Aug 15 • Articles • •
(
409 votes, average: 4.84 out of 5)
HPS lamps: a light source that was retired too early.
As we promised, an article about HPS (High Pressure Sodium Tubular Arc) lamps has finally arrived. Anyone who has worked or is working in the field of lighting technology knows firsthand about the HPS lamp. But if anyone doesn’t know, let’s explain it in simple terms: HPS lamps are like a Kalashnikov assault rifle for lighting streets and illuminating plants - a time-tested and reliable, but not without its shortcomings, light source.
Actually, this article about HPS lamps is more for beginners; material presented competently, but in an accessible language: without schematic diagrams of connection and a complete explanation of the basics of maintaining the discharge column in the burner of a HPS lamp. But we are sure that specialists will also like the sketch.
Actually, the subject: one of the invariations of the HPS lamp
Almost 100% of the world's roads (no one, of course, counted) until recently were illuminated by HPS lamps, until they began to be cut out of their supports in favor of LED lamps. However, even now, experienced designers prefer to stick a sodium lamp into the project out of harm’s way, because LEDs are 1. really more expensive, 2. not that much energy efficient and 3. still unpredictable, because The number of new LED manufacturers is simply off the charts. But more on that later.
Another option for a HPS lamp
HPS lamps come in different powers - from 50 to 1000 W (rarely, but they are found with a power of 2000 and 4000 W), which seems to hint at their “industrial” use rather than “household”. Basically, HPS lamps are used in luminaires for illuminating streets and roads, less often - in production in combination with white light sources (for example, with MGL lamps to achieve warmer light and greater energy efficiency). In the most perverted cases, they are put into production in their pure form. And then - before the first injury or the call “where to go.”
That rare case when HPS lamps are used in the wrong place
But the most indispensable application is lighting greenhouses, or supplementary lighting of plants (which, in fact, is the same thing, but the second is scientific).
Terminology
This is why we don’t like Wikipedia, because what they write there is either superficial and not clear, or boring and with all the details - which is also not clear to the uninitiated. The most offensive thing is that the essence of the name of the HPS lamp is given only as a decoding of the abbreviation, but here everything is much more interesting.
HPS lamps all over the world (except Russia) are called as they should be called - HPS Lamp (High-Pressure Sodium Lamp), that is, high-pressure sodium lamps (HPS). We also call them that, but no one uses this term. In the Soviet Union, when NLVDs first appeared, various factories began to produce them. The modifications and capacities were different and they had to be distinguished somehow.
A copy of the DNAT 250 lamp produced by the Lisma lamp plant
There were indeed many differences: the shape (ellipsoidal/tubular) and transparency (matte/transparent) of the bulbs, the lamp power (75/150/250/400/600/1000), the presence or absence of mirror coating in one of the hemispheres. So the Soviet-made NLVD had many names. The most common are HPS lamps with various power attachments (150, 250, etc.).
HPS lamp option with two burners for increased service life and quick “hot start”
It was something like branding. For example, now in Russia there are DNAT-250 lamps (with a note, “of such and such production”), and in Germany (and all over the world thanks to export, marketing and quality) there is a lamp, for example, VIALOX NAV-T 250 W SUPER 4Y manufactured by Osram.
Osram Vialox NAV T 250 lamp
So, by and large, HPS lamps are just variations of the lamp model, and not a type of light source . But the type of light source is NLVD, which includes lamps DNaT, DNa3 (with mirror coating) and even DNaS (with a light-diffusing bulb, so that it is less blinding). And, except for specialists, few people know this. That's it.
A cleverly twisted bourgeois HPS lamp with a corrected spectrum - an MGL burner has been added
By the way, if anyone is interested, you can look into the lamp museum (the site is in English, but with a lot of pictures) - there are countless different lamps collected here, incl. and sodium, throughout the history of the era of electric lighting. Very informative.
