- Characteristics 1.1. Light output 1.2. Color temperature 1.3. Ra coefficient
- Types of lamps 2.1. Incandescent lamps 2.1.1. Vacuum 2.1.2. Krypton 2.1.3. Halogen 2.2. LED 2.3. Gas discharge 2.3.1. Mercury 2.3.1.1. DRL lamp 2.3.1.2. DRI lamp 2.3.1.3. Mercury-quartz 2.3.1.4. Luminescent 2.3.2. Xenon 2.3.3. Sodium 2.3.4. Neon, argon lamps
- Conclusion
- Video
Scope of use
Before the advent of energy-saving lamps, incandescent light bulbs were used in industrial areas, household use, etc. This application was due to the ease of installation and operation. But even now these lamps can be seen often:
- Internal and external lighting of rooms, streets, offices.
- Workplace lighting.
- Automotive incandescent lamps.
- A small bulb of this type is also screwed into the flashlights.
- In public transport, trains, etc.
Characteristics
To describe the characteristic, the names of the indicator and its value are used.
These characteristics are shown in the table:
| Name | Index |
| Power, W | household use – 25-150W, other – up to 1000 |
| Filament incandescence, degrees | up to 2000-2800 |
| Voltage, V | 220-330 |
| Luminous efficiency, Lm/1W | 9-19 |
| Size and marking of the base | E 14, E 27, E 40 |
| Base type | Threaded, pin |
| Opening hours, hours | up to 1000 |
| Weight, g | 15 |
The declared working hours are carried out under optimal working conditions. Frequent switching on and off is not allowed.
Device and circuit
The design of an incandescent light bulb is almost the same for all types:
- The main working part is a tungsten helix. Has resistance three times greater than copper material. From it the smelting of the thinnest elements is achieved. The electrodes support this spiral and transfer the current.
- Glass flask. It is filled with inert gas. It is this that prevents the thread from burning and prevents the oxidation of metal elements.
- Basement part. It is present in all types except automobile ones. There is a thread cut into the base; its pitch may differ for each type.
A detailed diagram of the components is shown in the figure:
Operating principle
The principle of operation of an incandescent lamp is to heat a substance through which current flows. The substance is the filament itself, its temperature increases at the moment the electrical circuit is closed. This produces the result of electromagnetic thermal emission. It becomes visible to the eye when it warms up to more than 570 degrees, and a red glow begins.
The filament heats up to 2800 degrees. During the heating process, tungsten is converted into oxide (white surface deposit), which is why neutral gases are pumped into the cavity. When installing a light bulb (screwing it into a socket), the circuit closes and the process of heating the filament occurs, and light is supplied.
Base
Light bulbs with base markings E14, E27, E40 are considered common. Where the number means the diameter of the base itself. Without threaded elements are found in automotive production.
There are countries where the network voltage is different and, accordingly, light bulbs with a different base diameter are used - E12, E17, E26, E39.
Marking
Before purchasing, you need to study the labeling. It is represented by a letter and number combination. The letter marking and meaning are presented in the table:
| Letter marking | Meaning |
| B | double-spiral |
| BO | Bispiral with opal flask filled with argon |
| BC | Bispiral, flask filled with krypton |
| DB | Diffuse with matting inside the flask |
| IN | Vacuum |
| G | Gas-filled |
| ABOUT | Opal flask |
| M | Milk flask |
| Sh | Globular |
| Z | Mirror |
| MO | For local lighting |
The numbers indicate the limits of voltage and power.
Efficiency
These lamps have low efficiency (coefficient of performance). It is expressed by the ratio of radiation power noticeable to humans. When the filament is heated to 2700 K, the efficiency is up to 5 percent. The rest of the energy is spent on infrared radiation, which is not visible to the human eye, but is only felt as heat. If you increase the efficiency to at least 20 percent, it is necessary to increase the heating of the filament to 3400 K.
The light will be twice as bright, but the lamp life will be reduced by 95 percent. Conversely, reducing the voltage will increase the operating period many times. All this is taken into account in the production of emergency lighting, which requires reliability.
