What is electric current
The movement of free carriers of electric charges in a vacuum or substance in a fixed direction is called electric current. Free carriers in metals are electrons, in liquids or gases they are ions. The name "current" has two interpretations. The first one denotes the very movement of the electric charge in the conductor, the second one – an estimate of the number of electrons passing through the conductor in 1 s. Its strength can be determined by Ohm's Law. The formula used for this is:
I=U/R,
where U is voltage, V; R – resistance, Ohm.
DC and AC current
The socket has direct or alternating current
Electrons in conductors move from plus to minus. The movement is uniform, always with a constant value. If you ask yourself what currents are considered constant, you first need to have a good idea of where the current flows.
Attention! The direction of current is considered to be the direction in which positively charged particles move: from plus to minus. Although the path of free electrons runs from minus to plus.
DC direction
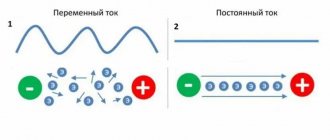
This means that direct current is the directed movement of charged particles that carry a positive charge and do not change their magnitude and direction over time. All other currents are variable. This is their difference.
Alternative Current – AC, this is how alternating current is designated on devices. Direct Current – DC is a clear designation for direct current.
Direct and alternating current
Types of electric current in everyday life
In order to determine what current is in the outlet, there is no need to study this issue at the university level. There are only two types of voltage - constant and alternating.
The answer to the question of whether the current in an outlet is alternating or direct is clear now, but at the beginning of the twentieth century, two great inventors argued on this topic - Nikola Tesla, who supported the idea of alternating current, and Thomas Edison, who advocated direct current. During this period, the outlet could have either direct or alternating current, depending on the country and the building's power supply.
In the end, Tesla's point of view won, and direct current is now used mainly in electric drives, which are powered from an alternating current network through diode or thyristor rectifiers.
Interesting! Some buildings in San Francisco retained DC-powered elevators in 2012. This equipment and the supply of such voltage to buildings were preserved as a rarity. In New York, such installations operated until 2007.
D.C
The international symbol for this DC voltage is Direct Current (direct current), and the symbol on electrical diagrams is “—” or “=”. The magnitude and polarity of this type of voltage are unchanged, and the current strength changes only when the load changes. This type of electric current is produced by batteries, batteries and elements of solar power plants.
The engines of trams, trolleybuses and other electric vehicles operate from the DC network. These electric motors have better traction characteristics than AC motors.
Information! Most electronic circuits operate on DC voltage, but they are powered by AC power through a built-in or external power supply with a rectifier.
Edison's ideas
Modern life cannot be imagined without electricity.
In order for it to serve civil and industrial purposes, it must not only be produced, but also delivered to the consumer. The first who decided to produce electricity in large quantities and transport it to factories, offices and households was the American entrepreneur Thomas Edison, one of the most influential inventors in the world. To implement his idea, he designed and tested DC steam generators, electricity meters and distribution network elements. Carrying out the first electrification of lighting was not easy at that time. The owners of gas companies viewed Edison as a dangerous competitor who could jeopardize the existence of their enterprises. But nothing could stop the inventor. Neither the colossal cost of laying cables in the sidewalks, nor accidents during testing prevented him from launching the first lighting network of five thousand lamps in September 1882.
After 5 years, more than 50 Edison power plants were already operating. Despite his great success, the inventor was unable to expand the geography of his electrical networks throughout the world. Residents of the areas where the power plants were located complained about smoke and soot, and forced the closure of Edison's production facilities. Thus, the first generation of coal-fired power plants eventually ceased operation, giving way to thousands of new ones generating AC.
What is DC current and what does it mean?
It is customary to call an electric current constant, the strength and direction of which do not change. In electrical engineering, a mixed mode with a predominant constant component is also called constant if the fluctuations are negligible for the intended effect, or if the fluctuations are the result of load fluctuations. Then the arithmetic mean is considered as direct current.
Power lines carry current to homes and businesses
For your information! In English it is usually denoted as Direct Current, or DC for short, which is also used for constant voltage. Alternating current is translated as Alternating Current, which means AC voltage.
