Who needs electrical safety training?
For ease of understanding, we will divide all personnel into “categories”:
- electrical (electrical) personnel (workers dealing with electrical equipment, electrical installations or power tools). This category of workers is assigned electrical safety group II-V (with the issuance of certificates);
- non-electrical personnel (workers who are not directly related to the repair and installation of electrical equipment, but use electrical devices to perform their duties (PC, printer, fax, other electrical devices) and perform work that may pose a risk of electric shock). This category of workers is assigned electrical safety group I (without issuing certificates).
The concept of induction training on electrical safety does not exist. Electrical safety training is carried out only for assignment to group I.
And to assign an employee a higher group, i.e. II – V gr., here you won’t get by with simple instructions. To do this, the employee must undergo a special training course at the training center in accordance with the training programs. Training programs differ in content for different qualification groups. After testing knowledge and passing exams, the employee is issued a certificate for the appropriate access group.
Based on the above, electrical safety training is carried out for all employees of the organization, except electrical personnel.
And the concept of “instruction” is applicable only for workers with electrical safety group I.
How often are employees’ knowledge tested?
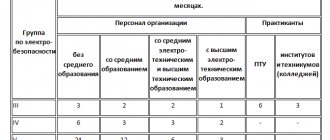
Electrical safety knowledge testing is carried out according to developed and approved programs, taking into account the specifics of the enterprise. Personnel with qualification group I undergo it annually , and with groups II–V :
- once a year - for electrical personnel who service existing electrical installations or perform any work or tests in them, as well as for employees who issue orders and orders;
- once every three years - for administrative and technical personnel not belonging to the previous group, as well as for labor protection specialists authorized to inspect electrical installations.
An employee can take the next knowledge test either at a training center or at a commission formed within the company. The commission should consist of five people, three of whom are certified by Rostechnadzor. As a rule, the person responsible for electrical equipment is appointed as the chairman of the commission, who, by the way, can only undergo a knowledge test in the Rostechnadzor commission.
Warns
Stanislav TIMOFEEV,
Director of the Smolensk branch of LLC "HSA Certification" (Smolensk)
If an employee has had a break in work for more than three years, his electrical safety group is lost. You will have to go through all stages of training again, starting with admission group II.
If an employee changes jobs, he will also have to undergo an extraordinary recertification to confirm his electrical safety group and receive a new certificate. The old document will be invalid at the new place of work.
What documents should there be?
To conduct training with assignment to Group I, you must complete a number of mandatory documents:
- List of professions and types of work that require assignment to group I in electrical safety. This list is approved by a local document, as a rule, this is an order (instruction) for the enterprise.
- A training program for assigning electrical safety group I, which should contain general information on electrical safety, information about the effects of electric current on the body and recommendations for first aid in case of electric shock.
- Logbook for training on assignment of group I in electrical safety to non-electrical personnel.
Main conclusions
To avoid problems and stress, you need to remember that electrical safety group 1 is assigned to non-electrical personnel, these are those who are not associated with electrical installations, but there is a possibility of electric shock.
Therefore, carry out instructions in a timely manner and record this fact in a journal, especially since the frequency is acceptable, once a year.
Everything is quite simple, but it teaches workers to be safe when using electrical equipment, because it has become so tightly integrated into our lives and surrounds us everywhere that without it it’s already “like having no hands.”
And injuries from electric shock are no exception to the general statistics of injuries, so personnel must know and be able to comply with electrical safety requirements, release the victim from the effects of electric current and provide first aid.
Only then can you “sleep peacefully” at work
I wish you safe and efficient work!
If you still have questions about assigning group 1 to personnel, write comments, we will discuss, and if you need help with paperwork, please contact us.
Who can provide electrical safety training?
A responsible person from among the electrical personnel with an electrical safety group of at least III, who has been trained and appointed by order of the enterprise, can assign electrical safety group I (i.e., conduct instruction).
Order for the enterprise
In organizations (enterprises) with a small number of employees, in which a responsible person has not been appointed, the instruction is carried out by the head of the organization (he must also be certified accordingly).
It is also possible to conclude a civil contract or a service contract for reading electrical safety instructions with a person who has the appropriate permits.
Responsible for electrical equipment
This is an employee who monitors the safe use of electrical installations in the organization. The person responsible for electrical equipment must have clearance group IV if the company operates electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V, and clearance group V when operating electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V. Usually the chief power engineer of the organization is appointed to this position.
If the company does not have production and only uses electrical equipment with a voltage of no higher than 380 V, then there is no need to appoint someone responsible for electrical equipment. With the consent of Rostechnadzor, his responsibilities will be assumed by the head of the organization.