Table of the ratio of lumens and watts in a light bulb
Luminous flux is measured in lumens (Lm). In LEDs, light fluxes fluctuate depending on the manufacturer, its product quality, and voltage. The approximate value for one W is 80-150 Lm. The table shows the ratio of Lm and W for incandescent light bulbs in relation to an LED lamp:
| LED lamp, W | Incandescent lamp, W | Luminous flux, Lm |
| 4-5 | 40 | 400 |
| 8-10 | 60 | 700 |
| 10-12 | 75 | 900 |
| 13-15 | 100 | 1200 |
Types of lamps
Incandescent lamps
The most common type of lamps in the recent past, which were used not only on stationary, but also on portable devices such as hand-held flashlights. A tungsten filament placed in a bulb heats up and emits light. The air has been pumped out of the flask, which is why they are called vacuum lamps; based on the composition of the gas in the flask, krypton and halogen lamps are distinguished.
Vacuum
For portable sources they operate at voltages of 12, 24, 36 V. For stationary sources, the voltage corresponds to the city electrical network - 220 V, 50 Hz.
Typically, the upper part of the bulb of such lamps is covered with mirror paint, which directs the light flux downward, which is important for ceiling lighting. The rest of the surface can be transparent or matte to get a softer light.
These lamps have one and most significant drawback, due to which today they are used less and less. This is a low efficiency - only 2-3% of the energy is used for lighting, and the rest is dissipated in the form of heat, which causes a low luminous efficiency - 7-17 Lm/W.
Such lamps use an Edison base or, in other words, an E-base, which varies in diameter in mm, which is indicated in the marking:
- Base E10 – flashlights;
- E14 – small base, “minien”;
- E27 – standard;
- E40 – outdoor lighting.
The advantages of the device include low price (on average from 10 rubles) and ease of installation, for this reason in the near past such lamps were very widespread. Disadvantages besides low efficiency - long-term operation is only 500-1000 hours, as well as fire hazard - use in plastic and wooden structures is not recommended.
Power varies from 5 to 500 W, color rendering is more than 90, color temperature is 2700 K.
Krypton
The inert gas krypton is added to the cylinder of this incandescent lamp. The characteristics are practically no different from a conventional incandescent lamp, with the exception of the increased operating time - approximately 1000-2000 hours. Such lamps are smaller in size and are not sensitive to voltage changes. Due to this, the cost is slightly higher - from 40 rubles.
Halogen
They contain halogen vapors - bromine and iodine, which increases light output and increases operating time up to 4000 hours. Small dimensions allow it to be used in suspended ceiling structures using E and G bases. The power of such lamps is also higher - 20-1500 W, the light output reaches 30 lm/W, and the light temperature is 3700 K.
The disadvantages include sensitivity to voltage surges and susceptibility to contamination - you need to wear gloves for installation, as grease will damage the lamp.
Analogues with infrared coating reflect thermal radiation, due to which they have increased operating time and reduced energy consumption. The cost of halogen lamps starts from 20 rubles.
LED
One of the most important disadvantages of LED elements is their high cost, which starts from 200 rubles. However, in terms of savings, they look quite attractive, as they help reduce costs due to their high operating time - up to 50,000 hours. Such lamps are used to illuminate streets, areas around the house (together with motion sensors), illuminate exhibits in museums and installations.
Used on E and G bases, they have a power of up to 2000 W, excellent luminous efficiency of up to 120 lm/W and good color rendering in the range of 60-89. Light temperature varies between 4-6 thousand K.
Their advantages do not end there - small dimensions and low heating, environmental friendliness, and resistance to damage. However, the beam of light is narrowly focused and towards the end the lamps begin to shine dimly due to the burnout of the LEDs.
Gas discharge
Such lamps work by passing an electric charge through a gas sealed in a tube. Depending on the type of gas, several gas discharge lamps are distinguished.
Mercury
Mercury lamps are toxic; remember that they must be disposed of at hazardous waste collection points.
DRL lamps
Arc mercury fluorescent lamps are not used in apartments and offices, or in any premises where people stay for a long time. Most often they are used to illuminate streets, industrial facilities, etc.
