Fluorescent lamps were invented a long time ago. Initially, the companies that made them followed virtually no standards. This was primarily due to the simplicity of the design of such lamps. Manufacturers' freedom of choice regarding the size and configuration of such lighting equipment was not limited in any way. However, in the end, the process of assembling such lamps did become more manageable. The list of types of fluorescent lamps supplied to the market today is wide, but still limited. Such equipment is classified according to various criteria displayed in the labeling. For fluorescent lamps it is usually applied directly to the bulb.
What types are there
All fluorescent lamps supplied to the market today may differ in the following ways:
- spectrum of light;
- flask diameter;
- power;
- number of socles and their characteristics;
- the presence or absence of starting equipment;
- mains voltage;
- flask shape.
Such lamps can also be classified according to the color of the glow and light temperature.
Of course, a consumer who decides to purchase a luminescent model must first of all be informed about all its technical characteristics. The latter are displayed, like any other equipment, in this case in the markings. For fluorescent lamps it looks something like this:
- LB T8 w8 FS G13 RS 220 V. 2U.
In some cases, the order of numbers may change. Also, in some cases, only part of the characteristics are displayed in the lamp code.
Main types, types and modifications
Compared to other light sources, fluorescent lamps are represented by a wide range of models, with various shapes, sizes, individual parameters and technical characteristics.
First of all, fluorescent lamps are classified according to high and low pressure. The first option is used for lighting industrial facilities and public places where high quality color rendering is not required. The second type of lamps, low pressure, is used mainly in everyday life. Such products are also known as energy-saving.
The form of fluorescent lamps is divided into two main types:
- Linear. Most of them are made in the form of straight tubes of various lengths and diameters. The most exotic products resemble the letter U or are made in the shape of a ring.
- Compact. They are distinguished by curved flasks, the shape of which significantly expands the scope of use. The sockets can be pin or threaded for standard sockets.
Differences in flask diameter and length
This parameter for fluorescent lamps can vary within fairly wide limits. Many of its other technical characteristics directly depend on the diameter of the flask of such equipment:
- range;
- luminosity;
- life time.
It is believed that the thicker the fluorescent lamp, the longer it can last.
The diameter in the marking of such equipment, according to international standards, is indicated by numbers following the letter T. Its unit is 1/8 inch. For example, the diameter of a flask marked T8 will be 26 mm. Such lamps are currently very common. Also, equipment of this type with flask diameters of 18 and 38 mm is very popular on the market.
Sometimes the dimensions of lamps in the markings can be given simply as numbers. For example, such equipment may have the designation 26/604. In this case, the first number will indicate the diameter, and the second will indicate the length of the flask in millimeters.
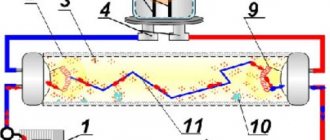
Device and principle of operation
The functioning of products is based on the process of luminescence. The inside of the flask is coated with a phosphor that “absorbs” ultraviolet radiation and produces a glow in the spectrum visible to the human eye. To form ultraviolet rays, mercury or an inert gas is used, which is filled with a flask. When an electric charge passes through, drops of mercury begin to evaporate, producing radiation.
The products consist of a flask with electrodes, one or two bases and ballasts (ballasts). The last component can be built-in or remote.
In turn, the ballast contains a choke and a starter. The first device limits the current supply, lowering the voltage to operating voltage, and the second accelerates the process of heating the electrodes and the light bulb reaching the specified mode.
The inclusion of the product is ensured by implementing the following steps:
- heating of electrodes;
- giving an impulse for ignition;
- reduction and stabilization of voltage.
What can be the power
This parameter is indicated in the marking by the letter W and the numbers following it. Knowing the power of a fluorescent lamp, you can determine how large a room it can illuminate. For example, this indicator can be coded as 11 W, 15 W, 20 W.