Application area
It is impossible to list all areas of application of HPS. They can be seen in street lighting, at train stations and airports, and in warehouses. The choice of HPS lamp depends on where it will be used. For use in greenhouses, kindergartens and flower beds, it is recommended to use HPS with a power of 150 or 250 W. When using a 400W lamp, it is important to maintain distance between plants and light sources. It must be at least 50 cm.
For street lighting, industrial premises and underground passages, 150 W lamps are used. In addition, the light source must be in a protected housing with a dust and moisture resistance class of at least IP65. The lamps have an anti-fog effect, so they provide good visibility even in bad weather.
The main manufacturers of HPS lamps are Philips, Osram, General Electric.
Help: It is necessary to work with HPS lamps only in cotton gloves or a cloth. During operation, the cylinder heats up to 300 degrees, and the left traces burn out, after which a thermally conductive carbon layer is formed. As a result, the lamp may explode.
Connecting a HPS lamp
The connection is also primitive to the point of disgrace, as is the device of the lamp. So we won’t dwell on this for long and will only present one of the most typical diagrams for connecting a HPS lamp.
Typical connection diagram for a HPS lamp
Although here it is worth mentioning that in reality there are a huge number of options for connecting a HPS lamp. A compensating capacitor is also a mandatory connection component. As a rule, connection diagrams are indicated on the IZU blocks. But the picture above shows the simplest schematic connection option.
Principle of operation
When voltage is applied to high-pressure sodium vapor, an electric arc is created. To connect the lamp you will need a special power supply (electromagnetic, electronic) and a pulse ignition device (IZU). GPS emission light turns out to be golden or yellow-orange in color. Various gas mixtures are used to change color, but in this case the efficiency and luminous flux are reduced. The greatest radiation occurs at a wavelength of 550-640 nm.
There are hydroelectric power plants, the operation of which does not require the use of IZU. Such devices use trigger antennas wrapped around a gas discharge tube.
Advantages of a HPS lamp
Energy efficiency of HPS lamp
This light source is still considered one of the cheapest and most energy efficient (2016). Yes, yes, you shouldn’t make eyes like that. They are quite competitive with LEDs, incl. and according to the lm/W parameter. So, from the best representatives of the industry with a power of 250 W it is quite possible to get up to 130 lm/W (proof). And from a lamp - up to 90...110 lm/W, depending on the manufacturer, diffuser, reflector, ballast and quality of the supply network.
A copy of the DNAT 1000 lamp made by the Russian company Reflux. 150 lm/W by the way.
Interestingly, the higher the power and luminous flux of a HPS lamp, the higher their light output. For example, there are almost no 50-watt lamps above 80 lm/W. But with DNAT 1000 you can safely get 150 lm/W - that’s crazy. Once again, just two years ago such parameters for LEDs in mass production were unimaginable.
Dependence of the luminous efficiency of a HPS lamp on its power
It is not entirely correct to simply talk about a lamp without a lamp, because only in it you can see all the pros and cons of the HPS lamp. The energy efficiency of lamps with sodium lamps is clearly illustrated by the characteristics declared by lamp manufacturers on their websites (they rarely lie). But we also have our own measured data obtained from the laboratory during testing of luminaires for the rating: – SBP KYRO 2 250 – 84 lm/W, – ZhKU20-150-001 Orion XO with GE lamp – 81 lm/W, – ZhKU15 -150-101B - 87 lm/W. Now comes the most interesting part. If we talk about direct replacement, i.e. when the old sodium lamp was removed and a new LED was hung in its place, you must understand that a lamp with a 150 W HPS lamp can never be replaced with a 50 or 70 W LED. The same applies to 250 W sodium lamps - they cannot be replaced with 100 and even 150 W LEDs (we are talking about ordinary lamps, and not about custom-made lamps with ideal characteristics and a luminous efficiency of 150 lm/W from the lighting device).
Price of HPS lamp
The cost of a HPS lamp varies from 300 to 10,000 rubles, depending on the power, manufacturer, seller and some other variables. An average 250 W light bulb costs around 1000 rubles (±700). But it’s also not entirely interesting to talk about the price of an abstract HPS lamp. It is interesting to talk about the cost of a lamp as part of a lamp with ballasts (starting and control equipment), a base, protective glass, etc.