Classic DRLs can now be found less and less often; combined lamps are used more often. Among the minuses, it is worth noting the low color rendering coefficient - varies between 40-59, the tube gets very hot, such a lamp can turn on for up to 15 minutes and this time depends on the ambient temperature - the colder it is, the longer. The DRL lamp is sensitive to voltage fluctuations. When disconnected for a short time, the lamp goes out and returns to work for a very long time.
DRI lamp
A mercury arc lamp with emitting additives is also called a metal halide lamp, since sodium, indium, etc. halides are added to the tube. It is used with E27, E40, R7S sockets. The cost is quite high and starts from 500 rubles, such a lamp lasts up to 10,000 hours, and the light temperature is 6000 K.
Mercury-quartz
Arc mercury tubular or direct mercury-quartz lamps are used in medicine for quartzing rooms for the purpose of air disinfection and in production.
Luminescent
They are otherwise called fluorescent lamps, and the markings on the packaging indicate the spectrum of emission. LB - white light, LD - daylight spectrum, LE - natural, LCB - cold, LTB - warm spectrum. The first number after the marking is the degree of color rendering (6-9), the second number is the color temperature. Used with G-socket.
The advantages include the soft light of the source, low temperature - it is safe to touch the source, and the operating time reaches 30 thousand hours. Of the minuses: the lamp is not silent, the operating temperature is above zero. The lamp takes a long time to turn on and is toxic - it must be disposed of at hazardous waste collection points.
Xenon
As a rule, xenon lamps provide an excellent color rendering index - about 100; depending on the area of use, the price of a light bulb varies from 200 rubles. up to 1-2 thousand rubles. They are used in projectors, photo flashes, car headlights.
Sodium
Sodium vapor lamps provide yellow light and are used on objects that do not require high color rendering - for example, when lighting plants in winter, as well as streets, roads, buildings, etc. They work with E27 and E40 sockets.
Neon, argon lamps
The bulb of neon lamps is filled with an inert gas. Such elements are used to illuminate advertisements, buildings, and various objects and operate for up to 8 thousand hours. The mixture of gases determines the shades of the lamps. The range is wide - from green and blue shades to red and orange.
Types of lamps and their functional purpose
The type of lamp is determined by its structural purpose, functional:
- Normal lighting is the most common type. Designed for general and decorative lighting. The release of this type is limited.
- Decorative - of different sizes, with a figured glass bulb. The appearance is very unusual and beautiful. Therefore, the application is special, decorative.
- Illumination - multi-colored external color. The tone is applied to the inside of the glass bulb. Inorganic pigments are used for coloring. External coloration is very rare. Power limit is up to 25 watts. The more use, the more the color and brightness changes.
- Signal - for illuminating signal devices. Now they have been replaced by LED lamps.
- Mirror incandescent lamps are of a peculiar shape. The inner glass surface is coated with a layer of aluminum. This gives the product a mirror-like appearance. The principle of operation is that the light flux is distributed and collected in a certain area. Application: trading floors, showcases, incubators (heating newborn chicks).
- Transport. Scope of application: car, motorcycle, tractor headlights, lighting. They differ in strength and vibration resistance.
- Double strand. Applicable for car headlights. One thread for low beam, the other for high beam. It is also used in places where constant lighting is required; when one thread burns out, the second one works.
Gas discharge lamps
The physical basis of the glow is an electrical discharge passing through a gas hermetically sealed in a tube.
Depending on the internal contents of the tube, the following types are distinguished:
- Mercury:
- DRL;
- DID;
- luminescent;
- Sodium.
- Neon, xenon, argon, etc.
The glow process must be started using a special ballast mechanism (PRM). Currently, luminaires are produced in which the PRM can be either built into the socket or mounted separately.
Mercury
All mercury-containing devices are highly toxic and require disposal through hazardous waste collection points. Under the Minamata Mercury Convention, the production, export and import of certain mercury-containing lamps will be banned from 2022, along with a similar ban on mercury-containing batteries and thermometers.
