Voltage parameters
Before you say that the voltage in your network does not meet the standard and file a claim with the energy supply organization, you need to know this standard. The voltage deviation range is set in normal mode: δUynorm= ± 5%, in the maximum permissible: δUylim= ± 10% of the nominal value.
In Russia, the rated voltage of the household network is Unom = 230 Volts (V), the upper range is 242 V. For Unom = 380 V, the upper range is 418 V. If the voltage is higher than these ranges and for this reason household appliances fail, you have the right to complain to the energy supply organization.
Voltage asymmetry
Voltage asymmetry is characterized by two indicators:
- negative sequence voltage asymmetry coefficient;
- zero sequence voltage asymmetry coefficient.
These indicators are defined as values averaged over an interval of 3 s.
The normally permissible and maximum permissible values of both voltage asymmetry coefficients are 2.0 and 4.0%, respectively. The zero sequence asymmetry coefficient makes sense only for four-wire electrical networks of 0.4 kV; the standards for the negative sequence asymmetry coefficient are the same for networks of any voltage.
Overvoltage in apartment buildings
Recently, overvoltage in apartment buildings built before the early 90s has become a real disaster. When these houses were built, microwave ovens, refrigerators (two), computers, home solariums, etc. were not included in the design load.
But, nevertheless, consumers enjoy these benefits of civilization. What ends up happening? In the electric power industry there is a concept of evening and morning load peaks. It is at this time that people go to work, cook, turn on many electrical appliances in general.
burnout of the neutral conductor
If in normal mode the voltage between the phase and neutral conductors is 230 V, then in this case there is no neutral conductor and the voltage will be between the phases, i.e. 380 V. As a result, the voltage “walks” along the riser. Its value depends on the load connected to the network and can be in the range of 140 - 380 V from the point where the neutral conductor burns out.
Maximum voltage deviation in the electrical network
The current in the network is, for natural reasons, not constant and varies in certain parameters. Within the framework of the new 230 V/400 V standard, the nominal deviation is permissible within 5% and a maximum of no more than 10% should be observed in short-term intervals. Thus, such a theoretical deviation is allowed within 198 V and up to 242 V. This range can be considered relevant for most current apartments.
What affects network fluctuations in energy supply and voltage loss:
- One of the most common reasons is obsolescence of equipment, including meters, electrical panels, wiring cables, and so on;
- Significant errors are also observed in a poorly maintained network;
- Errors when planning and performing installation work in the house;
- Significant increase in energy consumption indicators exceeding the established standard.
As already noted, network fluctuations of +-5% are acceptable. So, for example, according to the supplied indicator of 220 volts, the permissible deviation in the network is equal to 209 V and the maximum excess is equal to 231 V.
What should an energy consumer do?
The simplest way to protect against power surges is to turn off devices in a critical situation. Such devices are based on voltage control relays of the RN type and electronic control circuits. If there is an excessive drop in the network, household appliances turn off, and when they return to a stable state, they automatically turn on again.
Such devices are mounted directly at the entrance to the electrical appliance. With their help, most often, long-term operating devices (refrigerators, washing machines, etc.) are protected. If there are frequent and long-term fluctuations in the network, care must be taken to continuously maintain its parameters within normal limits. For these purposes, special devices are used - voltage stabilizers.
If the fluctuation occurs within the operating range, then the device constantly maintains the voltage at the nominal value (220 V) with a deviation of no more than 1-2%. When jumps exceed the permissible values, the device turns off and turns on again when returning to operating limits. Modern stabilizers have an operating range of about 160-250 V.
If voltage drops are caused by internal reasons (for example, poor quality wiring), then you need to call a professional electrician to correct the situation. He will find the reasons and eliminate the malfunctions. It’s another matter when there are network disturbances and a voltage that does not meet GOST requirements is supplied to the apartment’s input. If such cases are recorded frequently, then you should exercise your right as a consumer of the service.
Where to complain?
If you have a complaint about the quality of power supply, you can contact:
- management company;
- territorial power grid company;
- municipal housing and communal services department;
- Housing inspection;
- Rospotrebnadzor.
You can complain by visiting the organization in person, by letter or via email. Procedure:
- submitting an application to the organization servicing the house and calling an electrician;
- drawing up a report on deviations from the norm by an electrician;
- submitting an application with a report attached to the management company with a request to rectify the situation;
- if refused, send a complaint (claim) to the supervisory authority.
How to file a complaint?
