts. They consist of a conductor core, bare or covered with one or two layers of insulation. The insulation is made of dielectric material, for example, PVC, rubber, polyethylene, fluoroplastic. The cores are made of aluminum or copper. Also, according to the structure of the veins, there are:
- Single-wire - rigid. They consist of a solid cylindrical or shaped (sector) conductor, sometimes they are called monolithic.
- Multi-wire - soft. Consist of 7 or more thin wires. The exact number of wires is determined in the specifications for the product and in GOST 22483-2012, it depends on the cross-sectional area of the TPG and its flexibility class.
Interesting! As we have already said, the correct names for the types of cores are single-wire and stranded, but people often call them single-core and stranded. Therefore, sometimes confusion arises when talking about a stranded wire: are we talking about the number of conductive wires (more than one), or the number of wires in one core? For the purposes of this article, treat these terms as synonyms.
Connection of flexible and rigid wires
Connection of flexible and rigid wires
Typically, conductors of the same type are connected. But sometimes a connection between a flexible and a rigid wire is required, which is carried out in compliance with some nuances.
First, cut the cable so that its end is tapered. The rigid wire needs to be melted and a loop made at its end. A thin wire is passed through the loop made and wrapped around the rigid cable. The resulting connection must be treated with solder and reliably insulated. A similar method is suitable for aluminum conductors.
Characteristics of single-core wire
Single-core cable is most often used as additional heating. It is installed for underfloor heating in small rooms, in the kitchen, bathroom or toilet. The heating intensity is not very high. If there is a need to provide heating in a large room, then it is necessary to provide a long cable and lay it in frequent turns on the floor.
- A single-core cable is a system based on one rod, a core. Electric current passes through it. When heated, it acts as a heating device. The core is made of brass, galvanized steel or chrome.
- The rod is wrapped in insulating material. It can be fiberglass, fluoroplastic, polyvinyl chloride shell. Use 3-4 insulating layers.
- A reflective screen is placed on the insulation. It is designed to block electromagnetic radiation. Most often a thin layer of aluminum is used.
- The outer sheath of the cable is a protective film made of fiberglass or cross-linked polyethylene. They use heat-resistant, water-repellent material that protects the cable from external influences, including mechanical ones.
It is recommended to use the “warm floor” cable system under hard floor cladding. Even though the heater will be under the screed, it can be very vulnerable. It is not recommended to use linoleum or carpet as a finishing coating. An additional hard layer will be required to reliably protect the cable. Fiberboard sheets or plywood are used as a protective layer. Cable heating is widely used in Moscow, in apartments and country houses.
If you place furniture on the floor without first protecting the cable, “wire locking” may occur. The bottom surface of a cabinet or sofa will contribute to overheating of individual sections of the cable. The system will automatically sense the increased load and may shut down.
To control this process, it is recommended to install several temperature sensors in the floor covering. This will allow us to determine in which area the temperature began to decrease. Furniture is installed on legs. It is recommended to maintain a distance of 5 cm between the bottom panel of the cabinet and the floor.
Wires - device, composition, flexibility
Conductors for installation of household electrical wiring are a copper or aluminum conductor covered with an insulating layer based on PVC, polyethylene, rubber or fluoroplastic. Moreover, according to their structure, they are divided into 2 main types:
- Single-core . These are, as a rule, rigid conductors consisting of a monolithic cylindrical or sector rod. One of the most important characteristics of electrical conductors is bending resistance. This category is characterized by the minimum value of this indicator. For example, copper products can withstand about 70-90 cycles, while aluminum analogues are not able to withstand more than 10 kinks.
- Stranded . They are a twist of a large number of thin metal hairs, the number of which can vary widely - from 7 to several hundred. Multicore wires are made according to the principle of a metal cable. Moreover, the thinner the wires included in its composition, the higher the bending resistance. For example, for copper specimens belonging to flexibility class 5, its value can reach 30 thousand cycles.
A multi-core cable is a twisting of conductors with a smaller cross-section Source habb.md
Recommendation! Using stranded wires, it is convenient to connect terminals in sockets, as well as sockets in lamps - where single-wire analogues often break. The softness and flexibility of such conductors makes it possible to use them to connect to the network various types of electrical appliances that are characterized by an unstable position during operation, such as a vibrating washing machine, a constantly moving electric stove, a drill.
