07/04/2016 master
The modern lighting market today is represented not only by a variety of lamps, but also by light sources. Some of the oldest light bulbs of our time are incandescent lamps (ILVs).
Even taking into account the fact that today there are more advanced light sources, incandescent lamps are still widely used by people to illuminate various types of rooms. Here we will consider such an important parameter of these lamps as heating temperature during operation, as well as color temperature.
Features of the light source
Incandescent lamps are the very first source of electric light that was invented by man. These products can have different power (from 5 to 200 W). But the most commonly used models are 60 W.
Note! The biggest disadvantage of incandescent lamps is their high electricity consumption. Because of this, the number of LNs that are actively used as a light source decreases every year.
Before you begin to consider parameters such as heating temperature and color temperature, you need to understand the design features of such lamps, as well as the principle of its operation. An incandescent lamp, during its operation, converts electrical energy passing through a tungsten filament (spiral) into light and heat. Today, radiation, according to its physical characteristics, is divided into two types:
Incandescent lamp device
- thermal;
- luminescent.
By thermal, which is typical for incandescent lamps, we mean light radiation. The glow of an incandescent light bulb is based on thermal radiation. Incandescent lamps consist of:
- glass flask;
- refractory tungsten filament (part of the spiral). An important element of the entire lamp, since if the filament is damaged, the light bulb stops glowing;
- base
During the operation of such lamps, the t0 of the filament increases due to the passage of electrical energy in the form of current through it. To avoid rapid burnout of the filament in the spiral, air is pumped out of the flask. Note! In more advanced models of incandescent lamps, which are halogen bulbs, instead of a vacuum, an inert gas is pumped into the bulb. The tungsten filament is installed in a spiral, which is fixed to the electrodes. In a spiral, the thread is in the middle. The electrodes to which the spiral and tungsten filament are installed, respectively, are soldered to different elements: one to the metal sleeve of the base, and the second to the metal contact plate. As a result of this design of the electric light bulb, the current passing through the spiral causes heating (an increase in t0 inside the bulb) of the filament, as it overcomes its resistance.
Thermal state of various types of lighting fixtures
Depends on the power consumption of the lighting source, time of use, measurement points (bulb, cartridge, base). The temperature of a 25-watt incandescent lamp is 100, a 75-watt lamp is 250, and a photo lamp bulb is 550 °C.
Key indicators of other luminaire models
Luminescent lamps, which are a tube-shaped hermetic flask filled with mercury vapor and an inert gas, are widely used. An electric charge creates ultraviolet radiation in mercury vapor, which is converted into visible light using a phosphor.
The energy-saving characteristic allows the use of 5-V fluorescent instead of 60-W incandescent. The maximum heating at the base of the bulb of 15-watt fluorescent lamps is 139, over the entire surface - slightly above 70 °C. The disadvantage is the constant, barely noticeable flicker, which negatively affects the human organs of vision.
LED lamps are available in various versions and have low heating due to the aluminum body and heat-dissipating plastic. The temperature of LED lamps is about 65 °C, which sets them apart from incandescent and fluorescent lamps. In addition, the energy consumption of such a lighting source is an order of magnitude lower than an incandescent lamp, and 35% lower than a fluorescent lamp. The operation of LED lamps at low temperatures does not affect the quality of lighting. This allows LED lamps to be used optimally in different climates. Year-round operation negatively affects the intensity of light energy distribution. The lifespan of the lamp depends on the quality of the assembly, its operating conditions, faulty electrical wiring, and the lamp. The LED lamp heats up during operation - about 60% of the electric current is dissipated in the form of heat, which is removed by a radiator made of a material with high thermal conductivity. The lack of significant heating of the Gx53 lamp allows it to be installed on suspended ceilings without fear of fire.
