When operating standard incandescent lamps, which have low efficiency, a large amount of thermal energy is released. Overheating and destruction of lamp sockets, wiring or lamp shades occurs. The use of LED or fluorescent light bulbs with increased operating efficiency allows you to reduce energy costs while simultaneously reducing thermal radiation.
What lamps are best to use in an apartment?
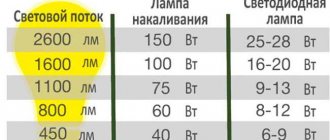
Light-emitting diode (LED) lamps are the most modern and reliable light sources. They last up to 25 times longer than incandescent lamps, and consume almost 8 times less electricity. They light up instantly, practically do not heat up and do not flicker. The quality of light is as close to natural as possible.
Interesting materials:
How to install msvcp120 DLL program? How to install Team Viewer? How to set the default Word program? How to install firmware on PS4? How to set dropdown list in Excel? How to install a browser extension? How to install the AdBlock extension in Google Chrome? How to install sliding doors on a suspended ceiling? How to install Realtek High Definition Audio Driver? How to install crack for gta 4 Steam?
Sources of light
Not all energy-saving light bulbs that are currently on the lighting market have low heating during operation. Therefore, in this situation, in order to determine which sources are most beneficial for tensile structures, it is necessary to consider in detail all potential options, since all of them, in any case, will heat up at least a little. All light bulbs can be divided into two main types:
- economical or energy saving. This includes light bulbs that, to varying degrees, can consume less electricity;
Energy saving light sources
Incandescent lamps
- incandescent lamps. These are the first models of light sources. Therefore, they are distinguished by very strong heating during their operation and, on top of that, they are wasteful in terms of energy consumption. Therefore, in any case, they cannot be used to illuminate rooms with suspended ceilings. However, they are still sometimes found, as they are suitable for chandeliers and other lighting fixtures according to the size of the base.
As you can see, only energy-saving light bulbs are suitable for suspended ceilings, which can not only save energy, but also heat up less during their operation. But is it? To understand whether all energy-saving light sources have little heating and can be used in a suspended ceiling structure, you need to consider them in more detail. Today, the list of potential candidates includes the following energy-saving lamps:
- LED;
- luminescent.
Each candidate from the above list is a more advanced model than incandescent lamps. But they are still not without advantages and disadvantages.
Where does thermal energy come from and where is it spent?
Like most well-known lighting devices, LED analogues have a conversion rate of energy into useful emitted power of less than 100 percent – it ranges from 30-40%. The reasons for this are hidden in the features of the design and functioning of radiating elements of this class. To understand where the vast majority of energy is spent, you should familiarize yourself with the intricacies of the conversion processes occurring inside the LEDs.
Their work is based on physical principles that are very different from those processes observed in fluorescent or conventional incandescent lamps. LED bulbs do not heat up in the truest sense of the word. They do not dissipate thermal energy into the surrounding space, since they spend it on heating the internal crystal of the emitter.
If heat is not purposefully removed from the semiconductor junction, the element crystal, under certain conditions, runs the risk of overheating and then completely burning out. Therefore, devices included in high-power LED products require special heat removal. The design of LED lamps with individual light bulbs placed in them provides a special substrate that performs this function. This technique makes it possible to maintain the integrity of the LEDs with a high degree of probability and extend their service life.
A few words about the design
LED lamps are a complex electronic device, the design of which is divided into several parts:
- Diffuser. It is a glass or plastic flask that serves to uniformly disperse the light flux.
- The chips are light-emitting diodes.
- The printed circuit board is the platform on which the LEDs are mounted. Made from material with high thermal conductivity.
- The radiator is a structure made of material with high thermal conductivity. Serves to remove heat.
- The driver is an LED power supply, used to convert the alternating voltage of a 220-volt electrical network into the power necessary for the normal operation of the LEDs.
- The socket is an important element that serves to connect the light bulb to the lamp socket.
It is clear from the design that the LED lamps heat up, and to remove the generated heat, a radiator made of a special material with high thermal conductivity is installed.
The radiator in an LED light bulb is designed to remove heat from its only heating part - a group of LEDs. In this light fixture, neither the bulb nor the base heats up (provided there is normal contact with the socket). The release of thermal energy occurs only on the LED crystals, and heat is removed from them.
Diffuser shape
The next important characteristic is the form of dissipation . There are only two main types:
- flat, having one main luminous surface;
- volumetric ones that shine around themselves, more like a flask in shape;
Accordingly, flat lamps provide only a spot of light underneath them, while volumetric lamps illuminate the space around them. Let's look at how light sources with different bases differ and where they are used most often :
Lamps with a GX53 base are perhaps the most successful solution for installation in built-in spotlights for a suspended or suspended plasterboard ceiling.
What kind of lighting do you prefer?
Built-in Chandelier
They have a small depth - from 15mm, which allows them to be installed even in small spaces. At the same time, they have a large diameter, on average 75mm. Such a lamp is almost entirely on one side - a light-emitting surface, which is very effective in lighting. The large surface diameter also allows this light source to be effectively cooled, making it last longer.