"Pure" and "pulsating" direct currents
What is the DC voltage?
With DC voltage, electrons always move in one direction. The voltage source thus always has the same polarity. However, the voltage level does not always have to be the same. The classic energy source for generating constant voltage is a conventional battery, in which the voltage level decreases during discharge.
Movement of electrons at constant voltage
In addition, most power supplies also generate DC voltage, although they are supplied with AC voltage. In the case of stabilized power supplies, in addition to the flow direction, great importance is also given to the AC voltage level, which can vary depending on the voltage, but will always have the same polarity.
Note! AC voltages supplied by mains transformers and generators can be converted by rectifiers. Then an electrical voltage arises that varies in magnitude, but not in sign.
Circuits with direct and alternating current
The AC voltage component can be reduced by connecting a large enough smoothing capacitor in parallel or in series with the smoothing coil so that only a small residual ripple remains. The larger the capacitor capacitance or coil inductance, the smaller the peak value of the imposed AC voltage will be.
Scope of application of DC current
Direct current has wide technical applications in electronics, solar energy generation and partly in railway power supply. Almost all electronic circuits (for example, in computers) work with them. If electronic devices are powered by power supplies other than batteries or accumulators, the rectifier in the power supply provides a constant value. So among the most popular devices are cell phones, laptops and computers.
Circuit boards in a laptop
Solar cells can also only generate DC. If photovoltaic systems are to feed the electrical energy they produce into the public grid, an inverter must be connected between them.
Solar panels
Electric vehicles that have recently become widespread use DC for their operation. It is also used in above-ground and underground public transport, such as trams, trolleybuses and metro trains.
Thus, AC and DC currents have significant differences. It is important to take this into account when connecting this or that equipment, and also so as not to confuse the scope of application.
Alternating current
The international designation for this AC voltage is Alternating Current, and the symbol on electrical diagrams is “~” or “≈”.
The magnitude and polarity of alternating current in the network changes all the time. The frequency of these changes is 50Hz in Europe and some other countries and 60Hz in the USA. Most household and industrial electrical appliances are manufactured to be powered by alternating voltage.
Almost all electricity used in everyday life and industry is variable. For transmission over long distances, it is increased using transformers, and at the end point of the line it is reduced to the required value. This allows you to reduce the cost of power lines and losses. In order to eliminate voltage fluctuations, stabilizers are installed for critical devices.
With increasing voltage and constant transmitted power, the current strength and cross-section of the wires decrease proportionally. If the voltage is not increased, then large cross-section cables must be used to supply electricity to the consumer, and transmission over long distances will be impossible. That's why the outlet has AC current.
There are two contacts in a home socket - phase and neutral. In some cases, a grounding cable is added to them. This single-phase voltage is part of a three-phase system. It includes three identical networks. The voltage in these networks is phase shifted by 120° relative to each other.
At first this system was six-wire. Nikola Tesla invented it in this form. Later, M. O. Dolivo-Dobrovolsky improved this scheme and proposed transmitting three-phase voltage over three or four wires (L1, L2, L3, N). He also showed the advantages of a three-phase power supply system over schemes with a different number of phases.
General concept of alternating current
Since alternating current in the general case changes in an electrical circuit not only in magnitude, but also in direction, one of the directions of alternating current in the circuit is conventionally considered positive, and the other, opposite to the first, is negative. In accordance with this, the magnitude of the instantaneous value of the alternating current is considered positive in the first case, and negative in the second case.
The strength of alternating current is a scalar quantity, its sign is determined by the direction in which the current flows in the circuit at the given moment in time - positive or negative.
The magnitude of the alternating current corresponding to a given moment in time is called the instantaneous value of the alternating current.
The maximum instantaneous value of the alternating current that it reaches during its change is called the amplitude.
A graph of alternating current strength versus time is called an alternating current diagram.
Expanded diagram of alternating sinusoidal current
The figure shows an expanded diagram of alternating current changing over time in magnitude and direction. On the horizontal axis - the time axis - time intervals are plotted on a certain scale, and on the vertical axis - the current strength, and the upward direction is positive, and the downward direction is negative.