Benefits of operation
Features of the use of LED devices are:
- robust design. The insides of the parting are protected by a durable metal case and shockproof thermoplastic glass;
- environmental cleanliness. The device does not contain mercury or other harmful substances. Completely safe for humans;
- economic benefit. The application allows you to save on power consumption, regular maintenance, and frequent replacement of failed lamps. With continuous operation, they can last about 100,000 hours without failure;
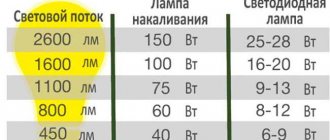
- The optical system ensures uniform illumination and does not create stripes or pulsations. The lighting device does not respond to frequent voltage surges or vibration. LEDs with E27 socket are used to replace LNs. To find out which LED lamps have increased power, you need to use a table that corresponds to the power of light sources (200 W in an incandescent lamp corresponds to 25–30 W in an LED lamp).
The disadvantage of the devices is their high cost. With long-term use, the positive qualities of the devices provide tangible financial savings.
Currently, LEDs are the most widely used - semiconductor devices that convert electric current into light and create optical radiation. The temperature of the LEDs depends on the control current, the quality of the heat sink, and the temperature of the environment. In practice, the temperature of the devices does not exceed 60 °C.
Working principle of a light bulb
Working incandescent lamp
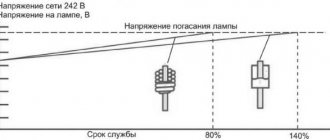
Heating of the LN during operation occurs due to the design features of the light source. It is precisely because of the strong heating during operation that the operating time of the lamps is significantly reduced, which makes them not so profitable today. In this case, due to heating of the filament, t0 of the flask itself increases.
The operating principle of the LN is based on the conversion of electrical energy that passes through the spiral threads into light radiation. In this case, the temperature of the heated thread can reach 2600-3000 oC.
Note! The melting point for tungsten, from which the spiral threads are made, is 3200-3400 °C. As we can see, normally the heating temperature of the filament cannot lead to the beginning of the melting process.
The spectrum of lamps with this structure differs markedly from the spectrum of daylight. For such a lamp, the spectrum of emitted light will be characterized by a predominance of red and yellow rays. It is worth noting that the flasks of more modern LN (halogen) models are not evacuated, and also do not contain a spiral thread. Instead, inert gases (argon, nitrogen, krypton, xenon and argon) are pumped into the flask. Such design improvements led to the fact that the heating temperature of the flask during operation decreased somewhat.
Advantages of ribbons that increase their popularity
A modern artificial light source has advantages over other used light fixtures:
- low power consumption;
- simultaneous ignition of diodes with switching on;
- scanty heat transfer;
- wide range of operating temperatures;
- high light output;
- long service life.
Using the characteristics of currently used light fixtures, we can conclude that the highest power loss due to heating is inherent in incandescent lamps. Their use increases the cost of paying for electricity and purchasing light sources that often fail. The most attractive, economically viable lighting sources are energy-saving lamps. For lighting large areas in front of residential buildings, highways, and supermarket windows, LED strips are the best. Their use additionally creates a festive atmosphere and good mood.
Advantages and disadvantages of the light source
Despite the fact that today the light source market is replete with a wide variety of models, incandescent lamps are still quite common on it. Here you can find products for different amounts of W (from 5 to 200 W and above). The most popular light bulbs are from 20 to 60 W, as well as 100 W.
Range of choice
LN continue to be used quite widely because they have their own advantages:
- when turned on, the light ignites almost instantly;
- small dimensions;
- low cost;
- models with only vacuum inside the flask are environmentally friendly products.
It is precisely these advantages that determine the fact that LNs are still quite in demand in the modern world. In homes and workplaces today you can easily find representatives of these lighting products rated at 60 W and higher. Note! A large percentage of LN use relates to industry. Often powerful models (200 W) are used here. But incandescent lamps also have a fairly impressive list of disadvantages, which include:
- the presence of blinding brightness of light emanating from lamps during operation. As a result, the use of special protective screens is required;
- During operation, heating of the filament, as well as the flask itself, is observed. Due to the strong heating of the flask, if even a small amount of water gets on its surface, an explosion is possible. Moreover, heating of the bulb occurs for all light bulbs (at least 60 W, at least lower or higher);
Note! Increasing the heating of the flask still carries a certain degree of danger of injury. The increased temperature of the glass flask, when touched with unprotected skin, can cause a burn. Therefore, such lamps should not be placed in lamps that a child can easily reach. In addition, damage to the glass bulb can cause cuts or other injuries.
