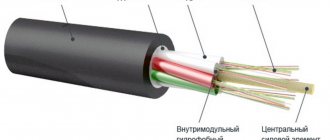
Connecting a house, transport facility or engineering structure to the power supply system involves performing a number of electrical installation works. Their list and execution parameters depend on the conditions for implementing the task, but almost always we are talking about a multi-stage project, including a wide range of operations. At the same time, there are standards for the technology of electrical installation work, which prescribe not only the rules for solving certain problems, but also safety requirements, as well as environmental protection.
Electrical Basics
The purpose of electrical installation production is to provide consumers with electricity. Through energy carrier channels, current is delivered to the point of its reception for further use for its intended purpose. At each stage of the movement of electric current from the station of its generation to the direct consumer, certain types of work of this kind can be carried out. For example, in the book “Technology of Electrical Installation Work” by V. M. Nesterenko, a wide coverage of transmission network infrastructure is proposed, taking into account the design of substations and high-voltage networks. In the most popular understanding, electrical installation is still associated with operations that are performed within the infrastructure of an electrical panel - apartment/house. On this circuit, in particular, the most common operations for laying electrical wiring, installing sockets, electrical appliances, protective devices, etc. are performed.
With a wider scope of electrical installation work, it is necessary to consider the measures that are used on the lines of the main networks with transformers, energy conversion and distribution units. As part of the general technology of electrical installation work, operations for connecting networks, installing substations and putting equipment into operation are united by a regulatory framework, however, in each case, the nature of the activities performed has its own nuances in terms of execution rules. Thus, the installation of a main power system unit involves the implementation of construction work with the connection of special equipment and the construction of a foundation for functional units. On the contrary, installation of the simplest lighting device requires only a few minutes and basic skills in handling power tools.
Lighting system
Installation of lighting fixtures is the stage that completes the electrical installation.
The lighting system is an important part of electrical installation.
The lamps will be equipped with sockets and conductors, their number and cross-section will be determined by the power of the bulbs and the type of light circuit.
The conductors of the lamp are connected to the terminals of the socket, the one into which the light bulbs are screwed.
Connecting wires to socket terminals requires a lot of attention to ensure that the wire is correctly connected to the phase and that all elements are insulated.
For commissioning, we will connect the lighting devices to the light circuit.
This operation is performed by joining or twisting if the installation is based on copper, or using special clamps if it is made of aluminum.
Finally, the light bulbs are installed by screwing them correctly into the socket, having first checked their filament.
General technology of electrical installation work
Regardless of the target site at which installation is being carried out and the subject of installation, work is carried out on the basis of a prepared design solution. Even within the framework of minor operations, a conscientious performer uses a diagram, instructions or general regulatory documentation in his work, which allows him to ensure the proper quality of the result. The choice of electrical installation technology is also determined during the creation of the project. The chief engineer, based on the principles of economic feasibility, energy efficiency and safety, determines the most appropriate way to solve the problem with optimal parameters. At this stage, in particular, questions about the method of laying the cable, the equipment used, the number of workers, etc. can be resolved.
The technical part of the work is directly related to installation and, in turn, is divided into two stages. At the first stage, the technology for performing electrical installation work involves installing fasteners and load-bearing devices, which allow, in principle, to solve the problem. For example, in the case of large-format energy systems, this stage will be expressed in the construction of the foundation and installation of the frame for the technical room. When installing the electrical panel, at the same stage the load-bearing elements will be fastened to the wall, and the installation of the socket will require screwing the fixing devices into the prepared niche.
The second stage of installation comes down to the direct installation/placement of a power system element or consuming equipment on a specific section of the supply line, as well as its connection. Again, the nature of the implementation of this stage will depend on the design technology for the work. Electrical installation work in relation to transformer substations, for example, is organized in order to fill the working units of the power system with functional equipment. To optimize installation and connection processes, manufacturers of electrical installation structures have long been developing special modules for integrating electrical devices for the corresponding purpose in a lightweight format. These can be cells and sections for input switches, feeders, distribution devices, elements of the converter unit, relay protection equipment, etc. To ensure convenient connection, electrical collector groups, splitters, blocks and other components can be used, which provide compact devices for fixing and connecting wires.