AC voltage
As we know from physics lessons, current is the movement of charged particles that occurs under the influence of an electromagnetic field, potential difference and tension. The main characteristic of any voltage is its dependence on time. Based on this, a distinction is made between constant and variable quantities. The value of a constant practically does not change over time, but the value of a variable changes.
In turn, a variable characteristic can be periodic or non-periodic. Periodic is a voltage whose values are repeated at regular intervals. The non-periodic is capable of changing at any period of time.
Voltage in an alternating circuit is a parameter that changes its value over time. To simplify explanations, sinusoidal harmonic alternating voltage will be considered in the following.
The minimum time during which a variable repeats is called a period. Absolutely any periodic quantity can be written as a dependence on any function. If time is t, then the dependence will be denoted by F(t). Thus, any period in time has the form: F(t+-T) = F(t), where T is the period.
The physical quantity that is the reciprocal of the period is called frequency. It is equal to 1/T. Its unit of measurement is the hertz, while the unit of measurement of the period is the second.
f = 1/T, 1 Hz = 1/s = s to the minus first power.
Important! The most common functional dependence of a variable network is in the form of a sinusoid. That is why it was taken as the basis for this material.
It is known from mathematics that a sinusoid is the simplest periodic function, and with its help, any other periodic functions can be represented from several sinusoids with multiple frequencies.
Sinusoidal voltage in absolutely any period of time can be described by the instantaneous characteristic: u = U * sin(ωt + φ), where ω = 2πf = 2π/T, where U is the maximum voltage (amplitude), ω is the angular rate of change, φ is the initial phase, which is determined by the displacement of the function relative to the zero coordinate point.
Part (ωt + φ) is a phase that characterizes the voltage value in a specific period of time. From this it turns out that amplitude, angular velocity and phase are the main characteristics of variable networks that determine their values in any time interval.
Important! When considering a sine function, the phase is often taken to be zero. In practice, they also often resort to some other parameters, including effective and average voltage, shape factor
AC generation
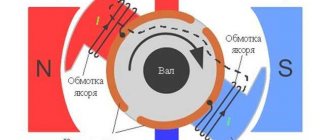
The simplest alternating current generator: if a flywheel with several pairs of permanent magnets installed in it is rotated around a wire coil wound on a magnetic core made of transformer steel, then a sinusoidal EMF will be induced in the coil (conventionally shown as one turn), and when a load is connected, an alternating current will appear in the electrical circuit current.
It is used on vehicles (mopeds, light motorcycles, snowmobiles, jet skis, as well as outboard boat motors), works in conjunction with a rectifier and voltage regulator (see Magdino). Main article: Alternating current generator The operating principle of the alternating current generator is based on the law of electromagnetic induction - the induction of an electromotive force in a wire circuit (wire frame) located in a uniform rotating magnetic field.
According to the number of phases, alternating current generators are:
- three-phase generators are the main type of powerful industrial generators; See also three-phase power supply system, three-phase motor, three-phase alternating current automobile generator.
- single-phase generators, used, as a rule, in low-power gasoline power plants, built into internal combustion engines of mopeds, light motorcycles, snowmobiles, jet skis, and outboard boat engines; See also capacitor motor, single-phase motor.
- two-phase generators are much less common compared to single-phase and three-phase.
AC networks
Four-wire power line 220/380 V; such power lines are common in single-story residential areas and in rural areas. The two bottom wires are the wired radio broadcast network.
Voltage conversion in electrical networks Wiring diagram for a three-phase network in multi-apartment residential buildings.
Electricity producers (hydroelectric power plants, thermal power plants, combined heat and power plants, nuclear and other power plants) generate alternating current of industrial frequency (in Russia - 50 Hz), with a voltage of about 10 - 20 kV.
Then the electric current flows to transformer substations, which are located next to power plants, where the electrical voltage increases.
