Almost every one of us, when choosing lighting for any purpose, has encountered the difficulty of choosing one or another lighting device.
Now there are a great variety of options on the market in this area, each of which has its own positive qualities and, of course, some disadvantages.
However, there are also those manufactured products that have been recognized by the consumer segment for a long time.
These products include fluorescent lamps, which are widely used almost everywhere. Their performance characteristics are noted at the highest level, and the disadvantages can be considered not too significant.
In short, for installing a lighting system this is a fairly optimal option, which is also distinguished by its efficiency.
What are fluorescent lamps and their characteristics
A fluorescent lamp is a fairly common phenomenon in our lives.
Surely each of us has visited some public institutions and noticed the specifics of lighting in these buildings. However, few people know what exactly this product is.
Fluorescent lamps are gas-charging devices that base their operation on the physical impact of an electric discharge in gases.
Such a device contains mercury, which provides ultraviolet radiation, which is converted into light in the lamp itself.
This process occurs with the help of a very important element - phosphor.
The phosphor can be a mixture of any chemical elements, for example, calcium halophosphate with something else.
By selecting any type of phosphor, you can achieve the most interesting effects, for example, changing the color scheme of the lamp light. When choosing a product, you should pay attention to one of the most important indicators - the overall color rendering index. It is designated by a combination of the letters Ra, and the higher the value indicated in the accompanying documentation for the lamp, the better it will perform its job.
Thanks to this lighting system, the fluorescent lamp has become a clear leader over the same incandescent lamps.
And if we take into account that its operational characteristics provide a much longer period of use, then there is no need to think about the correct choice in favor of a fluorescent lamp.
Ways to properly dispose of energy-saving lamps
An important disadvantage of energy-saving lamps is the use of mercury vapor in their design. This makes it unacceptable to throw them into the garbage chute or container. Their disposal is strictly regulated. There are two known methods of disposal:
- Burnt-out energy-saving lamps must be taken to the district DEZ or REU. They must have special containers installed. Acceptance in Moscow is carried out free of charge on the basis of the Order of the Moscow Government “On the organization of work on the collection, transportation and processing of waste fluorescent lamps” dated December 20, 1999 No. 1010-RZP. Other regions may have their own regional regulations governing disposal.
- If there are a lot of lamps (this applies to enterprises or offices), then an appropriate agreement is concluded with organizations that are engaged in the collection and disposal of mercury-containing products. On the Greenpeace website you can find a list of collection points for fluorescent lamps.
It should be remembered that our environmental safety depends on the correct disposal of hazardous devices.
Advantages and disadvantages of fluorescent lamps
Like everything around us, fluorescent lamps have their positive and negative sides. Fortunately, there are much fewer of the latter.
As mentioned earlier, fluorescent lamps are the clear leader among lighting means. The superiority over incandescent lamps is not difficult to notice even for the most inexperienced person in electrics.
Advantages
The advantages of this element include the following:
- it produces light output to a much greater extent, and the quality of light is somewhat higher than that of other lighting elements;
- long service life, ensuring no interruptions in operation of the lamps;
- The efficiency of such a product is much higher;
- Diffuse light, which causes less harm to the retina of the eye, which means that when using this lamp you can significantly reduce the risk of vision problems;
- wide range in terms of light colors.
Flaws
Of course, fluorescent lamps also have negative qualities. This list includes the following items:
- The mercury content in such products poses some chemical hazard and requires special disposal;
- The strip spectrum is not distributed evenly, and this may cause some inconvenience in terms of perceiving the real color of objects that are illuminated by a fluorescent lamp; however, a certain reservation should be made here: there are specimens that represent an almost complete continuous spectrum, but the degree of light output in this case decreases;
- The phosphor contained in these lamps performs its work with less efficiency over time, this reduces the efficiency of the lamp and reduces the degree of light output;
- When installing a fluorescent lamp, it is necessary to buy an additional ballast, which will either cost the consumer a fairly large sum, but will have optimal performance, or it will be somewhat cheaper in price, but will provide a high noise level and unreliable operation;
- The power rating is low, therefore, this option is not very suitable for the electrical network. There are also less significant disadvantages, however, their influence does not play a very significant role in the use of fluorescent lamps.