With regard to power, the designations in the marking of fluorescent lamps correspond to certain codes of the same equipment with an incandescent filament. These ratios are indicated in special tables. The data presented in them can greatly facilitate the buyer’s choice. For example, the designation 11 W will correspond to an incandescent lamp power of 55 W, 15 W - 75 W, 20 W - 100 W.
Some information to make your choice easier
Naturally, the power of the lamp determines its durability, as well as the strength of the luminous flux, including after some time of operation. Knowing these parameters of fluorescent lamps, you can choose the optimal lighting device that will not spoil the mood during installation.
For example, with a power consumption of such a lighting device of 30 watts, the average service life will be 15,000 hours. The average luminous flux after 100 hours of burning for white (LB) will be equal to 140 lm, warm and cold white - 100 lm. For daytime it is 180 lm, and for daytime color this figure will be 80 lm. But the parameters of the LDC will be different.
Unusual fluorescent lamp
Do not forget that starterless lamps, although they consume no less electricity than lamps with a starter, still have a slightly longer lifespan. Therefore, the best option would be to purchase just such fluorescent lamps and then exclude starters from their circuit. This is not difficult to do, and such work will not take much time.
Decoding the markings of fluorescent lamps: characteristics of the bases
The design of the lamp may include 1 or 2 such elements. In the first case, the marking will contain the designation FS, in the second - FD. Sometimes you can see the FB code on fluorescent lamps. This is how compact equipment with a built-in electronic ballast type base is marked.
The characteristics of this part of the design of fluorescent lamps are indicated by a letter and two numbers. The sockets can be marked, for example, as:
- G - pin.
- E - threaded.
The numbers following the letter in the marking indicate the outer diameter.
Markings and sizes
Each LL has its own technical characteristics that determine its use. Typically, all information about the device is encrypted in the labeling.
The designation begins with the letter L, which means lamp. Then comes the letter designation of the shade.
| Marking | Meaning |
| D | day glow |
| B | White light |
| HB | cool white |
| TB | warm white |
| E | natural light |
| HE | cool natural light |
| G, K, Z, F, R | various shades depending on the type of gas used and the phosphor used |
Sometimes in the marking you can find the designation Ts or TsTs, which indicates improved color rendering of the phosphor. For example, the designation LDC is typical for a fluorescent lamp with improved color rendering.
This is followed by digital designations that comply with global standards. These are three numbers, the first of which determines the quality of color rendering, and the rest indicate a specific color temperature. The larger the first number, the better the color rendering. An increase in the remaining numbers indicates a cooler glow.
Figure 3. Types of LL base
LL devices vary in size. The dimensions are indicated by the designation “TX”, where X is a specific size parameter. Specifically, T5 means 5/8 inch in diameter, and T8 means 8/8 inch in diameter.
The sockets can be pin or threaded. In the first case, the designation looks like G23, G24, G27 or G53. The number indicates the distance between the pins. Threaded sockets are available with markings E14, E27 and E40. Here the number determines the thread diameter.
Additionally, the lamp indicates the supply voltage and startup method. If the box has the designation RS, it means that no additional equipment is required for operation. All the necessary elements are already built into the base.
Launch equipment
Modern industry today produces two main types of fluorescent lamps:
- in addition to which it is necessary to purchase a starter;
- with the possibility of inclusion in a circuit with ballast, without starting equipment;
- universal.
The first type of equipment is marked as Phs, the second - RS, the third - US. Sometimes the letters characterizing the method of starting the lamp may not be in the code. This means that the starter for this equipment is a mandatory element.
In what areas are they used?
With the help of fluorescent lamps, large areas can be effectively illuminated, while significantly improving indoor conditions, reducing energy costs, and also increasing the service life of the lighting system.
Devices with built-in electronic ballast and E27 or E14 screw threaded sockets are used in everyday life as an effective replacement for incandescent lamps. They are able to provide the necessary luminous flux, guarantee stability and absence of flicker. At the same time, there is no hum at all. They are used in apartments, houses, shopping centers, schools, hospitals, banks, etc.