So, for example, a 250 W lamp with a sodium lamp (23.4 kilolumens, 275 W, 7 kg, 85 lm/W) costs some 5800 wooden ones. This, for a second, is 250 rubles per 1000 lumens of luminous flux (5800/23.4=247). For comparison, its LED analogues cost an average of 30 thousand rubles, which is 1200 or more rubles per kilolumen . Those. LED light costs 5 or more times more than sodium light. Agree, it’s not entirely fair competition with LEDs, especially against the backdrop of not the lowest cost of the euro-dollar in the history of our vastness.
Operating temperatures of the HPS lamp.
DNAT lamps are one of the high-pressure light sources (along with DRL, MGL, LEP - light emitting plasma and others). This, in particular, determines the high operating temperatures of the burner. It can heat up to ~1300 °C. But it's a burner. It is hidden in a shell - a transparent flask made of refractory glass. In turn, the latter can heat up to ~300...400 °C. All this, combined with a fairly simple circuitry for igniting the lamp, allows the lamp to start and operate in a very wide temperature range: -60...+45°C (different manufacturers have different ranges).
Visual demonstration of the temperature of the HPS lamp
Most ballasts for HPS lamps include chokes, which can also operate at very high temperatures (up to +130 °C on the winding in normal mode and up to +200 °C in emergency mode). Which, for example, cannot be said about most drivers of LED lamps. This is us, again, by the way.
Proven technologies
In 15 years, the HPS lamp (as a technology in the broad sense of the word) will turn 100 years old. Yes, there was a period when the lamp was not a “high pressure sodium lamp”. But they were first able to ignite sodium vapor under low pressure and produce light in the visible spectrum in the 30s of the last century. What are we talking about? Moreover, over 100 years (the main achievements have been in the last 20 years), HPS lamps have been brought to the ideal level as much as possible.
Over the years, the light source has been cured of all possible “childhood diseases”, they have learned to dim it, eliminated pulsations with electronic ballasts, straightened the spectrum (MGL is a development of the technology of high-pressure sodium lamps) and the burners have been brought to perfection. But the most important thing is that in almost every country there is at least one manufacturer of lamps for these lamps. And in the most developed ones there are dozens of them. The designs of luminaires for HPS lamps have also been brought to the ideal (the most outstanding ones have an efficiency of 95%), reducing to a minimum losses on the reflector, protective glass and ballasts.
Weight of the HPS lamp (and lamps for it at high and ultra-high power)
The weight of the HPS lamp is not large. Some manufacturers, which is typical, do not even indicate it in the specifications. Depending on the power, it ranges from 150 to 500 grams. But as in the case of other parameters, we are more interested in the weight of the lamp with all the accessories (ballasts, protective cap or glass, base, fasteners).
The street lamp for the DNAT-400 lamp weighs 8 kg. By the way, this lamp (from the link provided) illuminates the entire Moscow Ring Road. Taking into account its luminous flux of 42,000 lumens, we are looking for an LED analogue from another manufacturer (Galad’s outdoor LEDs are of very high quality and with tempered glass - lamps of a higher level). Here, almost NoName Chinese lamp, the lightest we could find, with the same luminous flux (43,000 lumens) weighs 11 kg. We emphasize - the lightest, with a radiator that claims to be of high-quality heat dissipation. More or less serious lamps with casting and normal glass weigh 20-40 kg. They will object to us that there are already many LED solutions based on heat pipes, but not everything is simple with them either. High-quality heat pipes are rare, and low-quality ones are happy to rot in the open air in our climatic conditions - approx. ed.
Operating principle and connection diagram of DNAT
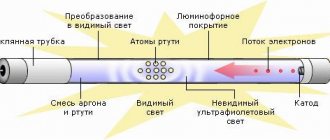
The principle of operation of sodium sources is the breakdown of the gas gap between two electrodes inside the discharge tube.