Below is an approximate list of basic installation operations by type of electrical installation work, [p.19]
Types of electrical installation work [p.20]
Along with installation sections that carry out the entire range of electrical installation work for one or a group of Objects, in some cases it is advisable to create specialized sections that carry out only certain types of electrical installation work, for example, installation of lighting in residential buildings and cultural and community facilities, installation of power lines. [p.42]
Installation sites and sites of work producers can be organized both on a territorial basis (complex performance of work on a group of objects) and by type of electrical installation work (installation of cable networks, installation of electric lighting, construction of overhead power lines). [p.46]
The possibilities for increasing the level of industrialization for different types of electrical installation work are not the same. [p.86]
High rates of comprehensive mechanization of work have currently been achieved mainly in the construction of overhead power lines. In general, complex mechanization of various types of electrical installation work requires further comprehensive development. The solution to this problem determines the main direction of increasing the level of mechanization of all types of electrical installation work. In particular, it is necessary to comprehensively mechanize all rigging work on the installation of electrical equipment, starting from loading the equipment at on-site warehouses and ending with its installation in the installation area. [p.99]
The wear periods of tools are determined taking into account the specific conditions of their use, while it was kept in mind that the same tools may have different service lives depending on the type of electrical installation work. Tool consumption rates were determined for five types of electrical installation work and separately for central workshops, and when calculating the Average consumption rates for all types of electrical installation work, the following specific weight of individual types of work, % was accepted [p.127]
According to the prices of Price Book No. 8, the estimated cost of all types of electrical installation work is determined, with the exception of the installation of overhead power lines and electric lighting of residential and public buildings, the cost of which is established according to the collections of Unified Regional Unit Prices (EREP) No. 25 and 35. [p.167]
The physical volumes of work (km of pipes, pieces of panels, electric motors, etc.) and their volumes in value terms are calculated on the basis of estimates drawn up according to working drawings. Estimated output and wage funds are determined by approximate indicators of output and wages of workers at installation sites, depending on the structure and volume of individual types of electrical installation work, and estimated labor intensity is determined as the quotient of dividing the volume of work by the amount of output adopted for a given type of installation work. [p.193]
In the case of the simultaneous start of several types of electrical installation work that are not technologically related to each other, there may be several initial events. The final event is the completion of electrical installation and commissioning work on the facility and its delivery to the customer. [p.199]
Based on the drawings and estimates, the scope of work for each job is determined in physical and monetary terms. Then the labor intensity for individual work is calculated, while being guided by aggregated labor cost standards for the main types of electrical installation work and approximate output indicators for individual types of electrical installation work (see Chapter X). [p.199]
The scope of work that is advisable to perform at the first stage of installation is not the same for different types of electrical installations and depends on the type of electrical installation work. For example, most of the work on the installation of switchgears and substations can be performed at the first stage, and when installing electrical machines, laying cables and electrical wiring - at the second stage. [p.207]
In this regard, in construction production, labor costs are determined on the basis of enlarged standard production calculations developed by construction and design organizations for certain types of work. To plan labor productivity for installation sites, approximate indicators for output and wages have been developed for various types of electrical installation work. [p.300]
Any type of electrical installation work is carried out in two stages. At the first stage, procurement work is carried out in workshops and preparatory work directly on site. The second stage involves electrical installation work on site. [p.133]
TYPES OF ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION WORK [p.15]
Below is an approximate list of the main labor installation operations by type of electrical installation work, compiled in order of technological sequence. [p.16]
The wear periods of tools are determined taking into account the specific conditions of their use, while it was kept in mind that the same tools may have different service lives depending on the type of electrical installation work. [p.154]
Tool consumption rates are determined for five types of electrical installation work and separately for central workshops, and when calculating average consumption rates for all types of electrical installation work, the following specific weight of individual types of work in % was accepted [p.154]
For all types of electrical installation work, the prices of Price List No. 8 include overhead costs of 75%. [p.307]
Pending the development of production standards for the consumption of materials for all types of electrical installation work, the quantities of materials recorded in [p.313] are accepted as such.