Figure 5. LL in the interior
Marking of starters for fluorescent lamps
Such starting devices are small gas-discharge lamps with a glowing charge. The following codes can be applied to the starter flask:
- C - starter;
- the numbers in front of it are power (60, 90, 120);
- the numbers after it are the voltage (220, 127).
Also, the marking of starters for fluorescent lamps may be Western. In this case, on the equipment flasks:
- at 220 V with a voltage of 4-80 W, the code S10, FS-U or ST111 is applied;
- at 127 V with a power of up to 20 W - S2, FS-2, ST151.
LB, LD RF fluorescent lamps
Marking of fluorescent lamps:
L - fluorescent lamp; B - white; D - daytime color; U - universal.
Execution:
1 - straight rod; 2 - U-shaped rod.
Specifications:
| Name | Power, W | Current, A | Voltage, V | Overall dimensions, mm | Luminous flux, lm | Service life, hour | Execution | ||
| D | L1 | L | |||||||
| LD-18 | 18 | 0,37 | 57 | 26 | 604 | 589,8 | 880 | 12000 | 1 |
| LB-18 | 18 | 0,37 | 57 | 26 | 604 | 589,8 | 1060 | 12000 | 1 |
| LD-20 | 20 | 0,43 | 57 | 38 | 604 | 589,8 | 880 | 12000 | 1 |
| LB-20 | 20 | 0,43 | 57 | 38 | 604 | 589,8 | 1060 | 12000 | 1 |
| LD-36 | 36 | 0,43 | 103 | 26 | 1213,6 | 1199,4 | 2300 | 12000 | 1 |
| LB-36 | 36 | 0,43 | 103 | 26 | 1213,6 | 1199,4 | 2800 | 12000 | 1 |
| LD-40 | 40 | 0,67 | 103 | 38 | 1213,6 | 1199,4 | 2300 | 12000 | 1 |
| LB-40 | 40 | 0,67 | 103 | 38 | 1213,6 | 1199,4 | 2800 | 12000 | 1 |
| LD-65 | 65 | 0,87 | 110 | 38 | 1514,2 | 1500 | 3750 | 12000 | 1 |
| LB-65 | 65 | 0,87 | 110 | 38 | 1514,2 | 1500 | 4600 | 12000 | 1 |
| LD-80 | 80 | 0,87 | 99 | 38 | 1514,2 | 1500 | 4250 | 12000 | 1 |
| LB-80 | 80 | 0,87 | 99 | 38 | 1514,2 | 1500 | 5200 | 12000 | 1 |
Advantages and disadvantages
Mercury lamps are distinguished by high luminous efficiency (2–3 times greater than that of general-purpose incandescent lamps), long service life and compactness, making them well suited for regulating the luminous flux.
Their disadvantages are the high cost of the lamp and auxiliary equipment, a bluish-green tint of light and a slow restart.
The color of a mercury lamp is corrected by using an internal phosphor coating.
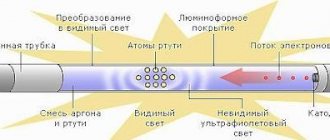
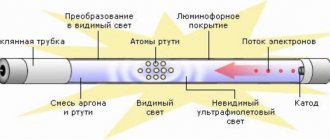
Fluorescent lamps.
Fluorescent lamps consist of the following main parts: a glass cylinder, two bases (with lead contacts) at both ends of the cylinder and two heated cathodes (electronic emitters) made of tungsten filament or steel tube.
The cylinder is filled with mercury vapor and inert gas (argon); A phosphor coating is applied to the inner walls of the cylinder, which converts the ultraviolet radiation of the gas discharge into visible light.
The design of the lamp is typical of the most common 40-W lamps.
The lamp operates as follows.
An electrode at one end of the lamp emits electrons, which fly along the lamp at high speed until they collide with an encountered mercury atom.
In doing so, they knock the electrons of the atom into a higher orbit.