Rice. 2. Operating principle of a HPS lamp
To do this, a high voltage is applied to the spark gap - in the range from 2 to 5 kV, which should be sufficient for instant breakdown. However, it is impossible to ensure breakdown from a household network, so starting, as in other gas-discharge lamps, occurs using a ballast (ballast). Today, in practice, two types of ballasts are used for arc sodium and mercury gas-discharge lamps - electronic and electromagnetic.
The ballasts for gas-discharge lighting sources include three components:
- choke-transformer - to limit a sharp increase in the current curve flowing in the circuit, it allows you to build the parameters of electrical quantities in accordance with the characteristics of the HPS lamp;
- pulse ignition device (IZU) - designed to briefly increase the voltage to a value sufficient to produce a discharge that ignites a tubular lamp;
- capacitor - is not a mandatory component, but allows you to compensate for the voltage vector biased by the inductor.
Today you can find several options for HPS connection diagrams, which differ both in the characteristics of the components and in the factory features of the lighting devices. Therefore, all circuits for switching on a lighting source can be with or without a capacitor; the IZU can have a two-pin or three-pin connection. Let's look at them in more detail.
Rice. 3. Connection diagram with a two-pin IZU
As you can see, this method of starting sodium light bulbs involves parallel connection of the IZU in relation to the load. But at the same time, a high potential is also supplied to the inductor, which over time will lead to deterioration in performance and subsequent breakdown of the insulation. Moreover, modern single-winding chokes have only weak impregnation without a paper layer. Therefore, this HPS connection scheme is relevant for low voltage sodium tubular models.
Rice. 4. Connection diagram with a three-pin IZU
This circuit does not have the disadvantages of two-pin IZUs, since the HPS lamp has a separate high-voltage output from the IZU, which is separated from the connection point to the inductor. Please note that in any circuit the inductor must be connected to the phase conductor, otherwise the sodium lamp will fail in the event of a short circuit.
With a three-pin circuit, it is important to correctly observe the polarity of the IZU markings:
- B – connects to the ballast (throttle);
- Lp – phase output to the high pressure lamp;
- N – to the zero terminal of the lamp and network.
In addition, a circuit with a capacitor connection can be used:
Rice. 5. Connection diagram with capacitor
As you can see in the diagram, together with the use of an IZU, a capacitor located before the ballast transformer is connected in parallel to the consumer in the HPS lamp circuit. This circuit compensates for reactive losses that do not relate to the quality of the light flux.
In addition, to protect the HPS lamp in its power supply circuit, you can install protection with a fuse or circuit breaker.
Disadvantages of HPS lamps
Color rendering index of HPS lamp
Perhaps this is the biggest disadvantage, often reducing all its advantages to nothing. In the lamp samples we measured, the value of the general color rendering index was: – SBP KYRO 2 250 – Ra = 27, – ZhKU20-150-001 Orion XO with GE lamp – Ra = 15, – ZhKU15-150-101B – Ra = 19. But here It is worth making an amendment that the color rendering index of the lamp, as well as the color temperature, may differ slightly from the same parameters of the lamp, since the protective glass makes its own adjustments. Especially if it is made of low-quality material and becomes cloudy, yellow or green over time. The most resistant in this sense are tempered borosilicate glasses (the same SBP KYRO). But this seriously makes the lamp heavier, increases the requirements for housing rigidity, and generally increases the cost. So all manufacturers look for a compromise in price/quality in different ways.
Comparison of the spectral composition of the radiation of a standard DNAT 1000 lamp and a standard LED (green line)
The “curve” of the color rendering index is due to the gas that is ignited inside the burner. Without going into all the serious chemical composition, let's just say that it is sodium vapor (although the composition there is much more complex). Initially (in low-pressure sodium lamps) the spectrum was even worse, but in the 60s there was a breakthrough in this area. Now we have a pronounced peak in the orange region of the spectrum. The almost complete absence of green and blue components in the lamp’s radiation will lead to the fact that at night on the street illuminated by sodium lamps, we most likely will not distinguish a dark blue car from a dark green one.