Logbooks for registering work on labor protection
You can download the logbook for assigning group I electrical safety to non-electrical personnel here
The assignment of group I is registered in the Logbook for the assignment of group I for electrical safety to non-electrical personnel. A certificate of assignment of clearance group I is not issued to employees.
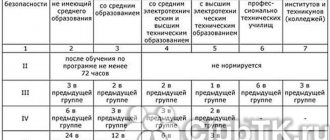
To initially obtain Group II admission, workers with or without secondary education must undergo specialized training for at least 72 hours and pass exams at the certification commission of Rostechnadzor. Those who successfully pass the knowledge test are assigned admission group II and are issued a certificate in the established form.
If an employee has a secondary or higher electrical engineering education in his specialty or a higher technical education, then group II is assigned automatically. Further, in order to increase the electrical safety group, you will need to gain some experience, data on which is given in Table 2.
Table 2. Information about the work experience required to increase the electrical safety group
| Electrical Group security | Minimum experience in electrical installations | |||
| Employees | ||||
| without secondary education | with secondary education | with secondary electrical and technical education | with higher electrical and technical education | |
| III | Three months in the previous group | Two months in the previous group | Two months in the previous group | One month in the previous group |
| IV | Six months in the previous group | Three months in the previous group | Three months in the previous group | Two months in the previous group |
| V | Two years in the previous group | One year in the previous group | Six months in the previous group | Three months in the previous group |
Advises
Natalia YUROVA,
General Director of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration of OOO “WOT “Berkana”” (Moscow)
Electrical personnel who will test electrical equipment must have not only theoretical knowledge, but also undergo practical training in the workplace. It is carried out by an experienced employee for at least two work shifts. If you have employees with at least three years of experience in their specialty, you can exempt them from internship.
Electrotechnological personnel
The situation is completely different with the Electrotechnological personnel. According to the definition, Electrical Technological Personnel means personnel of production workshops and areas that are not part of the energy service of the organization, operating electrical technological installations and having electrical safety group II and higher (in their rights and responsibilities they are equal to electrical personnel and are technically subordinate to the energy service of the enterprise) ; personnel whose main component in the technological process they control is electrical energy (for example, electric welding, electric arc furnaces, electrolysis, etc.), who use hand-held electric machines, portable power tools, lamps, etc. in their work. I deliberately use the second part of the definition highlighted because it is with this that significant leapfrog and confusion in categorization are associated. Who is classified as non-electrical and electrical technical personnel? This question will first have to be answered by the one who will compile the “List of Positions...”. The gradation is fully entrusted to the employer and the person authorized by him. There are also errors that the inspector can point out... The main thing is to understand that, first of all, electrical engineering personnel include persons who cannot perform their job duties without the use of any electrical equipment. Thus, if the employee’s position sounds like an electric welder, ultrasound doctor, x-ray technician, etc., then it should be understood that such a person cannot perform his job duties without the use of appropriate electrical equipment, which means he must be classified as electrical engineering personnel , train at least group II in electrical safety (for example, a group of at least III is provided for a welder) and ensure recertification once a year. But, for example, positions such as general practitioner, hairdresser, accountant, etc., may involve the use of some kind of electrical equipment, but from time to time. That is, in the course of their main activity, an employee may not use it at all: a hairdresser can cut hair using only scissors, an accountant and a therapist can do without the use of computers or any other electrical equipment, so they can be classified as non-electrical personnel and limited only by holding an annual lecture.
It is important to remember that, in accordance with clause 1.4.3 of PTEEP, “managers who are directly subordinate to electrical engineering personnel must have an electrical safety group no lower than that of subordinate personnel. They must provide technical guidance to these personnel and supervise their work.”
I would like to note several features when finding the line that turns non-electrotechnical personnel into electrotechnical personnel. For example, in my practice, there have been cases when supervisory authorities issued orders to conduct training and certify Group II electrical safety for workers in such professions as computer operators and programmers. It would seem, what type of activity can now do without the use of personal computers? Nevertheless, the order was given in accordance with the above definition. That is, these workers in their production activities cannot do without the use of electrical equipment, which is a computer.
General electrical safety requirements
As much as I have been working in the field of labor protection, I have been faced with the lack of knowledge among managers of why this beast called electrical safety is needed. And if you describe what it is in simple language, then it sounds like this.
Electrical safety is a procedure aimed at preserving the health and life of the organization’s employees, through compliance with requirements and rules, from the effects of harmful and dangerous factors:
- electricity;
- electric arc;
- electromagnetic field;
- static electricity.
In this article I will try to explain how we, as occupational safety specialists, can organize the work of this area of production, and understand what electrical safety requirements are imposed at the enterprise, since most of it, especially paper, falls on our shoulders.
I was lucky, at the beginning of my journey as an occupational safety specialist I had good mentors: the chief engineer and the chief power engineer, with whom I learned step by step what and how. I will try to convey to you the knowledge that was given to me.