When the ejected electron returns to its original orbit, the atom emits ultraviolet radiation.
The latter, passing through the phosphor, is converted into visible light.
FLUORESCENT LAMP - a typical cold cathode lamp design designed for below average currents. 1
- mercury;2
– stamped glass leg with electrical inputs;
3
– pumping tube (during manufacture);
4
– output pins;
5
– end socket;
6
– cathode with emitter coating.
The tube is filled with inert gas and mercury vapor. The inner walls of the tube are coated with phosphor.
Types of lamps.
Fluorescent lamps are divided into two groups according to the type of electrodes: with heated cathodes and with cold cathodes.
In lamps with heated cathodes, which are designed for high currents (1–2 A), as a rule, spiral activated tungsten filaments are used.
Cold cathode lamps have cylindrical electrodes coated with emitter materials and are designed for lower currents.
The average service life of lamps with heated cathodes depends on the operating time per start: 7500 hours with 3 hours of operating time per start and more than 18,000 hours in continuous mode.
For lamps with cold cathodes, the service life does not depend on the number of starts and reaches 25,000 hours.
Lamps with heated cathodes, according to the method of their start-up, are divided into lamps with pre-heating, quick start and instant start.
Like all other gas-discharge devices, lamps with heated cathodes cannot be connected to a power source without a ballast device that limits the current.
Preheat lamps also require a starter; When such a lamp is started, the starter closes, and the cathodes connected in series are connected to the power supply, so that current passes through them.
Once the cathodes are hot enough to emit electrons, the starter automatically opens and the lamp lights up.
Under favorable conditions, the entire start-up takes a few seconds.
In quick-start lamps, the cathodes are constantly heated, and a discharge occurs when the voltage increases.
No starters are required and start-up times are significantly faster than pre-heated lamps.
Instant start lamps do not require heating of the cathodes or the starter.
Simply, an increased voltage is applied to the cathode, which causes the emission of electrons and ignition of a discharge in the lamp.
Voltage
Most fluorescent lamps produced by modern industry are designed for use in a standard household electrical network. That is, most often such equipment operates at a voltage of 220 V.
However, fluorescent lamps of 127 and 75 V are also available for sale today. The first type of such equipment, designed for reduced voltage, is used in the subway. 75 V lamps are usually installed in electric trains.
The markings indicate the voltage required for such equipment directly. That is, exactly 220 V, 127 V or 75 V.
Phosphors and spectrum of emitted light
The phosphor converts ultraviolet rays into visible light. Cheap models have a single-layer luminescent substance on the inner surface of the tube. The lamps have a yellow or bluish glow with color distortion.
For expensive types, the phosphor coating consists of three or five layers. This allows the radiation to be evenly distributed and achieve a semblance of natural light. Special types of lamps use ultraviolet rays. They are used for poultry farms and for disinfecting premises in hospitals.
Depending on the composition of the spectral radiation, lamps are:
- Standard. The surface is covered with a single-layer phosphor. The glow has different shades of white. Light sources are used to illuminate public buildings.
- Improved color rendering. Three and five-layer phosphors are used. The luminous flux increases by 12% compared to standard lamps. More accurate color reproduction creates better conditions for perception. Lamps are used in places where accurate information about illuminated objects is required: in shop windows, furniture showrooms, museums, exhibitions.
- Special. Spraying with additives or a special type is used. The spectrum contains bands of a given frequency, depending on the purpose of the lamp. An example is bactericidal lamps that disinfect air, premises, and water.
Lamp shape
There are also many types of luminescent equipment for this parameter. In the marking of a lamp, the shape of its bulb can be indicated as:
- U - horseshoe-shaped.
- 4U - four-arc.
- S - spiral.
- C - candle-shaped.
- R - reflex type.
- G - spherical.
- T - in tablet form.
The linear shape of the bulb is not displayed in any way in the lamp markings.
