Aug 15 • Articles • •
(
409 votes, average: 4.84 out of 5)
HPS lamps: a light source that was retired too early.
As we promised, an article about HPS (High Pressure Sodium Tubular Arc) lamps has finally arrived. Anyone who has worked or is working in the field of lighting technology knows firsthand about the HPS lamp. But if anyone doesn’t know, let’s explain it in simple terms: HPS lamps are like a Kalashnikov assault rifle for lighting streets and illuminating plants - a time-tested and reliable, but not without its shortcomings, light source.
Actually, this article about HPS lamps is more for beginners; material presented competently, but in an accessible language: without schematic diagrams of connection and a complete explanation of the basics of maintaining the discharge column in the burner of a HPS lamp. But we are sure that specialists will also like the sketch.
Actually, the subject: one of the invariations of the HPS lamp
Almost 100% of the world's roads (no one, of course, counted) until recently were illuminated by HPS lamps, until they began to be cut out of their supports in favor of LED lamps. However, even now, experienced designers prefer to stick a sodium lamp into the project out of harm’s way, because LEDs are 1. really more expensive, 2. not that much energy efficient and 3. still unpredictable, because The number of new LED manufacturers is simply off the charts. But more on that later.
Another option for a HPS lamp
HPS lamps come in different powers - from 50 to 1000 W (rarely, but they are found with a power of 2000 and 4000 W), which seems to hint at their “industrial” use rather than “household”. Basically, HPS lamps are used in luminaires for illuminating streets and roads, less often - in production in combination with white light sources (for example, with MGL lamps to achieve warmer light and greater energy efficiency). In the most perverted cases, they are put into production in their pure form. And then - before the first injury or the call “where to go.”
That rare case when HPS lamps are used in the wrong place
But the most indispensable application is lighting greenhouses, or supplementary lighting of plants (which, in fact, is the same thing, but the second is scientific).
What is a sodium lamp
A sodium lamp is understood as a lighting device with the designation HPS and the decoding “sodium arc tubular” lamp. The element is reliable, simple and accessible. Many companies still produce them, which indicates that there is demand.
The devices first appeared in the thirties, but they were quickly replaced by metal halide sources. The elements are used for street lighting, illumination of agricultural crops, in gyms and underground passages.
Appearance of a sodium lamp
For a long time, sodium elements were installed in street lamps and highway lighting systems. Now the devices are being replaced with LEDs. However, a large number of designers prefer sodium sources due to their availability, long service life, high power and light output.
HPS lamps are often installed in enterprises together with metal halide lamps. Sodium lighting produces warm colors and is more comfortable to work with.
Area of use
HPS light sources are not used in residential areas due to excessive power and distorted color rendering: for example, green often “turns” into black or dark blue. However, light bulbs have found application in other areas:
- Lighting of streets and roads. The lamps performed especially well when working in foggy areas;
- Underpasses, railway stations and airports, parking lots, tunnels;
The lamps work well even in fog and rain
- Industrial premises, warehouses, workshops, parking lots, sports complexes, for which the correct transmission of light is not important;
- Illumination of monuments and buildings;
- For greenhouses, flower beds and other complexes in which plants are grown. This allows you to grow plants all year round, regardless of the season.
You may be interested in Features of light bulb sockets
In greenhouses they use lamps with a power of 150-250 W; a 400 W lamp is also suitable, but it will need to be placed further away. For the street, lamps with a power of 70-150 W are required.
Important! For street lighting, it is important to choose lamps that are protected from moisture and dust.
Varieties
All sodium lamps are divided into high and low pressure elements. The main difference is the pressure level in the flask and the difference with the atmospheric indicator. This determines the specifics of the equipment’s operation and application in specific situations.
High pressure
There are three types of high pressure elements:
- HPS is the most common high pressure sodium arc lamp found in street lamps.
- DNaZ is a type of DNAT that has a mirror coating on the inner wall of the flask. The element is characterized by lower power, but increased light output.
- DRI (DRIZ) – a device with radiating additives. May have a mirror layer on the flask. Relatively good color reproduction, but some colors look dull.
Types of gas discharge lamps
Low
sodium lamps were not popular with users from the very beginning and are no longer used . Even increased energy efficiency was not a reason to use it. The reason is poor color rendering, which makes it difficult to identify the color and sometimes the shape of an object.