Flexibility classes and their differences
Whether a conductor belongs to a particular flexibility class shows how much it can bend during operation without irreversible changes in the structure. According to this indicator, wires are graded into 6 categories. At the same time, class 1 means the highest rigidity, class 6, on the contrary, the greatest flexibility.
The flexibility class and conductor structure, as a rule, have a direct relationship. The higher the flexibility index, the greater the number of cores and vice versa.
The flexibility of the wire depends on the type and cross-sectional area Source strojdvor.ru
A good example is two wires with a cross section of 1 mm2 of the 3rd and 5th flexibility classes. The first is made of wires with a diameter of no more than 0.43 mm, the second - no more than 0.21 mm. Thus, the number of cores in a 5th class specimen will be greater than in a 3rd class analogue.
Cable: types and scope of application.
One or more conductors (cores) that have personal insulation and are collected in a common hermetic sheath are called a cable. Both the inner sheath of each core and the overall sheath can be made of various materials: rubber, PVC, aluminum or lead. If operating conditions provide for the possibility of external influences, then the upper shell can be additionally armored with a steel coating.
A cable with one core is called single-core and has a rather limited scope of application. Multicore (2, 3, 4 cores) copper flexible cable is much more popular. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages; they differ in the degree of flexibility, cross-section, weight and price. The cross-section of the cable corresponds to the current it can carry.
Solid (single-core) copper cable (wire) is used in a situation where it will not move after installation. For example, in electric motors or internal electrical wiring. If you need to power equipment with a large range of motion (for example, a gantry crane), if the wiring device requires a large number of bends, then it is optimal to use a flexible stranded copper cable, since it is softer. This is especially true for wires with a large cross-section of cores. As a rule, flexible cables are made from pure or tinned copper wire. It all depends on the required flexibility parameters so that the cable does not break when bent (flexibility class must be at least 5).
The lower price segment is occupied by single-core wires without protection. The more cores in the cable and the stronger its protection (armor), the more expensive the cable. The weight also depends on the number of cores (from 1 to 37 with sections from 0.75 to 800 mm2) and braid. The cost of copper single-core cables is 3-4 times higher than aluminum cables.
There are classes of flexible copper cables based on the specific use. For example, power has found its application in the creation of cable lines for the transmission and distribution of electricity in power electrical installations, lighting networks, and as wiring in residential and industrial buildings. It is characterized by the presence of several conductors of the same cross-section, with the exception of the grounding conductor, which may have a smaller cross-section. A copper multicore cable must have stable mechanical, electrical and thermal characteristics, since the operating parameters of the power cable must remain unchanged when operating in any conditions. Conventionally, they are divided into low voltage (up to 1 kV) and high voltage (up to 30 kV) cables, they have different external insulation materials (PVC, halogen-free, cross-linked polyethylene), they differ in the presence of a screen, the type of cores, and the nature of their twisting.
Copper cables come in different types:
- Control flexible cables are widely used in electrical work, automated transportation systems, security systems and control automation.
- Fire-resistant and halogen-free cables meet the requirements for increased fire resistance and non-combustibility to maintain functionality in the event of a fire and for fire alarm systems.
- Control cables offer increased flexibility for use in robots, conveyors and conveyor belts.
- Data cables with signal protection from external interference.
- Cables for frequency converters and servos.
- Cables for data transmission for office equipment, recording studios, external communication lines, for medical equipment. They have design features (twisted cores in pairs, additional screens).
- Special heat-resistant cables with a silicone sheath that can withstand temperatures up to 800 degrees (refrigeration or heating installations, steel production, shipbuilding and aviation industries, cement, glass industries, saunas and solariums).
- Crane cables, which are necessary to ensure the operation of lifting mechanisms (cranes, hoists, elevators). They are highly resistant to mechanical stress, withstand torsional and tensile forces, and have a chemically resistant shell.
And many more - all-weather rubber cable, flat, compensation, coaxial (radio frequency), video cable, installation, telephone, BUS cable, cables with connectors, for alternative energy and media technologies, spiral and marine cables.
Difference in insulation quality
But still, in any comparison, the quality of insulation comes first. It plays an important role depending on the installation conditions.
Many cables can be placed in aggressive environments in an open form without any cable ducts or corrugated sleeves.
