At an early age, many of us learned from personal experience or from eyewitness accounts that if you plug in an iron and try to cut the power cord, you will definitely experience a painful shock. This is how electric current affects the body. At school they write above the sockets: “220 V, dangerous, will kill!” At substations, in transformer booths and in other high-voltage installations, warning signs are posted: “Danger to life, high voltage!” So what exactly is dangerous to humans and why? What hits: current or voltage? First, let's understand these concepts.
What danger does high voltage pose to humans?
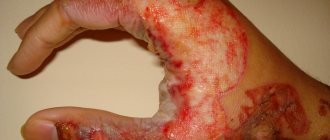
Even the smallest exposure to electric current on the human body can cause damage. It is necessary to take into account not only the fact of how strong the electric shock will be, but also how long it will act on the body. Dangerous stress for a person can even be minimal, since much still depends on the body itself. The current cannot be seen with your own eyes, determined by sound or smell; the effect begins when a person comes into contact with it.
How can current affect the human body?
Electric current can instantly spread upon contact throughout the body. In order for it to pass through the body, it needs an “entry” place, and then the current, passing through the entire body, has an irritating effect on it. For example, the effect of current on the human body is divided into several types:
- Thermal, when you get a burn.
- Mechanical, when soft tissue ruptures.
- Chemical is directly electrolysis itself.
As a result of an electric shock, a person’s muscles may involuntarily contract, breathing may be paralyzed, and the heart may stop.
What voltage is considered dangerous for humans?
If a person is in a dry room, then the voltage for him is dangerous, which turns out to be over 36 volts. Death can occur with a shock of 0.1 ampere. A current of 0.05 amperes is also dangerous to life. The fact is that with such a current strength, convulsions occur that do not give a person the opportunity to move away from the source of the lesion.
If we are talking about static electricity, then such electricity does not pose a danger to human life. The maximum that the human body can feel from the impact of a spark discharge is an injection. Alternating current poses a great danger to human life. Dangerous voltage for humans is over 50 V, and under unfavorable conditions (humidity, for example) – over 12 V. Dangerous current – 50 mA. It is the current of this force that can cause damage, and its effect on the human body within 5 seconds can become fatal.
Consequences of electric shock
It is characterized by the fact that it sharply excites the nerve endings of tissue cells at the site of the impulse. Spontaneous chaotic contractions of muscle tissue occur.
Degrees of electric shock depending on the state of the human body
| Degree of damage | State |
| 1 | Muscle cramps, full consciousness |
| 2 | Muscle cramps, lack of consciousness |
| 3 | Freezing of the diaphragm, the heart is pumping |
| 4 | Cessation of breathing, cardiac paralysis - clinical death |
Heart failure
A vital organ stops functioning due to electric shock to the heart muscle. This happens when an electrical current tends to pass directly through the sternum.
Current paths
Fibrillation
The heart works normally when all the ventricles pump blood rhythmically. The current can cause the heart to flutter. As a result, the living pump ceases to perform its function. Blood stops circulating in the vessels, pressure drops sharply, and death can occur within 5-8 minutes. Timely first aid (combined use of chest compressions and artificial respiration) can save the victim.
Electric shock
An electric shock causes a severe neuro-reflex state in the body. Blood pressure drops, respiratory organs freeze, and metabolic problems arise. A person finds himself in a complete stupor for ten to fifteen minutes, and can remain in this state for 24 hours. If emergency assistance is not provided, the injured person may die. Timely assistance will lead to the victim making a full recovery.
Factors that affect the body during electric shock
It is necessary to take into account not only the strength of the electric shock, but also what path it will take through the body. It is worth remembering that the longer the current path through the human body, the more severe the consequences will be. As we have already said, alternating current is considered life-threatening; direct current does not have such a destructive effect on the human body. There are a number of additional factors that may increase the danger:
- High current strength.