DRL lamp (mercury arc fluorescent)
A high-pressure mercury lamp should not be used in rooms where people stay for a long time (apartments, offices).
These lighting devices find their application in street lighting, in automated industrial workshops, and in agriculture.
Minuses:
- Low Ra: 40 – 59.
- Long switching time (up to 15 minutes), depending on the ambient temperature (the colder it is, the longer the illumination process takes).
- The tube gets very hot.
- Sensitivity to voltage changes: with frequent short-term power outages, the device will go out, and then, after being turned on again, return to operating mode for a long time.
Classic DRLs are gradually falling out of use.
Currently, combined type devices are produced for household use (for example, by OSRAM).
DRI lamp (mercury arc lamp with emitting additives)
Also called metal halide.
DRL lamps, into the bulb of which halides of certain metals (sodium, indium, etc.) are added.
Base E27, E40, R7S (base with recessed contact, used primarily in high-intensity lighting installations, after marking the base the length of the bulb is indicated in mm - 78 or 118):
| Base | E27, E40, R7S |
| Power | 20 – 2000 W |
| Luminous output | 70–95 lm/W |
| Color rendering Ra | more than 90 |
| Light temperature | 3500 – 6000 K |
| Price | from 500 rub. |
| Life time | 8,000 – 10,000 hours |
Mercury-quartz lamps (PRK, DRT)
Arc high-pressure heat pumps of the DRT type (arc mercury tubular, obsolete - direct mercury-quartz, PRT) are used in medical equipment (that is, quartz cabinets) for disinfecting air and products. DRTs are also used in some technological processes (such as photopolymerization).
Fluorescent lamps
Or, in other words, fluorescent lamps.
The marking of domestic devices indicates the emission spectrum:
| Marking | Hue |
| LB | white |
| LD | day |
| LE | natural |
| LHB | cold |
| LTB | warm |
After the letter markings there are numbers: the first indicates the degree of color rendering (the higher it is, the more natural the light looks, range 6–9), the next two indicate the color temperature:
- 30 (3000 K) – warm white;
- 35 (3500 K) – white;
- 40 (4000 K) – cool white;
- 54 (5400 K) – daylight;
- 65 (6500 K) – cold daytime;
A G-base is used, which is a socket into which the cylinder is attached using pins. Used for halogen and fluorescent compact lamps (to reduce dimensions). There are a large number of markings for this type of base, so each time it is necessary to compare the type of fastening (it is indicated on the bulb); the bases are not interchangeable.
Pros:
- Low operating temperature (safe to touch).
- Soft light.
- Operating time up to 30,000 hours.
- Modern compact models can be connected to a regular socket (fluorescent lighting devices of the previous generation were made in the form of tubes and required the use of special cylinders for their connection).
Minuses:
- The operation of the source is not silent (the glow process is accompanied by a hum).
- Plus operating ambient temperatures.
- Toxicity - requires disposal to special landfills (free for the population through hazardous waste collection points).
- Quite a long switch-on period during which the light reaches its maximum.
- Sensitivity to frequent on-off switching.
From the listed features it is clear that it is advisable to install such equipment in places where it is necessary to provide illumination for a long time with a minimum number of switches. For example, on the first floors of stairs.
If the mode of use involves a short period of operation with frequent switching on (for example, in bathrooms), it is better to choose another source.
Characteristics:
| Base | G |
| Power | 4 – 140 W |
| Luminous output | 40–90 lm/W |
| Color rendering Ra | from 60 to more than 90 (for various types) |
| Light temperature | 3000 – 6000 K |
| Price | from 100 rub. |
| Life time | 30,000 h. |
Sodium lamps
Sodium vapor discharge lamps
These lamps produce monochrome yellow light. They are used where a high color rendering index is not required: in street and road lighting, for illumination of buildings, etc. High pressure lamps (HPL) are used in agriculture for additional illumination of plants in winter.
