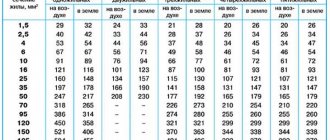
What is allocated electrical power?
The allocated power (or permitted power) is the maximum permissible one-time load in kW on the consumer's network (apartment, private house or cottage), which cannot be exceeded.
The rules for connecting private houses and apartments to the electrical network are set out in SP 31-110-2003 “Design and installation of electrical installations of residential and public buildings” and RM-2696-01 “Temporary instructions for calculating electrical loads of residential buildings.” According to these documents, each apartment or private house should be allocated from 5 to 7 kW if a gas stove is installed, and from 8 to 11 kW with an electric stove installed. In addition, the allocated power must be specified in the electricity supply contract.
For comparison, during the Soviet era in apartments, as a rule, the established electricity rate was only 1.5-3 kW, but the increase in the number of household electrical appliances and their power consumption gradually required an increase in this parameter.
Private houses and dachas located in horticultural, gardening and dacha non-profit partnerships, as a rule, are allocated electricity within the limits of the connected power specified in the technological connection act, which is no more than 15 kW in a three-phase network (5 kW for each phase) or no more than 5.5 kW in a single-phase network. This norm is established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 334 “On introducing amendments to certain acts of the Government of the Russian Federation on improving the procedure for technological connection of consumers to electric networks.”
Dedicated power and input machine
In accordance with the value of the allocated power, a corresponding input circuit breaker (or circuit breaker) is installed in the electrical panel, where the external power cable of the electrical network is supplied, which is located immediately after the electric meter.
The device is a box with a switch designed to protect the entire electrical wiring of the house from overload and short circuit currents, as well as a general disconnection of its power supply from the external line. As a rule, after the introductory circuit breaker, additional circuit breakers are installed for various types of loads.
Input circuit breakers can be single-pole, two-pole (used in single-phase electrical networks) and three-pole (used in a three-phase network and allow each phase to be disconnected). For example, with an authorized power of 5.5 kW, a 25 A input circuit breaker (C25) will be installed in the electrical panel. On the Internet you can easily find tables that indicate the permitted power of each circuit breaker model.
What determines the power of the electrical network?
The change in electrical network capacities depends both on the external conditions of their supply and on the installation of limiting devices (automatic, semi-automatic) that regulate the supply of capacitive power to the source of consumption. This can be done at different levels, from the household panel in the house to central power distribution devices.
The power of the electrical network can be determined with a special device or calculated through mathematical calculations (if you know the current and voltage parameters).
To measure power with a device, you need to connect the tester to a current source, configure it specifically to receive the necessary data, because the tester works both in wattmeter mode and in ammeter mode. Therefore, you can find out the network power in another way. By measuring the current and knowing the operating voltage of the 220V network, you can multiply these values and get the required amount in Watts.
The passage of a certain amount of power through the electrical network requires the use of power supply equipment and the supply of materials to the power network that will meet the requirements of the required nominal values.
How to determine what the allocated electricity capacity is in your home?
There are several ways to determine the exact allocated power that a private house or summer cottage has.
1) View the rating of the input machine
The easiest way to determine the allocated power of electricity to a house is by the value of the operating current for which the input circuit breaker installed in the electrical panel is designed. To do this you will need to perform a simple calculation. For example, on the body of the input machine the operating current is indicated as 32 A. It is necessary to use the following formula: P max = U x I, where:
- U – rated mains voltage (220 or 230 V – will depend on what mains voltage is supplied to the house);
- I – indicator of the operating current of the input circuit breaker in amperes.
The problem with this method is that the rating of the input machine does not always coincide with the official allocated power.
For example, this occurs when an external line has been upgraded with an increase in its power, and also if the electrical wiring has not been changed for a long time or its installation was performed poorly.
If the allocated power of electricity significantly exceeds the capabilities of the input circuit breaker, then it would be advisable to replace it and bring all electrical wiring in the house into compliance.