Advantages of LL
- They are characterized by high efficiency/light output (several times higher than incandescent lamps in efficiency and until recently successfully competed with LEDs).
- The final emission spectrum is adjustable during manufacturing (due to the composition of phosphors).
- Long service life (from thousands to tens of thousands of hours) in the absence of frequent on-off switching.
Classification and typology of fluorescent lamps
Naturally, progress in the production of products such as fluorescent lamps does not stand still, and if previously mostly similar units with similar technical characteristics were used, today the consumer can choose the option that will be the most optimal and effective for him.
There are many signs by which these lamps can be classified, but nevertheless, the most basic one, nevertheless, will be the sign of pressure indicators.
At the moment, gas-charged mercury specimens of high and low pressure are available on the market.
High pressure lamps have found their use mainly in outdoor lighting. Since such products have high power, their light inside the building will be quite unpleasant for the eye to perceive.
Also, high-pressure lamps are excellent for assembling any lighting installations.
Low pressure lamps have comparatively lower power, which means they are suitable for use inside buildings.
The purpose of the room can be absolutely any: fluorescent lamps of this indicator are suitable for workshops and industrial buildings, and for residential premises.
In addition to dividing lamps according to the principle of pressure, there is also a classification according to the diameter of the tube or bulb of the lamp , as well as according to the ignition pattern.
For example, you can take products from the most famous manufacturers, for example, Osram and Philips. If you look closely at the data on the packaging, you can see a letter and a number next to each other. These are the product type markings.
So, fluorescent lamps are divided into :
- T5 - lamps with this indicator are a rather rare phenomenon that has not found recognition among the consumer segment. Their cost is quite high, but the degree of light output shows excellent results - up to 110 lm/watt. It is worth noting that now manufacturers have significantly increased the production volume of fluorescent lamps with this indicator.
- T8 is a new product that has a fairly high price and is designed for a load of no more than 0.260 A.
- T10 is an analogue of lamps labeled T12, characterized by a rather low quality and level of efficiency.
- T12 is the market leader in fluorescent lamps . It includes a wide variety of subtypes, what can I say, almost all standard models belong to this group. Their number includes representatives of almost all fluorescent lamp manufacturers.
The above-mentioned principle of classification according to the ignition circuit has two types: those requiring a starter and those not requiring it.
Power is also a fairly significant characteristic of fluorescent lamps; accordingly, this also became a factor for identifying a separate classification.
According to power indicators, lamps are divided into:
- Standard – marked T12;
- HO - high power lamps, however, have a comparatively lower light output;
- VHO - lamps that can withstand a load of up to 1.5 A;
- "Economy" - options for fluorescent lamps.
The criteria by which lamps can be divided into groups include length.
There are a great many options for this differentiation. As a rule, manufacturers are required to indicate this data in the instructions or on the packaging.
Classification by starter use
It is also worth noting the fact that fluorescent lamps can be divided into types and according to the type of connection.
You can read more about how to connect fluorescent lamps in various ways in this article.
However, in this case, it is quite difficult to identify any exact categories, since each type, distinguished, for example, by power or the need for the presence of a starter, requires compliance with its own nuances.
Features of operation
When considering the pros and cons of fluorescent lamps, we should dwell in detail on the features of their operation, which differ significantly from conventional incandescent light bulbs.
Therefore, when using fluorescent lamps, we must not forget about the following mandatory rules:
- These light sources do not tolerate frequent switching on and off. A similar situation is associated with the use of a starter and throttle in the circuit. With each start-up, the electrodes evaporate, as a result, the ends of the tubes begin to turn black. High current consumption by ballasts during starts causes increased loads and premature failure. Therefore, low-power lamps, up to 15 W, are recommended to be turned on and off once a day. If you can’t do without this, you need to buy more expensive lamps with a soft start system that will work without any problems.
- Increased sensitivity of fluorescent lamps to voltage changes, especially downward. The starting device begins to consume even more current, otherwise the lamp simply will not start. As a result, frequent low voltage causes premature wear of the ballasts.
