Modern fluorescent lamps (FL) do an excellent job of lighting large residential, work and technical premises and can reduce overall electricity consumption by 50-83%, thus reducing utility bills.
In this article, we will consider the operating characteristics of LLs, their design, and analyze the main advantages and disadvantages in comparison with other types of lighting devices. In addition, we will provide thematic photos and diagrams, as well as videos about the operating principle of fluorescent light bulbs and the features of their application.
What is a fluorescent lamp
The low efficiency of traditional incandescent lamps has long been a headache for electrical equipment manufacturers. The problem of saving energy became more and more urgent and in 1936 a solution was proposed. In Russia, special gas-discharge devices have appeared that can combine lighting with energy savings.
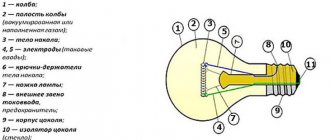
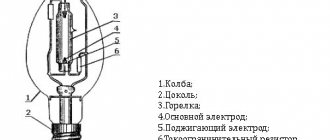
A fluorescent lamp is a structure made from a bulb with electrodes placed inside. The shape can be any; operation is affected only by the gas composition. After applying voltage between the electrodes, the process of electron emission starts, which creates radiation.
Figure 1. Fluorescent light source
However, the radiation received at this stage is in the ultraviolet range and is not visible to the human eye. To make the light visible, the top of the bulb is coated with a special compound - a phosphor.
Inside the flask there is an inert gas or mercury vapor to maintain a glow discharge between the electrodes. Inert gas is a safe option because it does not interact with the surrounding space in any way. But devices with mercury vapor are extremely dangerous. Devices with such contents must be disposed of according to all rules, and care must be taken when handling flasks.
Why does an LED lamp glow when the switch is off?
Miracles do not happen and I, as an electrician, responsibly declare that if an LED light bulb lights up after turning off, there can be only 2 reasons for this:
- the switch does not break a phase, but a zero, and there is a section in the wiring with poor-quality insulation;
- A backlit switch is used.
Let's consider both cases in more detail.
Illuminated switch
The most common reason for an LED lamp to glow after being turned off is the use of a backlit switch.
Inside such a switch there is an LED with a current-limiting resistor. The LED lamp glows dimly when the lights are turned off because even when the main contact is turned off, current continues to flow through them.
Why does an LED lamp burn at full heat and not at full power? Thanks to the limiting resistor, the current flowing through the electrical circuit is extremely insignificant and insufficient to light an incandescent electric lamp or ignite fluorescent lamps.
The power consumption of LEDs is tens of times lower than the same parameters of an ordinary incandescent lamp. But even a small current flowing through the backlight diode is sufficient for the LEDs in the lamp to glow weakly.
What does it look like? There can be two lighting options. Either the LED lamp lights up continuously after turning off, which means that sufficient current flows through the LED backlight of the switch, or the light flashes periodically.
This usually happens if the current flowing through the circuit is too small to cause a constant glow, but it recharges the smoothing capacitor in the power supply circuit.
How to fix? The simplest is to remove it from the backlight switch. To do this, we disassemble the housing and unscrew or bite off with wire cutters the wire going to the resistor and LED. Or change the switch in the house to a regular one, without backlight.
Another option would be to solder a shunt resistor in parallel with the lamp. According to the parameters, it should be designed for 2-4 W and have a resistance of 50 kOhm. Then the current will flow through it, and not through the power driver of the lamp itself.
You can purchase such a resistor at any radio store. Installing the resistor is not difficult. It is enough to remove the lampshade and fix the resistance legs in the terminal block for connecting the network wires.
If you are not particularly friendly with electricians and are afraid to “interfere” with the wiring yourself, another way to “fight” backlit switches can be to install a regular incandescent lamp in the chandelier. When turned off, its spiral will act as a shunt resistor. But this method is only possible if the chandelier has several sockets.
Incorrect connection of the lamp
The reason for the continuous burning of the lamp may be hidden in connection errors. If, when installing the switch, a zero was connected instead of a phase, it will turn off when the circuit is opened. At the same time, due to the preserved phase, the wiring (and, accordingly, the light bulb) will be constantly under voltage. The LED light will illuminate when the switch is off, due to leakage current through worn insulation or poorly insulated connections.
Violation of polarity (phase and zero) during installation causes a constant supply of current, which leads to the glow of LED devices even when the switch is off. This situation is quite dangerous for the inhabitants of the apartment: since the device is energized, even if it is turned off. And you can accidentally get an electric shock (for example, when replacing a light bulb).