If the tenant refuses to eliminate the violations, he has the right to file a complaint with any of the above authorities. The basis for its design is the Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 05/06/2011 No. 354 and GOST 32144-2013, which establishes electricity quality standards. The complaint is submitted in writing in free style. Some points are mandatory:
- Name of the organization and full name of the person to whom the claim is being written.
- Full name, passport details and address of the person filing the complaint.
- Reasons for appeal and complaints with references to the legislation of the Russian Federation.
- Finally, you need to describe your requirements.
- Add date and signature.
It is important to clearly indicate the violations identified.
The following claims can be considered justified:
- excessively low or high voltage;
- long periods of unstable voltage and its complete loss;
- signal frequency deviation from the norm;
- the appearance of impulse voltage.
The consumer has the right to make the following demands:
- Tariff reduction by 0.15% for each hour of supply of electricity of inadequate quality (Resolution No. 354).
- Compensation for losses in the event of failure of household appliances due to a sudden power surge.
The complaint is accompanied by an act of violations, a report or a certificate from the repair shop about the failure of the equipment.
We do not recommend completing the documents yourself. Save time - contact our lawyers by phone:
8 (800) 350-14-90
In what time frame should it be responded to?
The organization responsible for the power supply of the house is obliged to respond to the complaint within 3 days PP 354, if the complaint is filed with a government organization, then up to 30 days, Federal Law-59 Art. 12. To clarify the causes and assess the damage, she has the right to send a special commission, as well as attract independent experts. The corresponding condition assessment report is sent to the applicant.
Mandatory voltage regulation in electrical networks
Carrying out your own voltage regulation is not only labor-intensive, but also requires financial investment. An even more difficult option is to seek stabilization of the current in the network from the supplier organization. This can be done by filing complaints, personal appeals, and lawsuits, however, the result is not always achieved even by these methods.
If you still decide to correct the picture yourself, then this is possible in the following way:
- Method of centralized voltage regulation. This approach involves calculating how many changes will be needed to stabilize the situation and adjusting the central power supply accordingly.
- Linear impact method. This is done using a so-called linear regulator, which changes the phases using a secondary winding on the circuit.
- Use of capacitor banks in the network. This method is theoretically called reactive power compensation.
- Also, an extremely unstable network can be corrected using longitudinal compensation. It involves connecting capacitors in series to the network.
Another relevant option, if the deviation from the established norm is not too pronounced, is to install one large or several small stabilizers in the network. This will require some financial investments, special installation skills, and is also not suitable for highly fluctuating power supply systems, because they simply cannot do a large amount of work and regulate a large amount of voltage.
So, as has already been determined, the new generally accepted standard is the network voltage in an apartment from 230 V to 400 V. For example, the voltage scale can be 240 V, 250 V, taking into account the maximum permissible error. However, for the e1f outlet we are used to, the operating voltage is still the same 220V level, which has been familiar to us all since the Soviet period.
Safety, electricity and electrical maintenance
Maintaining electrical appliances is often the responsibility of a home handyman. Safety precautions and electricity in the house are two inextricably linked axioms that should be observed. Maintenance of electrical networks must be carried out by a specialist who has the appropriate clearance to work with the specified voltage level in the house.
Never touch live wires, first turn off the power source and only then, after three to five seconds, start working.
Do not rely on insulated tool handles; they only protect against accidental contact with exposed wires.
Do not use improvised materials for insulation; use only electrical tape.
Wear rubber-soled shoes when working with electricity.
Avoid humidity; it is dangerous to work with electricity in a damp room, and with wet hands you should not even come close to exposed wires.
Before completing the work, analyze your actions and make sure that you have not overlooked anything.
Full voltage standards in the electrical network: GOST
Despite the fact that the majority of ordinary people and people who do not belong to the category of knowledgeable in the field of voltage in their electrical network will affirmatively say that the standard voltage is 220 V. To their surprise, even despite the old and familiar stickers, on which indicates the generally accepted standard are no longer relevant.
Such acts have also been adopted in Ukraine and the Baltic countries, including Belarus.
What did the change in standard lead to:
- The operating voltage on the power cable has changed;
- Fluctuations have become a little more significant than before, but still within the acceptable limits of 5% and the maximum – 10%;
- The potential payment for electricity supply services has not increased by a completely symbolic amount;
- Voltage supply frequency – 50 Hz.