There are several markings for domestically produced sodium arc (NA) light sources:
- DNaT – tubular DN;
- DNaS - DN in a light-scattering flask, are a replacement for DRL;
- DNaMT – frosted;
- DNaZ – mirror;
| Base | E27, E40 |
| Power | 50 – 100 W |
| Light outputNLND (low pressure)NLHD | 200 lm/W150 lm/W |
| Color rendering Ra | from less than 39 to 59 |
| Light temperature | 3000 – 6000 K |
| Price | from 200 rub. |
| Life time | 30,000 h. |
Xenon lamps
Allows you to get very good color rendition.
They are used in car headlights, as well as in projectors, flashlights and other lighting devices.
Depending on the application, their price varies from several hundred to several thousand rubles. They have a highly specialized purpose.
Characteristics:
| Base | N (special base for xenon) |
| Luminous output | 50 – 90 lm/W |
| Color rendering Ra | OK. 100 |
| Light temperature | 3000 – 12,000 K |
| Price | from 200 rub. |
| Life time | 3000 |
Neon, argon, etc.
Gas discharge lamps, the bulb of which is filled with an inert gas.
They have a long service life (up to 80,000 hours), and depending on the composition of the gas mixture, they make it possible to obtain light sources of various shades (from blue-green to red-orange). Used for advertising lighting and to indicate network voltage.
Advantages and disadvantages
Incandescent lamps have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Ease of manufacture. Therefore, their price is appropriate.
- Ease of use. There is no need to install additional elements when connecting to the network. Lamps with a power of 150 W are often used in lighting greenhouses. Their light is close to natural. In addition to illumination, they also provide warmth.
- Does not affect human vision.
- No warm-up time required.
- Withstands temperature changes.
- Dispose of as household waste.
- The composition does not contain harmful elements.
Flaws:
- Short service life.
- Dependence on power outages and frequent switching on/off is the cause of filament rupture in incandescent lamps. To eliminate voltage difficulties, stabilizers are installed.
- Low level of efficiency. This is due to the expenditure of most of the energy on heat.
- Fire hazard. Because heat builds up around the lamp.
- Fragility.
- There is a possibility of the housing rupturing, which can lead to injury.
When purchasing an incandescent light bulb, you should take into account all the advantages and disadvantages in order to avoid unpleasant factors during operation.
We recommend watching the video:
Halogen lamps
Halogen lamp with regular base
Halogen lamps are not much different from incandescent lamps; the operating principle is the same. The only difference between them is the gas composition in the cylinder. In these lamps, iodine or bromine is mixed with an inert gas. As a result, it becomes possible to increase the temperature of the filament and reduce the evaporation of tungsten.
Lamp for built-in lamp
That is why halogen lamps can be made more compact, and their service life increases by 2–3 times. However, the heating temperature of glass increases quite significantly, which is why halogen lamps are made of quartz material. They do not tolerate contamination on the flask. Do not touch the cylinder with an unprotected hand - the lamp will burn out very quickly.
Halogen linear lamp
Linear halogen lamps are used in portable or stationary floodlights. They often have motion sensors. Such lamps are used in plasterboard structures.
Halogen compact mirror lamps with G4 base
Compact lighting devices have a mirror finish.
The disadvantages of halogen lamps include sensitivity to voltage changes. If it “plays”, it is better to purchase a special transformer that equalizes the current strength.
Spotlight
Answers to frequently asked questions
Buyers often ask questions that interest them. This is due to the lack of complete information on the packaging.
Service life, cost
An incandescent lamp is affected by many factors that contribute to shortening its life.
Recently, the quality of light bulbs produced has dropped. Often the defect is noticeable immediately. Therefore, most buyers switched to purchasing goods from foreign manufacturers.
You need to pay attention to the socket of the lamp, chandelier, into which the lamp is screwed. In most devices it is made of plastic; when the temperature rises, it melts, cracks and becomes unusable. This causes the light bulb to overheat and fail.
Often a decrease in operating time occurs due to high voltage in the network. In this case, the filament overheats, it decreases in thickness, and the bulb begins to darken. The spiral breaks. If the voltage deviates by just one percent, the lamp life is reduced by 14 percent.
The cost of a light bulb depends on the type, power, and manufacturer. It ranges from 7 rubles to 100 rubles (for home consumption).