Technological specialization refers to departments allocated to independent construction organizations that perform limited (separate) types of work (for example, plumbing and electrical installation work, installation of metal structures, etc.). This type of specialization in industry-specific construction organizations and in inter-industry organizations contributes to a clearer organization of the production process, the use of highly efficient machines, mechanisms, and power tools designed for the relevant types of work and processes, and, consequently, an increase in labor productivity, a reduction in the cost of construction and installation work, reducing construction duration. [p.182]
In turn, the main types and objects of electrical installation work consist of individual installation labor operations. [p.19]
When studying issues of economics, organization and planning of electrical installation work, it is most convenient to consider them by individual types of electrical installations and individual labor operations that make up the installation of electrical installations. [p.19]
Work on the installation of electrical installations (electrical installation work) is characterized by a variety of types of work and individual labor operations. [p.20]
The number of engineering and technical workers in electrical installation work is relatively higher compared to other types of special work. Currently, there is an average of one engineering and technical worker for every 6-8 electrical workers. [p.20]
Electrical installation work is divided into installation work for the following types of electrical installations: 1) switchgears and substations 2) power electrical equipment 3) lighting electrical equipment 4) internal wiring and networks 5) overhead power lines 6) external cable networks and conductors. In addition, there are a number of special works that may be part of the main types of installation work. These include electrical installation work: a) on large electrical machines b) on secondary circuits c) on batteries d) on capacitor banks e) on heavy busbars and some others. [p.20]
Modern methods of electrical installation work require dividing the installation process into two stages. The first stage includes preparatory work, installation of embedded parts and fastening parts during construction work, installation of communications for hidden laying of wires and cables, large-scale assembly of electrical installation elements into units and blocks, assembling equipment and materials for objects, inspection and preliminary adjustment of equipment. In the second stage, work is carried out on the installation of electrical equipment assembled in the form of units and blocks, laying networks along ready-made routes and connecting wires and cables to electrical equipment. [p.21]
General construction organizations carry out a wide range of construction and installation work, while specialized organizations carry out only one specific type, for example, electrical installation work, sanitary work, installation of metal structures, etc. [p.37]
The first stage in the implementation of any electrical installation is scientific and experimental research and development prior to design. During this period, the most advanced types of equipment and materials, power supply schemes, drive controls, etc. are being developed. Continuous scientific and experimental research is also carried out in the field of further improving the preparation and organization of electrical installation work. [p.68]
Industrialization means the transition to such forms of organizing the production of electrical installation work that are inherent in large-scale machine industry and mass industrial production. The industrial installation method is the division of installation labor into work in factory conditions (factories and partly workshops) and labor in the installation area. The higher the proportion of the first type of installation labor, the higher the level of industrialization and the general technical level of work. [p.83]
The level of industrialization of electrical installation work for different types of electrical installations is not the same. Thus, for the installation of switchgears and substations, which can be assembled from factory complete devices, the level of industrialization is much higher than, for example, for the installation of large electrical machines or for the installation of electric lighting, where the relative share of labor costs in the installation area is much higher. [p.84]
In order to obtain comparable values, one should proceed from equivalent categories, which is labor intensity for electrical work (for example, in man-days). Let us denote labor intensity by T. Then the formula for the coefficient of industrialization of work takes the form [p.93]
Integrated mechanization as the highest level of technology is characterized by the creation for the installation of each type of installation of a special system of machines, mechanisms and devices, which allows the mechanization of all successive stages of electrical installation work. [p.99]
| Rice. 6. Some types of inventory transport devices used in electrical installation work |
For example, for the installation of metallurgical enterprises, it is advisable to divide the entire range of work by performer into the following specialized types of electrical installation work: electrical structures (complete devices) transformers, and large electrical machines; electric motors and devices installed on mechanisms, and starting equipment installed in the workshop; power and feed pipelines and distribution networks, wires and connection of control cables, trolleys and busbars, lifting mechanisms, internal electric lighting.
[p.47] In individual departments, various aggregated standards for material consumption are used, including standards for material consumption per 100 thousand pyfi. estimated cost of electrical installation work. These aggregated norms are calculated [p.91]
Electrical installation work is currently one of the most common types of special work in construction. They are closely intertwined with the production of construction and related installation work (mechanical, sanitary, etc.). The cost of electrical equipment and its installation constitutes a large share in the total cost of construction and depends on the purpose of industrial facilities, the design decisions made for power supply schemes and types of electrical equipment, and the structure of electrical installation work. [p.10]
In the past, in the electrical installation industry, only mechanisms created for construction or other types of construction and installation work were used (excavators, pipe benders, etc.); currently, mechanisms are being developed and implemented, the designs of which take into account the specifics of electrical installation work for certain types of electrical installations. [p.100]
Electrical installation tools and consumables
There are several groups of technical means that are used in the installation of electrical networks and equipment serving them. The specific kits and consumables that will be used in the installation process are, again, determined by the design decision. The universal tools with which electrical installation work is carried out include the following:
- Keys for installing electrical cabinets.