But the wires, not even in an active environment, but only under the influence of water (rain), temperature changes or direct rays of sunlight, will gradually fail. Not to mention other extraneous influences.
Except of course SIP. But unlike cables, it cannot be laid underground, even in a pipe or corrugation.
Hence there will be a difference in price, although it would seem that both types are similar in design (with double insulation). Therefore, wires are used in buildings, closed switchgear (closed switchgear), and not on the street.
Sometimes, armored grades are used to lay cables in the ground and provide additional protection. In addition to all the layers of insulation, they have a layer of aluminum or lead sheath over the cores.
Single core wires for household use
Coloring of wires PV 1
Since 2001, the use of aluminum conductors in residential buildings has been prohibited, so only copper products should be considered.
- PV-1 - monocore in PVC insulation. The marking indicates the type of product - wire, insulation - vinyl (polyvinyl chloride), flexibility class - 1. According to GOST R 53768–2010, the product is marked PuV - installation wire, insulation contains vinyl. In residential premises, the relevant core cross-section is from 0.5 mm2 to 6 mm2. Models of this size are produced in yellow-green insulation, which is explained by the widespread use of PV-1 for PE grounding conductors. The wire is suitable for stationary single installation. The bending radius does not exceed 10 outer diameters. The basic version is versatile and inexpensive.
- PV-3 consists of an insulated row of twisted copper threads. The new marking is PuGV, where G is flexible. It differs from PV-1 in bending radius - 5+ diameters.
Theoretically, wires with one core are suitable for installing electrical lighting circuits and connecting various installations in residential and non-residential premises. It is more convenient to arrange power wiring with multi-core cables, and assign separate grounding or neutral to single-core cables.
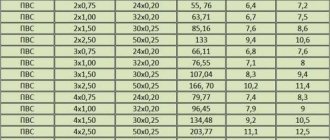
Rated current tables
If you need to find out how much load can be passed through conductors of different cross-sections, depending on the laying conditions, voltage and material of the conductors, use the tables of rated currents for cables and wires:
CL (Cu) rubber and PVC insulationCL (Al) rubber and PVC insulationCL flexible with rubber and PVC insulationCL (Cu) with paper insulation in the groundCL (Cu) with paper insulation in the airCL (Al) with paper insulation in the groundCL (Al) with paper isolation in the air
The average service life of a double-insulated cable is 30 years. Single wires - less than 15 years.
How is power calculated?
In order not to miscalculate the power, it is first determined whether the warm floor will be the main source of heating or an auxiliary one.
On a note. When performing calculations assuming an auxiliary source, you should take into account the power of the main heat source.
An approximate calculation for a two-room apartment, where, taking into account the correction coefficients for the heat transfer resistance of surfaces, the total heat consumption is 6 kW.
The logic is as follows:
- to heat 10 sq.m of living space, about 1 kW of thermal energy will be needed;
- the main heating system covers 90 percent of the area;
- underfloor heating as an auxiliary heating element requires compensation of 10 percent;
- taking into account 6 kW of total consumption, (10x6)/100 = 0.6 kW.
This calculation is correct if heated floors are installed in all rooms of the apartment.
Sometimes average values are used for calculations
- for kitchens and living areas 110-150 watts per 1 sq.m;
- for bathrooms 140-150 watts per 1 sq.m.
When choosing which underfloor heating is better, two-core or single-core, you need to take into account the level of comfortable temperature. Twin-core models heat the most intensely. Adjusting the temperature level depends on the heating time of the floor. When there are no special requirements for the microclimate, you can choose single-core modifications.
Characteristics of flexible cable
The main purpose of the flexible cable is to supply electric current to high-power mobile devices (about 660 Volts), portable devices (electric generators, guns), as well as connecting power cables to networks with voltages of up to 1000 Volts or more. It is often used as a welding cable, in which case it requires a strictly straight arrangement. These products have been designed to withstand mechanical stress in the form of creases and kinks at various angles. Due to its flexibility, the multi-wire electrical cable got its name, and its service life has also been significantly increased. Perfectly suitable for work both indoors and outdoors, resistant to various climatic conditions, applicable in the process of large-scale construction work for pulling power lines.
A flexible cable is a stranded wire, where each conductor consists of a large number of fibers, which provide the required flexibility and durability of use. The number of cores can be varied, but most often there is grounding.
