A person constantly tries to extend daylight hours by illuminating his home at night. This began at the dawn of civilization and continues to this day. Lighting devices have gone through an evolutionary path from a primitive torch to a high-performance light bulb. The parent of electric lighting was the incandescent lamp, a patent for which was received in the middle of the 19th century. And although innovative lighting resources are actively conquering the market, the good old “Ilyich light bulb” remains quite in demand.
Incandescent lamp.
Advantages and disadvantages
Currently, there are many lighting devices. Most of them have been produced in the last few years using high technology, but the classic LN still has many advantages or a set of parameters that will be more suitable if used correctly:
- fairly low price;
- resistance to different temperatures;
- instant ignition;
- do not flicker;
- have different light modes.
But, unfortunately, incandescent lamps have their disadvantages:
- The main disadvantage is the rather reduced efficiency. For 100 W bulbs the efficiency will be approximately 17%, for 60 W products this figure will be only 5%. One of the methods for increasing efficiency would be to raise the filament temperature, but in this case the service life will noticeably decrease;
Spiral for incandescent lamp
- short service life;
- increased temperature of the surface of the vessel, which can be up to 250°C for a 100W light bulb. This increases the risk of lamps catching fire or exploding;
- sensitivity to the environment;
- use of heat-resistant fittings.
The types and characteristics of incandescent lamps are described in detail below.
LED lamp: general characteristics, scope of application, advantages and disadvantages.
Main characteristics of LED lamps:
- Power. From 3 to 25 W. For household use, a 9-13 W light bulb is sufficient, which corresponds to 40-100 watt incandescent lamps.
- Voltage. Operating range from 176 to 264 Volts.
- Base type. Mostly E14 and E27 are used.
- Temperature of light. There are lamps with daylight white light, warm and cold.
LED lamps are considered the most modern. However, in addition to the advantages, it also has disadvantages.
Advantages:
- low energy consumption;
- long service life;
- low body heating;
- compactness;
- higher durability compared to other types of lamps.
Flaws:
- high price;
- small angle of light scattering.
LED lamps are used in lighting streets, industrial premises, and offices. The main area of application of LEDs is the organization of external lighting of architectural structures. Most floodlights also use LEDs.
Characteristics
One of the main parameters of incandescent light bulbs will be the power, indicated in watts. The purpose of the lamps is different, so the range of choice is large - from 0.1 W “lamp” to 23 thousand W floodlights for airfields.
In everyday life, low-power light bulbs are used, usually from 15 W to 200 W, and in production they use lamps with a power of up to 2000 W.
The quality of the light beam and the level of dispersion are regulated by the material of the vessel.
car light bulb
The greatest light transmission is inherent in products with transparent glass, because they do not absorb light. The matte surface of the lamp absorbs 5% of light rays, and the white surface absorbs 15%.
The size of incandescent light bulbs can be from 60 mm to 130 mm. Depends on the scope of application.
Gas discharge lamp, its classification
Gas discharge lamps are classified according to the type of light source and pressure.
By light source
According to the type of glow there are:
- Luminescent. In such lamps, the light source is atoms and molecules, which are excited by a discharge produced in a gaseous environment.
- Gas-light. Lighting is achieved thanks to phosphors, which are also activated using a gas discharge.
- Electro-pre-light. They operate due to electrode glow produced using a gas discharge.
By pressure value
GRL by pressure value.
- High-pressure gas-discharge lamps (from 25 to 1000 kPa) are characterized by the presence of an impressive luminous flux, but they are not too energy-consuming. Based on the type of filling, they are most often classified as mercury. They do not tolerate low temperatures well, but have high light output.
- Low pressure lamps (from 0.1 to 25 kPa) are most often fluorescent. They have a different emission spectrum. During their operation, ultraviolet radiation is generated, which is obtained thanks to phosphors. Among low pressure HRLs, sodium lamps have the highest light output.