The pin contacts here have thickenings at the edges, thereby allowing the light bulb to be securely fixed in the lamp socket during installation.
Standard size: Diameter 75mm, depth from 15mm
Application: Lamps with GX53 socket are often used for decorative lighting, but most often, due to their qualities, they are elements of main lighting. A group of such lamps replaces traditional chandeliers, creating more even illumination of the room.
Marking GX53: GX – pin contacts, distance between contact axes 53 mm.
Standard size: Diffuser with a diameter of ~50mm, depth from 50mm.
Application: The most common type of lamp previously was MR16, which has survived to this day. It is equally used for basic and decorative lighting of rooms. The ability to fix the lamp in the connector allows it to be used in lamps of various designs, incl. in turning spots, etc.
Marking GU10: GU – pin contacts, distance between pin axes 10 mm.
Standard size: Bulb diameter 13-18mm, height from 35mm
Application: In spotlights for decorative and accent lighting.
Marking G9: G – pin contacts, distance between contacts 9 mm.
Type: Volume lamp, capsule type
Application: In spotlights for decorative and accent lighting.
Marking G6.35: G – pin contacts, 6.35 – distance between the axes of the contacts in mm.
These are perhaps the smallest of the volumetric lamps that are used in spotlights. Due to their size and focused light, they are effective in decorative lighting.
Expert opinion
It-Technology, Electrical power and electronics specialist
Ask questions to the “Specialist for modernization of energy generation systems”
Light bulbs for suspended ceilings - Man in The functional characteristics are superior to all those discussed above; less heat is generated, resulting in a fairly high efficiency, long service life, and a very bright flow of light. Ask, I'm in touch!
Which light bulb doesn't heat up?
Lamps that do not produce heat do not exist in nature. This is explained by the physical principle of the formation of light radiation. From the point of view of the classical science of physics, any light bulb is a converter of electrical energy into its variety. In this case, no more than 40 percent of the power taken from the current source is converted into light radiation. Its remnants are dissipated in the form of heat into the environment, the more, the lower the efficiency of this light element.
As an example, three different options are considered and compared:
- The upper zone of the bulb of an incandescent lamp, for example, at one hundred watts of power heats up to almost 280°C, while the temperature of the base reaches 70°C.
- For a compact fluorescent light with a power of 15 W, the base that overheats the most is the place where the spiral is located. Its temperature sometimes reaches 130°C. At the same time, the heating of the base part in the area where the electronic ballasts are located does not exceed 60°C.
- In LED lamps, the metal-plastic base of the housing heats up the most. For this reason, it is in this place that a radiator is installed, which allows heat to be removed from the LEDs and prevents the light bulb from heating up above the permissible norm.
If we consider the issue of the thermal output of lamps based on their heating of the surrounding space, LEDs do not belong to “cold” lamps, which in certain situations can be touched with hands.
LED light sources
LED light bulbs are considered the best and most popular light sources today. They are used not only for chandeliers (bronze, wood, crystal, etc.) and spotlights, but also for wall sconces, table and floor lamps and other types of lighting fixtures.
LED bulbs
Such light bulbs have gained enormous popularity due to the fact that they have a number of advantages:
- long service life, which is about 50,000 hours. These are the longest lasting light sources in existence;
- excellent characteristics of the luminous flux created by LEDs;
- minimal heating. Of course, the elements of LED lamps still heat up. But the heating is extremely insignificant and cannot affect the tension surface made of polyvinyl chloride;
- suitable for all types of lighting fixtures: chandeliers, sconces, spotlights, etc.;
- These are the most economical light bulbs. When using them, it is possible to save up to 90% of electricity;
- possibility to choose the color of the light flux: warm, neutral or cold.
But among all the advantages that are undoubtedly in great demand in the modern world, LED light bulbs still have one drawback that has not allowed them to completely displace other types of light sources from the market. This disadvantage lies in the high cost of LED products. However, it will more than pay for itself with all the advantages listed above. These are the bulbs you should use if you are dealing with suspended ceilings.
Design features of LED lamps
The design of the products is based on the principle of using a large number of LED chips placed on a special heat-removing substrate. All components are securely hidden under a matte, translucent hemisphere. In addition to the base, which acts as a radiator, the light bulb includes the following mandatory components and elements:
- light diffuser (cap);
- printed circuit board with a set of point LED emitters;
- a radiator used to remove heat from diode crystals;
- electronic control unit - driver;
- light bulb base.
To get acquainted with the internal parts of the LED lighting device, you will need to completely disassemble it, separating the hemispheres of the cap, fastened with reliable latches.
A little about the advantages of LED lamps
LED-based light bulbs are the most environmentally friendly and safe of all types of lamps on the market today. They do not contain mercury vapor, like fluorescent lamps, and do not explode with a mass of fragments scattered, like modern low-quality incandescent light bulbs.
The service life of an LED lamp today is measured in many tens of thousands of hours. Therefore, its higher cost over a long period of time is offset by significant energy savings.