Multi-core flexible cable
The design of the cable system is as follows:
- Conductive copper conductors, consisting of small fibers, belonging to a certain class of flexibility;
- Each conductor is protected by a specialized synthetic film that prevents the cores from sticking to each other during installation and heating. Depending on the manufacturer, many people replace this film with specialized talc or powder;
- Each core has its own rubber insulation made of polyethylene terephthalate film, which can withstand various temperature fluctuations;
- A protective rubber sheath of the entire wire (made from rubber), giving the necessary flexibility and protecting against mechanical damage.
The marking of this type of material is on the protective upper rubber insulation, indicating the manufacturer, cable cross-section and number of cores, cable flexibility class (there are 7 classes from 1 to 7), in some cases the date and time of manufacture may be present, as well as the abbreviation “GK " In addition, each core has its own color scheme (brown, blue, black), and grounding, according to international standards, is distinguished by a greenish-yellowish tint.
Multi-core flexible cable
Manufacturers produce cables of both round and flat shapes. Current-carrying conductors are most often made from copper, but you can often find old-style products with an aluminum conductor. It is worth remembering that aluminum wiring, when compared to copper wiring, can withstand a lower electrical load with the same type of cross-section and number of cores.
Cable cross-section
The selection of wiring for a wooden house or apartment is made from those available with copper conductors, with a minimum cross-section of 1.5 mm². It characterizes throughput. For such elements, 1 mm² transmits 8-10 A, and for aluminum ones - only 5 A. The calculation of electrical wiring lines in a private house or other building is carried out separately according to the load, after which the cable cross-section is selected.
The table shows the cross-sections used for home electrical wiring (VVGng-LS cable).
| Purpose | Section, mm² | Maximum power, kW | Recommended rating of the protective circuit breaker, A |
| Lighting | 3x1.5 | 4,1 | 10 |
| Sockets | 3x2.5 | 5,9 | 16 |
| For electric stove or hob | 3x6 | 10,1 | 32 |
Deviations regarding single-core. Single-core and stranded wire, what is the difference
Quite often you can hear people trying to compare these two types of cable products and find out which wires are better, multi-core or single-core? Let us say right away that such a formulation of the question is generally incorrect and shows the incompetence of the questioner. After all, you can also ask: “Which is better, a shovel or a hammer?”, and the answer depends not on the objects, but on the type of activity that will be carried out with the help of a certain tool.
The choice of conductor type in a cable or wire equally depends on 1) location and 2) operating conditions. Therefore, instead of breaking spears, it is better to “get to know” the candidates for selection, find out their features and differences, and only then decide which one is better.
What is single-core and what is stranded wire
In the literal sense of the word, the expression "single-core and stranded" does not apply to this issue, since the word "core" refers to the total number of conductors in a cable or wire, and not to the structure of an individual core. It would be correct to say single-wire or multi-wire. But, for some reason, the expression “multi-core” has stuck. To ensure the truthfulness of the information, we will use the correct term, but we will also not condemn those who have become accustomed to another option, it is not our business.
Single-wire wire - having only one core as a current-carrying element, with a cross-section from the standard series (0.5-1-1.5-2.5-4, etc. mm sq.)
A stranded wire - as a conductive element - is several conductors intertwined with each other, having a total cross-section in the same standard values. It is allowed to weave a non-conductive thread (usually resembling nylon) into the conductive cores to further increase the elasticity of the entire cable.
Features of each of the two types of wires
Both a flexible blade of grass and a rigid tree can withstand a hurricane, so we must understand that the same properties of wires (under certain circumstances and installation requirements) can also become both a disadvantage and an advantage. And, instead of promoting debates about “best,” we will present the full picture, pointing out the features of each type of vein that help in making the right choice for specific situations.
1. Single-wire core.
Bottom line: no matter what “home-grown” electricians say, in most household electrical systems it is more efficient and competent to use wires with single-wire cores. In most, but not all, let's look at the other side of the coin.
2. Stranded core.
Application areas for single- and multi-wire wires
So a reasonable conclusion suggests itself: each of them is good if it is in its place. The properties indicated above show, without controversy or hesitation, where it is more appropriate to use each type of wire.