Gas discharge lamp device
Gas discharge lamp: general characteristics, scope of application, advantages and disadvantages.
Main characteristics of gas discharge lamps:
- Light output. From 40 to 220 lm/W.
- Work resource. From 3000 to 20000 hours.
- Emission color. Warm white (3000 K) or neutral white (4200 K).
GRLs are used in closed lighting fixtures with protective glass. Bulbs of this type are also sensitive to voltage changes. Let us consider the advantages and disadvantages of GRL in more detail.
Advantages:
- high level of light output;
- practicality;
- ability to work in extreme climatic conditions;
- low cost.
Flaws:
- high level of color flow pulsation;
- difficulty of inclusion;
- for stable combustion a voltage limiter is required;
- the temperature inside the flask affects the pressure of the working steam, and can provoke an accident.
GRL is used in organizing the lighting of store windows, office premises and public places. HID light bulbs are often seen in outdoor lighting. Outdoors during the cold season, such lamps are used with special shades. GRL can be used in professional lighting for theatrical productions and filming. Gas discharge lamps are also used in the automotive industry.
Principle of operation
When electric current passes through the coil, it quickly heats up to high temperatures of almost 2500 degrees. This is due to the fact that the spiral has a high resistance to current and a large amount of energy is required to pass it.
The heat heats the metal (tungsten) and the lamp begins to glow. Since there is no oxygen inside the lamp, tungsten does not oxidize.
Color temperature table
The efficiency of the old-style 100 W incandescent lamp, where the role of the filament body was played by a coal rod, was much less than that of the latest models. This is due to the additional costs of convection. Spiral filament bodies have a lower percentage of such losses.
Specifications
It is interesting to observe the relationship between light energy and lamp power. The changes are not linear - up to 75 W, the luminous efficiency increases, and if it is exceeded, it decreases.
One of the advantages of such light sources is uniform illumination, since light is emitted with equal strength in almost all directions.
Another advantage is associated with pulsating light, which at certain values leads to significant eye fatigue. The normal value is considered to be a ripple coefficient not exceeding 10%. For incandescent lamps the maximum parameter reaches 4%. The worst indicator is for products with a power of 40 W.
Of all the electrical lighting available, incandescent bulbs run the hottest. Most of the current is converted into thermal energy, so the device is more like a heater than a light source. Luminous efficiency ranges from 5 to 15%. For this reason, the legislation contains certain rules prohibiting, for example, the use of incandescent lamps of more than 100 W.
Typically, a 60 W lamp is enough to illuminate one room, which is characterized by slight heating.
When considering the emission spectrum and comparing it with natural light, two important observations can be made: the luminous flux of such lamps contains less blue and more red light. However, the result is considered acceptable and does not lead to fatigue, as is the case with daylight sources.
Operating Parameters
When using incandescent lamps, it is important to consider the conditions of their use. They can be used indoors and outdoors at temperatures not less than –60 and not more than +50 degrees. Celsius. In this case, air humidity should not exceed 98% (+20 degrees Celsius). The devices can operate in the same circuit with dimmers designed to regulate light output by changing the light intensity. These are cheap products that can be replaced independently even by an unqualified person.
Types of lamps
Incandescent lamps are divided into several types:
Decorative light bulb models
- vacuum;
- argon or nitrogen-argon;
- krypton;
- halogen with a connected infrared light reflector inside the bulb, which increases efficiency;
- with the coating necessary to convert infrared light into the visible spectrum.
General, local purpose
The characteristics of general purpose LN are specified in GOST 2239-79. These light bulbs are used to connect to luminaires for the main lighting of domestic and public places, as well as outdoor spaces.
The main voltage can be 127 and 220 V. The range of products is divided into groups depending on the type of filament (spiral or bi-spiral) and medium (vacuum, gas).
Proper storage of the product
The shape of the vessel, installation method, product brand and type of base are selected based on cost, practicality of technology, and at least 100 hours of operation. It must be emphasized that in recent years the efficiency of such lamps has been assessed based on a variety of characteristics.