At the same time, they are reliable, consume little energy, and produce excellent light. Suitable in rare cases exclusively for street lighting.
Summary
HPS lamps are a reliable, time-tested type of lamp that is used throughout the world to illuminate streets, highways and greenhouses. Its main advantage is high energy efficiency and low price. Thanks to this, this type of lamp will compete with all innovative light sources, including LEDs, for a long time.
HPS lamps
Specifications
The main ones include luminous flux, luminous efficiency and operating time. There is a direct relationship between the power of the element and the resource - high-power models last longer.
Below are the technical characteristics of popular HPS sources with a power of 150, 250 and 400 W. All of them are connected to the lamp using an E40 type socket at a voltage of 120 V.
DNAT 150
Technical characteristics of the lamp DNaT 150
| Power, W | Flow, Lm | Light output, lm/W | Length, mm | Diameter, mm | Resource, h |
| 150 | 14 500 | 100 | 211 | 48 | 6 000 |
DNAT 250
Technical characteristics of the lamp DNaT 250
| Power, W | Flow, Lm | Light output, lm/W | Length, mm | Diameter, mm | Resource, h |
| 250 | 25 000 | 100 | 250 | 48 | 10 000 |
DNAT 400
Technical characteristics of the lamp DNaT 400
| Power, W | Flow, Lm | Light output, lm/W | Length, mm | Diameter, mm | Resource, h |
| 400 | 47 000 | 125 | 278 | 48 | 15 000 |
Advantages of a HPS lamp
Energy efficiency of HPS lamp
This light source is still considered one of the cheapest and most energy efficient (2016). Yes, yes, you shouldn’t make eyes like that. They are quite competitive with LEDs, incl. and according to the lm/W parameter. So, from the best representatives of the industry with a power of 250 W it is quite possible to get up to 130 lm/W (proof). And from a lamp - up to 90...110 lm/W, depending on the manufacturer, diffuser, reflector, ballast and quality of the supply network.
A copy of the DNAT 1000 lamp made by the Russian company Reflux. 150 lm/W by the way.
Interestingly, the higher the power and luminous flux of a HPS lamp, the higher their light output. For example, there are almost no 50-watt lamps above 80 lm/W. But with DNAT 1000 you can safely get 150 lm/W - that’s crazy. Once again, just two years ago such parameters for LEDs in mass production were unimaginable.
Dependence of the luminous efficiency of a HPS lamp on its power
It is not entirely correct to simply talk about a lamp without a lamp, because only in it you can see all the pros and cons of the HPS lamp. The energy efficiency of lamps with sodium lamps is clearly illustrated by the characteristics declared by lamp manufacturers on their websites (they rarely lie). But we also have our own measured data obtained from the laboratory during testing of luminaires for the rating: – SBP KYRO 2 250 – 84 lm/W, – ZhKU20-150-001 Orion XO with GE lamp – 81 lm/W, – ZhKU15 -150-101B - 87 lm/W. Now comes the most interesting part. If we talk about direct replacement, i.e. when the old sodium lamp was removed and a new LED was hung in its place, you must understand that a lamp with a 150 W HPS lamp can never be replaced with a 50 or 70 W LED. The same applies to 250 W sodium lamps - they cannot be replaced with 100 and even 150 W LEDs (we are talking about ordinary lamps, and not about custom-made lamps with ideal characteristics and a luminous efficiency of 150 lm/W from the lighting device).
Price of HPS lamp
The cost of a HPS lamp varies from 300 to 10,000 rubles, depending on the power, manufacturer, seller and some other variables. An average 250 W light bulb costs around 1000 rubles (±700). But it’s also not entirely interesting to talk about the price of an abstract HPS lamp. It is interesting to talk about the cost of a lamp as part of a lamp with ballasts (starting and control equipment), a base, protective glass, etc.
So, for example, a 250 W lamp with a sodium lamp (23.4 kilolumens, 275 W, 7 kg, 85 lm/W) costs some 5800 wooden ones. This, for a second, is 250 rubles per 1000 lumens of luminous flux (5800/23.4=247). For comparison, its LED analogues cost an average of 30 thousand rubles, which is 1200 or more rubles per kilolumen . Those. LED light costs 5 or more times more than sodium light. Agree, it’s not entirely fair competition with LEDs, especially against the backdrop of not the lowest cost of the euro-dollar in the history of our vastness.