- Round nose pliers and thin nose pliers.
- Pliers.
- Strippers and other devices for removing cable insulation.
- Cable cutters.
- Soldering irons.
- Press jaws.
- Electrical tweezers.
In addition, an electrical fitter works with instruments to measure network performance. This group includes multimeters and testers, as well as specialized instruments such as voltmeters and ammeters.
As for consumables, electrical installation technologies, depending on the conditions of the project, may include the use of the following auxiliary accessories:
- DIN rails.
- Insulating tape.
- Cable channels and boxes.
- Insulating agents.
- Clips and terminals.
- Metal sleeves.
- Distribution devices.
- Brackets and electrical installation masts.
- PVC pipes and profiles to protect wiring.
- Trays and traverses for cable placement.
Installation of electrical substations
One of the first critical nodes on the path of transporting electricity from a current source (nuclear power plant, thermal power plant, hydroelectric power station, etc.) is a complex transformer substation. With its technical arrangement, construction and installation activities are carried out in the following general sequence:
- Preparing the site for work.
- Transportation of building structures and equipment.
- Installation of the substation frame with modules for installing equipment.
- Installation and connection of electrical equipment.
- Commissioning works.
The actual technology for electrical installation work is implemented from the moment the construction of the station buildings is completed and its revision. Next begins the installation of nodes with voltage winding terminals, connection of automatic machines and distribution devices. During installation, contact bars, compression plates with plugs and other electrical fittings are used, through which the transformer infrastructure is formed.
Technologies for installing overhead power lines
A power transmission line is constructed from the substation to other functional nodes of the energy network for distribution, transformation or direct supply to consumers. The installation item is a self-supporting insulated wire, which is stretched over a certain distance. The phased implementation of the technology for electrical installation work of this type can be presented as follows:
- Fixing the bandage tape on the supporting support. Such tapes are necessary to hold the fastening hooks. They are passed through special holes in the hooks, after which they are pulled and secured with clamps.
- Rolling out the electrical wire. By the time this operation is performed, special rollers must be prepared on the above-mentioned hooks for passing the cable. The wires are led from a special drum from rollers on one pole to another. The ends of the wires are secured with grip stockings and adjusted with traction cables.
- Pulling the wire. According to regulatory requirements, the distance between pillars should not exceed 50 m. This is necessary so that the line does not sag. Modern electrical installation technologies use a combination of a hand winch and a carabiner to achieve optimal tension on a power line. In this case, specific force indicators are monitored using a dynamometer.
Mounting sockets
The installation of sockets must be done professionally; the correct functioning of consumers largely depends on them.
There are various models of sockets on the market: electrical sockets, sockets for telephones, Internet and cable TV.
It’s good to think in advance where exactly you will install them. Consider the location of furniture and equipment.
Installation of sockets
A qualified electrician will be able to optimize energy consumption.
Typically, the wire colors used for wiring are brown or red for phase, blue for neutral, and yellow or green for ground.
The actual installation involves drilling a hole in the wall. Installing the wiring box, installing wires, connecting the socket and checking it.
The socket is checked using measuring instruments or by connecting any electrical appliance.
Grounding during electrical installation work
During operation, bare surfaces may form in different sections of power supply lines that are dangerous to people and animals. The complex of protective measures to insure against such situations uses the method of grounding the electrical circuit. Its essence lies in the fact that the part of the power system that is energized is connected to the ground, thereby reducing the ability to resist current in case of accidental contact with other objects. In the same book “Technology of Electrical Installation Work” Nesterenko V.M. proposes to consider grounding devices not just as a conductor for a specific circuit or equipment surface, but as a general integrated solution for connecting the entire local power network to the ground surface. What does it mean? The function of wire elements is performed not only by a random metal object or wire, but by an electrical installation previously calculated in the project, which has a connection to the ground. This solution has two technological features:
- Technically formed by special electrodes that increase the protective function of grounding.
- From the side of connection to the target equipment or network section, it is assumed not a single input, but a group of modules or a block, part of the connecting grooves of which is always free. That is, if it is necessary to ground a new circuit or equipment, it is enough to connect a line from it to the input group. This is usually done via a PE bus, standardized for the needs of protective wiring.
Electrical safety groups for electricians
Any profession related to electricity requires levels of access to systems maintenance - the so-called electrical safety groups.