You might be interested in Energy-saving lamps: recommendations for choosing
LN for local use, produced under GOST 1182-78, the voltage should not be higher than 36 V, and for industrial premises where there are flammable substances - 12 V. The power of lamps for local use is limited and will be 15, 25, 40 and 60 W. The service life of each incandescent lamp must be at least 75% of the average glow duration.
For street lighting, more powerful lamps are used so that they do not have to be changed every month or two. Since this is a rather labor-intensive process.
Illumination lamps 15 W
Decorative
Decorative light bulbs can be of various shapes, round, oval, spiral and so on. The radiation source will be a tungsten filament. It creates a cozy and warm light in the room. The factory mainly produces designer products for the classic E27 base, but there are models for the E22 and E40 base. The voltage required for correct operation is 220 V. The service life of decorative products with tungsten filament can be in the range of 2000-3400 hours, but no more. The lighting temperature is characterized by a parameter of 2700 K.
Such products are often used to decorate rooms, staircases or Christmas trees. Large shopping centers use decorative light bulbs suspended from high ceilings. It looks truly beautiful and at the same time cozy. They will harmoniously combine with the Loft style in a house or apartment.
Illumination
These incandescent lamps are produced with a colored inner layer of the bulb and are necessary for New Year's garlands or illumination of stairs, shops and shop windows. It has a wide range of colors, including cold, white, day and night shades. Quite a long service life of up to 25,000 hours, with proper operation. The main disadvantage will be the heavy installation. The closer the end of the product's life, the weaker it will work. The light will begin to scatter poorly.
Airplane front lights
Signal
Signal lights are mainly used in various industries. The simplicity of the device and a large range of models help you choose products for work in different areas of production. Lamps can be mounted on machines, control panels, special vehicles, and so on. Very often used in mechanical engineering, woodworking or metallurgy.
Attention! You can connect one light bulb to perform several operations, or use 2-3 products for different purposes at the same time. Based on the scope of use, the color and shape of the lamp is selected.
Modern incandescent lamps are manufactured specifically for use for industrial purposes, which provides a number of advantages over conventional light signaling lamps:
Mirror lamp r65
- various color modes providing more informative signaling;
- many choices of lamp shades;
- suitable for any electrical network;
- easy installation on machines using a screw connection system;
- ability to replace contacts;
- the use of high-brightness LED bulbs to improve visibility in any industrial areas;
- convenient case with the ability to select the desired size;
- energy saving;
- ease of use.
Mirror
The mirror-type product differs from other LPs in the rare shape of the bulb, as well as the presence of a coating with light reflection, which is similar to thin foil.
What is an incandescent light bulb made of?
This coating is sprayed onto the lamp in order to diffuse its light radiation in the room, in order to more correctly distribute it within a certain point, so that it is possible to clearly illuminate a certain room.
To get this option in a regular lamp, you need to place a large light reflector behind it.
Mirror bulbs are mainly connected to directional luminaires used for spot lighting of stores to illuminate the necessary areas. They are also used for offices, stairs, architectural monuments.
Mirror lamps can be multi-colored and transparent, matte, or with the effect of UV rays. They are produced by all well-known lighting factories.
Types of products
Transport
Transport incandescent lamps are used as lighting for cars. In an electrical circuit, the filament of the body heats up and at the peak temperature a glow begins. The energy of the light beam perceived by the ordinary eye will be small. The bulk of the energy will be in the form of heat.
A transport lamp consists of a bulb, several filaments, a base and leads.
You might be interested in: Features of architectural lighting at home
Filaments in two-filament products can work differently. Car headlights and interior lamps are equipped with double-filament bulbs.
The filament is sure to withstand elevated temperatures and is also quite small. Therefore, it is made from medium-sized tungsten wire, curled into an elongated spiral.