How to fix? It is necessary to turn off the power supply, disconnect the wires, and then mount them in the correct way (phase to switch).
Types of fluorescent lamps
All fluorescent lamps are usually divided into two large groups: high and low pressure devices.
High pressure devices are often used in street lamps. They are capable of producing a strong luminous flux, but the color rendering parameters are at a low level. On sale you can find lamps with different levels of light output and shades of glow. They are used for powerful lighting, as decorative lighting for buildings.
Figure 2. Types of LL
Low pressure LL is more common. They are widely used in everyday life and in production. Most often, the models look like small cylinders. Such electrical appliances have ballasts that reduce the pulsation coefficient and make the glow more uniform. The component is a small circuit housed in the base of a light bulb.
Consultation and recommendations from a specialist
Get a free consultation from our specialist:
- Consultation is free.
- A specialist will respond within: 30 minutes.
- Pickup and showroom in 2022.
- Free shipping
: delivery time is 3-5 days. - Delivery: Transport company, mail and courier.
- Address
: Bagrationovsky proezd, 7 - Opening hours
: daily 9.00-19.00. - Payment upon receipt
is possible , 1 year warranty! - Federal Law-44 We participate in government tenders. We work under a contract. Non-cash payment is possible by card (VISA, Mastercard) and to a bank account
Markings and sizes
Each LL has its own technical characteristics that determine its use. Typically, all information about the device is encrypted in the labeling.
The designation begins with the letter L, which means lamp. Then comes the letter designation of the shade.
| Marking | Meaning |
| D | day glow |
| B | White light |
| HB | cool white |
| TB | warm white |
| E | natural light |
| HE | cool natural light |
| G, K, Z, F, R | various shades depending on the type of gas used and the phosphor used |
Sometimes in the marking you can find the designation Ts or TsTs, which indicates improved color rendering of the phosphor. For example, the designation LDC is typical for a fluorescent lamp with improved color rendering.
This is followed by digital designations that comply with global standards. These are three numbers, the first of which determines the quality of color rendering, and the rest indicate a specific color temperature. The larger the first number, the better the color rendering. An increase in the remaining numbers indicates a cooler glow.
Figure 3. Types of LL base
LL devices vary in size. The dimensions are indicated by the designation “TX”, where X is a specific size parameter. Specifically, T5 means 5/8 inch in diameter, and T8 means 8/8 inch in diameter.
The sockets can be pin or threaded. In the first case, the designation looks like G23, G24, G27 or G53. The number indicates the distance between the pins. Threaded sockets are available with markings E14, E27 and E40. Here the number determines the thread diameter.
Additionally, the lamp indicates the supply voltage and startup method. If the box has the designation RS, it means that no additional equipment is required for operation. All the necessary elements are already built into the base.
Application area
Fluorescent lamps have become widespread due to their advantages. They are used for lighting in houses and apartments, offices, factories and warehouses, in street lighting and illuminated advertising.
Depending on the color rendering spectrum, lamps are:
- similar to solar radiation - used in lighting offices, production workshops, and administrative organizations;
- with increased color rendering - suitable for exhibitions, galleries, museums, hospitals, organizations selling dyes, fabrics and other artistic devices;
- with increased radiation in the red and blue spectrum - used for illumination of aquariums, greenhouses, plant stores, greenhouses;
- with a shift to the blue and UV part of the spectrum - decorating aquariums;
- light in the UV spectrum – solarium;
- High power UV radiation – antibacterial lamps.
Before the active use of LEDs, fluorescent light bulbs were used to backlight LCD monitors. Powerful luminescent devices are used in street lighting of highways, stadiums, and playgrounds.
Power and spectrum
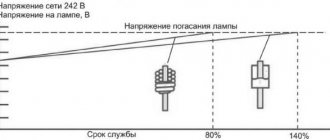
In order for the lighting source to work normally, it must be connected to a 220 V network with a frequency of 50 Hz. Deviation may negatively affect the stability of lighting, significantly shortening the service life.
Voltage fluctuations can change the power of an electrical appliance, reducing its efficiency. Even the most powerful lamp will glow dimly if there is insufficient voltage.
Must watch: a ban on fluorescent lamps will come into force in 2022.
Modern LLs have almost any shade. The color temperature spectrum varies from classic warm to daylight. Each lamp is marked accordingly by shade.