High voltage alternating current is transmitted to consumers via power transmission lines (PTL). Increasing the voltage is necessary in order to reduce losses in power line wires (see Joule-Lenz law, as the electrical voltage increases, the current in the electrical circuit decreases, and heat losses decrease accordingly).
The highest voltage power line in the world, Ekibastuz-Kokchetav, operated at a voltage of 1 million 150 thousand volts.
At the other end of the power line there is a step-down transformer substation, where high-voltage alternating current is reduced by transformers to the value required by the consumer.
In the vast majority of cases, three-phase current is transmitted through power lines, but there are direct current power lines, for example, the Volgograd-Donbass high-voltage direct current line, the Ekibastuz-Center high-voltage direct current line, mainland South Korea - Jeju Island and others. The use of direct current allows you to increase the transmitted electrical power, transfer electricity between power systems using alternating current of different frequencies, for example, 50 and 60 hertz, and also not synchronize neighboring power systems, as was done on the border of the Leningrad region with Finland (see box DC Vyborg - Finland).
In Russia, general purpose electrical networks use three-phase current with a phase-to-phase voltage of 380 Volts.
The quality of electrical energy - its electrical voltage and frequency must be strictly observed.
Residential buildings (on rural streets) are supplied with four-wire (three phase wires and one neutral (neutral) wire) power lines (overhead or cable power lines) with a phase-to-phase voltage of 380 volts (since 2003, 400 volts according to GOST 29322-2014). A phase wire and a neutral wire are supplied to a separate apartment (or rural house), the electrical voltage between the “phase” and “zero” is 220 volts (since 2003, 230 volts according to GOST 29322-2014). You can determine which wire is which using a phase indicator.
For example, phase “A” is supplied to the first apartment, phase “B” to the second apartment, phase “C” to the third apartment, and so on.
Current differences
Ignorance of the differences leads to incorrect connection of voltage consumers to power supplies. This causes damage to appliances or worse, life-threatening situations.
Lethal current for humans
To clearly understand which current is called alternating and which is constant, you need to compare the parameters.
When comparing the characteristics of these two types of electricity, the differences are distinguished:
- Physical - with alternating current, the strength and direction depend on time. In a household network, the pulsation frequency is 50 Hz. The polarity changes in a sine wave 50 times per second. Direct current charge carriers do not change direction.
- Constructive - DC has “+” and “–” on its terminals or contacts, while AC has “zero” and “phase” on its electrodes. In the case of a three-phase network, there are 4 contacts: one “zero” and three “phase”.
- The principle of generation is that direct current is obtained as a result of electrolytic and chemical oxidation reactions, the operation of direct current generators and solar panels. Alternating current is produced by three-phase generators.
- In conversion - both types are obtained by converting one into the other using semiconductor rectifiers and inverters.
For information. There are two main standards for frequency and voltage in the consumer AC network in the world. The European standard is 50 hertz, 220-240 volts, and the American standard is 60 hertz, 100-127 volts.
Story
Does the outlet have direct current or alternating current?
Electricity is relatively rare in nature: it is generated by only a few animals and exists in some natural phenomena. In their quest to artificially generate electron flow, scientists realized that it was possible to force electrons to flow through a metal wire or other conductive material, but only in one direction, as they were repelled from one pole and attracted to the other. Thus, batteries and DC generators were born. The invention is attributed mainly to Thomas Edison.
At the end of the 19th century, another famous scientist, Nikola Tesla, was developing ways to produce alternating current. The main reasons for work in this area were the discovered shortcomings of direct current when transmitting electricity over long distances. It turned out that for alternating current it is much easier to increase the voltage of transmission lines, thereby reducing losses and making it possible to transport large volumes of electrical energy, but effectively increasing the voltage on direct current lines was not feasible in those days.
To produce alternating current, Tesla used a rotating magnetic field. If the MF changes direction, the direction of the electron flow also changes and an alternating current is generated.
The change in direction in the electron flow occurs very quickly, many times per second. Frequency measurements are made in hertz (equal to cycles per second). Thus, alternating current at a frequency of 50 Hz can be thought of as performing 50 cycles per second. In each cycle, the electrons change direction and return to their original direction, so the flow of electrons changes direction 100 times per second.