Double thread products
The spiral is connected to the electrodes and generally has the shape of a straight line or a semicircle arc. The melting point of tungsten will be about 4000 degrees. During operation, the coil heats up to 2500-2800 °C. As the tungsten temperature increases, the brightness and luminous efficiency of the rays on the laser increases. But if the readings exceed 2500 °C, tungsten will quickly evaporate and remain on the walls of the glass vessel, resulting in a layer of plaque that will reduce the quality of lighting. The service life of such products is usually from 4 months to six months. Depends on the manufacturer and the quality of production raw materials.
Double strand
This product can be of three types:
Traffic light lamps
- for cars. One thread is used for low beam, the second for high beam. If we talk about lamps for rear signals, the same threads can be used for brake lights and side lights. An additional screen will remove beams that in the low beam signal can blind the owners of oncoming cars;
- for an aircraft. In a landing light, the first filament is used for low illumination, the second for high illumination, but if the second one works for too long, cooling may be necessary, otherwise a fire may occur;
- for traffic lights on railways. Both threads are needed to increase reliability - if one burns out, the other will work.
Types of flasks
Operating principle and design features
When heated to a certain temperature, the metal begins to glow. This property is used in incandescent lamps. At the same time, several problems had to be solved that prevented the creation of an effective lighting element. Firstly, it was necessary to select a material that would not melt when heated. As a result, the spiral is made of tungsten, the cheapest of the refractory metals. Secondly, the heating process accelerates the oxidation process, which has a negative effect on the condition of the metal. This means that it was necessary to prevent contact of the hot spiral with oxygen, i.e., with air.
The result is a lamp design that overcomes all problems and at the same time amazes with its simplicity:
- a pear-shaped glass bulb with a metal base attached to the narrow part. It has a thread with which the device is screwed into the cartridge. Some models do not have threads, but other solutions are available to suit the operating conditions;
- Inside the flask there is a glass leg with two soldered electrodes. With their upper ends they are attached to the edges of the spiral, and with their lower ends - to the base. Moreover, one is soldered to the body, and the second to the contact on its bottom;
- a tungsten spiral string is attached to electrodes and holders (legs) made of refractory metal (molybdenum). They prevent the spiral from sagging when heated and breaking. Depending on the purpose of incandescent lamps, there may be several spirals, which means the number of contacts and supporting legs increases accordingly.
The air is pumped out of the flask and filled with an inert gas or a vacuum environment is left. This solves the problem of oxidation. Passing through the tungsten helix, the electric current heats it up. Moreover, this happens unnoticed by the human eye and the luminous flux as a result of the conductor’s incandescence spreads almost instantly.
How does an incandescent light bulb work?
The structure of an incandescent lamp
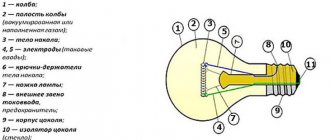
The design of the different types of incandescent light bulbs does not differ much, but three common components can be emphasized, the filament, the glass bulb and the electrical inputs. They differ in the design of the filament body brackets, the type of bases, and sometimes come without bases.
To prevent the bulb from deforming when the coil overheats during operation, the incandescent lamp is equipped with a ferronickel fuse; it is mainly located in the leg. At the point where the spiral breaks, an electric arc appears, due to which pieces of the spiral melt and fall on the flask, which can lead to its damage. By using fuses this process can be avoided. But in the last 5 years they have rarely been used, as they are not very effective.
Argon light bulb
Incandescent lamp design:
- flask;
- filament coil;
- electrodes on both sides of the body;
- hooks on which the spiral is held;
- leg;
- current input;
- base with insulator;
- contact at the end of the socket.
Flask
The glass bulb protects the spiral from the harmful effects of air; when it is deformed, the filament body oxidizes and quickly explodes. The composition of the lamp bulb varies; it can be filled with a vacuum or a gaseous environment. The first incandescent lamps were produced with a vacuum container, but their power was not high. To fill modern products, nitrogen-argon substance or exclusively argon is used. Some types of light bulbs can be filled with krypton or xenon. The heat transfer of a light bulb depends on the molar mass of the filler.