Separately, it is worth considering lighting devices with ultraviolet glow. They are marked LUF, while reflective blue devices are marked LSR. UV lamps are used for bactericidal treatment of premises.
Most fluorescent lamps produce a flux similar in length to ordinary sunlight. You can see the similarities between the spectra in the picture below.
Figure 4. Comparison of the spectrum of sunlight and LL
The spectrum of sunlight is shown on the left; the spectrum of a high-quality fluorescent lamp is shown on the right. The light from the sun has a more even characteristic, but the similarities are definitely there. LL has a pronounced peak in the green region, while in the red region there is a decrease.
It has been scientifically proven that the closer the light from an artificial source is to natural light, the better it is for health. For this reason, fluorescent lamps are preferable to LED fixtures.
Advantages and disadvantages of fluorescent lamps
It has long become clear that the economic component has intervened like a cancerous tumor in the rational path of human development. Moreover, we are not talking about the feasibility of producing a particular product, but rather about the economic profit of corporations at minimal production costs.
Progress has stopped and is moving in the direction indicated by the monopolists. Supply now creates demand created by supply.
We can talk about this topic for a very long time, using facts, but let's have this conversation in relation to the technology in question, and try to understand the real advantages of the most common light sources.
Let’s say right away that we do not claim to have an opinion in the last instance, we are simply expressing our simple and logical thoughts, which have probably visited many people more than once.
Advantages of LEDs over fluorescent lamps
Marketers, when promoting a particular product, present its advantages over competitors, often operating on properties for which these products were not originally intended. It's like, for example, comparing a racing car with a road sedan.
Yes, the first one will definitely go through the route faster, looks brutal and unusual, captivates the eyes of passers-by, but... On public roads it will be useless - uncomfortable, inconvenient, clumsy. Try standing in such a car in a traffic jam.
Having caught this idea, we begin to compare the lamps.
- We often hear how effective the use of energy-saving light sources is compared to classic incandescent lamps, but this point still remains in question. The savings are very controversial, and the use of hazardous substances, such as mercury, in fluorescent lamps indicates associated environmental pollution. LEDs have rushed into this race, with safety, low heating temperature, incredibly long lifespan, leaving everyone behind.
Comparison of LED lamp with incandescent lamp
- So, a fluorescent lamp has high efficiency. Where a regular light bulb will burn 10 watts of energy, this one only burns two, at the same light intensity. An LED lamp should only use 1 watt of energy.
Interesting to know! Let's start right away with the fact that when compiling indicators, manufacturers use only laboratory measurements, and the best samples take part in the tests. This means that such a lamp will be on the store counter is extremely unlikely. We will use our own experience, and everyone, if desired, can repeat the experiments on their own.
Lamps for indoor lighting - shine brighter
- If you compare lamps in laboratory conditions, the result will be exactly the same, but in everyday life other laws come into force. Your humble servant has been installing ceramic tiles for a long time, which requires high-quality lighting. Usually a carrier with a 200-watt incandescent lamp was used, which was enough for work. One day it was replaced with a 25-watt LED lamp, which should produce even more light, but no miracle happened. The lighting was dimmer and there were eerie shadows that strained the eyesight.
- The reason is the following - manufacturers use the cheapest electronics and the lamps do not produce the declared indicators, plus LED lamps emit a narrow beam of light, which means it does not fill the room evenly, which is where the shadows appeared.
- Fluorescent lamps scatter light in all directions, which is their undoubted advantage, but the problem with the output power remains the same.
- Now let's look at the cost of the lamps. A good incandescent lamp will cost no more than 25-40 rubles, while fluorescent and LED lamps cost far more than 200-300 rubles. Today the market offers LEDs for 80 rubles, but when buying something like this, you should remember about your health and short service life. Yes, they are guaranteed for a year, but for many they will not last much longer, and not many people keep receipts for purchases with boxes.
Manufacturer warranty comparison
- Fluorescent lamps in the inexpensive segment also do not last long, since their efficiency largely depends on the starting equipment.
- According to classical measurements, an incandescent lamp lasts 1000 hours (for modern halogen lamps this figure has increased to 2000 hours), a fluorescent lamp lasts 15,000 hours, and an LED lamp lasts 30,000-70,000 hours.