Safety regulations for working personnel provide for five such groups. For the profession of an electrician, they are of critical importance, since the level of clearance can be used to judge the skill and experience of a specialist. 1 group
. It is given to workers who do not have direct contact with electrical circuits and are not involved in repairs.
2nd group
. Assigned to novice electricians who have completed primary safety training. Allows you to repair systems up to 1000 V under the supervision of a more qualified specialist.
3 group
. It is used only by electrical technical personnel. Gives you the right to independently repair, turn on and off systems with voltages up to 100 V.
4 group
. Electricians with this level of clearance have the right to service electrical installations with voltages over 1000 V.
5 group
. Given to specialists responsible for certain energy areas. They also have the right to supervise personnel during repairs and maintenance of systems.
Electrical panel installation and equipment
An electrical panel or cabinet performs the tasks of distributing and receiving electricity to supply end consumers. Initially, a wiring diagram is planned and the optimal location for installing this structure is determined. Depending on the operating conditions of the electrical panel, certain requirements for external protection may be imposed on its housing. For example, household structures have a protection class of IP65, which allows them to operate stably even in conditions of high humidity.
Installation is carried out using brackets and anchors to the wall. That is, holes are prepared in advance for hanging the structure while maintaining the possibility of third-party cable connections. As for the internal contents, modern electrical installation technologies are focused on the individual assembly of the power distribution system of the panel. In special compartments, RCD protective devices and automatic circuit breakers are installed for specific load indicators, which are determined in the design solution. Modular automation, contactors and protection relays are required to be integrated. More modern installations also provide additional functionality with digital measuring devices and indicator lights.
What an electrician should be able to do
Regardless of where he works, a good electrician should always be aware of the dangers of electricity, so he needs to follow safety precautions.
This is the most important condition for a specialist’s work, although, of course, it is far from the only one. Among other things, working with electricity requires considerable theoretical knowledge - at least a basic school course in physics (electrodynamics) and chemistry. This should also include knowledge of metrology, electrical power engineering, the ability to use instrumentation and, of course, understand the structure and circuits of electrical networks.
Placement of wiring, switches and sockets
From the electrical panel to the house or apartment, local wiring circuits for power supply devices are laid. The wiring is placed according to a previously prepared plan diagram in an open or hidden format. In the first case, it may also be necessary to install and assemble cable channels, and in the second, wall grooves are formed to form channels for laying the line at a depth of 2-3 cm. Joints, turns and connections are made using mounting boxes with contactors and a DIN rail.
After the installation of cables is completed, sockets with wiring outlets should remain at the operation site. They install sockets, switches and other electrical infrastructure devices. In this part, the technology of electrical installation work requires the installation of a junction box. It is provided when organizing new electrical wiring. This is a practical solution that will facilitate further work on connecting new electrical devices. The junction box is made of plastic and is mounted in the power cable output unit. Its internal filling contains small-format blocks and distribution rails for connection with distribution wires leading to lighting devices, switches and other points of control and electricity consumption.
Masking an electrical installation
An experienced electrician can easily help you disguise the electrical wiring. It will hide the cables in the walls, it all depends on the original plan that was approved. Sockets are located in convenient places to use.
Hidden wiring is ideal in any home. If you decide to lay cables above the wall, they will be pulled through special tubes and boxes.
Installation of hidden wiring
There are two methods of electrical installations on the market: one hidden under the plaster mentioned above, and the other applied to the wall using special boxes.
Wiring to the top of the wall
Technology of electrical installation work on ships
As is the case with the energy supply of buildings, apartments and engineering structures, a project for the installation of electrical equipment and electricity delivery circuits is first developed for the vessel. The main electrical installation measures in this case include the following:
- Along the entire route of laying the power line, the wire is placed, cut, terminated and tested with an insulation check after installation.
- Target electrical equipment is installed at points of direct consumption.
- The main main channels are coiled and tied in the bottomhole areas. We can say that this is backup wiring, which should be reliably protected from damage during periods of inactivity.
- At the final stage, commissioning activities are carried out with measurements of power grid indicators and testing of equipment operation.
Today, parallel technology for performing electrical installation work on ships is increasingly being used, according to which the external and internal organization of the power system is carried out simultaneously. This method is especially effective for block layout of ships. It allows you to optimize installation processes, but it also has its drawbacks. For example, when implementing this method, a strict calculation of energy resources is necessary, since they can be simultaneously used in several functional areas. In addition, there are also organizational problems when installing parallel wiring and connecting equipment in several blocks at once.