Design features
What is this lighting device? Essentially, it is a glass tube sealed on both sides. Its inner surface is treated with a phosphor, air is pumped out of it and gas - argon - is added. Also, only one drop of mercury is added inside. It turns into vapor under the influence of temperature.
In order for the lamp to glow, it is necessary to apply an electric current inside its structure, which will raise the temperature. Therefore, electrodes are installed in the glass tube, which are tungsten wires twisted in the form of a spiral. Tungsten is coated with a special alloy of barium or strontium salt oxide. It is this layer that increases the service life of the electrodes. Here, two so-called hard electrodes are installed parallel to the spiral. They are nickel. Each such electrode is connected at one end to one of the ends of the spiral.
Additional information: color
Quite often, manufacturers in the labeling of fluorescent lamps also display such characteristics as the color of the glow and light temperature.
In this case, the cipher will contain three digits. The first one displays the color rendering index. This indicator should not be confused with the luminosity spectrum. Most often, the color rendering index is determined by the color of the lamp bulb. It indicates the degree of compliance, declared by the manufacturer, with a natural shade. In the color marking of fluorescent lamps, it is indicated as 1x10 Ra. That is, for example, the code 742 (number 7) displays the equipment color rendering index of 70 Ra.
The last two digits in the marking in this case indicate the color temperature of the light emitted by the lamp, measured in Kelvin. In our example, it will be equal to 4200 K. That is, a lamp with this marking will emit cold light.
The numbers indicating the color rendering index and temperature are usually placed at the very end of the code on the lamp. Before their combination there is the word Color.
Specifications
The final operation of the LDS—the required lighting—depends on the technical characteristics.
Power
The light output, which affects the illumination area, depends on the LL power indicator. Lamps of various wattages are common in implementation.
Lamps 4–6 W
Suitable for small rooms. Great for agricultural areas, guardhouses or tents. These LDS are unpretentious in terms of electricity consumption, and thanks to transformer converters, these lamps are able to operate on 12 volts, which makes it possible to start the lamp by connecting it to a car battery in conditions of no power supply. Low-power fluorescent devices are also used to illuminate plants or aquariums.
18 W
The most common LL in terms of lamp power. They can be found everywhere: in a room, car garages, offices, pavilions.
36 W
They have also become widespread. They are used in the same rooms as LL 18 W, with the difference in increasing the lighting area.
58 W and 80 W
These high-power LDS are used only in large production workshops, storage facilities and hangars, in underground areas.
Sometimes LLs of such power can be found in open areas in conditions of high light scattering. Such LLs, unlike 18 W and 36 W lamps, are more energy-consuming and their use in everyday life or office lighting is unprofitable. They are also equipped with additional fluorescent lamps, which makes their use even more irrelevant as ceiling fluorescent lamps in small areas.
Colorful temperature
Another main parameter of LDS. The quality of lighting depends on the quality of light and color temperature. These parameters are displayed as a three-digit value on the device bulb.
Value 627
Complies with devices with 60% light quality and 2700K color temperature.
Value 727
Lamps with 70% light quality and similar color temperature.
Value 765
The color temperature is 6500 K, which is what all LDS have without exception. Color quality at 70%.
It is necessary to take into account that 2700 Kelvin is the color temperature of incandescent light bulbs, and a LL with the same color temperature will emit rays perceived by human vision that are yellow. Taking into account the human perception of the color of the glow, luminescent devices of different color temperatures are manufactured.
Many compact-shaped LLs (energy-saving light sources) emit yellow light. A color temperature of 6500 is common to all linear devices and corresponds to white light with a slight blue tint. Narrow-profile luminaires with a color temperature of 1300K are also manufactured, when turned on, a red tint is observed. In some cases, colored LDS are used to obtain a unique shade of glow.
Codes for lamps of other types
In addition to fluorescent ones, incandescent light bulbs are, of course, very popular among domestic consumers. There is also a wide range of LED models on the market today. In this regard, the consumer may have a question about which markings do not apply to fluorescent lamps.
