Electrical networks are often confused by consumers with power transmission lines (PTLs). In fact, this is a complex structure that includes a number of electrical installations - substations, transformers, power lines, etc. - whose task is to supply and distribute electricity from its source (power station) to consumers. Without going into technical details, we note that the transmission of high power electricity and especially over long distances is economically feasible only at high voltage in order to avoid its losses. Therefore, power transformers are widely used in electrical networks, with the help of which the voltage of the electric current changes. At the input from power plants to power lines it increases, and at the output it decreases.
Thus, household consumers receive a single-phase low voltage electric current of 220 V. Therefore, the statement “low voltage in the network” is not entirely true. It would be more correct to talk about low, insufficient, weak, etc. voltage. But the phrase “low voltage” (LV) has long been ingrained in everyday life.
Causes of low voltage in internal consumer networks
External
The appearance of low voltage electricity already at the input to the consumer may be the fault of its supplier as a result of:
- supply of electricity by a substation to too many consumers. In this case, its transformer is overloaded;
- incorrect calculation of the cross-section of wires in power lines (it is small);
- a break or unreliable “zero” contact in a power line, which is fraught with voltage imbalance - some consumers receive a current of too high a voltage, while others receive an extremely low one.
These “external” causes of NV occur most often online. It is quite natural that you cannot solve them yourself. It is necessary to involve neighbors and contact the relevant departments of local authorities.
In addition, voltage in electrical networks may drop due to their aging, poor maintenance, wear and tear of wires and equipment, and an uncontrolled increase in the number of consumers. In addition, the power of electricity consumed by the population is growing - the number of electrical appliances in families, their power, etc. is constantly increasing. Sometimes this is due to differences in seasonal consumption: in residential buildings it is higher in winter, and lower in summer; in holiday villages it is the other way around.
Domestic
This is often the reason for low voltage in electrical networks. It could be:
- too small cross-section of the input cable (from the power line to the house);
- poor contact of this cable at the junction with the power line supplying electricity;
- incorrectly selected cross-section of wires connecting the protective circuit breakers with the internal wiring;
- bad contacts of wires in distribution boxes (boards), etc.
What is the network voltage
Since 2003, a standard voltage of 230V should have appeared in the sockets of our apartments and private houses. But for the past 17 years this transition has not been completed.
From September 30, 2014, instead of GOST 29322-92, GOST 29322-2014 (IEC 60038:2009) was adopted, establishing what the standard voltage should be in Russia. Now its value is 230 V (±10%) at a frequency of 50Hz (±0.2). But still quite often there is 220 V in the electrical network instead of the expected 230 V.
The rated parameters of AC power networks up to 1000 V are indicated in the table given in GOST 29322-2014.
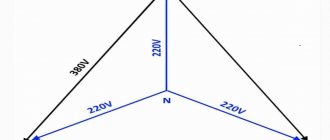
In the first and second columns, the smaller values are the voltage between phase and neutral (phase), the larger values are between phases (linear). If one value is specified, it is the voltage between phases of a three-phase three-wire system.
The standard voltage of 230/400 V appeared as a result of the evolution of the 220/360 V and 240/415 V systems. Currently, the 220/360 system is no longer used in Europe and other countries, but 220/380 V and 240/415 V are still actively used.
The change in standards was caused by the need to bring electricity into full compliance with European parameters to facilitate the export and import of electricity and electrical devices.
Sensitivity of individual devices to low voltage
Connecting some devices to a reduced voltage network is not dangerous, but it does affect their operating efficiency. For example, you might see the following:
- regular incandescent lamps work, but they shine dimmer;
- electric stoves, ovens, kettles, irons, etc. heat up more slowly.
But this does not threaten the latest model TVs - they can operate over a wide input voltage range.
Low voltage is dangerous for electric motors, electromagnets, and control boards. For example, when the voltage drops, the load on the windings of electric motors increases significantly - the current increases - which leads to their overheating, and often to combustion. This causes refrigerators and pumps to fail at very low voltages. And they don’t burn out only thanks to the built-in protection, which simply turns them off in time. Low voltage is also dangerous for all kinds of electronic devices.
High line voltage: the facts
According to GOST, “voltage deviations at the point of transmission of electrical energy should not exceed 10% of the nominal or agreed voltage value.” Electricity quality standard is 220 volts. Therefore, if the voltage in the outlet is above 242 volts, then this situation is not normal. This is a problem that needs to be solved.
- Some facts about high line voltage
- when operating at higher voltage, the operating life of power supplies for household appliances (especially imported ones) is reduced; when the voltage increases to 250 volts, the service life of household appliances is reduced by approximately half
- Significant excess of the input voltage level leads to equipment failure , often to fire
- the most sensitive to high voltage are electronics and all electronically controlled devices
- With increased mains voltage, power consumption increases
How to solve these problems
The search for the cause of low voltage in the network should begin by interviewing neighbors in the house or apartment.
If they have no complaints about a voltage drop, then the reasons are located directly in your home - in the electrical wiring. They are listed above and should be eliminated. If things are the same with your neighbors with network voltage, then the electricity supplier is to blame. But, if he and the local authorities do not respond too actively to requests, the problem with low voltage in a house or apartment can be solved by installing a voltage stabilizer at the input. This is effective, but it is also expensive and requires the involvement of specialists. You can use small stabilizers when turning on certain particularly sensitive electrical appliances. For private homes, there are other ways to increase the voltage in the network, but they are technically complex and require considerable costs and consultations with relevant specialists.