Definition of LN
Gas medium
The gas environment in the lamp must be inert. Since the temperature of the spiral reaches 2500 degrees, it can react to any gas, but not inert. Therefore, argon is most often used for filling.
If water suddenly gets on a hot or working lamp, it may rupture under the influence of gas.
Sometimes lamps are filled with xenon, but this will be relatively expensive.
In many lamps, the gas environment will be a safety feature. In others, an electrical discharge produces beautiful colored radiation. The shade will depend on the properties of the inert gas.
filament body
The types of filament bodies can be different and depend on the functional purpose of the light bulbs.
Types of light sources
The most popular ones will be made from wire with an oval cross-section, but sometimes there are also strip filament bodies (consisting of a metal strip).
As already mentioned, the first filament bodies were made from coal. Modern LPs use only filament bodies made of tungsten, less often of osmium-tungsten substance.
You might be interested in: Twilight light sensors
To reduce the size of the filament, it is usually made in the form of a spiral, sometimes it is re-processed to form a coil. The efficiency of such products is higher due to reduced heat loss during convection.
Electrical parameters
The luminous efficiency of such products is quite low. It will be the lowest among popular light bulbs and ranges from 5 to 10 lm/W. The increased brightness of the filament in combination with its small size allows the products to be used in floodlights.
Classic plinths
LNs have a wide range of medium voltages and powers. This type of product can function in a wide range of ambient temperatures, which is limited only by the thermal stability of the raw materials used in its production (-100...+350 degrees). The light emission of the LN is adjusted by transforming the operating voltage.
With this minus, there will be an increased operating temperature and the amount of heat released during combustion. Since the temperature of the light bulbs is high, they become vulnerable under the influence of water or a sharp change in degrees (from minus to plus and vice versa).
In the modern world, many have long abandoned the use of incandescent lamps. In developed cities, only 20% of people use such products. Everyone is switching to halogen lamps.
When the light bulb is turned on, the filament body is at normal temperature, then the resistance of the product will be much less than the operating resistance. When turned on, a large amount of current flows. As the thread splits, its resistance increases and the current decreases.
Manufacturing process at the factory
Unlike the newest products, older models of incandescent lamps with carbon filaments had a reverse process when turned on, with an increase in current. The increasing resistance function of the filament allowed the lamp to be used as a primitive electrical stabilizer.
Base
The threaded base type for the classic incandescent lamp was designed by Joseph Wilson Swan. The sizes of the socles had their own standards. Products of the usual type (for home) had a base of E14, E27.
Sometimes there are bases without threads (in this case, the light bulb is held in place by friction), as well as baseless lamps, more often used in cars. The E40 size will be rare; it is used for more powerful products from 500 W.
Efficiency
Electric current in incandescent lamps is converted not only into light visible to the eye. One part is used for radiation, the other is transformed into heat, and the third is converted into infrared light, which is not detected by the visual organs. If the conductor temperature is 3350 K, then the efficiency of the incandescent lamp will be 15%. A conventional 60 W lamp with a temperature of 2700 K is characterized by a minimum efficiency of 5%.
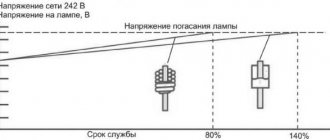
The efficiency is enhanced by the degree of heating of the conductor. But the higher the heating of the filament, the shorter the service life. For example, at a temperature of 2700 K, a light bulb will illuminate for 1000 hours, at 3400 K - several times less. If you increase the supply voltage by 20%, the glow will double. This is irrational, since the service life will be reduced by 95%.