How to increase service life
There are several ways to increase the life of a light bulb:
- Dimmer installation. This simple device can extend its service life several times. To do this, after connection, the percentage of lighting is adjusted. When lighting storerooms, entrances, etc., it is enough to set the lamp performance to 75 percent.
- Since failure is often caused by voltage surges, it is enough to install a stabilizer.
What gas is in the lamp
The product flasks cannot contain air or any gas. There should only be inert gas (xenon, krypton, argon). This is due to the fact that the temperature of the coil heats up to more than 2000 degrees.
At these temperatures, the tungsten filament will react with all gases except inert ones. Helium and neon are expensive, so they are not used.
Temperature
The light temperature depends on the type of gas injected. Thus, a gas-free vacuum environment promotes heating to 2700 K. In this case, warm white light is emitted. When heated to 4200, natural white light is emitted. When pumping xenon, krypton halogen, the heating temperature is from 4000 to 6400 K. At the same time, cold white light is emitted.
What causes the spiral to break?
Tungsten filament is very thin and fragile. Its breakage occurs due to a decrease in diameter due to the evaporation of the material when exposed to high temperature. Also, the thread often breaks due to mechanical action - shaking.
Light flow
The purpose of the luminous flux is lighting. Created by conversion of thermal energy. The unit of measurement is Lumen (Lm). The increase in flux depends on the lamp power
Incandescent lamps of the same power emit different luminous flux. The higher the voltage, the higher the luminous flux value.
How much does it consume?
Power 60 W - energy consumption will be 60 W or 0.06 kilowatts in 1 hour Power 95 W - consumes electricity 95 W 0.095 kilowatts in 1 hour Power 100 W - will consume 100 or 0.1 kilowatts of electricity in 1 hour.
We recommend watching the video:
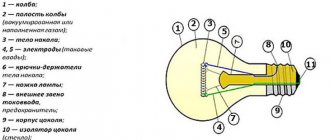
Structure
A typical lamp consists of the following structural elements:
- flask;
- vacuum or inert gas pumped inside it;
- filament;
- electrodes - current terminals;
- hooks needed to hold the filament;
- leg;
- fuse;
- base, consisting of a housing, an insulator and a contact on the bottom.
In addition to standard versions made of conductor, glass vessel and leads, there are lamps for special purposes. Instead of a base, they use other holders or add an additional bulb.
The fuse is usually made of an alloy of ferrite and nickel and is placed in the gap on one of the current terminals. Often it is located in the leg. Its main purpose is to protect the flask from destruction in the event of a thread break. This is due to the fact that if it breaks, an electric arc is formed, leading to the melting of the remnants of the conductor, which fall on the glass bulb. Due to the high temperature, it may explode and cause a fire. However, for many years the low efficiency of fuses has been proven, so they are used less frequently.
Flask
The glass vessel is used to protect the filament from oxidation and destruction. The overall dimensions of the flask are selected depending on the deposition rate of the material from which the conductor is made.
Gas environment
If previously all incandescent lamps without exception were filled with vacuum, today this approach is used only for low-power light sources. More powerful devices are filled with inert gas. The molar mass of the gas affects the heat emitted by the filament.
Halogens are pumped into the bulb of halogen lamps. The substance with which the filament is coated begins to evaporate and interact with the halogens located inside the vessel. As a result of the reaction, compounds are formed that decompose again and the substance returns to the surface of the thread. Thanks to this, it became possible to increase the temperature of the conductor, increasing the efficiency and service life of the product. This approach also made it possible to make the flasks more compact. The design flaw is associated with the initially low resistance of the conductor when applying electric current.
Filament
The shape of the filament can be different - the choice in favor of one or the other depends on the specifics of the light bulb. They often use a thread with a round cross-section, twisted into a spiral, and much less often - ribbon conductors.
A modern incandescent lamp is powered by a filament made of tungsten or an osmium-tungsten alloy. Instead of conventional helices, bi-helices and tri-helices can be twisted, which is made possible by repeated twisting. The latter leads to a decrease in thermal radiation and an increase in efficiency.