High mains voltage: causes
- Highlight 3 main reasons for the appearance of high voltage in the network, from 240-250 volts and above:
- uneven distribution of load between phases or “misalignment” of phases. When the load increases on one phase, the voltage drops on it, and on the other phase the voltage increases
- deliberate increase by electricians of the output voltage of an electrical substation . This is done in order to increase the voltage for consumers located far from the transmission line. As a result, consumers located close to the transformer substation will have a voltage above 220 volts.
- accidents on power lines and internal lines . Occur due to a break in the neutral wire and high voltage current entering 220V household networks.
Why is high voltage dangerous?
We figured out why increased voltage occurs in the electrical network, but what is its danger? This phenomenon on the network is dangerous primarily for household appliances. Although modern devices install switching power supplies with stabilized output circuits, their input stages experience increased loads and may fail prematurely.
Heating devices are also affected - boilers, electric stoves, heating elements of washing machines, etc. Due to the high voltage, increased current flows through their spirals. Accordingly, more power is released and service life is reduced. This is especially dangerous for air heating elements, for example, convector filaments and spirals.
Such a problem with the electrical network is also unfavorable for equipment with engines, such products include refrigerator compressors, air conditioners, fans and pumps. Their windings will heat up and may eventually fail. The same applies to network transformers.
Do not forget that since the high voltage increases the current consumption, the wiring is also loaded. At best, the consequences will lead to damage to contact connections (especially if there are twists), and at worst, to burning of wires, melting of insulation and fire.
Learn more about the causes of low voltage and methods to solve this problem
Voltage drop in power line
One of the global reasons for the voltage drop is the insufficient power generation and electrical transformation capacity in the region. Insufficient financing of the electrical industry, on the one hand, and the rapid growth of electricity consumption in recent years, on the other hand, leads to problems with the quality of power supply. We practically cannot influence the solution to this problem; the only solution in this situation is the purchase and installation of a step-up voltage stabilizer.
Low power distribution transformer or incorrect setting
This often happens. A certain number of consumers were connected to one transformer and there were no problems with power quality. Then more new houses are connected to the same transformer or substation, and its power turns out to be insufficient, this leads to a decrease in voltage in the entire connected network. This phenomenon is often observed in holiday villages, and voltages of 180, 170, 160 and even 150 Volts are not uncommon there. What are the solution methods? The most correct way is to replace the transformer with a more powerful one. But for this you need to have a common solution for all consumers and financial capabilities. In this case, you can individually solve the problem by installing step-up voltage stabilizers for the entire house or the desired group of devices.
Phase imbalance in the distribution network causing voltage reduction and methods of solution
The reason for the decrease in voltage at the entrance to the house may be an uneven distribution of consumers in the distribution network or “phase imbalance”. As a rule, this phenomenon is observed in rural areas, in holiday villages and the private sector. Homes on these networks are connected to the electrical grid individually as new properties are built. Often the connection is made according to the principle “it’s so convenient for the installer” or “this wire is closer.” As a result, there are more consumers on one “phase” or one “arm” of the network than on others. The voltage in this part of the power grid will be lower. It will not be possible to correct the situation by increasing the voltage value on the supply transformer, since this will lead to an increased (or dangerously high) voltage value in other parts of this power network. The correct solution is to eliminate the uneven distribution of consumers and switch to power from another phase of the network. But often this is not physically possible. The second solution to the problem is to install a voltage stabilizer at the entrance to the house.
Problems in the home network that lead to low voltage and methods for eliminating them
The first thing to do if you have low voltage at your outlet is to find out whether the problem is internal or external. First. The simplest thing is to find out if your neighbors have power problems. Second. Turn off the circuit breakers in the distribution board and measure the voltage at the input to the house. If the voltage is low, then the problem is in the external network. If the voltage entering the house is normal, then the problem is in the house. Here is a list of common problems in the electrical network of a house or apartment:
- A decrease in voltage can be caused by poor contacts at the input to the distribution board or poor contacts in the distribution board itself;
- a decrease in voltage can be caused by poor contacts in indoor distribution boxes and on the sockets themselves;
- A decrease in voltage may be caused by an incorrect choice of wire cross-section in the wiring.
If you cannot identify the exact cause on your own, you should seek help from a professional electrician.
How to increase voltage using stabilizers
There are two main ways to solve the low voltage problem. The first method is to install a large, powerful stabilizer at the entrance to the house. Such a stabilizer must have high power, a large input voltage range and high reliability. We recommend SKAT ST voltage stabilizers with power from 3.5 kW to 12 kW. The following video shows the capabilities of the SKAT ST-12345 stabilizer.
The second method is to install local stabilizers to power individual electrical appliances. Such stabilizers must have sufficient power, a large input voltage range, compact size and high reliability. We recommend SKAT ST voltage stabilizers with power from 1.5 kW to 3 kW. The following video shows the capabilities of the SKAT ST-2525 stabilizer.
Conclusions: to solve the problem of low voltage in the house, it is necessary to establish the causes of this phenomenon, try to eliminate problems in the network, and use voltage stabilizers.
Quite often, inconsistencies in the quality of power supply in the household network become a headache for Russians; this is mainly expressed in a significant decrease in voltage from standard values. This article will describe why the voltage drops, the reasons for the appearance of deviations in the values of the main characteristics of the power supply, the negative impact on electrical appliances, and provide a number of possible examples of solving problematic issues with the supply voltage.