Tungsten filament glow
- high electricity consumption;
- if they fail, they cannot be repaired;
- low service life. Incandescent lamps quickly fail due to the fact that when the light is turned on or off, the filament of the spiral can be damaged due to frequent heating.
As you can see, using LN carries many more disadvantages than advantages. The most important disadvantages of incandescent paws are considered to be heating due to the increase in temperature inside the bulb, as well as high energy consumption. Moreover, this applies to all lamp options with a power from 5 to 60 W and higher.
Design of a modern incandescent lamp
A pear-shaped lighting device familiar to the eye consists of 11 structural elements (from 7 different metals!) involved in the process of introducing electrical energy, conducting it through the filament body, ensuring the strength of the circuit connection, protecting the bulb from destruction when the filament breaks. This thread can have a round cross-section or be made in the form of a flat metal ribbon (or several metal ribbons). Therefore, it is customary to call the energy conversion element in a lamp the filament body.
Incandescent lamp design
The dimensions of the glass bulb (round or pear-shaped) are determined by the deposition rate of the material used for the filament body. The flasks are transparent, matte, opal, white-painted, double and with a partially mirrored surface.
The LON threaded base was proposed by J.W. Swan and standardized for Europe (European lamp bases may not fit US equipment). In household appliances, Edison sockets are used (E14-minion, E27, E40 - according to the outer diameter in mm). There are modifications of the bases connected to the socket by friction, pin, pin or movement with rotation (bayonet connection) - characteristic of the UK. High power lamps (200-300W or more) are produced only with a threaded base.
Important Evaluation Parameters
One of the most important parameters of LN operation is the light coefficient. This parameter has the form of the ratio of the radiation power of the visible spectrum and the power of consumed electricity. For this product this is a fairly small value, which does not exceed 4%. That is, LN is characterized by low light output. Other important operating parameters include:
- light flow;
- color t0 or glow color;
- power;
- life time.
Let's consider the first two parameters, since we figured out the service life in the previous paragraph.
Recommendations
Comments 6
Halogen should get hotter. Its lion's share of radiation is IR...
55W in the fogs is quite a lot, if you throw in 35W halogen and test it. The price for them is truly outrageous, and there is no intermediate one in the form of 45W.
on the Korean, I actually had 27W light bulbs and the light was quite suitable for its purposes (i.e. there is no need to turn the fog lights into an additional low beam)
There is one thing but it’s a question of whether it’s too much or not. in focus is the PTF for the H11 socket, in turn, a halogen lamp with this socket exists only in the form of H11 55W 12V -> the manufacturer initially prepared this PTF for this lamp, it is not possible to insert a lamp with a different socket and lower power there. In Korean, yes, it was H27/1 or H27/2, this lamp is 27W 12V, i.e. there PTF is tailored specifically for this lamp, there is no way to insert another one there. But if we take the H3 lamp as an example, then there are H3 55W and H3 35W, and if, for example, 55W constantly cracks the glass, you can also install 35W. As for converting the PTF into an additional low beam, this is not possible with the help of a lamp, the PTF reflector has a completely different design, but what kind of lamp to put there was initially laid down by the manufacturer, not us...
I’m not talking about this, many people use two-story light, where it is necessary and where it is not necessary. Then they are surprised that the glass is cracked, etc. PTF with its 55W is more likely to be used in courtyards where the lighting is worse, and for its intended purpose in fog.
I drove a Korean car with PTF without a low beam as clean as a DRL, 27W does not shine so brightly.
ah, I misunderstood the message))) but yes, I agree with this... alas, there are plenty of people who drive with all the lamps in the car on.
If you think about the fact that a 35-watt light bulb shines much weaker than a 35-watt xenon, you can come to the conclusion that the energy in a xenon source is spent more on light and less on heat and not measure anything.