Thus, the network voltage should be considered slightly increased in everyday practice. But in reality, everything is different, and this promises the presence of pitfalls in the supply of electricity to organizations. Despite the generally accepted standard, organizations supplying voltage to apartments in houses supply everything according to the same standards adopted back in Soviet times and equal to 220 V. All this happens officially in accordance with GOST 32144-2013, which is what suppliers are guided by.
Can damage caused by a power surge be compensated?
What to do in case of power surges and is it possible to compensate for damage to damaged household appliances? This is possible, the approximate procedure is as follows:
Important! If a power surge occurs in your presence, immediately call emergency services, report the incident and request that a report be recorded. Call an emergency team, who will be able to record the fact of a fault in the power supply on the spot. In the future, this measure will serve as evidence in court.
- Determine who is responsible for causing the damage.
Typically, this is one of two organizations: the electricity supply company; a company that provides home electrical services. To fulfill this point, you must write a statement to both organizations and demand a response indicating the reasons for the network problems. The organization has 30 days to submit a response. To determine the causes of damage, companies may create special commissions or engage third-party experts who will examine the condition of power supply networks and failed equipment. One copy or a copy of the inspection report is sent to the applicant. - Take the damaged household appliance to a service center
and ask for an opinion on the causes of the malfunction and the possible cost of repair. You can have the damage assessed by an expert. The cost of this service must subsequently be included in the statement of claim. - Send a written request to the person responsible for the damage
demanding compensation for the damage. Please attach copies of expert reports and inspection reports to your application. - If the guilty organization (or a specific person) refused, or did not respond at all to the appeal within 30 days, then the next step is to file a claim in court under Article 17 of the Federal Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”. Another option for this action is to contact the prosecutor’s office with a request to protect violated rights. In this case, the claim will be filed by the prosecutor.
It happens that the culprit of causing harm is a specific person (for example, a neighbor), who independently carried out repairs and violated the rules for installing or operating electrical installations.
If the culprit of the damage is the electricity supply company, then the statement of claim contains a reference to Article 309, Part 1 of Article 539 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Part 1 of Article 547, Articles 4, 7 and 14 of the Federal Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”.
If the culprit is a company that services utility networks at home, then refer to the violation of Article 309 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Articles 4, 7 and 14 of the Federal Law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights”, paragraphs 49 and 51 of the “Rules for the Provision of Public Utilities to Citizens”, paragraph 5.6 of the “Rules” and norms for the technical operation of the housing stock,” paragraph 7 of the “Rules for the maintenance of common property in a residential apartment building.”
IMPORTANT: To make it easier for the judge to make a decision in your favor, additionally attach to the statement of claim evidence from neighbors who find themselves in a similar situation.
To summarize the article, it should be noted that it is easier to take measures in advance to protect home equipment from power surges in the network than to waste time and nerves in the courts.
Preface
It is necessary to know what voltage is in the network to comply with safety rules during maintenance.
Contents
A lot depends on the voltage in the house: the performance of household appliances, their service life and fire safety. It is necessary to know what voltage is in the network to comply with safety rules during maintenance. This material talks about voltage in the house, discusses the main technical aspects, and gives recommendations. It is possible to ensure stable voltage in the AC network by relying on a knowledge base and practical experience. Therefore, it is best to trust a specialist from the energy supply organization to regulate the mains voltage. But knowing what voltage is in the network is also useful for the home handyman, for example, when replacing household lighting fixtures.
To transmit electricity over long distances, voltages of several tens, hundreds, and thousands of volts are used. This is done not at the whim of specialists, but, first of all, in order to save wire material. The higher the voltage, the less electric current flows through the conductor (when transmitting the same unit of energy), and the amount of heat released in the conductor is proportional to the square of the current. This means that if you wanted to transmit electricity at a voltage of, for example, 220 V, you would have to use thick wires; thin wires would quickly heat up and burn out. But thick wires over long spans will break under their own weight. Therefore, electricity is transmitted at high electrical voltages, and at transformer substations the voltage is reduced to values used in everyday life (hundreds of volts). Compared to the voltage of high-voltage power lines (330-750 kV), the voltage of 220 V is low, and it is sometimes called low voltage, but let us note right away that “low” voltage is not “safe”. If you touch bare wires or other live parts energized by 220 V, an electric current will pass through the human body. Depending on the strength of the current, which, in turn, depends, among other things, on the moisture content of the skin of the hands, and on the type of shoes, etc. (i.e., on the resistance of the human body), there can be very disastrous consequences, even to death.
GOST 29322-92. Standard voltages
Of all the former republics of the USSR, Russia, Ukraine, and the Baltic countries switched to the “230V” standard.