- Fluorescent lamps require extremely careful handling. First of all, this is due to the mercury vapor contained inside the flask. If it is broken, harmful substances will enter the environment. Therefore, during transportation or storage, the lamps must be in a reliable, stable position. When replacing the lamp, wear gloves, since traces of fat on the bulb may cause an explosion when heated.
- The need to control the duration of operation of light bulbs. For this purpose, the date of commissioning is recorded in a special journal. This is done due to the deterioration of the quality of the luminous flux over time. In reality, this rule is almost never observed and the lamp is replaced only after it fails.
- For fluorescent lamps, it is recommended to use open-type lamps. During operation, some of them become very hot, and closing the lighting devices does not provide the necessary ventilation. In addition, the matte surface of the lampshade delays the light flux and transmits it only partially. Open lamps do not heat up at all and create maximum brightness with the same energy consumption.
- The energy savings expected to be achieved largely depend on the manufacturer of the fluorescent lamps. Cheap devices are made of the same materials, so the quality of light and service life leave much to be desired. It is better to purchase products from well-known brands that are as close as possible to the stated technical characteristics.
Where are fluorescent lamps used?
As mentioned earlier, fluorescent lamps are widely used almost everywhere.
Despite some negative aspects of using this product, its advantages are still quite difficult to overestimate.
Each of us went to school, visited health care institutions, administrative buildings, etc.
So the lighting system in these rooms is based on the use of fluorescent lamps.
As a rule, these are quite large-scale tubes that provide high-quality lighting in buildings with some architectural features.
But if public buildings are distinguished by their dimensions, for example, high ceilings, large halls and rooms where fairly powerful and constant lighting is required, then at home fluorescent lamps, which will be optimally used there, will not be suitable.
Fortunately, the level of manufacturing skills has increased significantly, which means fluorescent lamps adapted for home conditions have appeared.
They are much smaller in size and contain electronic ballasts that can be connected to sockets used in home electronics.
And despite the freshness of this innovation, adapted lamps are already firmly conquering this market segment.
By the way, there is a rather interesting fact. The already familiar plasma TVs have fluorescent lamps in their mechanism!
Of course, this is also an option adapted in accordance with the specific application, but, nevertheless, the principle of its operation lies in the same phenomenon. Liquid crystal screens, by the way, were previously produced only using fluorescent lamps, but later they were replaced by LEDs.
We have all seen illuminated advertisements on the streets of the city. She also could not do without the use of a fluorescent lamp! Building facades are also illuminated with this product.
Although at the moment, SMD and DIP screens compete with fluorescent lamps in the field of illuminated advertising.
Also, fluorescent lamps are widely used in the field of crop production for growing plants.
Generally speaking, highlighting the main idea of using a fluorescent lamp, we can conclude: it makes sense to use them in cases where it is necessary to supply large rooms with light.
Working together with digital lighting interface systems with the ability to address allows you to ensure high light output and, at the same time, not spend large sums on electricity bills, because compared to incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps can reduce energy consumption by more than half ! Thus, being energy saving.
In addition, the lamps reduce costs and the duration of their use.
Where can you meet LL
In addition to the long (more than a meter) luminaires already familiar to the eye, in indoor lamps dating back to “Soviet” times, one can much more often find short straight luminaires for suspended ceilings and compact luminaires (their tube is rolled up like something U-shaped or is generally a multi-turn spiral) with individual ballasts (start-up and control equipment). The latter can be screwed into standard sockets for incandescent lamps indoors.
Until the beginning of the 21st century and the “dawn of the LED era,” LLs were often found in LCD monitors and scanners: they were used as backlight elements (these lamps were no thicker than a match and quite long, which is why their ignition/operating voltage could reach up to kilovolt).
Difficulty of choice
When purchasing fluorescent light sources, it is important to pay attention to their size, light flux, operating temperature limits, emitted shade, as well as the required mains voltage. When choosing a base, things are a little simpler, since their variety allows you to choose a lamp for any type of floor lamp or lamp.
At the same time, selection must be made based on the type of room where the LL will be installed. For example, for residential spaces, samples with a threaded base, with an electric ballast, not prone to the risk of flickering and operating silently are suitable. In the hallways you can already install powerful lamps with intense and diffused glow. It is better to insert compact models into wall sconces that emit warm light (930) and have good color rendition. Under the ceiling (on the cornice) you can mount a ribbon garland with cold light bulbs (860) or a monolithic tubular structure.