Advantages of AC
AC symbol
Rechargeable batteries are practical as a source of constant electricity. However, they cannot endlessly supply current collectors with energy without recharging. Therefore, the creation of time-varying current and its delivery to the consumer are the main tasks of the country’s power system. The advantages of this type include:
- ease of conversion from one voltage value to another;
- permissibility of long-distance transmission via power lines to distribution networks;
- the ability to implement three-phase power supply schemes;
- focus on consumers of production enterprises designed for alternating current power supply.
It is easier to reduce or increase the AC voltage value. To do this, you just need to pass it through a transformer. The high efficiency of this converter is 99%, power loss is only 1%. The transformer, having separate voltage windings, also separates high voltage from low, which makes it possible to separate installations up to 1000 V and over 1000 V.
Nuclear and hydroelectric power plants are located in places remote from the central areas where consumers are located. Therefore, the voltage of the extracted electricity is increased to hundreds of kW in order to reduce losses during transportation, and transmitted via power lines to the desired location, where it is lowered again.
Hydroelectric power station - hydroelectric power station
By using three-phase alternating voltage, the performance of the power system structure is increased. Transmitting the same power in a three-phase network requires fewer conductors, unlike a single-phase line.
Important! If we compare two transformers of the same power, then the dimensions of a single-phase transformer are larger than those of a three-phase one. Asynchronous motors are cheaper to manufacture than DC motors. They do not have a commutator and brushes; in terms of power, with the same dimensions, asynchronous motors are 2-3 times faster than constant motors.
Where is it used and what are the advantages of AC and DC current?
Various tasks may require the use of both AC and DC power. Each type of current has its own disadvantages and advantages.
Alternating current is most often used when there is a need to transmit current over long distances. It is more expedient to transmit such current from the point of view of possible losses and the cost of equipment. That is why most electrical appliances and mechanisms use only this type of current.
Residential buildings and enterprises, infrastructure and transport facilities are located at a distance from power plants, so all electrical networks are alternating current. Such networks power all household appliances, industrial equipment, and train locomotives. There are an incredible number of devices operating on alternating current, and it is much easier to describe those devices that use direct current.
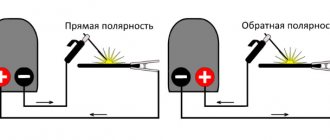
Direct current is used in autonomous systems, such as on-board systems in cars, aircraft, ships or electric trains. It is widely used in powering microcircuits of various electronics, in communications and other equipment where it is necessary to minimize the amount of interference and ripple or eliminate them completely. In some cases, such current is used in electric welding work using inverters. There are even railway locomotives that run on DC systems. In medicine, this current is used to introduce drugs into the body using electrophoresis, and for scientific purposes to separate various substances (protein electrophoresis, etc.).
Disadvantages of DC
In addition to the fact that sources of this type of current have a complex design, they are more difficult to operate. With an efficiency of 94%, the maximum power of these machines is no higher than 20 MW. There are also other disadvantages:
- complex circuits are used to increase or decrease voltage;
- motors designed to consume such electricity are also structurally complex and expensive;
- decoupling low and high voltage requires complex solutions.
It is not possible to completely abandon such sources and consumers, since they are in demand and have their own advantages.
What is the current in the outlet - direct or alternating?
People who are more or less familiar with electrical engineering can easily answer the question of what current is in the outlet. Of course it's variable. This type of electricity is much easier to produce and transmit over long distances, and therefore the choice in favor of alternating current is obvious.
There are two types of current - direct and alternating. To understand the difference and determine whether the outlet has direct or alternating current, you should delve into some technical features. Alternating current has the property of changing in direction and magnitude. Direct current has stable qualities and direction of movement of charged particles.
Alternating current comes out of the power plant generators with a voltage of 220-440 thousand volts. When approaching an apartment building, the current is reduced to 12 thousand volts, and at the transformer station it is converted to 380 volts.
Advice
The voltage between phases is called linear. The low-voltage section of the step-down substation produces three phases and a zero (neutral) wire. Energy consumers are connected from one of the phases and the neutral wire.