If we talk only about energy efficiency, cost and safety, by and large the driver does not need to distinguish colors at night (there is still no clear opinion from the scientific community on this issue). This is indirectly indicated by the fact that the color rendering index (as well as color temperature) on roads is not standardized in regulatory documents. Although there is a suspicion that the standard was written for existing technologies (under NLVD, NLND). Well, just like it is now (under LEDs). But if we talk about the level and quality of life, then the low color rendering index of the HPS lamp, whatever one may say, is the main reason for the relatively rapid displacement of sodium by LEDs from highways, parks, squares and open parking lots.
HPS lamp pulsation coefficient
The pulsations of the light flux from a HPS lamp are merciless. Depending on the ballast, the pulsation coefficient (PF) of the light flux can vary from 15 to 40%. On electronic ballasts, the gearbox can be zero. But due to their high cost, they are rarely used: historically, in street lamps for mass use, performance, reliability and maintainability are often much more important than the quality of light.
It is important to note that CP in street lighting is not standardized. However, these pulsations should be taken into account (and the illumination pulsation coefficient should be calculated) in industrial lighting, when a combined MGL + HPS lighting installation is made.
Long start and hot ignition
One of the very significant disadvantages of a HPS lamp is the long ignition of the burner. Depending on the ambient temperature, the type of ignition unit and the lamp manufacturer, the time it takes for a HPS lamp to reach operating mode ranges from 5 to 10 minutes. You have probably noticed more than once that when sodium street lights are turned on, for the first minute they shine very dimly and, by the way, with white light. Then the brightness gradually increases, and the spectrum acquires a characteristic amber hue.
Ignition of the HPS lamp
Moreover, if the HPS lamp is abruptly turned off and then turned on, it may not light up and not return to operating mode. The burner needs to cool down. This is the “hot start” problem. To solve this problem, at facilities where short-term voltage dips often occur, electronic ballasts and lamps with two burners are used.
Luminous flux and other basic technical characteristics
The abbreviation DNaT 400 stands for tubular sodium arc lamp with a power of 400 W. The device has a simple design. The outer glass shell contains a cylindrical aluminum oxide exhaust pipe. Inside the tube there is a mixture of inert gases: sodium and mercury vapor, as well as xenon. Two electrodes are welded to the edges of the tube. There is emptiness inside the glass flask.
The DNAT 400 lamp has the following technical characteristics:
- pulsation coefficient up to 70%;
- voltage 220 V +/- 5%;
- basic type E40;
- operating temperature from -30C to + 40C;
- color rendering 20-30 Ra;
- color temperature 2000 K;
- Efficiency 30%;
- diameter 48mm.
- duration 12000-25000 hours;
- length 278 mm;
- luminous flux 47,000 lm;
- ignition time 6-10 minutes;
- shape - tubular;
- luminous efficiency 130 lm/W;
- power 400W;
Parameters such as luminous flux, luminous efficiency and average burning time depend on the power of the device. HPS lamps are available in 70, 100, 250 and 400 Watts. HPS has lower performance than its LED counterparts, but is used more often due to its lower cost.
Important! Efficiency directly depends on the ambient temperature. With negative values, devices perform worse.
There are other types of sodium lamps:
- DNaZ - sodium arc mirror.
- DNaS - sodium arc in a light-scattering lamp, replacing mercury gas-discharge lamps;
- DNaMT - opaque sodium arc;
Since sodium lamps contain harmful substances, they are disposed of in a special way.
Application of a HPS lamp
As already mentioned, if we put aside all sorts of perversions, HPS lamps are used mainly in lamps for lighting roads and for supplementary illumination of plants.
Road lighting
The main reason why road workers are hooked on HPS lamps is their incredible energy efficiency and unpretentiousness. Now, of course, a parameter of 100...130 lm/W from a lamp will not surprise anyone, but in the middle of the last century it was a breakthrough.