For example, LED models, in addition to power (W), base type, color indicators and voltage, may contain codes in the code:
- maximum permissible operating temperature (usually from +40 to -40 °C);
- duration of the operating period (usually 50 thousand hours).
The bulb type code for LED lamps differs from the code for fluorescent lamps. In this case, the designation comes after the letter A.
The code for an incandescent light bulb usually contains one or two Cyrillic letters and five numbers. The letters indicate the type of model (V - vacuum, B - double-spiral, Ш - spherical, BO - double-spiral argon with an opal flask, etc.). The first three digits in the marking of such equipment indicate the operating voltage, the last two indicate the power. Sometimes the code of such light bulbs also contains the date of their release.
How to install a lighting fixture yourself
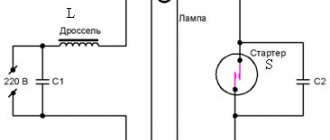
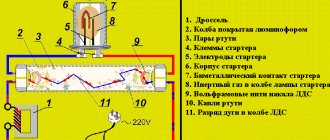
Installing the structure is not that difficult. Anyone can do the job. If any difficulties arise, step-by-step instructions posted on the Internet will come to the rescue. The simplest scheme is with a starter and throttle. Consists of two separate devices with personal sockets. There are two capacitors in the circuit, the first is connected in parallel to stabilize the voltage, and the second is located in the starter housing and allows you to increase the duration of the starting pulse. The circuit is called “electromagnetic ballast”.
The functioning of the connection diagram for fluorescent lamps with a starter is as follows:
- Power connection.
- The current passes through the inductor, entering the first tungsten helix.
- By means of the starter, it moves into the second spiral and leaves through the neutral conductor.
- The tungsten filaments begin to heat up, as do the starter contacts.
- The starter has two contacts: fixed and movable bimetallic. In normal condition they are open.
- The passing current heats the bimetallic contacts, which leads to its bending. When bent, it closes with a fixed contact.
- The connected contacts contribute to an increase in current in the circuit (on average 2–3 times). The throttle acts as a limiter.
- A sharp jump occurs, which leads to rapid heating of the electrodes.
- When the starter bimetallic plate cools, the contacts break. The rupture leads to a sharp surge in voltage at the throttle. Due to the high voltage, electrons penetrate the argon medium. Ignition appears and the lamp begins to function in operating mode.
Experts recommend taking product disposal seriously. They cannot be thrown away like regular trash because they contain mercury vapor inside. There are a number of specialized organizations that deal with the disposal of hazardous waste and mercury-containing light bulbs.
Osram lamp color designations
The numbers after the word Color in the marking of fluorescent equipment are one of the most important codes for the consumer. For example, popular Osram lamps may have the following color designations:
- 765 (70...79 Ra, 6500 K);
- 865 (80...89 Ra, 6500 K);
- 965 (90...99 Ra, 6500 K);
- 954 (more than 90 Ra, 5400 K), etc.
Colors such as SKYWHITE and INTERNA are patented by this manufacturer. The first of them is designated in the labeling of Osram fluorescent lamps as 880 (80...89, 8000 K), the second - 827 (80...89, 2700 K).
What it is
Energy-saving lighting devices are electric lighting devices that have a large luminous flux while consuming minimal power. Compared to classic incandescent lamps, such devices provide low electrical energy consumption, but last significantly longer and are not inferior in lighting quality.
In a broad sense, energy-saving devices are considered to be fluorescent lamps of various types and sizes, although with the development of technology a new type of lamp has appeared - LED.
Philips colors
Equipment of this brand also enjoys well-deserved popularity among domestic consumers. Philips fluorescent lamps are labeled as standard. The color rendition of this equipment can be indicated by numbers from 4 to 9. The temperature of lamps of this brand is encrypted by numbers from 27 to 65. Also, the marking of Philips models may contain their series (for example, TL-D).