Best before date
The service life of a product depends on its quality. LN should be stored in a cardboard box. This is necessary so as not to accidentally break it or so that it does not give an imperceptible crack that will ruin the whole work. Because of such a crack, the gas will evaporate; as a result, after the light bulb is screwed into the lampshade, it will work for no more than 2-3 hours. You must follow safety rules when screwing the lamp into the lampshade. Children should not be allowed to participate in this process, and it is also advisable to completely turn off the electricity supply in the room.
Note! Used light bulbs must be disposed of properly and should not be thrown away with food waste. Every city has special bins for such waste.
If you follow all the rules of storage and use, the lamp will last as long as possible, without defects.
Vintage Edison lamp
The history of the creation of the first lighting elements
The origins of the first incandescent lamps go back to the beginning of the 19th century. Or rather, the lamp appeared a little later, but they had already tried to observe the effect of the glow of platinum and carbon rods under the influence of electrical energy. Scientists faced two difficult questions:
- finding high-resistance materials that can heat up under the influence of current to the point of emitting light;
- preventing rapid combustion of the material in the air.
The most fruitful research and inventions in this area were the Russian scientist Alexander Nikolaevich Lodygin and the American Thomas Edison.
Lodygin proposed using carbon rods, which were in a sealed flask, as an incandescent element. The disadvantage of the design was the difficulty of pumping out air, the remnants of which contributed to the rapid combustion of the rods. But still, his lamps burned for several hours, and his developments and patents became the basis for the creation of more durable devices.
The American scientist Thomas Edison, having become familiar with Lodygin's work, made an effective vacuum flask into which he placed a carbon filament made of bamboo fiber. Edison also provided the lamp base with a threaded connection, characteristic of modern lamps, and invented many electrical elements, such as the plug connector, fuse, rotary switch and much more. The efficiency of Edison's incandescent lamp was small, although it could work for up to 1000 hours and was put to practical use.
Subsequently, instead of carbon elements, it was proposed to use refractory metals. Tungsten filament, used in modern incandescent lamps, was also patented by Lodygin.
Incandescent lamp device
The main parts that make up the LN design are the base, vessel, electrodes, holders for filament filaments, filament body, contacts and insulation. In Figure 10 you can see the structure of a light bulb.
Before purchasing a lamp, it is advisable to consult a specialist. It is not recommended to choose an unknown manufacturer, as you may end up with defective products that will not work as expected, or even rupture under voltage. Quality manufacturers always provide a guarantee of at least 30 days on incandescent lamps. The buyer has the full right to exchange the product or return the money if the lamp's operation was less than 10 hours or it burned out instantly.
In conclusion, it should be noted that incandescent lamps have long ceased to be popular among people. However, it must be emphasized that among such products there is a huge selection, for cars, street lighting, airplanes and so on. Unfortunately, LN cannot be used near products made of wood. Since sometimes there is strong heating and rupture of the spiral, which can cause an emergency situation.
Lighting lamp, difference in operating principle.
An incandescent lamp is a source of artificial lighting in lighting fixtures that produces heat during operation.
The design is a spiral of refractory metal, which is placed inside a flask filled with inert gases or vacuum. The environment inside the flask prevents oxidation of the metal. There are many varieties of light bulbs, but the main reason for their rise in popularity is affordability. The HID lamp is a more modern version of the light source with a coil inside a glass bulb. Its device also involves a gaseous environment inside the flask, only electrodes are used instead of a spiral. Lighting is obtained through electrical discharge.
The light-emitting diode (LED) lamp is considered the most environmentally friendly source of lighting. This is the most advanced device, which consists of an LED block, a radiator, a light-diffusing cap, a driver unit and a base.
LED bulbs
LEDs, semiconductor light-emitting devices, are called the light sources of the future. If we talk about the current state of “solid-state lighting technology,” we can say that it has come out of its infancy. The achieved characteristics of LEDs (luminous efficiency up to 140 lm/W, Ra = 80–95, service life 70,000 hours) have already provided leadership in many areas.