- The gap is colossal, but, we repeat, such a result is achievable only when using high-quality electronics and when working in ideal conditions, without voltage drops, correct connection, compliance with thermal conditions, and so on. In practice, it has been noted more than once that fluorescent and LED lamps in the budget segment last 1-1.5 years. Some specimens last up to 2-3 years, and only expensive products provide the stated parameters. Incandescent lamps can easily last the same year or two without burning out if they are not used constantly.
- As a result, the situation with savings on lighting becomes ambiguous. Since fluorescent lamps have a limit of on/off switching of around 2000 times. That is, it is not advisable to place them in places where the light is often turned on. For the same reason, they are not recommended to be used in conjunction with motion sensors. The energy saved eventually covers the cost of expensive lamps, but more often the lamp must work for at least a year for this to happen.
As a result, we conclude that in order to save money, you need to buy expensive high-quality lamps, paradoxically, and use them only where necessary, where the light is constantly on.
How do lamps heat up?
- Fluorescent lamps produce less heat than incandescent lamps. LEDs tried to get into the fight, positioning themselves as cold light sources, but in fact they produce a fair amount of heat, it simply spreads in the opposite direction from the light flux, as can be seen in the photo above. For this reason, powerful devices must have a radiator installed at the base. If these are lighting systems for greenhouses and aquariums, then you cannot do without active cooling systems. So, according to this indicator, fluorescent lamps remain the most efficient.
Without effective cooling, LEDs quickly burn out
- The quality of color rendering plays a huge role in the perception of the surrounding space by the human eye. The standard is considered to be lamps with a mark of 100 Ra. Anything less starts to distort the colors. Incandescent lamps generally have a high indicator for their glow temperature, but LEDs and fluorescent lamps need to be chosen correctly. And is it worth saying that the indicator affects the price.
Changes in color perception with changes in Ra
- The glow spectrum of an incandescent lamp is pleasant to the human eye. The color temperature is 2700 K, while modern sources can shine in the cold spectrum - 6500 K. The emission spectrum of fluorescent lamps is regulated by the composition of the phosphor, which allows you to get any desired option, but there is a catch - it is often lined, and therefore unpleasant to the human eye. Low-quality LEDs lose part of the spectrum to which the pupil reacts by narrowing. Because of this, harmful rays easily reach the retina of the eye, damaging it.
White and blue LEDs can cause eye damage
This is where the advantages of fluorescent lamps end, and the disadvantages begin:
- The high efficiency of the lamp cannot be maintained throughout its entire service life. Due to the burnout of the phosphor, it decreases, plus the light spectrum changes. The same thing happens with LEDs.
- Both lamp options have flickering - the network frequency multiplied by two, that is, 100 times per second. Electronic ballasts (electronic starting control apparatus) are installed in fluorescent lamps. If the capacitors built into it have the necessary capacity, this effect can be eliminated. In LED lamps, the capacitor is the culprit for the appearance of stray currents. They can be removed using special protection blocks.
- A fluorescent lamp cannot operate directly from the mains, so it requires starting equipment that takes up space. LEDs need a reduced voltage, so a transformer is necessarily present in the design.
Lamp in use
- From a purely technical point of view, a fluorescent lamp has a low power factor, which for the network is an example of a failed load.
As we can see, LEDs have many disadvantages, so why then did they continue to develop electronics?
Do not forget about the potential danger of fluorescent light sources due to the mercury used, which is the main reason for the impossibility of recycling with your own hands. They also have a durable body, are environmentally friendly in production, have the best service life, and operate at subzero temperatures.
In what areas are they used?
With the help of fluorescent lamps, large areas can be effectively illuminated, while significantly improving indoor conditions, reducing energy costs, and also increasing the service life of the lighting system.
Devices with built-in electronic ballast and E27 or E14 screw threaded sockets are used in everyday life as an effective replacement for incandescent lamps. They are able to provide the necessary luminous flux, guarantee stability and absence of flicker. At the same time, there is no hum at all. They are used in apartments, houses, shopping centers, schools, hospitals, banks, etc.
Figure 5. LL in the interior
Using lamps
Most often, recessed fluorescent lamps mounted on the ceiling are used at home. In rooms of small height, overhead lighting sources are used; in rooms with sufficient height, recessed ones are used.
An excellent solution is to install lamps around the entire perimeter as lighting or a modular design involving several interior elements. For example, multi-level ceilings, cornices and canopies.
Fluorescent devices with LED elements look original and harmonious. Wall lamps perfectly illuminate paintings or mirrors in antique frames.
