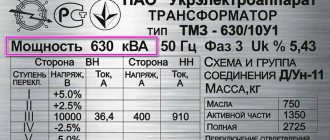
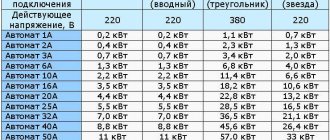
Both the quality of the work performed and the health of the worker who performs it depend on the amount of light in the workplace. Not only this requires a sufficient amount of illumination in lux per unit area. Human habitation on the planet and the normal existence of flora and fauna require a certain standard of illumination. Light sources are natural and artificial emitters.
Illumination per unit area
Typical illumination, examples
The interpretation of the illumination unit 1 lux looks like this: 1 lux (the designation of this value in the SI system) corresponds to the order of illumination of 1 m2 of surface by an incident light flux of 1 lumen (Lm).
When it comes to the brightness of light, there are two positions to consider:
- the strength of light emitted by any source;
- the amount of light falling on the surface.
The second position is the illumination in question.
Examples of typical illumination values, in accordance with external perception
| Illumination value, lux | External perception |
| 0,0001 | moonless starry sky |
| 0,01 | quarter moon |
| 0,27 | full moon in a clear sky |
| 1 | the ability to distinguish the outlines of objects, free orientation in space, a short time for vision adaptation when moving from a brightly lit space |
| 5 | easy visual perception of the watch dial, the ability to read newspaper headlines |
| 10 | illumination of the space next to the candle |
| 15-20 | light from a cigarette at a distance of 300 mm |
| 20-35 | light in the cinema during intermission |
| 50 | you can read the text in the newspaper, lighting the living room |
| 100 | allows for long periods of newspaper reading, but is tiring for the eyes |
| 300 | comfortable conditions for reading printed materials |
| 400-500 | typical lighting for libraries and offices |
| 1000 | clear day an hour before sunset |
| 2000 | clear morning an hour after sunrise |
| 25000 | summer cloudy day at 10 am |
| 65000 | clear summer day at 10 o'clock in the morning |
| 100000 | midday on a clear summer day |
Attention! The determination of the illumination of objects is not limited to visual perception. For this purpose, a device called a “lux meter” is used. This is a simple device, which is based on a photocell that converts light energy into electrical energy and displays the readings on the display. It allows you to measure illumination.
Luxmeter CEM DT 1308
Multiples and submultiples
Zener diode TL431
The unit of illumination - lux, like all metric quantities related to each other, has multiple and submultiple units of measurement or designations.
Information. Multiple units are those that are an integer number of times higher than the unit of the original physical quantity, and submultiples are those that are an integer number of times lower than this value.
Multiples and submultiples of lux units (lx)
The illumination of the earth's surface from Sirius is 1*10-5 lux, from the Sun at winter noon - 1*104 lux.
Application in technology
How to charge a lithium ion battery
The widespread use of surveillance cameras to protect objects and organize a surveillance structure requires them to have a certain sensitivity. The sensitivity of these electro-optical devices is measured in lux. This parameter is considered in such devices as a lux meter and a pulse meter.
Example of technical characteristics of the Vt-326 H Wir SpaceTechnology camera
In what units is illumination measured?
If we talk about such a physical quantity as illumination, which is measured in lux, then in the GHS system it is considered in photos.
PTE of power plants and networks
1 phot = 10,000 lux = 1*104 lx, which corresponds to the required level of illumination on the surgical operating table.
For your information. GHS is a classification of absolute physical units (for example, centimeter, gram, second), which was used before the adoption of SI. It was based on three quantities: length, mass, time. The remaining dimensions were reduced to them through mathematical calculations: multiplication, exponentiation and division.
List of basic units of light measurement
With the abundance of various sources of light radiation on the market, confusion arises in terms. The consumer is poorly oriented in the markings applied to lighting devices. The question often arises: 1 lumen is how much lux? There is a significant difference between these concepts.
The main light characteristics include:
- lux – the amount of light radiation per unit area;
- lumen - the total amount of light emitted by a source around itself;
- candela (candle) - the strength of monochromatic radiation from a source in a certain direction.
Important! If we talk about power (W) as a characteristic of a lighting device, then this will not be entirely correct. There is some difference. The power of the luminous flux is measured in lumens. This is the amount of light energy that radiation transfers through any surface per unit time.
Illumination concept
Illumination is an indicator that is measured as the ratio of the amount of light flux to a unit area onto which it falls perpendicularly.