It should be understood that electrical equipment manufactured in Russia and for Russia must operate normally at both 220V and 230V. As a rule, devices have a voltage range from -15% to +10% of the nominal voltage.
Geography of countries with standard voltages: 100V, 110V, 115V, 120V, 127V, 220V, 230V, 240V
Different countries around the world have adopted different mains voltage standards. You can find the following standards: - 100V in Japan, - 110V in Jamaica, Haiti, Honduras, Cuba, - 115V in Barbados, El Salvador, Trinidad, - 120V in the USA, Canada, Venezuela, Ecuador - 127V in Bonaire, Mexico, - 220V in many countries in Asia and Africa, - 230V in many countries of Europe and parts of Asia, - 240V in Afghanistan, Guyana, Gibraltar, Qatar, Kenya, Kuwait, Lebanon, Nigeria, Fiji
Geography of countries where voltages of 220V and 230V are accepted
The most widely used standards are 220V and 230V; these standards are accepted in more than 150 countries around the world.
In practice, of course, the network voltage is constantly changing and depends on many factors. Often the permissible voltage range is indicated on the back of the product or on the electrical plug of the device. The most demanding in terms of power quality are devices that have electric motors (refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, heating boilers, pumps). It is clear that for any devices used in Russia, both 220V and 230V voltages are good.
What are the deviations in power quality? It is well known that our networks often have significant deviations from power quality standards. And the voltage can be significantly lower than 220V or significantly higher than 230V. The reasons for this phenomenon are also known: aging of existing electrical networks, poor maintenance of networks, high wear and tear of network equipment, errors in network planning, and a large increase in electricity consumption. Problems in networks include: low and low voltage, high and high voltage, power surges. voltage dips, overvoltage, change in current frequency.
There is a solution to the problem! And every lover of country life has the right to provide himself with stable voltage using our equipment. We are waiting for your questions and comments by email. email [email protected]
5 reasons to buy a stabilizer from us
- urban comfort in your countryside, thanks to the stable operation of all electrical equipment
- consultation from our professional engineers to solve your specific problems
- warranty on our equipment is 3 (three!) years
- free delivery directly to you within the city
- installation of equipment by a professional electrical engineer
What is the network voltage
Since 2003, a standard voltage of 230V should have appeared in the sockets of our apartments and private houses. But for the past 17 years this transition has not been completed.
From September 30, 2014, instead of GOST 29322-92, GOST 29322-2014 (IEC 60038:2009) was adopted, establishing what the standard voltage should be in Russia. Now its value is 230 V (±10%) at a frequency of 50Hz (±0.2). But still quite often there is 220 V in the electrical network instead of the expected 230 V.
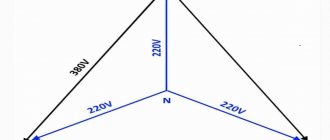
The rated parameters of AC power networks up to 1000 V are indicated in the table given in GOST 29322-2014.
In the first and second columns, the smaller values are the voltage between phase and neutral (phase), the larger values are between phases (linear). If one value is specified, it is the voltage between phases of a three-phase three-wire system.
The standard voltage of 230/400 V appeared as a result of the evolution of the 220/360 V and 240/415 V systems. Currently, the 220/360 system is no longer used in Europe and other countries, but 220/380 V and 240/415 V are still actively used.
The change in standards was caused by the need to bring electricity into full compliance with European parameters to facilitate the export and import of electricity and electrical devices.
Non-sinusoidal voltage
Non-sinusoidal voltage is characterized by two indicators:
- voltage waveform sinusoidal distortion factor;
- coefficient of the nth harmonic component of voltage.
These indicators are defined as values averaged over an interval of 3 s.
Rice. 8.18. Permissible voltage fluctuation ranges
The sinusoidal distortion coefficient is determined by the formula, %:
The harmonic values are normalized to n = 40. The permissible KU values are given in table. 8.4.
Table 8.4
Acceptable values of sinusoidal distortion coefficient
Normally permissible values of the coefficient of the nth harmonic component of voltage are given in table. 8.5.
Table 8.5
Normally permissible values of the coefficients of harmonic components
Normally permissible values given in table. 8.5 for n equal to 3 and 9 refer to single-phase electrical networks. In three-phase three-wire electrical networks, these values are taken to be half those given in the table.
The maximum permissible values of the coefficients of the harmonic components of voltage are 1.5 times higher than the normally permissible values.