Single-lamp linear lighting sources will reveal the world of plants or aquariums in all its colors. This light is especially useful for the plant sphere, replenishing the lack of sun and promoting plant photobiosynthesis (more information about this can be found on the website https://komnatnyecvety.ru).
- How to install electrical wiring in a wooden house
Urgent entry into a construction SRO
Gasoline power plants
A variety of models of fluorescent lamps allows you to make a good choice for any interior design project. But besides this, you will get an economical and durable lighting source.
Specifications
The technical characteristics of a particular lighting device are encoded in the labeling and indicated on the packaging. This is information about the lamp power, base type, size, color temperature, service life.
Most modern fluorescent devices can operate for 8-12 thousand hours. The indicator depends on the type and size of the device.
Efficiency is expressed as 80 Lm/W, which is significantly more than traditional incandescent lamps. During operation, a moderate amount of heat is generated; the devices are resistant to wind and can operate stably at temperatures from +5 to +55 °C. If a heat-resistant coating is present, the device can be used at +60 °C.
Figure 6. Specifications
The color temperature is usually from 2700 to 6000 K. The efficiency can reach 75%.
How the lamp works
The operating principle of any fluorescent lamp involves applying voltage to the electrodes located inside the bulb. A glow discharge occurs between the electrodes, which is supported by an inert gas or mercury vapor located inside the flask.
Figure 7. Operating principle
The glow discharge generates radiation in the ultraviolet range, which, through a phosphor applied to the flask, is converted into visible light of the desired shade.
To produce ultraviolet radiation, gas-discharge lamps are used. Ordinary glass does not transmit ultraviolet radiation, so special quartz glass is used to make the flask. There is no phosphor coating in this case. The devices are widely used in solariums and for disinfecting premises.
Consultation and recommendations from a specialist
Get a free consultation from our specialist:
- Consultation is free.
- A specialist will respond within: 30 minutes.
- Pickup and showroom in 2022.
- Free shipping
: delivery time is 3-5 days. - Delivery: Transport company, mail and courier.
- Address
: Bagrationovsky proezd, 7 - Opening hours
: daily 9.00-19.00. - Payment upon receipt
is possible , 1 year warranty! - Federal Law-44 We participate in government tenders. We work under a contract. Non-cash payment is possible by card (VISA, Mastercard) and to a bank account
Why do you need a choke in a fluorescent lamp?
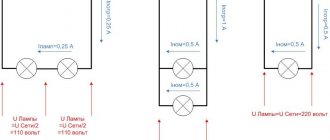
The standard connection diagram for a fluorescent lamp includes the light source itself, a starter and a choke.
The inductor is an inductor with a plate core. It plays the role of a ballast, stabilizing the voltage and preventing the lamp from quickly becoming unusable.
When turned on, the starter receives a significant voltage, several times higher than that required for the lamp. The choke reduces this voltage and only then supplies it to the contacts of the lighting device.
Figure 8. Connection diagram of the inductor to the lamp
The circuit can be supplemented with a capacitor connected in parallel to the power supply, which significantly improves system stability, extends service life and reduces flicker.
How to choose the right one
When choosing a fluorescent lamp, you need to pay attention to:
- temperature conditions of use;
- voltage;
- size;
- luminous flux strength;
- lighting temperature.
Devices with a threaded base and minimal flicker are effective in everyday life.
Figure 9. When purchasing, pay attention to the size of the base
Hallways need strong lighting, so choose lamps with an intense luminous flux. But in the bedroom or living room, compact devices with soft, dim light are appropriate.
In the kitchen it is better to use multi-level lighting, including general and local appliances. It is advisable to select warm shades with a power of at least 20 W.
It will be useful to read: Choosing fluorescent lamps for plants.
Lamp disposal
Fluorescent lamps contain substances harmful to the environment, so waste disposal must be handled as responsibly as possible.
One lamp can contain about 70 mg of mercury, which is quite dangerous. However, there are a lot of similar lamps in landfills, this is a serious problem.
If mercury enters the human or animal body, it quickly provokes poisoning. Storing faulty lamps in the house for a long time is prohibited due to the likelihood of mechanical damage to the bulb with subsequent leakage of harmful substances.
Figure 10. Designation of the place where disposal of devices is permitted
Disposal of devices:
- All lamps are collected and stored in special containers.
- Using a press, the devices are crushed.
- The resulting crumbs are sent to the heat treatment chamber.
- Harmful substances enter the filter, where they remain.
Sometimes gases are exposed to liquid nitrogen and become solid. The resulting mercury is reused.