In addition to the usual ones, this manufacturer also produces luminescent equipment intended for installation in aquariums - TLD AQUARELLE. Such lamps differ from standard ones in that they emit light with a high density in the blue spectrum. This shade not only emphasizes the beauty of the underwater world, but also contributes to:
- creating optimal conditions for photosynthesis;
- stimulating the formation of oxygen in water, which is very beneficial for fish.
The diameter of the bulbs of these lamps can be 16 mm or 28 mm (T5, T9). Also in the TLD AQUARELLE marking there are codes G5 and G13, which characterize the parameters of the bases. The power of these lamps can be 8-58 W.
Tube designations
Bulbs are usually designated by a code, such as FxxTy, where F stands for fluorescent lamps, the first number (xx) indicates either the wattage or the length in inches, T indicates that the shape of the lamp is tubular, and the last number (y) is the diameter in eighths inches (sometimes in millimeters, rounded to the nearest millimeter).
Typical diameters are T12 or T38 (1 1⁄2 inches or 38 mm) for household fixtures with magnetic ballasts, T8 or T26 (1 inch or 25 mm) for commercial energy-saving lamps with electronic ballasts, and T5 or T16 (5⁄8 inch or 16 mm) for very small lamps that can even be operated by a battery-powered device. Comparison of diameter designations for fluorescent lamps
| Designation | Tube diameter | Additional | |||
| (V) | (mm) | Connector | Notes | ||
| T2 | 1⁄4 approx. | 7 | WP4.5×8.5d | Osram Fluorescent miniature (FM) tubes only Sylvania Luxline Slim T2 Linear | |
| T4 | 1⁄2 | 12.7 | G5 bipin | Thin lamps. Power ratings and lengths are not standardized (or the same) across manufacturers | |
| T5 | T16 | 5⁄8 | 15.9 | G5 bipin | Original 4-13 W range from the 1950s or earlier.[1] Two new series, High Efficiency (HE) 14–35 W, and High Performance (HO) 24–80 W, introduced in the 1990s.[2] |
| T8 | T26 | 1 | 25.4 | G13 bipin/single contact/double recessed contact | Since the 1930s[3] more common format since the 1980s.[4] |
| T9 | T29 | 1 1⁄8 | 28.6 | G10q four-pin contact | Only round (circular) fluorescent lamps |
| T10 | 1 1⁄4 | 31.75 | G13 bipin | ||
| T12 | T38 | 1 1⁄2 | 38.1 | G13 double channel / single contact / double recessed contact | Also from the 1930s, not as efficient as newer bulbs.[5] |
| T17 | 2 1⁄8 | 54 | G20 Mogul bipin | Large size for F90T17 (preheat) and F40T17/IS (instant start) | |
| PG17 | 2 1⁄8 | 54 | R17d Double recessed contact | General Electric's Power Groove tubes only | |
- According to T2 - T12, T17 number indicates the pipe diameter is 1⁄8 inches, for example T2 = 2⁄8 and T17 = 17⁄8 inches. While T16, T26-T38 indicate the diameter of the tube in millimeters.
Reflectors
Cross section of a typical fluorescent lamp with and without a reflector.
Some lamps have an internal opaque reflector. The reflector coverage ranges from 120° to 310° of the lamp circumference. Often a lamp is labeled as a reflector lamp by adding the letter "R" to the model code, so an F ## T ## lamp with reflector will be coded as "FR ## T ##". Very High Output (VHO) lamps with reflectors may be coded as VHOR. There is no such designation for the degree of coverage of a lamp reflector.
Reflector lamps are used when light is desired to be emitted in only one direction or when the application requires the maximum amount of light. For example, these lamps can be used in solariums or backlit electronic displays. The internal reflector is more efficient than standard external reflectors. Another example is color-matched iris LEDs (with an opening angle of about 30°) used in the food industry for robotic quality inspection of finished products.