Thus, single-phase alternating current with a voltage of 220 volts enters the building.
The distribution diagram of electricity between houses is presented below:
In the home, electricity is supplied to the meter, and then through automatic machines to the boxes of each room. The boxes contain wiring throughout the room for a couple of circuits - electrical outlets and lighting equipment.
The machines can be provided one for each room or one for each circuit.
Taking into account how many amperes the outlet is designed for, it can be included in a group or connected to a dedicated circuit breaker.
Alternating current accounts for approximately 90% of all electricity consumed. Such a high specific gravity is due to the peculiarities of this type of current - it can be transported over considerable distances by changing the voltage at substations to the required parameters.
Sources of direct current are most often batteries, galvanic cells, solar panels, thermocouples.
Direct current is widely used in local networks of automobile and air transport, in computer electrical circuits, automatic systems, radio and television equipment.
Direct current is used in contact networks of railway transport, as well as on ship installations.
The diagram below shows the fundamental differences between direct and alternating currents.
Home electrical network parameters
The main parameters of electricity are its voltage and frequency. The standard voltage for home electrical networks is 220 volts. The generally accepted frequency is 50 hertz. However, in the USA a different frequency value is used - 60 hertz. The frequency parameter is set by the generating equipment and is unchanged.
It will be interesting➡ How to check the voltage with a multimeter?
The voltage in the network of a particular house or apartment may be different from the nominal value (220 volts). This indicator is influenced by the technical condition of the equipment, network loads, and substation load. As a result, the voltage may deviate from the specified parameter in one direction or another by 20–25 volts.
Current load
All sockets have a certain marking, by which you can judge the permissible current load. For example, the designation "5A" indicates a maximum current of 5 amperes. Acceptable indicators must be observed, since otherwise the equipment may fail, including fire.
The markings on the sockets are shown in the figure below:
All legally sold electrical appliances are accompanied by a passport indicating the power consumption or current load rating.
The largest consumers of electricity are household appliances such as air conditioners, microwave ovens, washing machines, electric stoves and ovens.
For normal operation, such devices will need an outlet with a load of at least 16 amperes.
note
If the documentation for electrical household appliances does not contain information about the consumed amperes (current strength in the outlet), the required values are determined using the electric power formula:
The power indicator is in the passport, the network voltage is known. To determine electricity consumption, you need to divide the power indicator (indicated only in watts) by the voltage value.
Disadvantages of AC
When transmitting the energy of a current changing direction over long distances, difficulties arise. The creation of the Unified Energy System revealed a number of shortcomings:
- the capacity of cable lines is low due to the capacitance between the conductors and the ground;
- when merging and looping system branches located at large distances from each other, it is impossible to synchronize stations;
- The threshold stability limit required for coordination ends at line lengths exceeding 500 km, which requires an increase in voltage to 450 kV, which leads to an increase in the cost of terminal equipment.
For your information. When the voltage increases, a corona discharge occurs near the overhead lines. This is the process of ionization in conductors with a small radius. To prevent electricity from draining in this case, it is necessary to increase the diameter of the wires, this leads to an increase in the cost of the line.
Centralized and decentralized energy supply
Large power plants have long dominated the electricity supplier segment by centrally distributing their energy to surrounding areas. But the rise of renewable energy is causing the grid to become more decentralized and more local, with electricity often consumed where it is generated.
The advantages of alternating current are of no use here. But even over long distances, alternating current is not ideal. Losses during the transmission of electricity over a distance have increased significantly. That's why China is building complex power grids based on high-voltage direct current (also known as HVDC) transmission lines that can transfer large amounts of power from hydroelectric dams in the interior to bustling cities on the coast. In Germany, the government also plans to build two similar lines to transfer excess wind energy from the coast to the south. HVDC transmission lines are twice as expensive as conventional systems. However, due to lower energy losses, these costs pay for themselves from a distance of about 400 kilometers, or just 60 kilometers in the case of floating wind farms.