But the funny thing is that this light source at that time was not the most energy efficient. HPS lamps were high pressure sodium lamps (HPS). And their predecessor - a low-pressure sodium lamp (LPNS) - doubled the light output of a newborn. That is, it produced up to 200 lm/W (by the way, this is still an almost unattainable result, even for LEDs in mass production and at an affordable price).
Actually, the ancestor of the HPS lamp is the low-pressure sodium lamp
But NLND had an even narrower spectrum (well, completely crimson-orange), so the market simply turned a blind eye to such minor losses and accepted the new lamp with open arms, because the colors of objects in its rays became at least somehow distinguishable.
Most highways, open parking lots, and interchanges all over the world are now illuminated with HPS lamps. Actually, here it is:
Non-illusory proof of the involvement of the HPS lamp in illuminating everything
… and so:
HPS lamps illuminate almost 100% of roads
As, again, already mentioned, luminaires for HPS lamps are produced all over the world by hundreds (maybe thousands) of companies. In Russia, housing and communal services have become the most common. This is also terminology dating back to Soviet times, when everything, including product names, was standardized and regulated. ZHKU stands for “ZH” Console Street. “F” is not deciphered in any way, because this letter is simply assigned to designate sodium lamps. Why "F"? There is probably some explanation for this, but it certainly doesn’t fit with ordinary logic. GKU - “G”, metal halogen lamp - understandable. RKU - “R”, Mercury lamp - understandable. DKU - “D”, LEDs - understandable. Housing and communal services... it’s not clear. Let’s simply associate this with a color close to DNAT – Yellow.
A very typical housing and communal services lamp for a DNAT 150 lamp
There are a lot of options for housing and utility services and their manufacturers in Russia. But the leader in the production of Russian utility lamps is Galad, Reflax and Lighting Technologies. How are the leaders? No one thought this, they were just on everyone’s lips. Moreover, Reflux also produces HPS lamps. But we'll talk about this below. There are also countless other manufacturers who import utility housings from Asian countries and sell them in Russia under their own brand.
HPS lamps for additional illumination of plants
By the way, this is a huge, vast topic for holivars on these Internets of ours. What is better for lighting parsley or tomatoes - sodium light or LED? Perhaps we will drop this topic now. But let us note: without exception, all greenhouses in the world, with the exception of experimental ones, and also without taking into account the manual labor of home gardeners, are illuminated with sodium and only with it.
Light for plants
Moreover, greenhouse lamps designed for HPS lamps, as a rule, do not require any serious bodywork in the form of tempered glass, IP housings and other clutter. As a result, a lamp with ballasts, base and reflector weighs 2 times less than their street counterparts.
HPS lamps guard the greenhouse economy
So that you understand what an LED lamp looks like, replacing HPS 1000 lamps, the CREE company has released an analogue of 1 kW HPS. Now there is a lot of discussion on the forums - will the load-bearing structure of the greenhouse withstand such a load, and in general, is it analogous? To be fair, we note that this is the so-called. Reference design is an attempt to show the capabilities of LEDs using a specific example with measurements and calculations, and not a finished product.
Experimental farms for illuminating seedlings with LEDs
Main conclusions
HPS sodium lamps are the most commonly used light source in highways, stadiums, train stations and other applications where weather resistance is important.
The sodium arc tube lamp is one of a kind, although it has its disadvantages, the main ones being color distortion and difficulty in disposal. But good brightness, minimal energy consumption and durability take it to a leading position among lamps.
Connecting a lamp is more difficult than similar lighting devices; you need to have certain skills and abilities. It is important to follow the wiring diagram and select the correct components.
DNAZ lamps
DNAZ, by the way, is one of those domestic products that we (our entire editorial team) are sincerely proud of. No seriously. You will not find a more erotic solution in lighting technology in its simplicity and brevity.
DNAZ lamp 600 W with IP68 socket
Engineers have been struggling for years with the problem of the high temperature of the protective flask, with simple ways of forming the CSC, with minimizing losses in the lamp, and with reducing the weight of the lighting device. And voila - Soviet engineer Vladimir Pchelin makes a lamp with internal mirror coating, opens the Reflax company, patents this business and puts it into mass production. Profit.