Operating temperatures of the HPS lamp.
DNAT lamps are one of the high-pressure light sources (along with DRL, MGL, LEP - light emitting plasma and others). This, in particular, determines the high operating temperatures of the burner. It can heat up to ~1300 °C. But it's a burner. It is hidden in a shell - a transparent flask made of refractory glass. In turn, the latter can heat up to ~300...400 °C. All this, combined with a fairly simple circuitry for igniting the lamp, allows the lamp to start and operate in a very wide temperature range: -60...+45°C (different manufacturers have different ranges).
Visual demonstration of the temperature of the HPS lamp
Most ballasts for HPS lamps include chokes, which can also operate at very high temperatures (up to +130 °C on the winding in normal mode and up to +200 °C in emergency mode). Which, for example, cannot be said about most drivers of LED lamps. This is us, again, by the way.
Proven technologies
In 15 years, the HPS lamp (as a technology in the broad sense of the word) will turn 100 years old. Yes, there was a period when the lamp was not a “high pressure sodium lamp”. But they were first able to ignite sodium vapor under low pressure and produce light in the visible spectrum in the 30s of the last century. What are we talking about? Moreover, over 100 years (the main achievements have been in the last 20 years), HPS lamps have been brought to the ideal level as much as possible.
Over the years, the light source has been cured of all possible “childhood diseases”, they have learned to dim it, eliminated pulsations with electronic ballasts, straightened the spectrum (MGL is a development of the technology of high-pressure sodium lamps) and the burners have been brought to perfection. But the most important thing is that in almost every country there is at least one manufacturer of lamps for these lamps. And in the most developed ones there are dozens of them. The designs of luminaires for HPS lamps have also been brought to the ideal (the most outstanding ones have an efficiency of 95%), reducing to a minimum losses on the reflector, protective glass and ballasts.
Weight of the HPS lamp (and lamps for it at high and ultra-high power)
The weight of the HPS lamp is not large. Some manufacturers, which is typical, do not even indicate it in the specifications. Depending on the power, it ranges from 150 to 500 grams. But as in the case of other parameters, we are more interested in the weight of the lamp with all the accessories (ballasts, protective cap or glass, base, fasteners).
The street lamp for the DNAT-400 lamp weighs 8 kg. By the way, this lamp (from the link provided) illuminates the entire Moscow Ring Road. Taking into account its luminous flux of 42,000 lumens, we are looking for an LED analogue from another manufacturer (Galad’s outdoor LEDs are of very high quality and with tempered glass - lamps of a higher level). Here, almost NoName Chinese lamp, the lightest we could find, with the same luminous flux (43,000 lumens) weighs 11 kg. We emphasize - the lightest, with a radiator that claims to be of high-quality heat dissipation. More or less serious lamps with casting and normal glass weigh 20-40 kg. They will object to us that there are already many LED solutions based on heat pipes, but not everything is simple with them either. High-quality heat pipes are rare, and low-quality ones are happy to rot in the open air in our climatic conditions - approx. ed.
Design Features
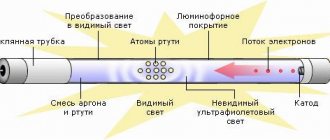
All sodium lamps consist of a high-strength aluminum oxide bulb connected to two electrodes. The element material can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to sodium vapor. The flask is filled with a mixture of inert gases, mercury, sodium and xenon. The presence of argon in the gas mixture facilitates the formation of a charge, and mercury and xenon serve to improve light output.
The design looks like a flask within a flask. The burner is installed in a smaller flask, and a vacuum is created in it. Connects to the network via a socket. The external element performs the function of a thermos, protecting the internal parts from the negative effects of low ambient temperatures and reducing heat loss.
Recommendations for selection
For specific use, lamps are selected according to the type of installation solution (column, floor lamp, string, wall). The problem of obtaining the required illumination (in lux) is solved by the power of the lamp, the type of reflector (reflective or white flat) or diffusing element. The color of the flow can be changed by the color temperature of the lamp or by selecting a filter in the lampshade.
It is also important that the style of the lamp matches the architecture of the house. Thus, a stylish minimalist lamp fits well into the facade of a modern building with a flat roof and rectangular architecture, while lamps reminiscent of antique gas lanterns are more suitable for a classically shaped house.