Fixed wiring of power cables in houses, apartments and industrial facilities with medium and large cross-sections of cable cores is preferably carried out using single-wire conductors (unless there are special requirements). On electrified railways, all contact wires have exactly this design, serving reliably and for a long time.
Electrical cables can be divided into single-core and multi-core, they are also called hard and soft, or solid and flexible. Whatever you call them, the former have one vein, and the latter have several veins. Single and multi-core
Rules for connecting a stranded conductor
Very often, when laying a multi-core cable or wire, it becomes necessary to connect it to such common elements of the electrical circuit as a circuit breaker, socket, meter, plug, lamp socket, and so on. Most often, copper wires are used, especially in everyday life. The main task is to ensure reliable contact with the clamping bolted connection of these devices and devices, and therefore to make the stranded wire as monolithic and homogeneous as possible. You can perform this procedure in several ways:
- Twist all the thin strands into a tight bundle and, if the cross-section allows, bend it in the opposite direction. This can be done with pliers or by hand, it all depends on the cross-section of the conductor. This method is the simplest and is used in modern wiring only in emergency cases, but it also has a right to exist. It will not be possible to perform this procedure with a large cross-section cable in this way, so it is more suitable for supplying voltage to a plug, socket, or socket of a low-power lighting fixture.
- By tinning the conductor. This method is more effective than the previous one and will ensure reliable contact. Its main disadvantage is that you do not always have a soldering iron at hand, and even electricity for its operation. Tinning can be done either with a straight conductor or with a terminal block bent into a ring along the diameter of the bolt, but before doing this, again, it is necessary to tightly twist all the thin wires. This method can be applied in all cases of connection to electrical appliances, to a machine, socket, etc., if the cross-section allows it.
- Tip crimping. The tips allow you to achieve reliable and durable contact without soldering. There are two types of tips: bolt-on and simply sleeved. Depending on the element to be connected, you need to select the appropriate type and appropriate cross-section. With a tip and sleeves you can connect any type of cable, of any cross-section, both stranded and single-core, but for this you will need a special tool that will need to be purchased before carrying out installation work, especially at a professional level. Connecting a stranded wire in this way in the panel, to the terminal block, to the meter not only looks aesthetically pleasing and correct, but also reduces the likelihood of heating at the connection points. The photo below shows NShVI type lugs on stranded wires.
Although tinning is a good method, in practice the cores are often terminated with lugs; this is faster, easier and often more reliable than other methods. However, do not crimp the tips with pliers - the core will simply jump out of them and you will not get a good connection. To do this, it is better to buy crimping pliers with square dies; you can find them for about 1000 rubles.
Methods for connecting different wires to each other
Connecting wires using the twisting method
This method can be considered the easiest way to fasten wires together. When performing this method, you can use any variation of wire twisting. The first option for fastening 2 stranded wires is performed in the form of parallel twisting. It is distinguished by the reliability of the unit, but does not withstand shaking and strong impact on the unit.
The use of parallel twisting provides electrical communication between several wires at once. By analogy, the bonding of aluminum single-core and stranded wires is carried out.
This type of twisting is often used to attach another wire to the electrical wiring. Before this, the required section of the wiring is freed from insulation and another wire is simply screwed on.
The second option for fastening several wires is to sequentially wind a separate thin wire onto the previous one. This option can connect no more than 2 wires together.
It is also possible to fasten the wires together using a twisting bandage. Its essence is as follows: the wires that need to be connected are laid along each other. Then they are wrapped with another wire over the cleaned area.
To ensure good contact, the bandage must be wound as carefully as possible. This method is used when connecting several wires.
Before starting work, it is imperative to clean the necessary areas from the insulating coating and oxidation products. When working, it is better to use pliers - this will ensure that the wires are twisted tightly.
Connection using a soldering iron
Thanks to the soldering iron you can get the most effective connection. However, for this you need to have a soldering iron, the necessary substances for the soldering process and experience with a soldering iron. More often a substance such as rosin is used. It is more common, but has a significant drawback: after rosin, residues appear on the connection, which are difficult to remove.
Initially, the connected wires must be carefully prepared: cleaned of dirt and oxidation products. Heat the soldering iron high enough and dip it into a jar of rosin. Then we lower the solder onto the tip of the soldering iron and carefully transfer it to the stripped wire.