2) Contact the operating organization
The allocated power per home can also be found in the electricity supply contract. If it is missing, then you must contact the operating organization, which must issue a certificate of actual power consumption and installed power. In Moscow and the Moscow region, this is done by Mosenergosbyt OJSC. The company provides the service for a fee, its cost is on average 2 thousand rubles.
If a private house is serviced by a management company, then it is the company that is obliged to issue the owner a certificate of allocated power or permission to connect to the house’s electrical networks and an act of delimitation of balance sheet ownership and operational responsibility.
In SNT, the data on allocated power for each site is owned by the chairman of the partnership, who must inform its users about this.
3) Study the energy supply agreement
You can find out the allocated power in the contract for power supply of an individual residential building (household) between Mosenergosbyt OJSC and the owner. Information about this is usually indicated in the “Subject of the Agreement” section with the following wording: the maximum power of a household is determined based on the parameters of the technological connection of the subscriber’s power receiving devices to electrical networks and is 5 kW.
Calculation of the total power consumption of the load in the house
Calculation of the total power consumed by the load is necessary to find out whether there will be enough power to supply existing electrical appliances with electricity and connect new consumers in the future.
The power consumed by the entire load is calculated as the sum of the power consumption of all devices turned on at the same time. To do this, you need to find out the maximum active power of each consumer, taking into account its starting currents. It is indicated on the “nameplate” or in the data sheet of the device and is measured in W.
You can also find the designation of power consumption in volt-amperes (VA). But this is not the same meaning. Active power is measured in watts (denoted by the letter “P”), and in volt-amperes - total power (denoted by the letter “S”). To calculate the maximum load, you will need exactly the value in W. To convert VA to W, you need to use an online calculator or the formula: P = S x cos(φ), where cos(φ) is the power factor (if it is unknown, then the average value is usually taken, which is equal to 0.8).
After calculating the total load power consumption, it is necessary to add a reserve that takes into account a possible increase in the number of consumers in the future. As a rule, another 20-30% of the maximum load is added.
Power as a function of voltage and current
In electrical circuits, power depends on both voltage and current. Not surprisingly, this relationship bears a striking resemblance to the "proportional" horsepower formula above:
\[P=IE\]
However, in this case, power (P) is exactly equal to current (I) times voltage (E), rather than simply proportional to IE. When using this formula, the unit of measurement for power is the watt, denoted as “W” (or “W” in English literature).
It should be understood that neither voltage nor current alone constitutes power. Rather, power is a combination of voltage and current in a circuit. Remember that voltage is the specific work (or potential energy) per unit charge, and current is the rate at which electrical charges flow through a conductor. The strain (specific work) is similar to the work done when lifting a weight against gravity. The current (velocity) is similar to the speed at which the load is lifted. Together, as a product, voltage (work) and current (speed) make up power.
Just like a diesel tractor engine and a motorcycle engine, a high voltage, low current circuit can dissipate the same amount of power as a low voltage, high current circuit. Neither voltage nor current alone indicate the amount of power in an electrical circuit.
Selection of the “Calm” voltage stabilizer model for home protection
So, having data on the allocated power, you can easily select a suitable voltage stabilizer model to protect the entire electrical system in the house.
When choosing a stabilizer model for centralized connection of electrical appliances, you need to pay attention to its technical capabilities. For example, it is important that the device has terminal blocks through which it can be easily connected to the mains.
The design should also be taken into account. If the stabilizer will be installed next to the electrical panel, then it must be able to be wall mounted. The noise level is important when installing the device in a residential area.
Selection according to the nominal value of the introductory machine
Stabilizer for single-phase network
For example, a 220 V network with a permissible output power of 5.5 kW is installed in a house with a 25 A input circuit breaker installed. In this case, wall-mounted IS7000 voltage stabilizer models with an output power of 7000 VA / 5000 W or IS1106RT for floor or rack installation are ideal with output power 6 kVA / 5.4 kW.