When choosing a lamp, one should not forget about economics: street lamps should consume the minimum possible amount of energy. Automation should help with this, switching the maximum flow rate to average, minimum and zero according to the selected program, photo relay or timer.
Operating principle
An arc discharge must be maintained inside the sodium lamp bulb. For generation, a pulsed ignition device (IZD) is used. During switching on, the pulse can reach a power of 2-5 kW.
Under the influence of voltage, a breakdown occurs with the formation of a discharge. It takes about ten minutes to warm up the burner and reach the rated power of the device. At this time, the brightness increases and normalizes.
How DNAT works
In modern elements you can find a built-in choke, which limits the arc current and guarantees a stable supply of energy without ripples and other undesirable moments.
Ballast device
The ballast consists of three main components: • Inductive choke. • IZU. • Phase compensating capacitor. The choke serves to limit the arc current and its power must be the same as that of the lamp used. For example, if a HPS 250 lamp is used, then, accordingly, the power of the inductor should also be no less and no more than 250 Watts. Recently, the connection diagram for lamps often includes a single-winding choke, while double-winding ones are already obsolete. IZU is necessary to increase the voltage to several kilovolts in order to form an arc. The power of the IZU can range from 35 to 400 Watts. In addition, the device can be of a two-pin or three-pin design. Moreover, the use of three-pin IZU is preferable. As for the capacitor, this is an optional component. But its presence provides certain advantages, as it allows you to reduce the load on the household electrical network. In turn, this reduces the risk of a wiring fire to a minimum. More details will be discussed below.
Areas of application
Sodium lamps are used when economic considerations are more important than color rendering. They are not suitable for residential premises, public buildings and production workshops . In addition to poor color rendering, the lamp is dangerous if it malfunctions.
Can be used for seedling growth
DNAT is used to organize street or greenhouse lighting, illumination of architectural monuments and buildings. They are especially common in large cities. They can be recognized by their yellowish-golden hue. The most common elements are 250 and 400 W.
Relatively recently, low-power sodium lamps with a color rendering index of 80 appeared on the market. This indicator is significantly higher than that of other similar models. Therefore, such lamps are effective for lighting decoration in public places.
Sodium light sources are used in the final stages of seedling growth in greenhouses, where shades of blue are often present. Radiation of a significant proportion of the ultraviolet spectrum promotes plant growth. It is important to handle the elements with care, because... destruction of the flask can ruin the entire crop and spoil the soil.
Designers often use sodium elements to imitate fire or the light of the sun.
Advantages and disadvantages
HPS lamps have a large number of advantages, thanks to which they remain in demand today. Among its advantages:
- High level of light output compared to other light bulb models. High pressure lamps give up to 150-160 lm/W, low pressure lamps - up to 200 lm/W;
- Efficiency reaches 30%;
You might be interested in Lighting connection systems
The lamp produces a strong yellow light
- A wide range of temperatures at which the light bulbs operate: from −60 to +40 degrees. In this case, the lamp lights up even at low temperatures;
- Long period of operation: minimum period - 10-12 thousand hours, maximum - up to 30-32 thousand;
- Cost-effective: HPS consumes 1.5-2 times less electricity. The production of lamps is also inexpensive: it has been established for a long time and works well, expensive materials are not required;
- Anti-fog effect: yellow and orange colors are poorly absorbed by water, and therefore lamps with such lighting are better visible in rain and fog.
However, the disadvantages of DNAT are no less significant:
- Weak color rendering: all lamps have a pronounced yellow or orange color. Lamps cannot be used in residential premises;
- Long burn-up: the first 5-10 minutes the lamp burns weakly while it warms up;
The light bulb contains mercury, which makes it dangerous.
- Certain electrical requirements. Lamps can only be used in networks with a fairly stable voltage;
Important! The second option is to use high-quality chokes.
- Presence of mercury: for disposal, lamps must be taken to a special collection point. A broken lamp can be dangerous if removed incorrectly or not thoroughly;
- Temperature: despite the fact that HPS lamps can operate at −60 degrees, the optimal temperature for them is from −20 to +30 degrees. At higher or lower temperatures, the light output will be lower and the service life will be reduced;
- The presence of quite strong ripples, they can reach 50 Hz. This results in constant flickering, which is tiring for the eyes.