When making calculations, it is necessary to take into account that illumination:
- directly proportional to the strength of the luminous flux;
- inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source to the illuminated area;
- is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle at which the light flux falls.
Lighting can be:
- natural – penetrates into premises through openings of supporting structures;
- artificial – created by lighting devices;
- combined – natural, supplemented with artificial.
In a room, you can arrange a general (most often ceiling), local (supplying light to individual zones), combined (general, supplemented by local) lighting system.
Formulas for calculating specific values of candelas, lumens and lux
Currently, there are many programs for gadgets that allow you to convert lumens to lux. The calculator can recalculate and perform the necessary conversion of one value to another online. However, it won’t hurt to learn how to convert lux to lumen and vice versa using formulas.
The first definition you need to know is what a solid angle is. This is an angle that cuts out from a sphere a surface in the form of a circle with area R2 and having a center in a sphere with radius R. It is denoted by the letter Ω, its unit of measurement is 1 steradian (sr).
The angle is found by the formula:
Ω = S/ R2,
Where:
- S is the surface area of the spherical segment of the sphere;
- R is the radius of the sphere.
After the transformation you get:
Ω = S/ R2 = 4π R2/ R2 = 4π.
Solid angle Ω, graphical representation
The second definition that characterizes a light source is luminous intensity. This physical quantity is designated by the letter I and is measured in candelas (cd, cd).
The luminous intensity formula looks like this:
I = F/ Ω,
Where:
- I – luminous intensity, (сd);
- F – luminous flux (lm);
- Ω – solid angle, (sr).
Determination of luminous intensity
The next quantity that comes into relationship with the previous properties of light is luminous flux. It has the letter F, is measured in lumens (lm, lm ) and is calculated using the formula:
F = I* Ω.
Determination of luminous flux
Lux measures the amount of illumination, which is denoted by the letter E, with the unit of measurement lux (lx, lk). Its formula looks like:
E = F/S,
Where:
- E – illumination, lux;
- F – flow, lm;
- S – area of the illuminated surface, m2.
Using these formulas, you can convert some quantities into others without an electronic “online calculator” program.
Determination of illumination value
Attention! The main physical difference between lumen and lux is that as you move away from the radiation source, the value of illumination (lx) decreases, the value of luminous flux (lm) remains unchanged.
Physical differences between lux and lumen
Norms and calculation procedure
Lighting requirements depend on the purpose of a particular room and the type of human activity. The standards by which the indicator is measured are established in GOST R 54944-2012, the norms are in SNiP. All parameters apply not only to the floor, but also to the planes of the tables. Tables are available that can be used to determine lux for any property.
When developing a lighting system for a residential building (apartment), you can use the data from this table:
| Standard according to SNiP (LK) | Room |
| 20 | Passages to attics, basements |
| 20 | Electrical switchboards, boiler rooms, ventilation chambers |
| 20 | Stairs |
| 50 | Bathrooms. showers, toilets |
| 50 | Corridors and halls in houses (apartments) |
| 75 | Wardrobe rooms |
| 100 | Saunas, locker rooms, swimming pools |
| 150 | Living rooms and kitchens |
| 150 | GYM's |
| 200 | Children's rooms |
| 300 | Libraries, offices |
The calculation is carried out in 2 stages:
- determining the required level of luminescence;
- determining the number of light bulbs.
Formula for calculating the glow:
N*P*K, where:
N – norm (according to the table);
P – room area;
K – coefficient depending on the height of the ceilings (1 for 2.5-2.7 m, 1.2 for 2.7-3 m, 1.5 for 3-3.5 m, 2 for 3.5-4, 4 m).
To calculate the number of lamps, the result must be divided by the lumens indicated in the technical documentation of the lamps selected for installation.
If major repairs or reconstruction work is carried out, the contractor’s employees handle the calculations.
They take into account the design features and materials of lamps, light reflection from walls, floors, ceilings, and interior items, depending on the characteristics of the facing material. The type of lamps is preliminarily indicated in the design documentation and technical specifications.
The formula used for calculations is:
K=(E*k*S*k1)/(F*k2), where:
E – norm for horizontally located planes;
k – coefficient calculated taking into account deviations in the operation of the system when individual light sources burn out and interior items move;
S – area of the room;
k1 – coefficient of unevenness;
Ф – luminous flux from one light bulb (depending on power and type);
k2 – coefficient in shares.
When carrying out measurements and calculations yourself, it should be taken into account that reflected light in power may differ little from direct light.