Voltage drop in the home network
The so-called voltage drop can be fraught with many undesirable consequences. Moreover, it is undesirable both by the residents themselves and by the supplier organization, because it will be the one who will cover all unforeseen expenses. For objective reasons described earlier, power outages can reach record levels.
If there is no desire to correct the defects, this is grounds for filing a claim in court.
What are the consequences of exceeding or significantly reducing the established norms for voltage supply in the house:
- Light bulbs burn out faster;
- This is especially harmful for a refrigerator, washing machine and other electrical household appliances that require powerful and constant voltage;
- The service life of any electrical equipment, including microwaves, toasters, TVs, computers, and so on.
Thus, it becomes obvious that all classes of electrical engineering suffer from severe voltage fluctuations. This influence is especially destructive if the network voltage is low. And the obligation to provide uninterrupted, stable and high-quality current belongs to the organization that supplies it and, according to the contract, must ensure its high-quality service.
What to do if the power supply voltage is higher or lower than normal
Relations regarding the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings, owners and users of residential buildings, including relations between providers and consumers of utility services (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2011 No. 354) (hereinafter referred to as the Rules). These Rules establish the procedure for monitoring the quality of the provision of utility services, the procedure for changing the amount of payment for utility services when providing utility services of inadequate quality, and also regulate issues related to the onset of liability of providers and consumers of utility services.
Utilities are the activities of a contractor to supply consumers with any utility resource individually or 2 or more of them in any combination in order to ensure favorable and safe conditions for the use of residential, non-residential premises, and common property in an apartment building.
How much do you need for electrical appliances?
Equipment manufactured in Russia for domestic consumers operates at both 220 V and 230 V, because manufacturers provide the required margin from -15% to +10%. from face value. But in each specific case, the permissible range of power supply characteristics for the device is indicated in the product passport or on its label. For example, computers can operate at 140 - 240 V, and a telephone charger at 110 - 250 V. These markings are often applied to the product itself.
Devices with electric motors are most sensitive to power quality. Here, a reduced voltage can lead to difficulties in starting and shortening the service life of the equipment, while an increased voltage will lead to overloads, which also shorten the service life. If you take a regular incandescent lamp and lower the supply voltage by 10%, the glow intensity will noticeably decrease, and if you increase it, its service life will be reduced by 4 times.
The permissible maximum network limit is 253 V. This value may be too high for electrical equipment designed for 220 volts. The difference in voltage will lead to overheating of power supplies, network adapters, and premature failure of devices.
If you notice that your equipment has begun to overheat or break down, check the voltage in the network. If a deviation of more than 10% is detected, immediately contact your network company. They are required to take measures to eliminate the factors that caused the violations.
Now you know what the voltage standard in the Russian network is according to GOST. If you have any questions, ask comments under the article. We hope the information was useful and interesting for you!
Determining whether there is a deviation from the norm is quite simple.
When the voltage is low, electrical appliances will stop turning on or will work intermittently. With increased voltage, devices can completely fail and “burn out”. If the voltage in the apartment exceeds or falls short of the specified maximum standards, the owner has the right to contact the management company. Procedure:
- The owner makes a complaint to the company servicing the house.
- The electrician measures the voltage, draws up a report of work performed, and records deviations from the norm.
- The owner submits an act to the management company to eliminate the causes of deviations from the norm.
- If the management company refuses to correct the situation, the owner has the right to go to court.
Amount of permissible voltage drop: PUE
According to the accepted rules for the design of electrical installations (PUE) back in the former USSR, a voltage drop is the difference in voltage levels at different points of the network. As a rule, these are the starting and ending points of the chain. In established standards, the law requires a distinction between the concepts of voltage deviation and voltage loss. If the first case, on a generally accepted scale, is considered using the example of an incandescent lamp, the deviation indicator of which is recognized as nominal and mandatory, then in the case of the loss considered on the station buses, this is recognized as a recommended indicator.
Normal voltage drop in the network:
- In so-called overhead lines – up to 8%;
- In cable power supply lines – up to 6%;
- In networks of 220 V - 380 V - in the region of 4-6%.
In this case, a drop in the emergency mode is considered to be a drop of up to 12% in the network - this is the established limit. A fall above the established norm promises the activation of the automatic protective system, which should be activated when the lower norm is reached for at least 30 seconds.
Also in some sources you can find voltage standards that exceed even the new indicators of 230 V and 400 V. Do not confuse examples of domestic use with a plant or factory, where the indicators naturally significantly exceed the domestic environment.