HVDC lines are now extremely reliable. High-performance electronics have enabled advances in energy conversion, allowing direct currents of up to 800,000 volts to be converted without a transformer.
Electricity in homes and factories is distributed either through low-voltage power networks, through plug sockets, or through three-phase current connections. An increasing number of electrical appliances require direct current. Computers, LED lights, and other electronic devices operate on direct current and previously required a transformer to convert. Electric vehicles will be added to this list in the coming years. Industrial equipment is increasingly using DC-link frequency converters for speed control. DC networks with central voltage conversion will make all these transformers unnecessary. At the moment, there are already pilot projects in the automotive industry in which complex production equipment operates exclusively with direct current. They also have batteries for short-term energy storage.
Advantages of DC
What qualities make direct current irreplaceable? The advantages include:
- there is no reactive power in the circuits, which leads to losses;
- There is no need to synchronize generators running in parallel;
- increased range of energy transmission in large volumes;
- safety for humans in contact with live conductors.
Added to the advantages is that electricity, such as direct current, flows across the entire cross-section of the conductor, so power losses are minimal.
Charge density over the cross section of the conductor
Multiphase power supply system
Tesla noticed that Edison's DC power stations were inefficient, and Edison had already built up the entire Atlantic coast of the United States with them. To overcome the disadvantages of direct current, it was necessary, according to Tesla's idea, to use alternating current. Such a system is called multiphase because motors and generators have several phases (see explanations above).
Edison lamp
Edison's lamps were weak and inefficient when using direct current. This entire system had one major drawback in that it could not transport electricity over distances of more than 3 km due to its inability to vary the voltage to the high level required for long distance transmission. Therefore, DC power plants were installed at intervals of 3 km.
Scheme of operation of multiphase power supply systems
Alternating current, as written above, could reach high voltages and therefore could be transmitted over vast distances (go outside the house and look at the nearest high-voltage power lines, this is it).
When Edison learned that he had such a powerful competitor, he realized that he could lose his DC empire. This is exactly how the war began between Westinghouse and Tesla against Edison, which will be called the war of currents. Edison began strenuously trying to discredit Tesla's invention by showing that alternating current was more dangerous to life than direct current.
It is also worth noting that when Tesla came to the USA, he first offered his developments to Edison, but he called it all nonsense and madness.
Edison shocked animals with alternating current in public to infuriate them and prove that this type of current was dangerous. One day Edison learned about a doctor's idea about using alternating current to kill people. Realization was not long in coming. This is how the electric chair was invented, which was first used on William Kemmler, who was guilty of murdering his mistress.
For a long time, Edison could not come up with a name for his new invention, but he liked the word “Westinghouse” most of all, although none of them, as we now see, caught on.
The history of the appearance and “war of currents”
Nikola Tesla and Thomas Edison did not live to see the moment when a representative of the Consolidated Edison company put an end to the struggle between the two technologies. Alternating electric current won the day. In 2007, the company's lead engineer disconnected the cable representing New York City's DC power.
Back in 1882, Serbian scientist Nikola Tesla figured out how to apply the effect of a rotating electromagnetic field. At that time, Edison had already commissioned 2 power plants generating direct current, and organized the production of cables, lighting devices and dynamos. Tesla at one time worked for Edison's company and repaired DC machines. Edison promised Nikola to pay for engine modernization projects, but refused to pay remuneration for the work done. Tesla sold the patents of his inventions to George Westinghouse, president of Westinghouse Electric Corporation, for $1 million. The first power plant with 500 V of polarity-changing electricity was launched in 1886. The war of currents continued for more than a century.
Current voltage - what does it mean?
This term can be heard very often in colloquial speech. Current, in this case, is electric current. It turns out that current voltage is the voltage of electric current. It's just how we shorten it. As I said above, current can be alternating or constant. Direct current and constant voltage are synonymous, as are alternating current and alternating voltage. It turns out that the phrase “current voltage” tells us what the voltage is between two points or wires in an electrical circuit.
For example, to the question “what is the current voltage in the socket” you can safely answer: alternating current 220 Volts,” and to the question “what is the current voltage of a car battery,” you can answer “12 Volts DC.” So don't be scared).