Symbols on light sources
When choosing any light source, be it a light bulb, lamp or spotlight, you must carefully study the markings on the lighting fixture. Even if we remember that the amount of illumination is measured in lux, this data may not be found among the information. Marking applied to the visible part of the bulb or to the lamp body:
- manufacturer's trademark;
- the amount of voltage used, V;
- number of lamps in the lamp and power;
- lamp name and type;
- protection class;
- installation method;
- date of manufacture.
In some cases, the permissible distance to the illuminated surface is indicated if the lamp can cause a change in the temperature regime of the illuminated object.
Decoding the lighting fixture markings
Conclusion
Thus, it is clear that improper lighting poses a significant threat to the health of workers. Proper organization of lighting in the workplace is the key to health, high labor productivity, and a comfortable emotional and psychological state of a person. Proper organization of lighting involves not only compliance with regulatory requirements for the level of illumination and a number of other indicators, but also taking into account a number of qualitative indicators - light saturation, uniformity and homogeneity of lighting, shadow formation, color gamut of the lighting environment, etc.
Illumination and LED devices
In the organization of lighting, LED lamps, LED luminaires, LED panels and strips are becoming increasingly popular. An LED lamp is a device that includes:
- panel with RGB LEDs;
- LED power supply (driver);
- heat dissipation panel (radiator);
- base and bulb;
- lower and upper holders.
The illumination of the object is regulated by the number of LEDs installed in the lamp. The spectrum of white color varies from cool to warm, thanks to RGB LEDs. Three semiconductor chips in one package emit three basic colors: red (R), green (G), blue (B).
Light
Important! LED sources have high light output parameters. F – luminous flux, ranges from 50 to 100 lm per 1 W of power. This is 2-3 times more than halogen lamps, and almost 6 times higher than incandescent lamps.
LED sources practically do not lose power to heat the housing. Long service life (up to 100 thousand hours) with an efficiency factor (efficiency) of more than 85%.
How to choose LED lamps for a room?
LED lighting of premises should be guided by the following indicators:
- Scattering of light.
- Colorful temperature.
- The amount of luminous flux.
For example, when choosing matte light, soft diffused lighting is achieved (suitable for an office and small areas), while transparent light distribution is more relevant for large rooms. Warm light is more suitable for the lounge area, neutral white for illuminating work surfaces, and cold light for illuminating warehouses.
Types of spotlights
There are many options for spot lighting. Spotlights can be overhead (attached to walls or ceilings) or recessed. Depending on the type of adjustment, there are rotary and non-rotating devices, downlights, stops, gimbal LEDs and retractable devices.
How to calculate LED strip lighting?
LED strip is designed to decorate a room. The calculation method is based on the intensity of the luminous flux per 1 linear. m. tape. Of course, you can choose high-power LEDs. But they are more suitable for street lighting - facades, neon signs and billboards. For home decoration, 6.5-24 W lamps are sufficient.
Recommended lighting levels for residential premises
During the construction and further operation of premises intended for housing, the lighting of living rooms is calculated. The lack of light, both natural in the daytime and artificial in the evening and night hours, has a detrimental effect on people's health. Therefore, when calculating the number of lighting fixtures and making the necessary measurements of illumination on site, they adhere to the standards that can be found in SNiP.
Residential lighting standards
The unit of illumination is lux, as a parameter of lighting installations is not indicated among the characteristics, but is very important. The height of the source suspension and the angle of the light flux depend on the amount of illumination needed to be obtained on a surface or object.
Where are they used?
The concepts of “Lux” and “Lumen” are applicable to all products that emit light, so they are used to successfully solve the following household problems:
- Preventing excessive energy consumption for the operation of lighting devices.
- Checking and determining the lighting in a residential area for compliance with the standard. A lux meter is used for measurement.
Luxmeter
- Arrangement of lamps to create the same illumination anywhere in the room.
- Prevention of eye diseases arising from lack of light.
Important! SanPiN rules dated 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03 establish the average illumination of buildings, institutions, and residential premises. Suites help determine whether a room is lit enough for a person to live and work comfortably.
SanPiN
The standards for artificial lighting in residential premises are as follows:
- Corridor, bath and toilet – 50 Lx;
- Dressing room – 75 Lux;
- Children's room – 200 Lux;
- Office – 300 Lux;
- Kitchen, living room – 150 Lx.
Video
Coffee capsules Nescafe Dolce Gusto Cappuccino, 8 servings (16 capsules)
435 ₽ More details
Coffee capsule Nescafe Dolce Gusto Cafe O Le Coffee with milk, 3 packs of 16 capsules each
1305 ₽ More details
24 inch TVs