Stabilizer for three-phase network
Another example. A three-phase network of 380 V for 15 kW was installed in a private house. In this case, each phase accounts for 5 kW. Accordingly, three 25 A single-phase circuit breakers are installed in the electrical panel. In this case, there are several options to protect the entire electrical system of the house.
| Option | Description |
| 1) Installation of a single-phase stabilizer on each supply phase | If the house has only single-phase consumers, then the most convenient and functional option for providing protection would be to install one voltage stabilizer for each phase. For our case, the above IS7000 stabilizers for 7 kVA/5 kW or IS7000RT for 7 kVA/5.5 kW are also suitable. Note! This option has increased resistance to problems in the power supply, which is determined by the independence of the stabilizers from each other: a failure in a separate phase or a malfunction of one of the devices will not affect the functioning of the other two phases and the condition of the stabilizers installed on them. |
| 2) Installing a voltage stabilizer with a 3:1 configuration | Another option for providing centralized home protection from unstable mains voltage is to connect a voltage stabilizer that has a special configuration (three-phase input and single-phase output). The device can be installed immediately after a three-phase input circuit breaker. The line of models from the Shtil Group of voltage stabilizers with a 3:1 configuration includes the IS3120RT model with a power of 20 kVA/16 kW, which will provide reliable connection and protection of a single-phase load to a three-phase network with uniform loading of all supply phases, which eliminates the possibility of network imbalance and eliminates from the need for constant interphase balancing. It is important to note that the power of connected devices may be greater than the power of an individual phase. |
| 3) Connecting a three-phase voltage stabilizer | If there are three-phase consumers in the house, three-phase models of voltage stabilizers that operate on a 380 V network will be required. In the line of inverter stabilizers of the InStab series from the Shtil Group, the IS3320RT model with a power of 20 kVA/16 kW is presented, which will ensure protection of the entire volume as a three-phase , and single-phase electrical equipment in the house. |
Selection depending on the total load power
You can also select the necessary voltage stabilizer model for centralized home protection based on the total power consumption of the load that is currently connected or planned in the future.
For example, in a house with a 220 V network, the following single-phase electrical appliances are installed, to which a voltage stabilizer must be connected:
| electrical appliance | Power consumption, in W |
| TV | 200 |
| Lighting (indoor and outdoor) | 1500 |
| Boiler | 1500 |
| Fridge | 1500 (including starting currents) |
| Microwave | 1500 |
| Total power | 6200 |
To this amount it is necessary to add a 30 percent margin (6200 x 1.3), since when the mains voltage drops, the output power of the stabilizer will decrease, which can lead to its overload and switching to bypass mode. Therefore, the required output power of the stabilizer will be at least 8000 W.
If you choose from the line of inverter voltage stabilizers of the InStab series, then single-phase models are well suited for this example:
- IS10000 10 kVA/9 kW for wall installation;
- IS10000RT 10 kVA/9 kW for floor or rack mounting.
How does increasing battery voltage affect power?
Note that the power has increased, as we might have guessed, but it has increased slightly more than the current. Why? Since power is a function of voltage times current, and the voltage and current values have doubled from their previous values, the power will increase by a factor of 2 x 2, or 4 times. You can check this by dividing 432 W by 108 W and seeing that the ratio between the two is indeed 4. Using algebra to manipulate the formulas again, we can take our original power formula and modify it for cases where we don't know the voltage at the same time. and current, but we only know voltage (E) and resistance (R):
\[If \qquad I=\frac{E}{R} \qquad and \qquad P=IE\]
\[Then \qquad P=\frac{E}{R}E \qquad or \qquad P=\frac{E^2}{R}\]
If we only know current (I) and resistance (R):
\[If \qquad E=IR \qquad and \qquad P=IE\]
\[Then \qquad P=I(IR) \qquad or \qquad P=I^2R\]
Voltage stabilizers "Calm" for home
Our official online store of Shtil Group of Companies offers a wide selection of inverter voltage stabilizers for the home, namely:
- single-phase wall and floor/rack mounted models with output power from 0.3 to 18 kW;
- 3-in-1 configuration models (with three-phase input and single-phase output) floor/rack installation with output power from 5.4 to 16 kW;
- three-phase floor/rack mounted models with output power from 5.4 to 16 kW.
Depending on the output power, these devices are suitable both for providing centralized protection of all electrical equipment in a private home, and for targeted protection of a critical electrical appliance (for example, a gas boiler) or a group of critical equipment.