Sources of direct electric current
To obtain it, a special generator is used, the operation of which is based on the law of electromagnetic induction - EMF. If you rotate a metal frame, an EMF will arise in the area of the electromagnetic field, and electricity will flow through the frame.
DC generator
Attention! An increase in EMF is obtained by increasing the field strength or frame rotation speed. Reducing the pulsation of the resulting movement of electricity is achieved by adding the number of frames.
Non-mechanical producers of electricity of a constant nature:
- solar panels;
- galvanic cells;
- thermochemical elements.
Energy batteries from this group have a limited lifespan and require periodic recharging.
DC power supplies
Practical significance of the differences
This is what it is, alternating and direct current. It's not that difficult to figure out what the difference is. There is a difference and a very big one. A DC source will not allow you to connect a welding, or any other, transformer. When calculating insulation or capacitors, the maximum voltage value, rather than the effective voltage, is taken for breakdown. After all, the thought may certainly arise: “why do you need 400-volt capacitors in a 220-volt network?” Here is the answer, in a 220 V network the voltage reaches 380 V during normal operation, and in the event of a minor failure, 400 V is not the limit.
People have long been accustomed to the benefits of electricity and many do not care what current is in the outlet. On the planet, 98% of electricity generated is alternating current. It is much easier to produce and transmit over significant distances than constant. In this case, the voltage can change many times in value down and up. The current strength significantly affects the losses in the wires.
Transmission of electricity over a distance
The parameters of the home network are always known: alternating current, voltage 220 volts and frequency 50 hertz.
They are mainly suitable for electric motors, refrigerators and vacuum cleaners, as well as incandescent lamps and many other devices. Many consumers operate at a constant voltage of 6-12 volts. This especially applies to electronics. But the power supply of the devices must be of the same type. Therefore, for all consumers, the current in the outlet must be variable, with the same voltage and frequency.
Application
Use in electronics to power circuits is not the end use case for DC. Direct current has found use in the following cases:
- in electrolysis – production of metals from salts and solutions on an industrial scale;
- galvanoplasty and galvanization - metal coating of electrically conductive surfaces;
- in welding work – work with stainless steel;
- in transport - engines of trams, electric locomotives, trolleybuses, icebreakers, submarines;
- in medicine – the introduction of drugs into the body through electrophoresis.
For information. In the USSR, the electrification of the railway with direct current began on the sections of Baku - Suramsky Pass and Sabuchini. Before the Great Patriotic War, the voltage was 1.5 kV, then it was transferred to 3 kV. In total, half of the railway lines operated from this type of current.
Alternating current
Forced harmonic electromagnetic oscillations are a sinusoidal current. Oscillations occur at a frequency of 50 Hz per second. The voltage and current per period are on average zero.
How does direct current differ from alternating current, and what is its path from source to consumer?
Direct current does not oscillate; this is where direct and alternating current differ. The supply of Direct Current - DC to consumers also occurs through wires and cables. The Volgograd-Donbass power lines are still in operation.
What is alternating (AC) and direct (DC) current?
AC from English “alternating current” means alternating current, and DC “direct current” means direct current.
AC alternates the direction of current, but DC flows in only one direction.
Welding machines and electrodes marked DC have a constant polarity, while those marked AC change polarity 120 times per second with a current frequency of 60 hertz.
Conversion
For household appliances that require circuits to be supplied with DC type electricity, it is supplied through power supplies. These are circuits that include a step-down transformer and a rectifying unit. When connecting the power supply to the device, make sure that their voltage and power parameters match. The parameters are indicated on the device body.
Mains power supply 50 Hz
At the moment, both types of electricity get along well in the modern world. Mixed nutrition schemes of consumers only complement each other.
Video
Coffee capsule Nescafe Dolce Gusto Cafe O Le Coffee with milk, 3 packs of 16 capsules each
1305 ₽ More details
Coffee capsules Nescafe Dolce Gusto Café Au Lait, 16 pcs.
435 ₽ More details
Apple iPhone XR 128GB