Connection diagrams
Depending on the IZU, the schemes differ. The IZU can be two-pin or three-pin. Below are diagrams for both cases.
Connection via two-pin IZU
In the connection diagrams for sodium lamps, the inductor is always connected in series, while the igniter is connected in parallel.
Connection via a three-pin IZU
Power reactance during startup requires the inclusion of a capacitor in the circuit to reduce noise and inrush current. Typically an element with a capacity of 18-40 μF is used. The capacitor is connected in parallel to the power source. The capacitor stabilizes the voltage and slows down the degradation of the electrodes.
Use of a capacitor in a circuit
How to connect a lamp correctly
It will not be possible to connect the light bulb to a regular household network, since the available voltage is not enough to operate it. In addition, it is necessary to limit the arc current so that work proceeds without interruption.
Important! All sodium lamps, both HPS and HPS, are connected according to the same circuit.
To connect the lamp you need the following elements:
- IZU is a Pulse Ignition Device that helps increase the voltage in the network until an arc forms. IZUs can be 2-pin and 3-pin: the former are cheaper and simpler, the latter perform better in operation. When connecting a two-terminal IZU, when turned on, the discharge is applied to the lamp and ballast, when connecting a three-terminal IZU - only to the lamp;
To connect you will need several additional elements
- A ballast is an electronic or electromagnetic ballast that limits the current after starting. Electronic ballast or electronic ballast is an electronic circuit, electromagnetic is a choke (a coil with an open magnetic circuit). When connecting, the inductor must be connected in series with the DNAT, and the IZU in parallel.
The connection diagram for a two-pin IZU occurs in several steps:
- The IZU is connected in parallel with the lamp;
- The “phase” wire after the inductor must be connected to the desired terminal of the IZU;
- The second tip is connected to the remaining clamps.
The connection diagram for a high-pressure sodium lamp and a three-terminal IZU is a little more complicated:
- One negative wire must be connected to the light bulb, the second to the same type of IZU terminal;
- Next, you need to open the phase and connect one cable from the panel to the inductor;
- The middle conductor is connected to the light bulb.
When connecting a HPS lamp, you must use the diagrams. If in doubt, it is better to contact a specialist rather than connect it yourself.
Precautionary measures
When using sodium discharge lamps, it is important to remember:
- It is unacceptable to turn off the power to the element immediately after it has been turned on. You need to wait at least 1-2 minutes. Failure to comply with this recommendation may result in complete startup failure.
- The room with the lighting element must have a ventilation system. This is due to the increased heat transfer of the device and the presence of harmful substances in it.
- Do not touch the lamp or reflector with bare hands during operation as this will cause serious burns.
- It is advisable to use gloves when installing the flask. Fatty deposits when heated can cause the flask to explode. It is prohibited for water to enter open elements.
- The ballast used together with the light bulb can heat up to temperatures of about 150 degrees. It is recommended to place it under a fireproof casing to protect it from moisture and debris.
- Do not touch conductive elements with bare hands or allow them to get wet. It is also recommended to periodically check the wiring for damage, burns or short circuits. In this case, the wires must be special, designed to work with extremely high voltages.
Technical parameters of USB sockets
At the moment you can find USB sockets from Legrand of various modifications. This can be a single or double USB socket, a regular power socket with a USB connector, a socket equipped with a switch, or sockets with a special stand for gadgets that does not require additional fastening. But all these modifications use a single power unit built into the outlet.
USB power sockets
So:
- This USB outlet usually has a unit designed to operate from 100 to 240V. The frequency of the supply network should be 50Hz, the same frequency is used in domestic power networks.
- The output voltage of such a unit is 5V, and the rated current is 1500mA. These parameters are quite sufficient to charge almost any gadget.
Note! According to the manufacturer's instructions, it will take about 2 hours to fully charge currently known mobile devices from such an outlet. If two devices are connected at once, the charging time will be about 2 hours 45 minutes. To fully charge the tablet it will take from 3 and a half to 5 and a half hours.
- For sockets that do not have a switch in the primary circuit, the issue of energy consumption in idle mode becomes quite relevant. For power supplies from Legrand it is up to 0.1 W per hour. That is, in a month in passive mode, such charging will consume about 70W. The price of such energy consumption will be mere pennies.