Requirements for electrical safety at the enterprise
It is important to know that if the enterprise has at least one electrical equipment that is plugged into an outlet, for example, a computer, printer or table lamp, then it is necessary to organize work on electrical safety in accordance with clauses 1.1.2 and 1.2.4 of the Rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations ( Order of the Ministry of Energy dated January 13, 2003 No. 6)
By the way, these are very useful rules to prove to our bosses that there should be a person responsible for electrical safety in any organization.
Then decide on the package of documents that need to be completed. To do this, you need to know what equipment is on the organization’s balance sheet.
Any enterprise or organization is a consumer of electrical energy. If this is production, then machine tools, welding installations and other power electrical equipment can be used.
For this equipment, it is necessary to systematize regulatory legal documents that relate to the type of enterprise - PUE, PTEEP, building codes and regulations, state standards.
You must also always remember that all provisions and standards relate not only to equipment, but also to electrical personnel and other employees, regardless of the form of formation of the legal entity and property.
The standards apply to the following types of activities:
- routine maintenance and operational switching in electrical installations;
- performing installation and repair work on electrical equipment;
- measuring and testing operations.
Having collected all this information, we compile and draw up a list of documentation and it is approved by the manager, who will greatly facilitate your work. Based on it, you can draw up orders, training and personnel training programs, schedules, logs, protocols and other documents on electrical safety.
Inexperienced occupational safety specialists should be warned and emphasized that you only supervise all work on electrical safety and help in some ways, but all responsibility lies with the manager, who can delegate his functions to a deputy, chief engineer or other responsible employee of the enterprise from among the managers.
This appointment is made after testing their knowledge and assigning the appropriate clearance group:
- in installations with voltages greater than 1000 V - group V;
- up to 1000 V – group IV.
The person responsible for electrical safety, appointed by the manager, must develop and maintain the necessary documentation on issues related to the operation of installations.
And he, not you,
ensures safety during work of any type, monitors how electrical safety requirements are observed by personnel. Monitors the availability and timeliness of inspections and testing of tools, fire extinguishing and protective equipment.
The most necessary regulations
| Document | Will help you |
| POT R M-016-2001 “Inter-industry rules for labor protection (safety rules) during the operation of electrical installations” | Understand how electrical safety groups are assigned |
| Order of the Ministry of Energy of Russia dated January 13, 2003 No. 6 | Clarify what requirements apply to personnel working with electrical installations |
| Article 9.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and Art. 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation | Find out how an employer will be punished if he does not train employees in electrical safety |
Who is assigned 1st EB group
In accordance with the requirements of Order No. 6 of the Ministry of Energy dated January 13, 2003, all employees of the enterprise are divided into 3 parts: electrical, non-electrical and other personnel. The meaning of this division is that people from the first category have special access to the maintenance of electrical networks and electrical equipment, and workers from the second only use this equipment to carry out production activities. Other personnel include people who do not work with electrical appliances.
Electrotechnological personnel can perform the following functions:
- administrative and technical;
- repairs (permanent or urgent only);
- operational.
These are people whose responsibilities include maintaining electrical networks and ensuring the functionality of equipment connected to these networks. Depending on the qualifications and functions performed, they are assigned electrical safety group 2, 3, 4 or 5.
Full range of occupational safety services
Enter your phone number and I will calculate an estimate for your tasks. Enter without the eight. “Ekaterina Vorontsova’s Bureau” is a professional solution to your occupational safety problems. High quality and on time!
What are the requirements for electrical safety personnel?
It is required that any work operations be carried out only when the employee is in good health. To do this, you need to regularly undergo preliminary and periodic medical examinations at a medical institution.
Employees of manufacturing and other enterprises must know first aid techniques. Only having this knowledge can allow you to obtain permission to work independently.
Technicians working on electrical installations must also have the skills to free a person exposed to electrical current.
In order for all work to be safe, personnel must know electrical safety requirements and undergo specialized training. And training programs and instructions are very helpful in gaining knowledge in this area, which is a big trump card in the work, as it was written above, everything works on electricity.
We distribute the organization’s employees into categories and draw up a list of positions and professions of personnel who are required to have an appropriate electrical safety group.
An example of a list of positions and professions of personnel who are required to have an appropriate electrical safety group
Each enterprise has employees whose work is not related to the operation of electrical installations, but involves the possibility of electric shock.
This category of employees is assigned group 1 in electrical safety after training, which is conducted by a person with group 3 access and knowledge testing in the form of an oral survey.
A record of this is recorded in the journal and such employees do not receive certificates. But they undergo such inspection at least once a year.
And now a list of positions and professions of electrical and electrical engineering personnel has been compiled, now let’s figure out who is who.