The power range of LED sources, the implementation of different types of sockets in lamps, and lamp control made it possible to quickly meet the growing requirements for light sources. The main advantages of LEDs remain their compact size and control of color parameters (color dynamics).
The history of the creation and improvement of the incandescent lamp design
Over its more than 100-year history of existence of an incandescent lamp with a tungsten filament, the operating principle and basic design elements have undergone almost no changes. It all started in 1840, when a lamp was created that used the incandescent principle of a platinum spiral for lighting. 1854 – the first practical lamp. A vessel with evacuated air and a charred bamboo thread were used. 1874 - a carbon rod placed in a vacuum vessel is used as a filament body. 1875 - a lamp with several rods that glow one after another if the previous one burns out. 1876 - the use of a kaolin filament, which did not require pumping out air from the vessel. 1878 - the use of carbon fiber in a rarefied oxygen atmosphere. This allowed for bright lighting. 1880 - a carbon fiber lamp was created with a glow time of up to 40 hours. 1890 - the use of spiral threads made of refractory metals (magnesium oxide, thorium, zirconium, yttrium, metallic osmium, tantalum) and filling the flasks with nitrogen. 1904 – production of lamps with a tungsten spiral. 1909 – filling of flasks with argon. More than 100 years have passed since then. The principle of operation, the materials of the parts, and the filling of the flask have remained virtually unchanged. Only the quality of materials used in the production of lamps, technical characteristics and small additions have undergone evolution.
Compact fluorescent lamps
The development of fluorescent lamps led to the creation of compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs). This is a light source similar to a miniature fluorescent lamp, sometimes with a built-in electronic ballast and a threaded base E27 (for direct replacement of incandescent lamps), E14, etc.
The difference lies in the reduced tube diameter and the use of a different type of phosphor. A compact fluorescent lamp can successfully replace incandescent lamps.
Artificial light sources: types, features, scope of use
- Photomechanical (shock energy wave of light energy),
- Photothermal (when irradiated, fiber tissue is heated)
- Photochemical (photons of light can cause chemical changes in macromolecules)
Similar documents
Requirements for energy efficiency of lighting. Light intensity curve of a compact fluorescent lamp. Advantages of halogen lamps. Application of high incandescent gas discharge lamps. LEDs: concept, features of use. Lighting control systems.
Advantages and disadvantages of incandescent lamps, their types and applications, design and operation. Brands and characteristics of wires and cables used in electrical installation work. The mechanisms, tools and devices used; installation of incandescent lamps.
Technical characteristics, design and principle of operation of the general purpose incandescent lamp "Iskra". The advantages of Eurolamp energy-saving lamps: luminous efficiency, service life, low heat output, light distribution and the ability to choose the color of the lighting.
laboratory work [1.5 M], added 10/15/2013
Functional purpose and types of artificial lighting. Types of incandescent lamps, their design, main advantages and disadvantages. Gas-discharge lamps: sodium, fluorescent, mercury lamps, traditional areas of their application and operating principle.
course work [415.2 K], added 01/15/2010
A study of the history of invention, the advantages and disadvantages of incandescent lamps, as well as the harm from them. Characteristics of lamp design elements: body, bulb, current leads. Descriptions of the use of decorative, illumination, mirror, signal lamps.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Incandescent lamp. Electric heating devices - a lesson. Physics, 8th grade. The average service life of normal lamps is approximately 1000 hours of burning, provided that the rated voltage is maintained constant. Ask, I'm in touch!
How to replace a lamp
If the lamp burns out, but the bulb is not destroyed, then it can be replaced after it has completely cooled. In this case, turn off the power. When screwing in a lamp, you do not need to point your eyes in its direction, especially if it is not possible to turn off the electricity.
When the bulb has burst but retained its shape, it is advisable to take a cotton cloth, roll it in several layers and, wrapping it around the lamp, try to remove the glass. Next, using pliers with insulated handles, carefully unscrew the base and screw in the new lamp. All operations must be carried out with the supply voltage turned off.