- Passing it through the body. It should be noted that different tissues of the body have different resistance abilities; in most cases, the current passes through the blood vessels. The worst thing is when the path of the current runs along the entire body, for example, this can happen if the arm and legs are involved, then the current can pass through the heart, spinal cord or brain. But sometimes death can occur when current passes from hand to hand, it all depends on how high the dangerous voltage was.
- Exposure time. The time interval allowed for exposure to current should not exceed 2 seconds.
- Conductivity.
- The area where the electric shock occurs.
It is impossible to calculate exactly how the current will affect the body. Human attention plays an important role, therefore, in dangerous places, it is necessary to provide a special safety sign, which is called the “high voltage” sign.
Physiological effects of electric shock
Physiological effects vary at certain currents
Note that voltage is not considered here. The electric shock is relatively more severe if the current increases
For currents above 10 milliamps, the muscle contractions are so strong that the victim cannot let go of the wire, which shocks him.
At values above 20 milliamps, breathing becomes difficult and finally stops completely at values around 100 mA. Doctors say that at a current of 100 milliamps, the heart experiences ventricular fibrillation - uncoordinated twitching of the walls of the ventricles of the heart, which leads to death. Just above 200 milliamps, muscle contractions are so strong that the heart muscles are forcibly squeezed. This clamp protects the heart from ventricular fibrillation and increases the victim's chances of survival.
In some US states that carry out the death penalty, the electric chair is used. The electric chair uses a voltage of 2700 volts and a current of 5 amps for 15 seconds. The rules of use include up to three cycles of exposure. There are known cases where sentenced prisoners survived after three cycles of using the electric chair.
What current is safe
Thus, there is no absolutely clear answer to the question “what current is safe”.
In this case, you also need to remember Ohm's Law: current is equal to voltage divided by resistance. Body resistance ranges from MΩ (mega ohms) to kΩ (kilo ohms), depending on skin type, dryness and where the wires touch on the body.
What role does body resistance play?
The resistance of the body depends on the condition of its skin; the following factors can have an influence:
- What condition is a person’s skin in? For example, it can be clean, it can be dirty, wet, damaged.
- What was the area of contact of the current with the skin?
- The magnitude of the applied voltage.
- What frequency current passed through the body.
- General condition of the human nervous system.
If the skin has been scratched or abraded, the dangerous stress may be minimal for death to occur because the body's resistance is reduced. The ability to resist is lost in a person who has a sweaty or dirty hand. For example, a voltage of 30 volts with dry hands does not cause severe pain, but if you touch it with a wet hand, a person will not be able to unclench his fingers and will feel severe pain. In such cases, it is customary to say that a breakdown of skin resistance has occurred.
Skin resistance can decrease even when a low voltage is applied, 20-40 volts.
What voltage is considered acceptable?
Statistics indicate that most electrical injuries occur from touching exposed wires. There are three safe voltages:
- In rooms where there is no increased danger, 65 volts are allowed.
- In a room where there is danger - 36 volts.
- In high-risk areas - 12 volts.
In premises of the second and third types there must be a “high voltage” sign, which will warn of danger. Often, injuries occur to employees who, by the nature of their employment, are required to work with voltages up to 1000 V, but neglect safety precautions and do not use protective equipment.
The answer to the question of what voltage is considered dangerous can be quite simple: any electric shock can cause damage, but the most dangerous is considered to be voltage from 60 V, when respiratory paralysis and cardiac arrest can occur. But this may not happen if you pay close attention to everything that surrounds a person and in some way relates to electricity. Personnel who work with high voltage and electric current must always remember safety rules and be on high alert.
So, from this article you learned what voltage is life-threatening. We hope you find this information useful.
Video
Watch a video about alternating and direct electric current. These videos will teach you about the hazards and how to protect yourself from electrical shock.
Recommended viewing:
- Question: why can’t I install a duplicate counter?
- Various schemes for crimping twisted pair 4 and 8 cores
- Electromagnetic relay, what is it, what is the principle...
- Surge filters for electrical equipment
- Why didn't the circuit breaker trip? Video
- What is the correct name for a machine for high current...
2+