Schematically, this is roughly how it works
DNaZ lamps are easily used in the plant supplementary lighting sector by such global giants as Osram and Philips. And they are especially popular among Dutch plant growers, which seems to hint.
Vladimir Pchelin and his invention: a DNaZ lamp in a street lamp housing
Returning to the previous point, these lamps have gone viral not only among agronomists, but also among road workers, and their popularity is just beginning to grow. Most of all, we had the opportunity to see DnaZ lamps in the vastness of the Republic of Belarus, although more in rural areas. In Moscow they really like to put them in courtyards. And just a few months ago they illuminated one of the streets of Dolgoprudny, despite the fact that LED lights were being installed on the neighboring street. Pilot comparison?
Street lamp with DNaZ lamp
As part of the Verified-Lumen section, we were able to test one street lamp using a DNaZ lamp. Because Since the lamp has a built-in reflector to form a wide axial reflector, and its bulb simultaneously serves as protective glass, we can safely say that the measured characteristics of the lamp = the measured characteristics of the lamp (except for power). And, for a second, we got an honest 114 lm/W with a lamp weight of 2.5 (!) kg, a luminous flux of 30,000 (!) lumens and a cost of 7,500 rubles . Actually here it is.
In general, the DNAZ lamp, together with its inventor, deserve a separate article. And we will definitely write it. No. Seriously. Apart from the company's own website, you will find almost no information about this lamp. So we'll fix this.
Possible malfunctions
When connecting a lamp, the following basic errors occur:
- Incorrect connection of the four-pin choke. For many, voltage is supplied to some contacts, and a lamp is connected to others. This is incorrect; before connecting the lamp, you should study the diagram on its body.
- The lamp is screwed on with bare hands. This affects the reliability of the lamp. If contact occurs, wipe it with a clean, dry cotton cloth before starting.
- Using inappropriate choke power. Above this value, more current will flow through the lamp. In this case, the lamp will overheat and periodically burn out and go out.
- The flickering could be due to power surges. For normal operation, the voltage range should be 220V +/- 5%.
- Using a starter for the wrong lamp. If the HPS is enabled via the DRL choke, the unit's operating time will be reduced.
- Without capacitor. At the same time, the strands are constantly heated.
- Malfunction of the wire from the lamp to the IZU. At the same time, the IZU makes a wheezing noise, and the lamp itself does not turn on. It is recommended to replace the wires and check the condition of the contacts on the IZU.
- Problem with IZU. The lamp does not light up, the IZU does not make a sound. It is recommended to check the ballast with an ohmmeter or replace the IZU.
When working with a HPS lighting device, a number of safety precautions must be observed:
- do not place light bulbs next to flammable structures;
- do not touch the device without gloves;
- When working with electrical devices, general safety precautions must be observed.
- After turning off the lamp, do not touch it for 15 minutes until it has completely cooled down;
- the device requires constant ventilation to operate;
When used and connected correctly, the lamp can provide stable operation.
Summary
HPS lamps are a reliable, time-tested type of lamp that is used throughout the world to illuminate streets, highways and greenhouses. Its main advantage is high energy efficiency and low price. Thanks to this, this type of lamp will compete with all innovative light sources, including LEDs, for a long time.
HPS lamps
Types of DRL
There are several main types of DRL lamps:
- Standard mercury arc fluorescent - characterized by weak color rendering, and during the glow a large amount of heat is released. It takes about five minutes from the moment it is plugged into the network to reach operating mode. They are extremely unstable to voltage surges, so operation is permissible in circuits with a constant power source. Designs that use these lamps must have heat-resistant wires.
- Arc mercury erythema tungsten (DRVED) is a lamp that operates without a choke. Connects via active ballast in the same way as standard incandescent light bulbs. Due to the presence of metal iodides, light transmission increases and energy consumption decreases. For greater brightness, uviol glass is used. Best suited for rooms with little natural light.