Iris lamps have a distinct break in the phosphor coating, usually at an angle of 30°, to concentrate the light in one direction and provide greater brightness in the beam than a uniform phosphor coating can achieve. Lamps with an aperture include reflectors in the non-aperture area. Aperture lamps were commonly used in photocopiers in the 1960s and 1970s, when a series of fixed tubes were used to illuminate the copied image, but they are rarely found nowadays. Lamps with an aperture can emit a concentrated beam of light suitable for extreme vision.
Slimline lamps
Slimline lamps operate from an instant-start ballast and are recognizable by their single-pin base.
High/Very High Power Lamps
Bulbs with a higher output are brighter and have more power. electrical current, have different terminal ends so they cannot be used in the wrong fixture, and are marked F ## T ## HO or F ## T ## VHO for very high power output. From about the early to mid-1950s to the present day, General Electric developed and improved the Power Groove
lamp with label F##PG17. These lamps are recognizable by their large diameter (21/8″), tubular shape with grooves and R17d caps on each end.
Other tube shapes
U-shaped pipes FB ## T ##, where B means "bent". Most often they have the same designation as linear pipes. Round pipes - FC ## T #, with outer diameter
circle (
no
circumference or watts) in centimeters (inches in North America) being the first number and the second number referring to the tube size as linear.
Colors
The color is usually designated WW for warm white, EW for enhanced (neutral) white, CW for cool white (the most common), and DW for bluish day white. BL is used for UV lamps commonly used in bug zappers. BLB is used for a blue-black lamp that uses a Wood Glass envelope to filter out most visible light, typically used in nightclubs. Other non-standard designations are used for plant lights or grow lights.
Philips and Osram use numeric color codes. On lamps with three or more phosphors, the first number indicates the color rendering index (CRI) of the lamp. If the first number on the lamp says 8
, then the CRI of this lamp will be approximately 85. The last two digits indicate the color temperature of the lamp in Kelvin (K).
For example, if the last two digits on a lamp say 41
, the color temperature of that lamp will be 4100 K, which is the same as a typical cool white tri-phosphor fluorescent lamp.
| Halophosphate tubes | |||
| Digital color code | Color | Approximate color rendering index | Color temperature (K) |
| 29 | Warm white | ~52 | 3000 |
| 35 | white | ~56 | 3500 |
| 33 | Daylight/Cool White | ~66 | 4300 |
| 25 | Natural/Universal White | ~75 | 4000 |
| 54 | Tropical daylight | ~75 | 6500 |
| Deluxe Halophosphate Tubes | |||
| Digital color code | Color | Approximate color rendering index | Color temperature (K) |
| 27 | Deluxe Extra Warm White | ~95 | 2700 |
| 32 | Deluxe warm white | ~85 | 3000 |
| 34 | Deluxe White | ~85 | 3850 |
| 79 | Deluxe Natural | ~93 | 3600 |
| 38 | Deluxe Cool White / ° Color Rite | ~92 | 4000 |
| 55 | Northlight / Color selection | ~94 | 6500 |
| Triphosphorus tubes | |||
| Digital color code | Color | Approximate color rendering index | Color temperature (K) |
| 827 | Warm white | ~85 | 2700 |
| 835 | white | ~85 | 3500 |
| 840 | Cold white | ~85 | 4000 |
| 850 | sunlight | ~85 | 5000 |
| 865 | Cold daylight | ~85 | 6500 |
| 880 | Skywhite | ~85 | 8000 |
| Multi-phosphor lamps | |||
| Digital color code | Color | Approximate color rendering index | Color temperature (K) |
| 927 | Warm white | ~95 | 2700 |
| 941 | Cold white | ~95 | 4100 |
| 950 | sunlight | ~98 | 5000 |
| 965 | Cold daylight | ~95 | 6500 |
| Special purpose pipes | |||
| Numeric code | Fluorescent lamp type | Notes | |
| 05 | Germicidal lamps | No phosphors, using fused silica envelope. | |
| 08 | Black light lamps | ||
| 09 | Tanning lamps | ||