Upon completion of soldering, the wires are fastened using one of the above methods. It is imperative to clean unnecessary deposits from the soldering area on the twisted area. It is better to twist the wires using pliers. The resulting assembly is heated again with a soldering iron to increase the reliability of the connection.
Fastening wires using terminals
Before we figure out how stranded wires are connected using terminals, let’s look at what terminals are made from. A terminal is a special clamp for fastening wires. They are produced in various variations. The terminals provide reliability at the connection point and excellent conductivity of electrical current.
Most often they are made from brass. It is possible to use other materials in the manufacture of terminals, the main thing is that they do not interact with copper and aluminum wires. Brass terminals are used to secure connections between copper and aluminum wires.
In general, terminals are divided into:
- Clamp terminals. They hold the wires together thanks to a spring mechanism.
- Screw terminals. Fastening is done using a screw.
If we consider the specific situation of connecting copper and aluminum wires, then when using a terminal, they should be bent slightly.
When fastening thin plastic wires, it is possible to use special tips.
If you need to connect several wires to the terminal, they must be fastened together using one of the parallel twisting options. This will improve the conductivity of electricity and reduce the possibility of wires moving away from each other during operation.
In order to decide which wire is best to choose for wiring in a building, you should evaluate the load in the electrical network and foresee what electrical equipment will be connected to the room. The use of both single-core and stranded wires is common. The main thing is to ensure reliable and correct fastenings.
Types of wires
There are several types of cables depending on their purpose. Accordingly, their characteristics will differ significantly. This:
- Power cables.
- Wires.
- Cables for transmitting information.
- LED and electroluminescent.
- Special types.
To understand the purpose of each of them, it is necessary to study their main characteristics.
Power brands
Power cables include the most popular products such as VVG, KGVV and KOG. The first one is a flexible copper cable consisting of many cores. It is equipped with PVC insulation and is usually used for laying electrical wiring in various rooms. This product has proven itself in a variety of conditions, such as high humidity or explosive conditions. Due to its multi-core nature, VVG has increased flexibility, which allows it to be used in hard-to-reach places that require bending the wire.
KGVV is a control flexible multi-wire copper cable. It has models with an increased and high level of flexibility, capable of withstanding 100 flexion/extension cycles. Successfully used in control and power circuits.
The multi-core cable of special flexibility KOG has a rubber insulating coating; its cores belong to class 5 and are capable of withstanding 10-12 thousand bending cycles with a radius of up to 55 mm. Most often, this cable is used to connect welding machines - both automatic and semi-automatic. Not afraid of the influence of solar ultraviolet radiation and high humidity.
Mounting and transmitting information
Among the wires, the most common brands are PBPP (PUNP) and PBPPg (PUGNP). They are called installation, or in other words, installation.
BPP (PUNP) has a flat cross-section and includes two or three single-wire copper conductors with PVC insulation. Wires of this brand are used in the installation of lighting fixtures, as well as sockets and switches. The minimum bending radius is about ten wire diameters.
As a type of PUNP, there is a wire with cores made of aluminum wire - APUNP. Its flexibility is slightly less due to the characteristics of the material, but otherwise the characteristics do not differ from PUNP.
PBPPg (PUGNP) - flexible insulated stranded copper wire, distinguished by stranded conductors, and therefore flexibility, as evidenced by the letter G in the designation. The bending radius is at least 6. Other parameters are the same as the previous version. PUGNP exists only in a copper version.
Cables for information transmission include brands that are capable of transmitting not only electricity, but also energy information signals. These are all kinds of antennas - RG-59, RG-6, RG-58, as well as the RK 75 series; computer twisted pair cables, with the help of which computers are connected to each other and the Internet; wires for conducting a telephone line.
Decorative and special
As for LED and electroluminescent wires, they are used as power wires, and also perform decorative functions. There is also a practical side to the use of these wires - if damaged, a break will immediately be visible, since the LEDs in this place will stop lighting.
Copper multicore cables are used in many different areas of life and industry. They are used in private and apartment buildings, for laying lighting on ships, roads and in mines, with their help they connect furnaces in the food, chemical, steel and woodworking industries, are used in welding work and many other areas. In addition, these wires are used to transmit information signals and decorate premises, both external and internal. Copper cables have a wide temperature range - from -60 to +600 degrees Celsius.