The living room may well be illuminated with special small-sized models for decorative purposes - high-quality white will be an acceptable color. For a high-tech interior, it is possible to stretch a fluorescent strip of light sources along the ceiling (or exclusively in the corners).
For the bedroom, devices with soft and warm light with indicators of 930-933 units or similar are suitable.
Experts recommend equipping the kitchen area with several levels - local and one general. Compact low-power products up to 20 Watts with warm light of at least 840 lumens are suitable for placement on the ceiling. But the working kitchen area needs to be illuminated brighter, using special linear lamps that do not create glare on surrounding objects.
Operating principle of a fluorescent lamp
How does a fluorescent lamp work? First, freely moving electrons are formed. This occurs when the AC power supply is turned on in the areas around the tungsten filaments inside the glass cylinder.
These filaments, by covering their surface with a layer of light metals, emit electrons as they heat up. The external supply voltage is not yet sufficient to create an electron flow. As they move, these free particles knock out electrons from the outer orbits of the inert gas atoms that fill the flask. They are included in the general movement.
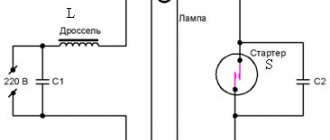
At the next stage, as a result of the joint work of the starter and the electromagnetic choke, conditions are created for an increase in current strength and the formation of a glow gas discharge. Now comes the time to organize the light flux.
The moving particles have sufficient kinetic energy necessary to transfer the electrons of the mercury atoms, which are part of the lamp in the form of a small drop of metal, to a higher orbit. When an electron returns to its original orbit, energy is released in the form of ultraviolet light. Conversion to visible light occurs in a layer of phosphor covering the inner surface of the bulb.
Why do you need a choke in a fluorescent lamp?
This device works from the moment of start and throughout the entire glow process. At different stages, the tasks performed by it are different and can be divided into:
- turning on the lamp;
- maintaining normal safe mode.
At the first stage, the property of the inductor is used to create a voltage pulse of large amplitude due to the electromotive force (EMF) of self-induction when the flow of alternating current through its winding stops. The amplitude of this pulse directly depends on the magnitude of the inductance. It, summed with the alternating mains voltage, allows you to briefly create a voltage between the electrodes sufficient for a discharge in the lamp.
When a constant glow is created, the choke acts as a limiting electromagnetic ballast for the low-resistance arc circuit. Its goal now is to stabilize operation to prevent an arc fault. This uses the high inductive reactance of the alternating current winding.
Operating principle of a fluorescent lamp starter
The device is designed to control the process of putting the lamp into operation. When the mains voltage is initially connected, it is completely applied to the two starter electrodes, between which there is a small gap. A glow discharge occurs between them, in which the temperature increases.
One of the contacts, made of bimetal, has the ability to change its size and bend under the influence of temperature. In this pair, it serves as a moving element. An increase in temperature leads to a rapid short circuit between the electrodes. Current begins to flow through the circuit, which leads to a decrease in temperature.
After a short period of time, the circuit breaks, which is a command for the self-induction EMF of the inductor to come into operation. The subsequent process was described above. The starter will only be needed the next time it is turned on.
This is interesting: The floor in the garage - how to insulate concrete and wood
Lamp marking
The markings are designed in such a way that customers can easily select the required lighting element. The most common designations according to Russian standards:
- LB (white light);
- LD (daylight);
- LHB (cool white light);
- LTB (warm white light);
- LE (natural light);
- LHE (naturally cold).
The visible shade directly depends on the color temperature. The color temperature of LDS is 6400-6500K, which is approximately the color of white light.
In addition to the type of lamp, the necessary technical characteristics of the lamp are also indicated: voltage, shape, size, etc.
The three-digit code on the lamp packaging usually contains information about the quality of the light (color rendering index and color temperature).
The first number is the color rendering index 1×10 Ra (a compact fluorescent lamp has 60-98 Ra, so the higher the index, the more reliable the color rendering).
The second and third numbers indicate the color temperature of the lamp.