Meaning and definition of personnel
The company's employees are divided into electrical and electrical engineering personnel.
Electrotechnological personnel include employees who use electrical energy in the course of their activities, for example, metal cutting, electric welding, electrolysis, etc.
As well as employees who use lamps, electric machines, portable power tools and other workers in their work, for whom knowledge of industrial safety equipment is established by the job description. All of them are assigned group 2 for electrical safety.
It should be remembered that employees with group 2 and above, who are not related to the energy department, are equal in their rights and responsibilities to electrical personnel.
The electrical technical staff includes:
- Administrative and technical workers. These are managers and specialists who, according to their responsibilities, are associated with operational and technical maintenance, adjustment, repair and installation activities in electrical installations.
- Operations employees - perform routine maintenance and management of installations. These employees, by the nature of their activities, carry out inspections, preparation of workplaces, operational switching, admission, supervision of other personnel and the performance of tasks within the framework of the current operation of the equipment.
- Operational and repair personnel are specially trained workers who perform maintenance of the installations assigned to them.
- Maintenance workers - provide maintenance, installation, testing and adjustment of equipment.
The personnel have been decided, but in order for the personnel to perform independent work, they must undergo appropriate training at their workplace. A similar rule applies if the employee’s activity is interrupted for more than a year.
Electrical Safety Training Requirements
Electrical safety requirements must be known to personnel, such as the Lord’s Prayer, when starting work, which is why it is so important to pay special attention to training. And for this, electrical and electrical engineering personnel undergo:
- All types of instructions.
- On-the-job internship.
- Education.
- Duplication.
- Various types of training, depending on the activities of the organization.
- Checking the norms and regulations on labor protection (PTE, POT, PUE).
Let's take a closer look at who, when and to whom tests knowledge, and what needs to be done for this. There are 5 qualification approvals in electrical safety.
We have already dealt with the 1st admission group. A whole article has been written about this on our website. But let’s take a closer look at the other groups.
Regarding certification for group 2 in electrical safety, not everything is so simple; there are subtleties and details, I recommend that you read the detailed note on this topic if you have questions.
An employee with group 3 is required to know the special electrical safety requirements that apply to a number of specific jobs, including monitoring the maintenance of electrical installations.
If a specialist receives group 4 in ES, he is assigned a list of responsibilities from all previous groups. He has the right to train personnel and conduct instructions and has extensive knowledge and skills in electrical engineering.
At the enterprise, by order of the manager, a commission is created. It must consist of at least five people. The chairman, as a rule, is appointed to be responsible for electrical facilities, and he must be certified by the state energy supervision authority, have an electrical safety group of at least V for voltages up to and above 1000 V and IV for voltages less than 1000 V, and must be present in the work of the commission.
All other members of the commission must have a group depending on the equipment being serviced, IV - up to 1000 V, V - over 1000 V, and must be certified by the State Energy Supervision Authority with the assignment of an electrical safety group.
If you are just starting to understand electrical safety groups and you need details and the procedure for assigning them, you can read this note.
So, we created a commission, we begin a knowledge test, which is divided into:
- primary;
- next;
- extraordinary.
An initial check is carried out for newly hired employees and if the gap in certification is more than 3 years. The next inspection is carried out once a year if he organizes and performs maintenance work on existing electrical units, carries out installation, adjustment, repair, and preventive tests.
Employees who have the right to issue orders, orders, and conduct operational negotiations also undergo a similar check. Administrative and technical personnel, as well as labor safety specialists who have the right to inspect electrical installations, undergo inspections every three years.
The need for an extraordinary inspection is determined by the responsible person, regardless of the date of the previous one, in the following cases:
- when introducing newly developed or revised rules and regulations;
- when installing new equipment, changing/reconstructing main technological and electrical circuits;
- when transferring/assigning to another job if the assigned duties require knowledge of an expanded list of rules and regulations;
- when employees fail to comply with regulations on labor protection;
- at the request of state supervision authorities;
- on the basis of the conclusion of the commission that investigated an accident involving people or a violation in the functioning of a power plant;
- when upgrading your qualifications to obtain a higher group;
- if there is a break in activity in this position for more than six months.
Only if they have sufficient qualifications, confirmed by successfully passing the exam, employees are assigned a certain electrical safety group, issued a certificate and allowed to obtain permission to independently perform job duties.
What does an employer face if employees are not trained in electrical safety?
An employer who allows uncertified personnel to work in electrical installations faces a fine :
- from 2000 to 4000 rubles – for an official;
- from 2000 to 4000 rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days - for an individual entrepreneur;
- from 20,000 to 40,000 rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days - for an organization (Article 9.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
If an accident occurs with an untrained employee, the employer may face criminal liability under Article 143 of the Criminal Code in the form of a fine of up to 400,000 rubles or even imprisonment for up to one year.