- DRLF is an improved DRL used to accelerate plant photosynthesis. The inside of the bulb is covered with reflective material, which is why the light bulb got its second name - reflector. Ideal for AC connection. It is used in greenhouses and greenhouses where an additional light source is required.
- Arc mercury tungsten - increased luminous efficiency, long service life without a ballast. An excellent option for lighting streets, parking lots, open areas, etc.
- https://lampagid.ru/vidy/lyuminestsentnye/drossel-dlya-drl
- https://fb.ru/article/336784/lampa-drl—harakteristiki-osobennosti-printsip-deystviya-i-otzyivyi
- https://proosveschenie.ru/proizvodstvennye-pomeshheniya/pravilnoe-podklyuchenie-lampy-drl.html
- https://www.asutpp.ru/lampy-drl.html
- https://svetosmotr.ru/5-oshibok-pri-podklyuchenii-lampy-dnat/
- https://220.guru/osveshhenie/istochniki-sveta/lampa-drl.html
- https://strojdvor.ru/elektrosnabzhenie/texnicheskie-parametry-i-sxemy-podklyucheniya-lamp-drl/
- https://lampaexpert.ru/vidy-i-tipy-lamp/fitolampy/drl-125-250-400-watt-harakteristiki
Calculated greenhouse lighting lamps Reflux DNAT / DNAZ
Information about the material Updated: June 14, 2016
- Seal
Table of calculated illumination levels for phytolights, irradiators with Reflux Dna3 lamps (with a mirror reflector) depending on the lamp power, the distance from the lamp to the tops of plants and from the illuminated surface.
The table is intended for an approximate calculation of greenhouse lighting and selection of the required number of DnaZ . Please note that the data in the table is for lighting greenhouses in groups, not with one lamp. The overlap of light fluxes from adjacent lamps is taken into account.
| Phytolamp | Power, W | Distance from lamp to plant tops, m | Lighting area, sq.m. | Size of illuminated area, m | Illumination level, Lux |
| Reflux / DNAZ | 70 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 0.7×1.5 | 4000-5000 |
| 0.5 | 1.36 | 0.8×1.7 | 3500-4000 | ||
| 0.6 | 2.0 | 1.0×2.0 | 2200-2500 | ||
| 0.7 | 2.4 | 1.2×2.0 | 1800-2000 | ||
| Reflux / DNAZ | 100 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 1.7×0.9 | 4000-6000 |
| 0.7 | 2.0 | 1.9×1.1 | 2500-4500 | ||
| Reflux / DNAZ | 150 | 0.7 | 2.0 | 1.9×1.1 | 5000-7000 |
| 1.0 | 2.5 | 2.1×1.2 | 3500-5500 | ||
| 1.5 | 3.0 | 2.3×1.3 | 2500-4500 | ||
| Reflux / DNAZ | 250 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 2.3×1.3 | 5500-8500 |
| 1.5 | 3.5 | 2.5×1.4 | 3000-5000 | ||
| 1.7 | 4.0 | 2.7×1.5 | 2000-4000 | ||
| Reflux / DNAZ | 400 | 1.5 | 4.0 | 2.5×1.6 | 5500-7500 |
| 1.7 | 6.0 | 3.0×2.0 | 3500-5500 | ||
| 2.0 | 8.0 | 3.4×2.3 | 2500-4500 |
Precautions for use
The outer bulb of the lamp heats up to a temperature of 250–300 degrees. Celsius. This determines the list of safety measures when working with it.
- Do not touch the lamp bulb for 10–15 minutes after turning it off.
- You should absolutely not touch the flask with your hands without gloves: traces of sweat and grease on the surface will lead to uneven heating and even an explosion.
- Provide good ventilation for the lamp and keep it away from flammable structures. The same applies to the ballast choke, which heats up to 150 degrees. Celsius.
In addition, protect the lamp from impacts: when the bulb explodes, fragments fly over a very long distance. If the burner is damaged, the room or area may be contaminated with mercury.