Therefore, the “827” label indicates a color rendering index of 80 Ra and a color temperature of 2700 K (corresponding to the color temperature of an incandescent lamp).
In addition, the color rendering index can be specified according to DIN 5035, where the color rendering range of 20-100 Ra is divided into 6 parts - from 4 to 1 A.
Color rendering codes according to the international system:
| Code | Peculiarities | Application |
| 530 | Light of warm tones with poor color rendering. Objects appear brownish and have low contrast. Mediocre light output. | Garages, kitchens. Lately it has become less and less common. |
| 640/740 | “Cool” light with mediocre color rendering and light output. | Very common, should be replaced by 840. |
| 765 | Bluish “daylight” light with mediocre color rendering and light output. | It is found in office premises and for illuminating advertising structures. |
| 827 | Similar to incandescent light with good color rendering and light output. | Housing. |
| 830 | Similar to the light of a halogen lamp with good color rendering and light output. | Housing. |
| 840 | White light for work surfaces with very good color rendering and luminous efficiency. | Public areas, offices, bathrooms, kitchens. External lighting. |
| 865 | “Day” light with good color rendering and mediocre light output. | Public places, offices. External lighting. |
| 880 | "Day" light with good color rendering. | External lighting. |
| 930 | “Warm” light with excellent color rendering and poor light output. | Living spaces |
| 940 | “Cool” light with excellent color reproduction and satisfactory light output. | exhibition halls, museums. |
| 954, 965 | “Day” light with a continuous spectrum of color rendering and mediocre light output. | lighting for aquariums, exhibition halls, |
The principle of Russian labeling
Instead of an epilogue
Fluorescent light sources are the best solution for lighting apartments and public places. Since their appearance, the demand for LED light sources has decreased somewhat. Fluorescent lamps are the most suitable option for use in workplaces, classrooms and other areas where strict lighting requirements are imposed and high reliability of lighting devices is important. We must remember that their use will be effective if you choose the right lamps for the lamps and the features of the place to be illuminated.
Characteristics of light sources
Fluorescent lamps have not only technical characteristics. Like any electrical product, they have electrical characteristics, and like a lighting device, they have light parameters.
Electrical characteristics include:
- Rated voltage. The mains voltage that is suitable for operating the lamp. Is 220 V or 110 V.
- Operating voltage. The value on the lamp when it is burning. Equal to half the nominal and is 100-110 V for a 220 V network and 45-60 V for a 110 V network.
- Ignition voltage. The amount on the light bulb required for a discharge to appear. It is significantly higher than the network value and is not a constant value. Depends on the ignition circuit and environmental conditions.
- Rated power. According to this indicator, low-power (up to 18 W), medium-power (up to 58 W) and high-power (from 58 W) devices are distinguished. You can also find high-intensity light bulbs with a power of 150 W on sale, but they are practically not used due to their low efficiency.
- Efficiency Fluorescent lighting provides an efficiency exceeding 20%.
- The diameter of the flask is 12,16,26,38 mm.
- Base sizes are 14 and 27 mm.
Lighting characteristics of gas-discharge lamps:
- Nominal luminous flux. Set 100 hours after combustion.
- Color rendering index. Depends on the version of the lamp. In standard devices it is 50-70%, in lamps with increased color rendering it is 97%.
- Colorful temperature. Shows what shade the glow will have. Fluorescent lamps are manufactured in the range from 2700 K to 6500 K.
Performance characteristics:
- Luminous output depends on color and power. The highest performance is achieved by household lamps LB 40 W – 80 lm/W. Of the lamps produced, the maximum luminous efficiency of the T5 series with electronic ballast is 104 lm/W.
- Average burning time. Depends on the electrodes and the strength of the oxide film covering them. Medium power lamps have a lifespan of 15,000 hours.
- Ripple factor. In most fluorescent lamps it is 23%, except for devices with improved color rendering, in which a value of 70% is achieved.
- Dependence on ambient temperature. At low temperatures, ignition conditions worsen. The operating temperature range is from 5 to 55° C.
- Disposal. Since the lamp contains mercury and other harmful components, it must be disposed of in a special way. To do this, the device must be taken and handed over to a special collection point.
In terms of their characteristics, fluorescent light sources are significantly superior to classic light bulbs.