- Another factor, which, although not related to technical parameters, is very important, is the depth of the mounting box for such sockets. Due to the presence of a power unit, it must be at least 40 mm, which is very important during installation.
Disposal
Disposal of devices
Sodium is a volatile substance that ignites easily when exposed to air. In addition, the elements contain mercury, a dangerous radioactive element that can cause severe poisoning. For this reason, it is unacceptable to simply throw away sodium lighting sources. They must be disposed of as potentially hazardous waste along with other energy-saving lamps.
In large cities, recycling bins are provided. If this is not possible, contact your nearest lighting repair shop, manufacturing facility, or hazardous waste collection service.
Classification of street lamps depending on design
Methodology for calculating lighting in domestic and industrial premises
Street lamps are structurally different, which is caused by the installation features.
Street ground lamps are represented by three types of devices.
- Reflector lights: illuminate highways and major highways. The light flux from a 250-400 W lamp is focused and converted into a directional one.
- Lamps with diffused lighting: used for equipment on secondary highways. The lamp power is selected within the range of 70-250 W.
- Forged street lamps with diffused lighting: the lampshade can be cylindrical or spherical. Lamp power – 40-125 W. Pedestrian areas (paths, sidewalks, squares) are equipped with such lamps. A variety of them can be pendant street lamps. A lantern of complex shape may have a cantilever fastener.
In addition to ground-based ones, there are street lighting lamps of other designs.
- Facade lamps are most often spotlights. They are mounted on walls, installed on parapets and directly on the ground. The latter are used to equip stairs and garden paths.
- Street ceiling lamps are mounted above the porch of entrances, in the halls of open-type stations. Another option is outdoor recessed lights.
- A street lamp suspension can decorate the front porch.
- The built-in waterproof device is used to illuminate fountains.
When choosing an outdoor lighting lamp, it is necessary to take into account not only its main characteristics. The device must be organically combined with the architectural style of the building. And it is desirable that it be inexpensive.
There are several types of gas discharge lamps:
Mercury: their light appears as a result of electrical discharges in mercury vapor with which the flask is filled. It is characterized by strong heating of the flask and surfaces that are nearby, which requires the use of heat-resistant materials. Mercury lamps (HLVs) are used in rooms with large square footage. Sodium (DNAT): work like mercury, but the flask is filled with sodium vapor. Protected from environmental influences by special glass. This safety measure is necessary, since sodium lamps are unstable to temperature changes and humidity. Metal halides (MHA): halides are added to the mercury vapor in the flask. They have high power (up to 2 kW), which is considered a guarantee of good room illumination
This is important for equipping large areas and sports facilities. Xenon: consist of tungsten electrodes, between which an electric discharge passes. The flask contains an inert gas and metal salts (mercury or sodium). Fluorescent: energy efficient lamps with a long service life
The big disadvantage is the use of mercury vapor that fills the flask. If the flask is damaged, the poisonous gas will become dangerous to human health. If luminescent devices are turned on and off very often, their service life is noticeably reduced. This characteristic does not prevent the use of these lamps for illuminating city streets. Induction: street lighting comes from ionized gas, which creates a plasma glow. The lighting is controlled using an inductance coil that generates a magnetic field.
LED floodlights for street lighting should be placed in a separate group. This light source is gradually being replaced by the ones listed above.
The outdoor LED lamp has the following characteristics:
- high efficiency;
- long service life (100 thousand hours or more);
- efficiency: electricity is not wasted on heating nearby objects. Serves to create a luminous flux
- resistant to various climate changes
- durable and not afraid of moisture
Advantages and disadvantages of DNAT
The advantages of this type of lamp are visible from the table above. First of all, it has greater energy efficiency. The working resource is also significantly higher. Due to its compactness, it can be installed in smaller luminaires. The color temperature matches natural sunlight. At this spectral frequency, the luminous flux is not affected by snow flakes, raindrops, fog or dust.
It also has its drawbacks. The time it takes to reach full luminous flux is very long - in severe frost, DNAT 250 can flare up to full power only after 15 minutes (the time depends on the power of the light source) . Due to the low color rendering index, interior items may have a completely different appearance when illuminated. During operation, flickering appears from an industrial network with a frequency of 50 Hz, which has a negative effect on the visual apparatus. You won't be able to work for long in this light.